
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Enterprise Resource Planning
- ERP Blogs by SAP
- Product Compliance in SAP S/4HANA Cloud, Private E...
Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
Get insights and updates about cloud ERP and RISE with SAP, SAP S/4HANA and SAP S/4HANA Cloud, and more enterprise management capabilities with SAP blog posts.
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
Product and Topic Expert
Options
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-31-2023
2:54 PM
SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition 2023 brings a range of new features and enhancements to simplify product compliance processes allowing organizations to address all compliance-related challenges to avoid delays in product launches or to respect delivery deadlines to your customers. With changing regulations across different geographical locations, the system helps businesses stay up-to-date and manage product compliance efficiently.
In the following blog, I will give you an engineering expert view of some selected highlights of our SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition for product compliance 2023 release, to demonstrate that automation, system integration, and end-to-end transparency can help companies build the foundation for the evolution of their long-term sustainability strategies.
The blog presents the key highlights for:
Whenever a company produces or sells a product, the company must ensure that the product meets all regulations: laws, industry standards, and company standards.
With Product Marketability and Chemical Compliance, you can manage chemical compliance for your products across your organization. It supports you in ensuring the marketability and compliance of products to secure the right to market, sell, and ship products throughout the product lifecycle.
Product Marketability and Chemical Compliance are integrated into checks in sales and delivery processes to prevent products from being sold into markets that are restricted or not assessed.
For more information, see Marketability Processes Overview.
Many countries have strict regulations about the kind of products that can be sold in their markets. To be able to sell the products in these countries, it's essential that the products comply with their regulations.
By using the Regulatory Content Update in SAP S4/HANA Cloud, private edition, businesses can automate this process and ensure that the products are always updated with the latest regulations. This can reduce risks, improve efficiency, and provide a competitive advantage in the global market.
With this new 2023 release, new and updated content is delivered to your system for product marketability. This release has 74 new compliance requirement versions, and 105 updates of existing compliance requirement versions are delivered with this release.
Picture 1: Use embedded and up-to-date regulatory content to ensure up-to-date product declarations.
A total of 145 compliance requirements in the area of product marketability include:
Newly introduced compliance requirements include:
123 examples of compliance requirements include:
For more information, see Activate Compliance Requirements - Product Marketability.
Phrases in product compliance play a crucial role in ensuring clear and consistent communication about product usage, handling, safety procedures, and any potential risks associated with the product. These are particularly significant in sectors such as pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and other industries where miscommunication can lead to serious consequences.
SAP delivers new and updated phrases in up to 47 languages, which you can use in your product compliance processes. You can view all SAP-delivered phrases using the Manage Phrase-Enabled Fields apps. You can also use this app to hide phrases so that they aren't displayed in the phrase selection for the corresponding field.
Phrases are delivered with the SAP application. In addition, you can use the Continuous Content Service to receive regular updates for phrases of SAP branded content.
Companies are also able to create and maintain their own phrases, based on their specific products, objectives, and target audience. This allows for better customization to the company's needs.
With this new 2023 release, you can synchronize company-owned phrases to reduce the time and effort needed to keep your phrases up to date. Additionally, it doesn't matter which of the synced phrases you change, all others in the group are automatically updated. This improved management of phrases helps to avoid extra data maintenance for similar phrases. The company-owned phrase information can be used for output on documents like safety data sheets, labels, and reports.
Picture 2: Avoid multiplied data maintenance for customers to maintain phrases.
For more information, see Manage Phrase-Enabled Fields.
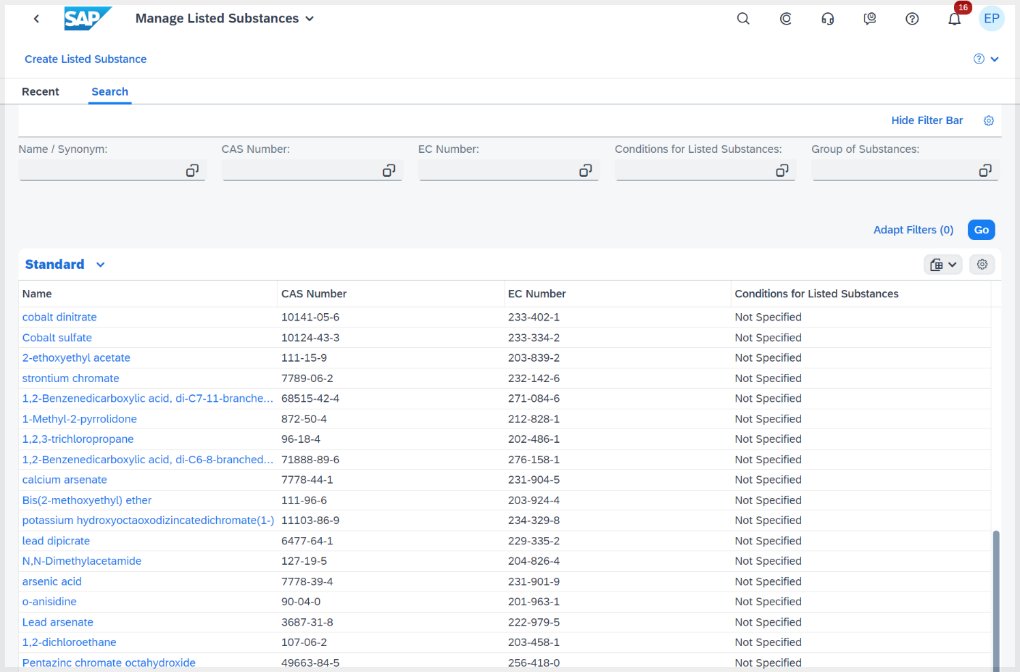
Listed substances (unique CAS numbers) are important in product compliance for several reasons:
Overall, the use of listed substances in product compliance is essential for accurate identification, regulatory compliance, safety considerations, international harmonization, and effective supply chain management.
Loading of regulatory content, like substances, has been streamlined for better performance and use of the regulatory content service. Instead of loading content into tables and updating only related to a specific release or support package, now all customers are able to have substance information delivered continuously. This content is delivered as part of the most current release. All content is available, without this relationship to a specific support package.
Picture 3: Enable customers to continuously consume listed substances and listed substance groups from SAP.
With this change, product compliance shall consume and load listed substances, listed substance groups, and listed substance conditions from the regulatory content service as the preferred source. Only when the regulatory content service isn't configured, listed substances, groups, and conditions are loaded from the MIME repository.
This ensures that all compositions are made up of the most current and accurate substances, which are the foundation of automated compliance checks within the system.
For more information, see Regulatory Content Service.
Substance Volume Tracking (SVT) is a regulatory requirement that helps ensure compliance with various product regulations, especially those related to hazardous substances. Many countries have strict regulations regarding the use and presence of hazardous substances in products. SVT helps track the volume and concentration of these substances, ensuring compliance with the regulations of both the exporting and importing countries.
With this new 2023 release, you can manage the substance volume tracking process for a compliance requirement and business process in the new “Enable Substance Volume Tracking - For Compliance Requirements” app (F6964). You can start initial tracking from the beginning of the current tracking period, and enable or disable the tracking process for a period of time, as needed. In addition, you can clear calculated data by compliance requirements or clear all substance volume tracking data, including retracking decisions.
Picture 4: Help ensure reliable maintenance of substance volume tracking data through the ability to clear calculated volumes or perform data reset.
The key features are:
In Customizing under Product Compliance > Product Marketability ad Chemical Compliance > Substance Volume Tracking > Integration, the configuration expert can do a preliminary setup for the substance volume tracking process by specifying document types and item categories that need to be excluded from tracking. The following activities are available:
For more information, see Enable Substance Volume Tracking – For Compliance Requirements.
With this new 2023 release, you can specify a responsible importer for a supplier raw material and set a validity period for the responsibility in the “Supplier Compliance for Raw Material” (F3040) app. You do this when you want to overwrite the determined responsible importer by the system, for example, due to additional agreements between the buyer and seller. The specified import responsibility is considered during the calculation of substance volumes for purchasing and retracking is performed accordingly if any changes occur.
Picture 5: Help ensure compliance with limits on substance volumes in purchasing scenarios when import responsibilities are changed.
The following table describes how a change in the validity of the specified import responsibility is reflected in the tracked substance volumes.
Tab 01: Changes to Validity of Import Responsibility: Effects on Substance Volume Tracking
For more information, see Supplier Compliance for Raw Material.
In import and export scenarios, substances could be subject to customs control depending on the relevant legislation. Many regulations for chemical substances are exempt from tracking substances for the time they are being stored in bonded warehouses.
Companies can use a plant or storage location on their premises as a bonded warehouse only after customs approval for a certain time. Bonded warehouses can be specified with their validity period in the “Manage Bonded Warehouses – Product Marketability” app (F6394). This way, bonded warehouses are considered in substance volume tracking when they are involved in the supply chain for purchasing and sales scenarios.
With this new 2023 release, you can specify that a storage location or plant in your company is used as a bonded warehouse in the new “Manage Bonded Warehouses - Product Marketability” app. You can also specify the period for which the bonded warehouse is active.
The key features are:
Picture 6: Accurately track substance volumes and improve compliance with chemical regulations in scenarios that involve bonded warehouses.
For more information, see Manage Bonded Warehouses - Product Marketability.
The PCN Assessments provide information on the hazardous properties and appropriate emergency response measures for chemical mixtures. This information allows poison centers to provide accurate advice in the event of an emergency involving these mixtures.
Companies must inform the appropriate national appointed bodies or poison centers about the dangerous mixtures they sell as part of the PCN Assessments. This notification must contain specific details about the mixture's ingredients, labeling, and packaging.
And as part of the PCN Assessments, each hazardous mixture must be assigned a Unique Formula Identifier (UFI). The UFI is a unique code that identifies the mixture and is printed on the product label. It helps poison centers quickly and accurately identify the mixture in emergency situations.
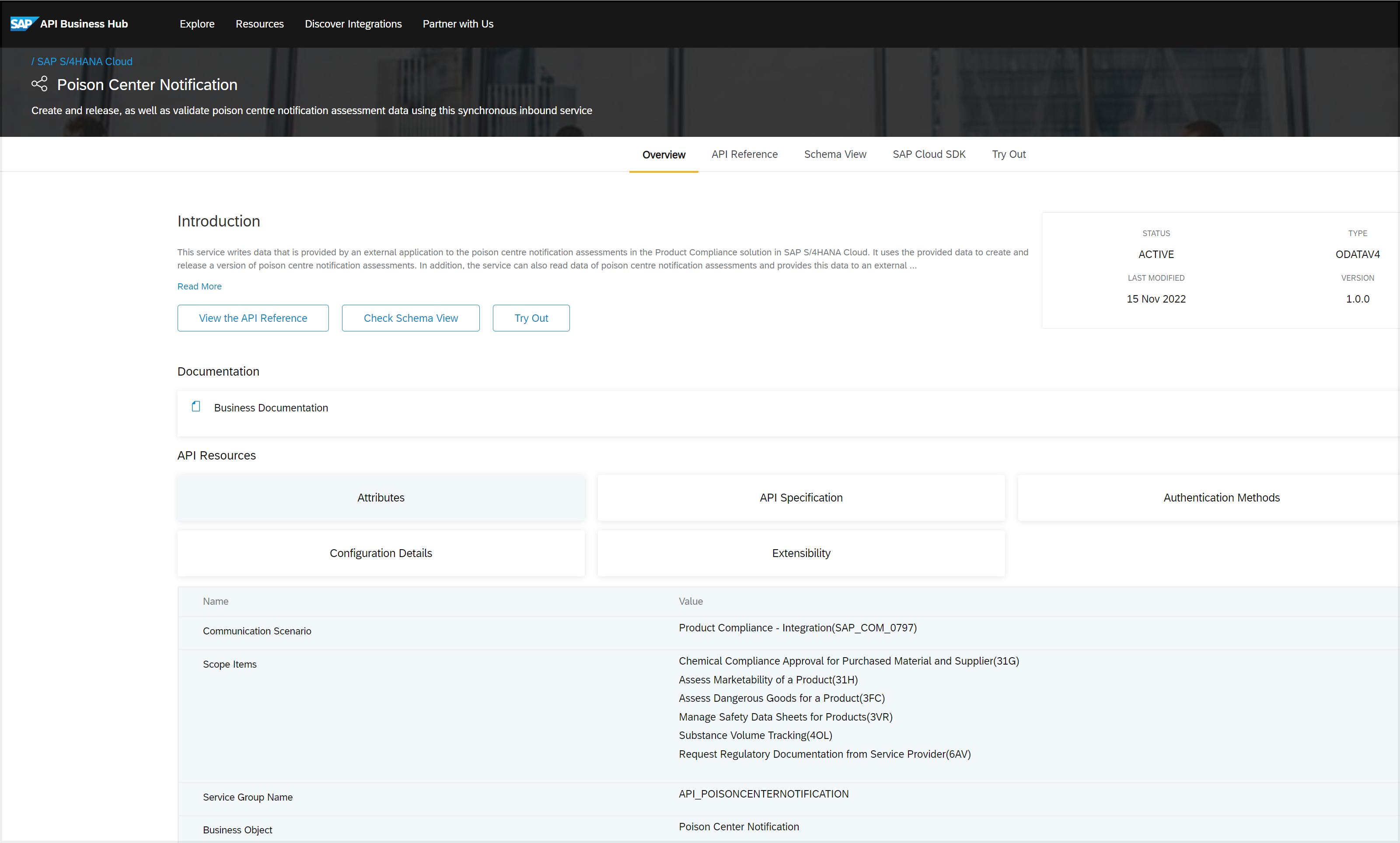
With this new 2023 release, you can write poison centre notification data that is provided by an external application into a compliance assessment. We have now:
Picture 7: Automates and integrates poison center notification information with SAP S/4HANA for product compliance apps through remote API.
This API is available on the SAP Business Accelerator Hub (https://api.sap.com).
To use the API service see, Integration of External Systems.
The use of confidential business information, including trade secrets, for substance names allows companies to protect their investments, maintain competitiveness, and preserve their intellectual property rights. It encourages innovation and supports the development of unique products while balancing the need for regulatory compliance and public safety.
With this new 203 release, you can now manage confidential business information for substances, including creating an alternative name for a substance in many different languages.
We have now:
Picture 8: Instead of printing the exact name or concentration, use generic data to mask or disguise the chemical identity of the substance and its concentration in a composition.
For more information, see Manage Substances Compliance.
The International Material Data System (IMDS) is a global web-based database that serves as a central repository for information on materials used within the automotive industry. It was developed by the automotive industry to meet legal and environmental compliance requirements, specifically related to the End of Life Vehicle (ELV) Directive and the Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive.
The primary purpose of the IMDS is to collect and manage data on materials and substances used in automotive products throughout their lifecycle. This includes information on the composition, material properties, recycling potential, and compliance with environmental regulations.
With this new 2023 release, the International Material Data System (IMDS) functionality is updated due to IMDS Release 14 (see here the RELEASE NOTES) which included an update of its IMDS Advanced Interface (AI).
The new enhancements are:
For details, see the following SAP Notes:
With the Extended Use of the advanced interface of the International Material Data System (IMDS 14), we add also new features concerning:
To safely transport hazardous materials, it is necessary to follow transportation rules and regulations. These regulations cover appropriate packaging, labeling, documentation, and adherence to specific transportation methods such as road, air, or sea. It is crucial to properly train all personnel involved in transportation to effectively handle any potential incidents or emergencies.
With this new 2023 release, new and updated content for Dangerous Goods Management is delivered to your system.
The content is used when you classify unpackaged dangerous goods according to one of these dangerous goods regulations. When you select an organic peroxide or a self-reactive substance that is included in this content as the technical name, the system uses the name from the respective list.
For this kind of substance, you can't change the technical name, but can display more information in the Select Technical Names dialog.
With this new release, we have:
7 new compliance requirement versions for:
4 extensions of existing compliance requirement versions with enclosure-specific list data for:
8 extensions of existing compliance requirement versions with organic peroxide list data for:
IATA-DGR ; CFR 49 ; NOM ; ANTT ; NCh382 ; ADG ; NZS ; SANS
8 extensions of existing compliance requirement versions with self-reactive substance list data for:
In total, the embedding of 14 compliance requirements for dangerous goods management:
Picture 9: Help ensure that organizations have the most up-to-date compliance information.
The delivery of a new list for a compliance requirement version has the following effects on existing data:
Effects on the Technical Name:
Effects on the Content:
For more information about the delivered content and the handling of technical names, see the product assistance for Product Compliance:
When a product is intended to be transported, you, as a dangerous goods specialist, are responsible for assessing this product. If the product is a dangerous good, you have to classify it according to the dangerous goods regulations that are applicable to the country/region in which the product is transported.
With this new 2023 release, you can now classify unpackaged and packaged products according to the Chinese JT/T 617.3 dangerous goods regulation.
For more information about the JT/T 617.3 compliance requirement, see Classification of Dangerous Goods According to Chinese JT/T 617.3 Regulation.
To support the classification according to JT/T 617.3, a new compliance requirement and a new app are delivered, and an existing app has been enhanced:
New Compliance Requirement
The new JT/T 617.3 compliance requirement is delivered with the JT/T 617.3-2018 version.
This new compliance requirement is based on the new JT/T 617.3 Content-Based Regulation compliance pattern.
New and Enhanced Apps
The new “Classify Dangerous Good According to JT/T 617.3 - Unpackaged Product” app (F7436) is delivered to classify unpackaged products according to JT/T 617.3.
The “Classify Dangerous Good - Packaged Product” app (F4833) is enhanced to support the classification according to JT/T 617.3.
Picture 10: Simplify classification of products by use of regulatory dangerous goods content for data maintenance.
For more information, see Preparing Basic Data for Dangerous Goods Assessments.
The process of classifying dangerous goods that are transported in tanks or bulk containers is different from the process of classifying already packed dangerous goods. For packing dangerous goods, you need, for example, information about the packaging, such as the code and quantity of the dangerous goods package and information about the inner package. This information is not needed for tanks and bulk containers. In addition, when you transport dangerous goods in packages, the shipping quantity per package is fixed and defined by the size of the package. When transporting dangerous goods in tanks or in bulk containers, the amount of the product that is filled in the tank or bulk container can differ from shipment to shipment.
This new 2023 release supports the classifying and shipping of dangerous goods in tanks and bulk containers as follows:
The new Tank or Bulk Container flag is introduced in the Specify Descriptions of Dangerous Goods Packages configuration activity. This flag indicates that the packaging is a tank or a bulk container.
If you select a packaging for which this flag is set, the system displays only the description of the dangerous goods package in the Edit Packaging Details dialog. The code and quantity information of the dangerous goods package and data for an inner package is no longer displayed.
The following new placeholders are delivered:
These placeholders are resolved with the amount of the product that is filled in the tank or bulk container as entered on documents within the value chain, such as sales orders, delivery notes, and freight orders. The placeholders are used for the enclosure variants UN Portable Tank, Regulation-Specific Tank, and UN Bulk Container.
The description templates are adapted to use the new placeholders when you select an enclosure variant for tanks and bulk containers.
Picture 11: Enable proper handling of dangerous goods filled in tanks or bulk containers.
In the Customizing under Product Compliance > Dangerous Goods Management, the Specify Descriptions of Dangerous Goods Packages activity is changed as follows:
You can find more information about classifying dangerous goods in the product assistance for Product Compliance. See Packaged Dangerous Goods Transported in Tanks and Bulk Containers.
Marking texts are graphics that indicate a special condition or property of a package, such as a mark for keeping dangerous goods away from heat. Hazard labels depict the hazard of a dangerous good. Hazard labels are shaped like diamonds with a background color that highlights the hazard. Marking texts and hazard labels are used for labeling dangerous goods packages.
For a packer of dangerous goods in a warehouse, it's important to know the labeling and marking information for a product that is to be transported. The packer has to make sure that all required marking texts and labels are affixed on the package to comply with the applicable dangerous goods regulations.
To support the packer, the “View Markings and Labels – Dangerous Goods” app (F7369) is provided. With this app, the packer can search by a business document ID and view the labeling and marking information for all items that are included in this business document.
Picture 12: Enable packers to create packages that are compliant with dangerous goods regulations.
The following business documents are supported:
For more information, see View Markings and Labels - Dangerous Goods.
The Dangerous Goods check in sales orders facilitate effective logistics planning. It helps determine the appropriate mode of transportation and packaging requirements and ensures compliance with restrictions imposed by regulatory authorities. This information can be used to optimize shipment routes, consolidate orders, and streamline the overall logistics process, resulting in cost savings and improved operational efficiency.
The sales representative can enter a shipping type, such as road, rail, sea, or air, in the sales documents to suggest the main mode of transport for transportation planning. If entered, this shipping type is then used in addition to the departure and destination country/region as input for the dangerous goods check that is carried out in this business document.
The system determines the dangerous good regulations that need to be checked for the shipping types as follows:
Picture 13: Reduce effort for the sales representative to check why the transport of a product might be restricted if the shipping type of the main leg is already known and defined in the sales order.
For more information, see Dangerous Goods Check in Sales Processes and Determination of the Applicable Regulations.
As a dangerous goods specialist, you want to get an overview of the dangerous goods data for a specific regulation or a specific UN number. This overview of the available regulatory data can help you in the process of classifying your product. In addition, to a certain level, this overview of data can replace your research in the printed versions of the dangerous goods regulations.
With this new 2023 release, we introduce a new SAP Fiori app “View of Regulatory Data for Dangerous Goods”. With this app, you can view all available regulatory data for a UN number for a certain regulation.
Picture 14: Provide available regulatory data directly in the classification process.
Remark: If you open the app in two separate browser windows, you can easily compare data from different regulations
For more information, see View Regulatory Data - Dangerous Goods.
To effectively plan and carry out logistics operations, logistic personnel require knowledge about dangerous goods. This involves identifying the most suitable mode of transportation, choosing carriers with the proper certifications and abilities to handle dangerous goods, and ensuring compliance with transportation regulations and guidelines. Having access to information about dangerous goods aids in optimizing logistics routes, overseeing storage, and handling conditions, and collaborating with relevant parties in the supply chain.
With this new SAP Fiori app “Dangerous Goods Information” (F7328), you can search for products for which you want to see the dangerous goods data, and you can view a list of all products that have the Transported logistics role assigned. In this list, you can search for products for which you want to see the dangerous goods data. You can use filter criteria to narrow down your results list. In the results list, you can select a product and navigate to the “Classify Unpackaged Dangerous Goods” or “Classify Packaged Dangerous Goods” apps where you can view its dangerous goods classification.
Picture 15: Enable more efficient compliance with dangerous goods regulations.
For more information, see Dangerous Goods Information.
A Safety Data Sheet, also known as a Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS), is a comprehensive document that provides detailed information about the hazards, handling, storage, and emergency measures associated with a particular chemical substance or product. SDS contains critical information such as chemical composition, physical and chemical properties, toxicity data, first aid measures, handling and storage instructions, disposal considerations, and regulatory compliance details.
Label management ensures that labels are compliant with applicable regulations, like GHS, OSHA, EPA, FDA, and other regional or industry-specific requirements.
With this 2023 release, new and updated content is delivered to your system. There are 65 updated compliance requirement and compliance requirement versions and 5 new versions added to support the data model. These include covering GHS regulations for Chile, Taiwan, Thailand, and the Philippines, as well as Exposure Scenarios for the European Union and the Korean number for safety data sheets. Additionally, there are 81 updated and 22 new compliance requirement versions for occupational exposure limits.
102 compliance requirements for safety data sheet management embedded.
109 compliance requirements related to safety data sheet authoring:
92 compliance requirements for occupational exposure limits
Picture 16: Enable customers to rely on embedded regulatory content, including phrases, graphics, and listed substances.
Customers may have different needs when it comes to receiving SDS, such as their preferred format, language, or delivery address. With Multi Address Support, companies can keep track of multiple addresses for each customer, guaranteeing that the SDS is delivered to the right place according to their individual requirements. This adaptability helps meet customer demands and improves overall satisfaction.
This new 2023 release enables the support of multiple addresses assigned to a business partner in processes for safety data sheet shipments.
This applies to the following safety data sheet processes:
Safety Data Sheet Shipment
Maintenance of the Sender Address for the Safety Data Sheet
International Address Version
Picture 17: Increase efficiency through the ability to handle multiple addresses and print multiple product names.
Remark: Safety data sheet processes consider multi-address assignments if the feature Multiple Address Handling in SD Documents Using SAP Business Partner is activated for Quote-2-Cash processes.
For more information, see Feature Overview for Multiple Address Handling and Multiple Address Handling in SD Documents Using SAP Business Partner.
Labels are crucial in providing consumers with necessary information about a product, allowing them to make well-informed choices about its safe and appropriate usage. These labels typically include safety warnings, hazard symbols, usage instructions, and precautions, all of which are vital elements. By ensuring that labels are clear and precise, consumers can be safeguarded from potential dangers associated with the product, ultimately minimizing the likelihood of accidents, injuries, or misapplication.
With this new SAP Fiori app “Validate and Print Labels” (F6656), you can validate and print labels. Labels can be validated based on the previous label configurations created in the “Manage Label Configurations” app and their assignment to a product in the “Manage Label Assignments” app. Depending on the business document, you can validate the completeness of relevant labels. Afterward, you can create a print request for a specific label. This assessment can help you make sure that the labels are properly set up prior to the printing process.
Picture 18: Improve labeling for general scenarios.
This “Validate and Print Label” app enables users to:
For more information, see Label Configuration and Label Assignment.
An exposure scenario describes how the exposure of humans and the environment to a substance or mixture can be controlled to ensure its safe use. An exposure scenario refers to an identified use or group of similar identified uses, such as formulation, processing, or production.
With exposure scenarios, you describe the operational conditions and risk management measures that ensure the safe use of the substance or mixture to adequately control the risks to human health and the environment. Exposure scenarios cover the entire lifecycle of the substance or mixture, including formulation, industrial and professional end use, consumer use, and production. An exposure scenario can be made up of contributing scenarios that provide additional information on the safe use of the substance or mixture.
With this new “Manage eSDS Annex” (F6751), you can create new or assign existing exposure scenarios to an unpackaged product. You can specify the data that is required as an annex to a safety data sheet to ensure that the unpackaged product stays compliant.
Picture 19: Create a new exposure scenario or assign an existing one to an unpackaged product.
For more information, see the Manage eSDS Annex.
With the new SAP Fiori app “Manage Exposure Scenarios” (F6749) you can provide detailed information on an exposure scenario to describe the operational conditions and risk management measures that ensure safe use of the substance or mixture. You can edit the data to ensure that it is up to date and that the unpackaged product stays compliant. You can also create a new or assign an existing contributing scenario. You can then release a version of the exposure scenario to use in the “Manage eSDS Annex” app.
Picture 20: Create a new or add an existing exposure scenario.
For more information, see Manage Exposure Scenarios.
With the new SAP Fiori app “Manage Contributing Scenarios” (F6750), you can provide detailed information on contributing activities for a specific use that are part of an exposure scenario. You can then release a version of the contributing scenario to use in the exposure scenarios.
Picture 21: Enter detailed information depending on the type of contributing scenario.
For more information, see Manage Contributing Scenarios.
If a safety data sheet is sent to South Korea, an SDS number must be printed in the header of the safety data sheet. This SDS number is assigned when the safety data sheet is submitted to the Korean Ministry of Employment and Labor (MoEL).
The Korean SDS Number consists of the following two parts:
The company-specific part is entered in the "Manage Legal Entities" app. The product-specific part is entered in the new “Manage Korean SDS Number” (F7414) app as part of the compliance assessment for an unpackaged product.
You can then create the legally required safety data sheet number for South Korea which consists of a product part and a company part. These two parts are combined together and printed on the safety data sheet during the final generation of the South Korean safety data sheet.
Picture 22: Allow the creation of Korean SDSs that are compliant with the current Korean regulations.
The key features are:
For more information, see Manage Korean SDS Number.
Thanks for reading this blog post.
If you are also interested in other Lines of Business and Industries for this new SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition 2023 release, I would like to draw your attention to my link collection blog – The Link Collection.
If you want to see the entire PDF presentation of all innovations, see here.
If you want to learn more about SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition, join our Partner Community. This group focuses on providing enhanced learnings and periodic updates with respect to the SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition product. Our goal is to facilitate collaboration with your peers and SAP subject matter experts.
For general roadmap information please check the SAP S/4HANA Roadmap.
For more information on SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition, check out the following links:
Follow the SAP S/4HANA Cloud tag and the PSCC_Enablement tag to stay up to date with the latest blog posts.
Follow us via @Sap and #S4HANA, or myself via @VoglerChrist and LinkedIn
In the following blog, I will give you an engineering expert view of some selected highlights of our SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition for product compliance 2023 release, to demonstrate that automation, system integration, and end-to-end transparency can help companies build the foundation for the evolution of their long-term sustainability strategies.
The blog presents the key highlights for:
- Product Marketability and Chemical Compliance,
- Dangerous Goods Management,
- Safety Data Sheet and Label Management,
Product Marketability and Chemical Compliance
Whenever a company produces or sells a product, the company must ensure that the product meets all regulations: laws, industry standards, and company standards.
With Product Marketability and Chemical Compliance, you can manage chemical compliance for your products across your organization. It supports you in ensuring the marketability and compliance of products to secure the right to market, sell, and ship products throughout the product lifecycle.
Product Marketability and Chemical Compliance are integrated into checks in sales and delivery processes to prevent products from being sold into markets that are restricted or not assessed.
For more information, see Marketability Processes Overview.
Regulatory Content Updates for Compliance Requirements
Background
Many countries have strict regulations about the kind of products that can be sold in their markets. To be able to sell the products in these countries, it's essential that the products comply with their regulations.
By using the Regulatory Content Update in SAP S4/HANA Cloud, private edition, businesses can automate this process and ensure that the products are always updated with the latest regulations. This can reduce risks, improve efficiency, and provide a competitive advantage in the global market.
Key Features
With this new 2023 release, new and updated content is delivered to your system for product marketability. This release has 74 new compliance requirement versions, and 105 updates of existing compliance requirement versions are delivered with this release.

