
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Technology
- Technology Blogs by Members
- Value Creation with Trusted Business Partner Data
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
High-quality business partner data is fundamental for enterprise success today. More than just accuracy, it's about having consistent, up-to-date information on customers and suppliers to make important decisions. Quality business partner data enables organizations to find new opportunities, build stronger relationships, and boost their market presence.
I am Kai Hüner, responsible for the SAP-endorsed app CDQ First Time Right at CDQ AG. In this blog post, I will discuss the importance of trusted business partner data. I will also highlight the dualistic role of artificial intelligence (AI) which both relies on and amplifies the potential of this trusted data. Additionally, I will explain the effective integration and utilization of this data in customers' SAP environments. For further insights, please refer to my blog post First Time Right with Trusted Business Partner Data in SAP Master Data Governance.
What is trusted business partner data?
Trusted business partner data is crucial information about customers and vendors, defined by its source, accuracy, and timeliness. Let's examine how different external data types contribute to this trust:
- Open Data: This is data everyone can access and republish without restrictions. Common sources include governments, NGOs, and certain businesses. When looking at business partners, databases listing registered entities, like their official names, addresses, and industries, are important. For instance, to verify a vendor's address, a national postal service's database might be the go-to resource. Many, like trade registers, are seen as reliable because they follow strict rules and, often, legal requirements, such as tax number registers.
- Commercial Data: These datasets come from specialized vendors at a cost, often highlighting their accuracy and updated nature. Consider databases offering deep insights into potential customers or vendors – from their financial status to their past activities. Companies like Dun & Bradstreet or Bureau van Dijk give detailed company profiles. However, trust levels in these providers can differ. Some companies might trust the data based on positive past experiences, while others might be more cautious.
- Shared Data: This is data that's exchanged in dedicated platforms or communities. An example is the CDQ Data Sharing community; if one member company updates information about a common business partner, every member gains from this new information. The combined checking by many companies can boost trust. On a related note, the SAP Business Network provides a platform for a range of data sharing and business network activities, making it another important reference in this context. Still, each company has its own level of trust in this shared data.
- Web Data: Company information found online, be it on official websites, social media, or news sites, offers a wealth of insights. A comment on a social media platform or a news release can provide key details. But the vast and changing nature of the internet means trust in this data often varies. Some might trust data from a well-known company site, while others might double-check it against other sources.
To conclude, trust in business partner data varies. Some sources, like trade registers, are widely trusted, but others depend on individual judgment. Companies need to navigate open, commercial, shared, and web data to create their own understanding of trust, aiming to get a complete and correct view of their business partners.
How does trusted business partner data create value?
Trusted business partner data serves multiple purposes across various domains of a business. Its role in optimizing processes, managing risks, and informing strategies is crucial. The entire lifecycle of such data, from its source to its application in business strategies, contributes significantly to a company's success. The following figure showcases this data value chain and the related data value formula that translates data into tangible business outcomes.
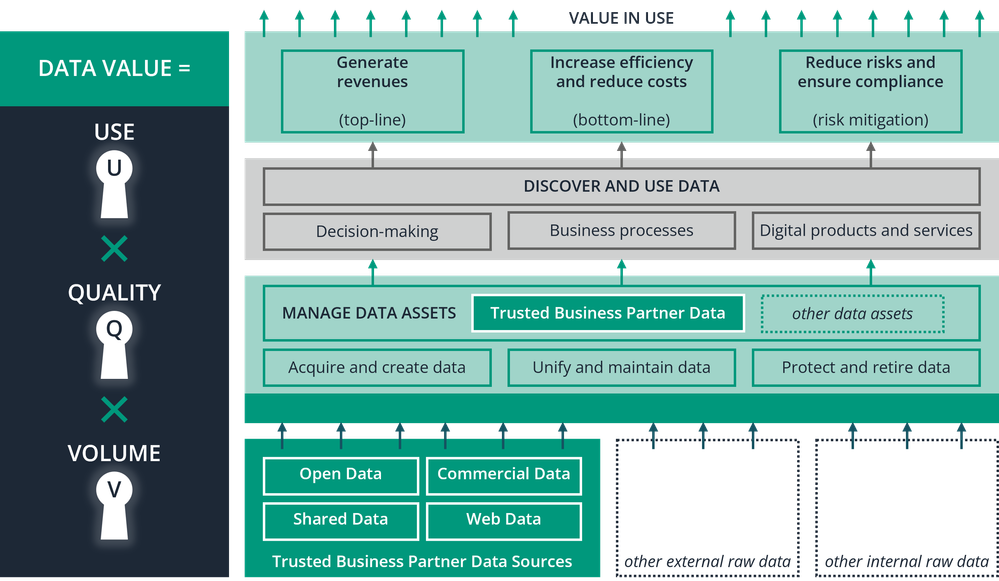
Utilizing this formula as a reference, let's further examine how trusted business partner data contributes to diverse business value:
- Digitalization of business processes: Efficient processes in areas like procurement, supply chain, marketing, and sales rely on accurate business partner data. Errors due to poor data can increase operational costs. According to the Tenfold Rule, the cost of rectifying poor data quality can be ten times higher than managing it correctly from the start.