Picture 1: Use embedded and up-to-date regulatory content to ensure up-to-date product declarations.
A total of 145 compliance requirements in the area of product marketability include:
- 144 substance-list checks (SLC)
- 1 poison-center notification
Newly introduced compliance requirements include:
- GB persistent organic pollutants (Dec 2022)
- JP CSCL general chemicals (Nov 2022)
- GB REACH SVHC status (Jan 2021)
- AU AIIC status (Mar 2023)
- GB REACH annex 17 status (Jul 2021)
- GB REACH annex 14 status (Jul 2021)
- GB PIC status (Jan 2021)
- EU REACH registration status (Jan 2021)
- TR KKDIK registration status (Jun 2017)
- GB REACH registration status (Jul 2021)
123 examples of compliance requirements include:
- 65 simple compliance documentation
- 1 customer compliance check
- 3 supplier information
- 46 substance list checks with substance volume-tracking enabled
- 8 compliance disclosure and due-diligence acts
For more information, see Activate Compliance Requirements - Product Marketability.
Ability to Keep Company-Owned Phrases Synchronized
Business Background
Phrases in product compliance play a crucial role in ensuring clear and consistent communication about product usage, handling, safety procedures, and any potential risks associated with the product. These are particularly significant in sectors such as pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and other industries where miscommunication can lead to serious consequences.
SAP delivers new and updated phrases in up to 47 languages, which you can use in your product compliance processes. You can view all SAP-delivered phrases using the Manage Phrase-Enabled Fields apps. You can also use this app to hide phrases so that they aren't displayed in the phrase selection for the corresponding field.
Phrases are delivered with the SAP application. In addition, you can use the Continuous Content Service to receive regular updates for phrases of SAP branded content.
Companies are also able to create and maintain their own phrases, based on their specific products, objectives, and target audience. This allows for better customization to the company's needs.
Key Features
With this new 2023 release, you can synchronize company-owned phrases to reduce the time and effort needed to keep your phrases up to date. Additionally, it doesn't matter which of the synced phrases you change, all others in the group are automatically updated. This improved management of phrases helps to avoid extra data maintenance for similar phrases. The company-owned phrase information can be used for output on documents like safety data sheets, labels, and reports.

Picture 2: Avoid multiplied data maintenance for customers to maintain phrases.
For more information, see Manage Phrase-Enabled Fields.
Listed Substance Provisioning through a Regulatory Content Service
Business Background
Listed substances (unique CAS numbers) are important in product compliance for several reasons:
- Identification: CAS numbers provide a unique identifier for each chemical substance. This helps to avoid confusion or ambiguity when referring to specific substances. Different substances can have similar or even identical names, but they will have distinct CAS numbers, allowing for accurate identification.
- Regulatory requirements: Many regulations and standards require the identification and tracking of specific substances. For example, certain chemicals may be restricted or banned due to their hazardous properties or environmental impact. By using listed substances, regulators can precisely define which substances are subject to these restrictions.
- International harmonization: CAS numbers are globally recognized and used across different countries and regulatory systems. This facilitates communication and consistency in product compliance efforts, as well as the exchange of information between different stakeholders.
- Supply chain management: CAS numbers are used to track and manage substances throughout the supply chain. Manufacturers, distributors, and retailers can use CAS numbers to ensure that the substances used in their products comply with regulations and standards. This helps to ensure product safety and compliance with legal requirements.
Overall, the use of listed substances in product compliance is essential for accurate identification, regulatory compliance, safety considerations, international harmonization, and effective supply chain management.
Key Features
Loading of regulatory content, like substances, has been streamlined for better performance and use of the regulatory content service. Instead of loading content into tables and updating only related to a specific release or support package, now all customers are able to have substance information delivered continuously. This content is delivered as part of the most current release. All content is available, without this relationship to a specific support package.
Picture 3: Enable customers to continuously consume listed substances and listed substance groups from SAP.
With this change, product compliance shall consume and load listed substances, listed substance groups, and listed substance conditions from the regulatory content service as the preferred source. Only when the regulatory content service isn't configured, listed substances, groups, and conditions are loaded from the MIME repository.
This ensures that all compositions are made up of the most current and accurate substances, which are the foundation of automated compliance checks within the system.
For more information, see Regulatory Content Service.
Control of the Substance Volume Tracking Process by Compliance Requirement
Business Background
Substance Volume Tracking (SVT) is a regulatory requirement that helps ensure compliance with various product regulations, especially those related to hazardous substances. Many countries have strict regulations regarding the use and presence of hazardous substances in products. SVT helps track the volume and concentration of these substances, ensuring compliance with the regulations of both the exporting and importing countries.
Key Features
With this new 2023 release, you can manage the substance volume tracking process for a compliance requirement and business process in the new “Enable Substance Volume Tracking - For Compliance Requirements” app (F6964). You can start initial tracking from the beginning of the current tracking period, and enable or disable the tracking process for a period of time, as needed. In addition, you can clear calculated data by compliance requirements or clear all substance volume tracking data, including retracking decisions.