- Risk management and compliance: Precise and consistent business partner data ensures that companies can effectively screen against sanction or embargo lists and adhere to key regulations. Quality data also helps in identifying potential financial and operational risks early on.
- Driving business insights and leveraging AI: Having a harmonized view of business partner data across the company sets the stage for deeper analyses. This includes evaluations such as assessing procurement volumes to refine sourcing strategies. Moreover, for AI-driven methods like customer segmentation or optimizing supply chains, quality master data is crucial, especially when integrated with other data sources.
- Integration with external data sources: Merging business partner data with other data types can deepen insights. For instance, merging supplier data with market insights might unveil hidden market opportunities.
- Data quality as an ROI (return on investment) multiplier: Reliable business partner data ensures that insights derived are dependable, leading to effective strategies. When marketing campaigns are built on accurate data, the returns are optimized.
- Empowering digital strategies: Quality vendor data can streamline e-commerce processes. Similarly, dependable customer data improves personalization, enhancing customer loyalty.
- Fostering collaboration and innovation: When businesses have mutual trust in their shared data's accuracy, they are more likely to collaborate, leading to innovative solutions and offerings.
How does trusted business partner data stand out in the age of AI?
In the current landscape where AI plays a prominent role, the significance of trusted business partner data becomes even more pronounced. AI systems, particularly machine learning models, operate at their peak efficiency when fed with accurate and reliable data. Trusted business partner data offers just that – a foundation of accuracy that these models can rely on.
For applications that require predictions, such as forecasting market movements or discerning customer preferences, the quality of the data being used becomes paramount. A machine learning model powered by detailed, high-quality business partner data is more likely to yield accurate results than one using less reliable data.
But trust in data extends beyond its accuracy. It is also about the origin of the data and its adherence to certain standards. Data that is sourced from credible origins, meets legal requirements, and aligns with ethical considerations holds a different value. When organizations base their decisions on such data, they are ensuring a level of responsibility and integrity in their actions.
Furthermore, as businesses become more interconnected and data-driven, the ability to verify the authenticity and ethical collection of data becomes vital. AI, for all its capabilities, is not equipped to evaluate these aspects of data on its own. While it can sift through vast amounts of information and identify patterns, it can't inherently determine if a piece of data was ethically sourced or if its origin is authentic.
This limitation underlines the importance of human involvement. Even in an era where AI is poised to take on an increasing number of tasks, the process of verifying and trusting data remains a distinctly human responsibility. As we rely more on AI for decision-making, ensuring the trustworthiness of the data we provide it becomes crucial. The partnership between humans and AI is strengthened by the quality and integrity of the data at its core, emphasizing the unique and continuing role humans play in the data validation process.
How to use trusted business partner data in an SAP landscape?
Within an SAP environment, using trusted business partner data is essential for enhancing operations and refining decision-making. SAP Master Data Governance (MDG) plays a key role in this approach, ensuring data remains consistent, unified, and accessible throughout the organization.
SAP MDG offers a distinct advantage through its data provider integration feature. This allows for the immediate incorporation of trusted external business partner data sources. Such a feature ensures timely access to top-tier data, minimizing errors and reinforcing the stability of operational processes.
For detailed guidance on configuring CDQ as a data provider for SAP MDG, please refer to my blog post First Time Right with Trusted Business Partner Data in SAP Master Data Governance.
Key takeaways
Trusted business partner data is about having essential, accurate, and timely information on customers and vendors. Its trust levels can vary based on the source, spanning open, paid, shared, and web data. This data is pivotal for optimizing business processes, managing risks, and ensuring compliance. Its significance isn't confined to its accuracy but extends to its capability to create tangible business outcomes.
Transparency in information origin and the availability of trusted sources are pivotal in an environment significantly influenced by AI. Ensuring that provenance information is accessible, and that data comes from reliable origins is fundamental, not only for AI operations but also for strategic decision-making. Such clear, trustworthy data maximizes the benefits and reliability of AI analyses and predictive models, enhancing their application across various business activities.