Picture 4: Help ensure reliable maintenance of substance volume tracking data through the ability to clear calculated volumes or perform data reset.
The key features are:
- Enable or disable the substance volume tracking process for specific compliance requirements and business processes.
- Perform initial tracking from the beginning of the tracking period.
- Clear calculated data per compliance requirement.
- Clear all recorded substance volumes.
Effects on Customizing
In Customizing under Product Compliance > Product Marketability ad Chemical Compliance > Substance Volume Tracking > Integration, the configuration expert can do a preliminary setup for the substance volume tracking process by specifying document types and item categories that need to be excluded from tracking. The following activities are available:
- Specify Excluded Document Types for Integration
- Specify Excluded Purchasing Item Categories
- Specify Excluded Sales Item Categories
- Specify Excluded Delivery Item Categories
For more information, see Enable Substance Volume Tracking – For Compliance Requirements.
Enhanced Business Processes through Integration of Substance Volume Tracking
Key Features
With this new 2023 release, you can specify a responsible importer for a supplier raw material and set a validity period for the responsibility in the “Supplier Compliance for Raw Material” (F3040) app. You do this when you want to overwrite the determined responsible importer by the system, for example, due to additional agreements between the buyer and seller. The specified import responsibility is considered during the calculation of substance volumes for purchasing and retracking is performed accordingly if any changes occur.