Within SAP environments, trusted business partner data stands out as a critical element. SAP MDG guarantees that data remains consistent and unified across the organization, and its data provider integration feature ensures access to quality data in real-time.
- SAP Managed Tags:
- Data and Analytics,
- SAP S/4HANA business partner,
- Artificial Intelligence,
- SAP Master Data Governance
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
"automatische backups"
1 -
"regelmäßige sicherung"
1 -
"TypeScript" "Development" "FeedBack"
1 -
505 Technology Updates 53
1 -
ABAP
14 -
ABAP API
1 -
ABAP CDS Views
2 -
ABAP CDS Views - BW Extraction
1 -
ABAP CDS Views - CDC (Change Data Capture)
1 -
ABAP class
2 -
ABAP Cloud
3 -
ABAP Development
5 -
ABAP in Eclipse
1 -
ABAP Platform Trial
1 -
ABAP Programming
2 -
abap technical
1 -
abapGit
1 -
absl
2 -
access data from SAP Datasphere directly from Snowflake
1 -
Access data from SAP datasphere to Qliksense
1 -
Accrual
1 -
action
1 -
adapter modules
1 -
Addon
1 -
Adobe Document Services
1 -
ADS
1 -
ADS Config
1 -
ADS with ABAP
1 -
ADS with Java
1 -
ADT
2 -
Advance Shipping and Receiving
1 -
Advanced Event Mesh
3 -
AEM
1 -
AI
7 -
AI Launchpad
1 -
AI Projects
1 -
AIML
9 -
Alert in Sap analytical cloud
1 -
Amazon S3
1 -
Analytical Dataset
1 -
Analytical Model
1 -
Analytics
1 -
Analyze Workload Data
1 -
annotations
1 -
API
1 -
API and Integration
3 -
API Call
2 -
API security
1 -
Application Architecture
1 -
Application Development
5 -
Application Development for SAP HANA Cloud
3 -
Applications and Business Processes (AP)
1 -
Artificial Intelligence
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
5 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) 1 Business Trends 363 Business Trends 8 Digital Transformation with Cloud ERP (DT) 1 Event Information 462 Event Information 15 Expert Insights 114 Expert Insights 76 Life at SAP 418 Life at SAP 1 Product Updates 4
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise Oil Gas IoT Exploration Production
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise sustainability responsibility esg social compliance cybersecurity risk
1 -
ASE
1 -
ASR
2 -
ASUG
1 -
Attachments
1 -
Authorisations
1 -
Automating Processes
1 -
Automation
2 -
aws
2 -
Azure
1 -
Azure AI Studio
1 -
Azure API Center
1 -
Azure API Management
1 -
B2B Integration
1 -
Backorder Processing
1 -
Backup
1 -
Backup and Recovery
1 -
Backup schedule
1 -
BADI_MATERIAL_CHECK error message
1 -
Bank
1 -
BAS
1 -
basis
2 -
Basis Monitoring & Tcodes with Key notes
2 -
Batch Management
1 -
BDC
1 -
Best Practice
1 -
bitcoin
1 -
Blockchain
3 -
bodl
1 -
BOP in aATP
1 -
BOP Segments
1 -
BOP Strategies
1 -
BOP Variant
1 -
BPC
1 -
BPC LIVE
1 -
BTP
13 -
BTP Destination
2 -
Business AI
1 -
Business and IT Integration
1 -
Business application stu
1 -
Business Application Studio
1 -
Business Architecture
1 -
Business Communication Services
1 -
Business Continuity
1 -
Business Data Fabric
3 -
Business Fabric
1 -
Business Partner
12 -
Business Partner Master Data
10 -
Business Technology Platform
2 -
Business Trends
4 -
BW4HANA
1 -
CA
1 -
calculation view
1 -
CAP
4 -
Capgemini
1 -
CAPM
1 -
Catalyst for Efficiency: Revolutionizing SAP Integration Suite with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and
1 -
CCMS
2 -
CDQ
12 -
CDS
2 -
Cental Finance
1 -
Certificates
1 -
CFL
1 -
Change Management
1 -
chatbot
1 -
chatgpt
3 -
CL_SALV_TABLE
2 -
Class Runner
1 -
Classrunner
1 -
Cloud ALM Monitoring
1 -
Cloud ALM Operations
1 -
cloud connector
1 -
Cloud Extensibility
1 -
Cloud Foundry
4 -
Cloud Integration
6 -
Cloud Platform Integration
2 -
cloudalm
1 -
communication
1 -
Compensation Information Management
1 -
Compensation Management
1 -
Compliance
1 -
Compound Employee API
1 -
Configuration
1 -
Connectors
1 -
Consolidation Extension for SAP Analytics Cloud
2 -
Control Indicators.