Picture 5: Help ensure compliance with limits on substance volumes in purchasing scenarios when import responsibilities are changed.
The following table describes how a change in the validity of the specified import responsibility is reflected in the tracked substance volumes.
| Change in Validity Period | Effects on Substance Volume Tracking |
| Extended for Seller or No Import | Substance volumes that are calculated for the buyer in the extended period are disaggregated and excluded from tracking. |
| Extended for Buyer | Substance volumes from material documents with a posting date in the extended validity period are calculated for the buyer. |
| Shortened for Seller or No Import | Substance volumes from the material documents with a posting date outside the shortened period are calculated for the buyer. |
| Shortened for Buyer | Substance volumes that are calculated for the buyer outside the shortened period are disaggregated and excluded from tracking |
Tab 01: Changes to Validity of Import Responsibility: Effects on Substance Volume Tracking
For more information, see Supplier Compliance for Raw Material.
Evaluation of Bonded Warehouse Configurations during Substance Volume Tracking
Business Background
In import and export scenarios, substances could be subject to customs control depending on the relevant legislation. Many regulations for chemical substances are exempt from tracking substances for the time they are being stored in bonded warehouses.
Companies can use a plant or storage location on their premises as a bonded warehouse only after customs approval for a certain time. Bonded warehouses can be specified with their validity period in the “Manage Bonded Warehouses – Product Marketability” app (F6394). This way, bonded warehouses are considered in substance volume tracking when they are involved in the supply chain for purchasing and sales scenarios.
Key Features
With this new 2023 release, you can specify that a storage location or plant in your company is used as a bonded warehouse in the new “Manage Bonded Warehouses - Product Marketability” app. You can also specify the period for which the bonded warehouse is active.
The key features are:
- New SAP Fiori app to set up a storage location or plant as a bonded warehouse with a validity period,
- Ability to consider bonded warehouses in the substance volume tracking process when they are involved in the supply chain for purchasing and sales scenarios.

Picture 6: Accurately track substance volumes and improve compliance with chemical regulations in scenarios that involve bonded warehouses.
For more information, see Manage Bonded Warehouses - Product Marketability.
Remote API to Create, Read, or Update Poison Centres Notification (PCN) Assessments
Business Background
The PCN Assessments provide information on the hazardous properties and appropriate emergency response measures for chemical mixtures. This information allows poison centers to provide accurate advice in the event of an emergency involving these mixtures.
Companies must inform the appropriate national appointed bodies or poison centers about the dangerous mixtures they sell as part of the PCN Assessments. This notification must contain specific details about the mixture's ingredients, labeling, and packaging.
And as part of the PCN Assessments, each hazardous mixture must be assigned a Unique Formula Identifier (UFI). The UFI is a unique code that identifies the mixture and is printed on the product label. It helps poison centers quickly and accurately identify the mixture in emergency situations.
Key Features
With this new 2023 release, you can write poison centre notification data that is provided by an external application into a compliance assessment. We have now:
- New service to create, read, and update the unique formula identifier (UFI), along with registered countries,
- Service based on the OData protocol and enabled for SAP Fiori apps and other user interfaces,
- Ability to search, discover, test, and consume poison center notification assessments through remote API.
Picture 7: Automates and integrates poison center notification information with SAP S/4HANA for product compliance apps through remote API.
This API is available on the SAP Business Accelerator Hub (https://api.sap.com).
To use the API service see, Integration of External Systems.
Maintaining Confidential Business Information (Trade Secrets) for Substance Names
Business Background
The use of confidential business information, including trade secrets, for substance names allows companies to protect their investments, maintain competitiveness, and preserve their intellectual property rights. It encourages innovation and supports the development of unique products while balancing the need for regulatory compliance and public safety.
Key Features
With this new 203 release, you can now manage confidential business information for substances, including creating an alternative name for a substance in many different languages.
We have now:
- A new feature to maintain names for confidential business information on the company substances level,
- A new feature in compositions to flag substances that should be masked because they contain confidential business information,
- Subsequent process that will make use of generic names instead of disclosing actual substance names.

Picture 8: Instead of printing the exact name or concentration, use generic data to mask or disguise the chemical identity of the substance and its concentration in a composition.
For more information, see Manage Substances Compliance.
Support for Release 14 of the International Material Data System (IMDS)
Business Background
The International Material Data System (IMDS) is a global web-based database that serves as a central repository for information on materials used within the automotive industry. It was developed by the automotive industry to meet legal and environmental compliance requirements, specifically related to the End of Life Vehicle (ELV) Directive and the Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive.
The primary purpose of the IMDS is to collect and manage data on materials and substances used in automotive products throughout their lifecycle. This includes information on the composition, material properties, recycling potential, and compliance with environmental regulations.
Key Features
With this new 2023 release, the International Material Data System (IMDS) functionality is updated due to IMDS Release 14 (see here the RELEASE NOTES) which included an update of its IMDS Advanced Interface (AI).
The new enhancements are:
- Enhancement to product compliance to meet the new requirements of release 14 of the International Material Data System (IMDS)
- For details, see SAP Note 3330966 - IMDS v.14 - Overview of Functional Changes in AI Interface.
- Deliveries realized through two SAP Notes and providing required adjustments within the functionality of product compliance to support:
- General release changes to the IMDS advanced interface (file header, OEM recipient fields, and end of file)
- Structure mix
- SC90 for filled and unfilled thermoplastics
- Phase-out of substance applications relations
- Additional attributes of SCIP article categories
- Object model and persistence
- Migrating recycling information from the specification database to CDO
- Importing material content certificates from IMDS
- Importing module and data sheets from IMDS with recycling information
- Exporting recycling information to IMDS
- Maintaining recycling information in the compliance workbench
- Checking IMDS modules and data sheets for recycling information
- Supporting the revealing confidential declarable substances
- Extended contact information in IMDS requests
For details, see the following SAP Notes:
- 3300012 - IMDS v.14 - Support for Functional Changes in AI Interface
- 3314028 - IMDS v.14 - Support for Functional Changes in AI Interface
- 3342570 - IMDS v.14 - Support for Functional Changes in AI Interface
With the Extended Use of the advanced interface of the International Material Data System (IMDS 14), we add also new features concerning:
- Chemical recycling, bio-based materials, and mechanical recycling information for the advanced interface of IMDS 14, including maintaining recycling information in the compliance workbench and checking IMDS modules and data sheets for recycling information,
- The revealing confidential declarable substances,
- Check for old MDSs,
- Extended contact information.
Dangerous Goods Management
To safely transport hazardous materials, it is necessary to follow transportation rules and regulations. These regulations cover appropriate packaging, labeling, documentation, and adherence to specific transportation methods such as road, air, or sea. It is crucial to properly train all personnel involved in transportation to effectively handle any potential incidents or emergencies.
Regulatory Content Update – New Versions and Lists of Dangerous Goods Regulations
Key Features
With this new 2023 release, new and updated content for Dangerous Goods Management is delivered to your system.
The content is used when you classify unpackaged dangerous goods according to one of these dangerous goods regulations. When you select an organic peroxide or a self-reactive substance that is included in this content as the technical name, the system uses the name from the respective list.
For this kind of substance, you can't change the technical name, but can display more information in the Select Technical Names dialog.
With this new release, we have:
7 new compliance requirement versions for:
- IATA-DGR 2023 ; IMDG 2022 ; ADR 2023 ; RID 2023 ; ADN 2023
- CFR 49 as of July 26th, 2022 ; NZS 2021
4 extensions of existing compliance requirement versions with enclosure-specific list data for:
- ADG ; ANTT ; NCh382 ; NZS
8 extensions of existing compliance requirement versions with organic peroxide list data for:
IATA-DGR ; CFR 49 ; NOM ; ANTT ; NCh382 ; ADG ; NZS ; SANS
8 extensions of existing compliance requirement versions with self-reactive substance list data for:
- IATA-DGR ; CFR 49 ; NOM ; ANTT ; NCh382 ; ADG ; NZS ; SANS
In total, the embedding of 14 compliance requirements for dangerous goods management:
- UNRTDG ; IMDG Code ; IATA-DGR ; ADR ; RID ; AND ; CFR 49
- TDG ; NOM ; ANTT ; NCh382 ; ADG ; NZS ; SANS

Picture 9: Help ensure that organizations have the most up-to-date compliance information.
Effects on Existing Data
The delivery of a new list for a compliance requirement version has the following effects on existing data:
Effects on the Technical Name:
- If you select an organic peroxide or a self-reactive substance when classifying a product according to the dangerous goods regulations containing organic peroxides lists and self-reactive substances lists, the Technical Name column is no longer displayed. You can't change any technical names because the system uses the names from the dangerous goods lists.
- If you've entered a technical name for an organic peroxide or a self-reactive substance in the Manage Technical Names for Substances app, this name is no longer used in the dangerous goods description for the dangerous goods regulations containing organic peroxides lists and self-reactive substances lists. The names from the dangerous goods lists are used instead.
Effects on the Content:
- For the updated compliance requirements, you need to confirm the changes in these compliance requirements using the “Activate Compliance Requirements - Dangerous Goods” app.
- For the new compliance requirement version, you need to activate this version using the “Activate Compliance Requirements - Dangerous Goods” app. After activating the compliance requirement version, you can use the “Manage Regulation Updates - Unpackaged Products” and “Manage Regulation Updates - Unpackaged Products” apps to reclassify your dangerous goods.
Related Information
For more information about the delivered content and the handling of technical names, see the product assistance for Product Compliance:
Dangerous Goods Regulation and Classification in China
Business Background
When a product is intended to be transported, you, as a dangerous goods specialist, are responsible for assessing this product. If the product is a dangerous good, you have to classify it according to the dangerous goods regulations that are applicable to the country/region in which the product is transported.
With this new 2023 release, you can now classify unpackaged and packaged products according to the Chinese JT/T 617.3 dangerous goods regulation.
For more information about the JT/T 617.3 compliance requirement, see Classification of Dangerous Goods According to Chinese JT/T 617.3 Regulation.
Key Features
To support the classification according to JT/T 617.3, a new compliance requirement and a new app are delivered, and an existing app has been enhanced:
New Compliance Requirement
The new JT/T 617.3 compliance requirement is delivered with the JT/T 617.3-2018 version.
This new compliance requirement is based on the new JT/T 617.3 Content-Based Regulation compliance pattern.
New and Enhanced Apps
The new “Classify Dangerous Good According to JT/T 617.3 - Unpackaged Product” app (F7436) is delivered to classify unpackaged products according to JT/T 617.3.
The “Classify Dangerous Good - Packaged Product” app (F4833) is enhanced to support the classification according to JT/T 617.3.

Picture 10: Simplify classification of products by use of regulatory dangerous goods content for data maintenance.
For more information, see Preparing Basic Data for Dangerous Goods Assessments.
Filling Process for Dangerous Goods for Tanks and Bulk Containers
Business Background
The process of classifying dangerous goods that are transported in tanks or bulk containers is different from the process of classifying already packed dangerous goods. For packing dangerous goods, you need, for example, information about the packaging, such as the code and quantity of the dangerous goods package and information about the inner package. This information is not needed for tanks and bulk containers. In addition, when you transport dangerous goods in packages, the shipping quantity per package is fixed and defined by the size of the package. When transporting dangerous goods in tanks or in bulk containers, the amount of the product that is filled in the tank or bulk container can differ from shipment to shipment.
Key Features
This new 2023 release supports the classifying and shipping of dangerous goods in tanks and bulk containers as follows:
The new Tank or Bulk Container flag is introduced in the Specify Descriptions of Dangerous Goods Packages configuration activity. This flag indicates that the packaging is a tank or a bulk container.
If you select a packaging for which this flag is set, the system displays only the description of the dangerous goods package in the Edit Packaging Details dialog. The code and quantity information of the dangerous goods package and data for an inner package is no longer displayed.
The following new placeholders are delivered:
- <<SHIPPED_QUANTITY_TANK>>
- <<CFR_DG_BASIC_DESCRIPTION_ROAD_RAIL_TANK>>
- <<CFR_DG_BASIC_DESCRIPTION_INLAND_WTRWY_TANK>>
These placeholders are resolved with the amount of the product that is filled in the tank or bulk container as entered on documents within the value chain, such as sales orders, delivery notes, and freight orders. The placeholders are used for the enclosure variants UN Portable Tank, Regulation-Specific Tank, and UN Bulk Container.
The description templates are adapted to use the new placeholders when you select an enclosure variant for tanks and bulk containers.