1 -
Controller-Service-Repository pattern
1 -
Conversion
1 -
Cosine similarity
1 -
cryptocurrency
1 -
CSI
1 -
ctms
1 -
Custom chatbot
3 -
Custom Destination Service
1 -
custom fields
1 -
Customer Experience
1 -
Customer Journey
1 -
Customizing
1 -
cyber security
3 -
cybersecurity
1 -
Data
1 -
Data & Analytics
1 -
Data Aging
1 -
Data Analytics
2 -
Data and Analytics (DA)
1 -
Data Archiving
1 -
Data Back-up
1 -
Data Flow
1 -
Data Governance
5 -
Data Integration
2 -
Data Quality
12 -
Data Quality Management
12 -
Data Synchronization
1 -
data transfer
1 -
Data Unleashed
1 -
Data Value
8 -
database tables
1 -
Datasphere
3 -
datenbanksicherung
1 -
dba cockpit
1 -
dbacockpit
1 -
Debugging
2 -
Defender
1 -
Delimiting Pay Components
1 -
Delta Integrations
1 -
Destination
3 -
Destination Service
1 -
Developer extensibility
1 -
Developing with SAP Integration Suite
1 -
Devops
1 -
digital transformation
1 -
Documentation
1 -
Dot Product
1 -
DQM
1 -
dump database
1 -
dump transaction
1 -
e-Invoice
1 -
E4H Conversion
1 -
Eclipse ADT ABAP Development Tools
2 -
edoc
1 -
edocument
1 -
ELA
1 -
Embedded Consolidation
1 -
Embedding
1 -
Embeddings
1 -
Employee Central
1 -
Employee Central Payroll
1 -
Employee Central Time Off
1 -
Employee Information
1 -
Employee Rehires
1 -
Enable Now
1 -
Enable now manager
1 -
endpoint
1 -
Enhancement Request
1 -
Enterprise Architecture
1 -
ESLint
1 -
ETL Business Analytics with SAP Signavio
1 -
Euclidean distance
1 -
Event Dates
1 -
Event Driven Architecture
1 -
Event Mesh
2 -
Event Reason
1 -
EventBasedIntegration
1 -
EWM
1 -
EWM Outbound configuration
1 -
EWM-TM-Integration
1 -
Existing Event Changes
1 -
Expand
1 -
Expert
2 -
Expert Insights
2 -
Exploits
1 -
Fiori
14 -
Fiori Elements
2 -
Fiori SAPUI5
12 -
first-guidance
1 -
Flask
1 -
FTC
1 -
Full Stack
8 -
Funds Management
1 -
gCTS
1 -
General
1 -
Generative AI
1 -
Getting Started
1 -
GitHub
9 -
Grants Management
1 -
groovy
1 -
GTP
1 -
HANA
6 -
HANA Cloud
2 -
Hana Cloud Database Integration
2 -
HANA DB
2 -
HANA XS Advanced
1 -
Historical Events
1 -
home labs
1 -
HowTo
1 -
HR Data Management
1 -
html5
8 -
HTML5 Application
1 -
Identity cards validation
1 -
idm
1 -
Implementation
1 -
input parameter
1 -
instant payments
1 -
Integration
3 -
Integration Advisor
1 -
Integration Architecture
1 -
Integration Center
1 -
Integration Suite
1 -
intelligent enterprise
1 -
iot
1 -
Java
1 -
job
1 -
Job Information Changes
1 -
Job-Related Events
1 -
Job_Event_Information
1 -
joule
4 -
Journal Entries
1 -
Just Ask
1 -
Kerberos for ABAP
8 -
Kerberos for JAVA
8 -
KNN
1 -
Launch Wizard
1 -
Learning Content
2 -
Life at SAP
5 -
lightning
1 -
Linear Regression SAP HANA Cloud
1 -
Loading Indicator
1 -
local tax regulations
1 -
LP
1 -
Machine Learning
2 -
Marketing
1 -
Master Data
3 -
Master Data Management
14 -
Maxdb
2 -
MDG
1 -
MDGM
1 -
MDM
1 -
Message box.