Picture 11: Enable proper handling of dangerous goods filled in tanks or bulk containers.
Effects on Customizing
In the Customizing under Product Compliance > Dangerous Goods Management, the Specify Descriptions of Dangerous Goods Packages activity is changed as follows:
- The new Tank or Bulk Container flag is added that indicates if the packaging is a tank or a bulk container.
- The descriptions in plural for tanks are replaced with the descriptions in singular because the shipment of multiple tanks is not supported.
- An entry for a bulk container is added in singular for all descriptions.
You can find more information about classifying dangerous goods in the product assistance for Product Compliance. See Packaged Dangerous Goods Transported in Tanks and Bulk Containers.
Support of Packers in Warehouse with Dangerous Goods Marking and Labeling Information
Business Background
Marking texts are graphics that indicate a special condition or property of a package, such as a mark for keeping dangerous goods away from heat. Hazard labels depict the hazard of a dangerous good. Hazard labels are shaped like diamonds with a background color that highlights the hazard. Marking texts and hazard labels are used for labeling dangerous goods packages.
For a packer of dangerous goods in a warehouse, it's important to know the labeling and marking information for a product that is to be transported. The packer has to make sure that all required marking texts and labels are affixed on the package to comply with the applicable dangerous goods regulations.
Key Features
To support the packer, the “View Markings and Labels – Dangerous Goods” app (F7369) is provided. With this app, the packer can search by a business document ID and view the labeling and marking information for all items that are included in this business document.

Picture 12: Enable packers to create packages that are compliant with dangerous goods regulations.
The following business documents are supported:
- Sales Order
- Outbound Delivery
- Freight Order
- Freight Unit
For more information, see View Markings and Labels - Dangerous Goods.
Additional Details for the Dangerous Goods Check for Sales Orders
Business Background
The Dangerous Goods check in sales orders facilitate effective logistics planning. It helps determine the appropriate mode of transportation and packaging requirements and ensures compliance with restrictions imposed by regulatory authorities. This information can be used to optimize shipment routes, consolidate orders, and streamline the overall logistics process, resulting in cost savings and improved operational efficiency.
Key Features
The sales representative can enter a shipping type, such as road, rail, sea, or air, in the sales documents to suggest the main mode of transport for transportation planning. If entered, this shipping type is then used in addition to the departure and destination country/region as input for the dangerous goods check that is carried out in this business document.
The system determines the dangerous good regulations that need to be checked for the shipping types as follows:
- If the shipping type is Air, the dangerous goods classifications for IATA-DGR are checked. In addition, the classifications for all applicable dangerous goods regulations in the departure and destination countries/regions for the modes of transport Road and Rail are also checked.
- If the shipping type is Sea, the dangerous goods classifications for IMDG-Code are checked. In addition, the classifications for all applicable dangerous goods regulations in the departure and destination countries/regions for the modes of transport Road and Rail are also checked.
- If the shipping type is Rail, the dangerous goods classifications for all applicable dangerous goods regulations in the departure and destination countries/regions for the modes of transport Road and Rail are checked.
- If the shipping type is Road, the dangerous goods classifications for all applicable dangerous goods regulations in the departure and destination countries/regions for the mode of transport Road are checked.

Picture 13: Reduce effort for the sales representative to check why the transport of a product might be restricted if the shipping type of the main leg is already known and defined in the sales order.
For more information, see Dangerous Goods Check in Sales Processes and Determination of the Applicable Regulations.
SAP Fiori app for Viewing Regulatory Data for Dangerous Goods
Business Background
As a dangerous goods specialist, you want to get an overview of the dangerous goods data for a specific regulation or a specific UN number. This overview of the available regulatory data can help you in the process of classifying your product. In addition, to a certain level, this overview of data can replace your research in the printed versions of the dangerous goods regulations.
Key Features
With this new 2023 release, we introduce a new SAP Fiori app “View of Regulatory Data for Dangerous Goods”. With this app, you can view all available regulatory data for a UN number for a certain regulation.
- You can access that app from a tile on the SAP Fiori launchpad or from the View Regulatory Data link in the apps in which you classify a product according to the required dangerous goods regulations.
- In the app, you can select various filters and search for regulatory data. In the search results list, you can select the data set to view details about the basic classification and enclosure-specific list data. For organic peroxides and for self-reactive substances, you can view more information, such as the name as it's used on the corresponding dangerous goods lists.

Picture 14: Provide available regulatory data directly in the classification process.
Remark: If you open the app in two separate browser windows, you can easily compare data from different regulations
For more information, see View Regulatory Data - Dangerous Goods.
New SAP Fiori app to View Dangerous Goods Information
Business Background
To effectively plan and carry out logistics operations, logistic personnel require knowledge about dangerous goods. This involves identifying the most suitable mode of transportation, choosing carriers with the proper certifications and abilities to handle dangerous goods, and ensuring compliance with transportation regulations and guidelines. Having access to information about dangerous goods aids in optimizing logistics routes, overseeing storage, and handling conditions, and collaborating with relevant parties in the supply chain.
Key Features
With this new SAP Fiori app “Dangerous Goods Information” (F7328), you can search for products for which you want to see the dangerous goods data, and you can view a list of all products that have the Transported logistics role assigned. In this list, you can search for products for which you want to see the dangerous goods data. You can use filter criteria to narrow down your results list. In the results list, you can select a product and navigate to the “Classify Unpackaged Dangerous Goods” or “Classify Packaged Dangerous Goods” apps where you can view its dangerous goods classification.

Picture 15: Enable more efficient compliance with dangerous goods regulations.
For more information, see Dangerous Goods Information.
Safety Data Sheet and Label Management
A Safety Data Sheet, also known as a Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS), is a comprehensive document that provides detailed information about the hazards, handling, storage, and emergency measures associated with a particular chemical substance or product. SDS contains critical information such as chemical composition, physical and chemical properties, toxicity data, first aid measures, handling and storage instructions, disposal considerations, and regulatory compliance details.
Label management ensures that labels are compliant with applicable regulations, like GHS, OSHA, EPA, FDA, and other regional or industry-specific requirements.
Regulatory Content Update - Safety Data Sheets
With this 2023 release, new and updated content is delivered to your system. There are 65 updated compliance requirement and compliance requirement versions and 5 new versions added to support the data model. These include covering GHS regulations for Chile, Taiwan, Thailand, and the Philippines, as well as Exposure Scenarios for the European Union and the Korean number for safety data sheets. Additionally, there are 81 updated and 22 new compliance requirement versions for occupational exposure limits.
102 compliance requirements for safety data sheet management embedded.
109 compliance requirements related to safety data sheet authoring:
- 1 accidental release measures
- 57 components with occupational exposure limits
- 1 exposure scenario
- 1 firefighting measure / 1 first aid measure
- 8 GHS classification / 10 GHS labeling
- 23 hazardous ingredients
- 1 Korean MSDS number / 1 NFPA rating
- 1 personal protection measure
- 1 registration of confidential business information
- 1 SARA classification
- 1 storage class / 1 waste code
92 compliance requirements for occupational exposure limits

Picture 16: Enable customers to rely on embedded regulatory content, including phrases, graphics, and listed substances.
Business Partner Multi-Address Support
Business Background
Customers may have different needs when it comes to receiving SDS, such as their preferred format, language, or delivery address. With Multi Address Support, companies can keep track of multiple addresses for each customer, guaranteeing that the SDS is delivered to the right place according to their individual requirements. This adaptability helps meet customer demands and improves overall satisfaction.
Key Features
This new 2023 release enables the support of multiple addresses assigned to a business partner in processes for safety data sheet shipments.
This applies to the following safety data sheet processes:
Safety Data Sheet Shipment
- The “Compliance Information - For Products” app (F3226) provides a value help to select the address if you have selected a customer that has multiple addresses assigned when you send a safety data sheet manually.
- The selected address of the ship-to party of delivery is considered in the shipment request for safety data sheets.
- In the “Monitor Shipments - Safety Data Sheets” app (F4309) you can view the selected address of the safety data sheet recipient.
Maintenance of the Sender Address for the Safety Data Sheet
- The “Manage Contact Data - Safety Data Sheets” app (F4521) provides a value help to select the sender address if you have selected a business partner that has multiple addresses assigned.
International Address Version
- With this feature international address versions (IAV) are considered when printing addresses on the safety data sheet and on the cover sheet.

Picture 17: Increase efficiency through the ability to handle multiple addresses and print multiple product names.
Remark: Safety data sheet processes consider multi-address assignments if the feature Multiple Address Handling in SD Documents Using SAP Business Partner is activated for Quote-2-Cash processes.
For more information, see Feature Overview for Multiple Address Handling and Multiple Address Handling in SD Documents Using SAP Business Partner.
New SAP Fiori app to Validate and Print Labels
Business Background
Labels are crucial in providing consumers with necessary information about a product, allowing them to make well-informed choices about its safe and appropriate usage. These labels typically include safety warnings, hazard symbols, usage instructions, and precautions, all of which are vital elements. By ensuring that labels are clear and precise, consumers can be safeguarded from potential dangers associated with the product, ultimately minimizing the likelihood of accidents, injuries, or misapplication.
Key Features
With this new SAP Fiori app “Validate and Print Labels” (F6656), you can validate and print labels. Labels can be validated based on the previous label configurations created in the “Manage Label Configurations” app and their assignment to a product in the “Manage Label Assignments” app. Depending on the business document, you can validate the completeness of relevant labels. Afterward, you can create a print request for a specific label. This assessment can help you make sure that the labels are properly set up prior to the printing process.

Picture 18: Improve labeling for general scenarios.
This “Validate and Print Label” app enables users to:
- Search among products as part of different business processes (for example, manufacturing, delivery, or sales),
- Determine needed labels for each product and business process,
- Send a print request to the external output system for the actual label printing.
For more information, see Label Configuration and Label Assignment.
New SAP Fiori apps to Manage Exposure Scenarios and Manage Extended Safety Data Sheet Annex
Manage eSDS Annex
An exposure scenario describes how the exposure of humans and the environment to a substance or mixture can be controlled to ensure its safe use. An exposure scenario refers to an identified use or group of similar identified uses, such as formulation, processing, or production.
With exposure scenarios, you describe the operational conditions and risk management measures that ensure the safe use of the substance or mixture to adequately control the risks to human health and the environment. Exposure scenarios cover the entire lifecycle of the substance or mixture, including formulation, industrial and professional end use, consumer use, and production. An exposure scenario can be made up of contributing scenarios that provide additional information on the safe use of the substance or mixture.
With this new “Manage eSDS Annex” (F6751), you can create new or assign existing exposure scenarios to an unpackaged product. You can specify the data that is required as an annex to a safety data sheet to ensure that the unpackaged product stays compliant.

Picture 19: Create a new exposure scenario or assign an existing one to an unpackaged product.
For more information, see the Manage eSDS Annex.
Management of Exposure Scenarios
With the new SAP Fiori app “Manage Exposure Scenarios” (F6749) you can provide detailed information on an exposure scenario to describe the operational conditions and risk management measures that ensure safe use of the substance or mixture. You can edit the data to ensure that it is up to date and that the unpackaged product stays compliant. You can also create a new or assign an existing contributing scenario. You can then release a version of the exposure scenario to use in the “Manage eSDS Annex” app.

Picture 20: Create a new or add an existing exposure scenario.
For more information, see Manage Exposure Scenarios.
Management of Contributing Scenarios
With the new SAP Fiori app “Manage Contributing Scenarios” (F6750), you can provide detailed information on contributing activities for a specific use that are part of an exposure scenario. You can then release a version of the contributing scenario to use in the exposure scenarios.

Picture 21: Enter detailed information depending on the type of contributing scenario.
For more information, see Manage Contributing Scenarios.
Management of Safety Data Sheet (SDS) Numbers on Korean SDSs
Business Background
If a safety data sheet is sent to South Korea, an SDS number must be printed in the header of the safety data sheet. This SDS number is assigned when the safety data sheet is submitted to the Korean Ministry of Employment and Labor (MoEL).
The Korean SDS Number consists of the following two parts:
- A product-specific part, also called the SDS Number (Product Part)
- A business-place-specific part also called the SDS Number (Company Part)
Key Features
The company-specific part is entered in the "Manage Legal Entities" app. The product-specific part is entered in the new “Manage Korean SDS Number” (F7414) app as part of the compliance assessment for an unpackaged product.
You can then create the legally required safety data sheet number for South Korea which consists of a product part and a company part. These two parts are combined together and printed on the safety data sheet during the final generation of the South Korean safety data sheet.

Picture 22: Allow the creation of Korean SDSs that are compliant with the current Korean regulations.
The key features are:
- New app to create the legally required product part of the SDS number of South Korea
- Enhancement of legal entities and legal entities mapping apps to define the company part of the SDS number of South Korea
- Printing of the combined product and company part on the SDS during the final generation of South Korean SDSs
For more information, see Manage Korean SDS Number.
Thanks for reading this blog post.
If you are also interested in other Lines of Business and Industries for this new SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition 2023 release, I would like to draw your attention to my link collection blog – The Link Collection.
If you want to see the entire PDF presentation of all innovations, see here.
If you want to learn more about SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition, join our Partner Community. This group focuses on providing enhanced learnings and periodic updates with respect to the SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition product. Our goal is to facilitate collaboration with your peers and SAP subject matter experts.
For general roadmap information please check the SAP S/4HANA Roadmap.
For more information on SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition, check out the following links:
- Collection blog for Product Compliance here
- Collection blog for EHS here
- SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition release info: com/s4hana
- SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition, and SAP S/4HANA Community here
- SAP S/4HANA PSCC Digital Enablement Wheel here
- Inside SAP S/4HANA Podcast here
- Best practices for SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition here
- Help Portal Product Page here
- Feature Scope Description here
- What’s New here
Follow the SAP S/4HANA Cloud tag and the PSCC_Enablement tag to stay up to date with the latest blog posts.
Follow us via @Sap and #S4HANA, or myself via @VoglerChrist and LinkedIn
- SAP Managed Tags:
- SAP S/4HANA for product compliance,
- SAP S/4HANA Private Cloud,
- SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud
Labels:
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
Labels in this area
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
1 -
Business Trends
363 -
Business Trends
24 -
Customer COE Basics and Fundamentals
1 -
Digital Transformation with Cloud ERP (DT)
1 -
Event Information
461 -
Event Information
24 -
Expert Insights
114 -
Expert Insights
159 -
General
1 -
Governance and Organization
1 -
Introduction
1 -
Life at SAP
415 -
Life at SAP
2 -
Product Updates
4,684 -
Product Updates
219 -
Roadmap and Strategy
1 -
Technology Updates
1,502 -
Technology Updates
89
Related Content
- Enhanced RISE with SAP Methodology with clean core quality checks in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
- Jumpstart your cloud ERP journey with guided enablement in RISE with SAP Methodology in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
- ISAE 3000 for SAP S/4HANA Cloud Public Edition - Evaluation of the Authorization Role Concept in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
- SAP Fiori for SAP S/4HANA - Composite Roles in launchpad content and layout tools in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
- Working with SAFe Epics in the SAP Activate Discover phase in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
Top kudoed authors
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 11 | |
| 10 | |
| 9 | |
| 7 | |
| 7 | |
| 7 | |
| 6 | |
| 5 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 |