1 -
Messages on RF Device
1 -
Microservices Architecture
1 -
Microsoft Universal Print
1 -
Middleware Solutions
1 -
Migration
5 -
ML Model Development
1 -
Modeling in SAP HANA Cloud
8 -
Monitoring
3 -
MTA
1 -
Multi-Record Scenarios
1 -
Multiple Event Triggers
1 -
Myself Transformation
1 -
Neo
1 -
New Event Creation
1 -
New Feature
1 -
Newcomer
1 -
NodeJS
3 -
ODATA
2 -
OData APIs
1 -
odatav2
1 -
ODATAV4
1 -
ODBC
1 -
ODBC Connection
1 -
Onpremise
1 -
open source
2 -
OpenAI API
1 -
Oracle
1 -
PaPM
1 -
PaPM Dynamic Data Copy through Writer function
1 -
PaPM Remote Call
1 -
PAS-C01
1 -
Pay Component Management
1 -
PGP
1 -
Pickle
1 -
PLANNING ARCHITECTURE
1 -
Popup in Sap analytical cloud
1 -
PostgrSQL
1 -
POSTMAN
1 -
Prettier
1 -
Process Automation
2 -
Product Updates
5 -
PSM
1 -
Public Cloud
1 -
Python
4 -
python library - Document information extraction service
1 -
Qlik
1 -
Qualtrics
1 -
RAP
3 -
RAP BO
2 -
Record Deletion
1 -
Recovery
1 -
recurring payments
1 -
redeply
1 -
Release
1 -
Remote Consumption Model
1 -
Replication Flows
1 -
research
1 -
Resilience
1 -
REST
1 -
REST API
1 -
Retagging Required
1 -
Risk
1 -
Rolling Kernel Switch
1 -
route
1 -
rules
1 -
S4 HANA
1 -
S4 HANA Cloud
1 -
S4 HANA On-Premise
1 -
S4HANA
3 -
S4HANA_OP_2023
2 -
SAC
10 -
SAC PLANNING
9 -
SAP
4 -
SAP ABAP
1 -
SAP Advanced Event Mesh
1 -
SAP AI Core
8 -
SAP AI Launchpad
8 -
SAP Analytic Cloud Compass
1 -
Sap Analytical Cloud
1 -
SAP Analytics Cloud
4 -
SAP Analytics Cloud for Consolidation
3 -
SAP Analytics Cloud Story
1 -
SAP analytics clouds
1 -
SAP API Management
1 -
SAP BAS
1 -
SAP Basis
6 -
SAP BODS
1 -
SAP BODS certification.
1 -
SAP BTP
21 -
SAP BTP Build Work Zone
2 -
SAP BTP Cloud Foundry
6 -
SAP BTP Costing
1 -
SAP BTP CTMS
1 -
SAP BTP Innovation
1 -
SAP BTP Migration Tool
1 -
SAP BTP SDK IOS
1 -
SAP BTPEA
1 -
SAP Build
11 -
SAP Build App
1 -
SAP Build apps
1 -
SAP Build CodeJam
1 -
SAP Build Process Automation
3 -
SAP Build work zone
10 -
SAP Business Objects Platform
1 -
SAP Business Technology
2 -
SAP Business Technology Platform (XP)
1 -
sap bw
1 -
SAP CAP
2 -
SAP CDC
1 -
SAP CDP
1 -
SAP CDS VIEW
1 -
SAP Certification
1 -
SAP Cloud ALM
4 -
SAP Cloud Application Programming Model
1 -
SAP Cloud Integration for Data Services
1 -
SAP cloud platform
8 -
SAP Companion
1 -
SAP CPI
3 -
SAP CPI (Cloud Platform Integration)
2 -
SAP CPI Discover tab
1 -
sap credential store
1 -
SAP Customer Data Cloud
1 -
SAP Customer Data Platform
1 -
SAP Data Intelligence
1 -
SAP Data Migration in Retail Industry
1 -
SAP Data Services
1 -
SAP DATABASE
1 -
SAP Dataspher to Non SAP BI tools
1 -
SAP Datasphere
9 -
SAP DRC
1 -
SAP EWM
1 -
SAP Fiori
3 -
SAP Fiori App Embedding
1 -
Sap Fiori Extension Project Using BAS
1 -
SAP GRC
1 -
SAP HANA
1 -
SAP HCM (Human Capital Management)
1 -
SAP HR Solutions
1 -
SAP IDM
1 -
SAP Integration Suite
9 -
SAP Integrations
4 -
SAP iRPA
2 -
SAP LAGGING AND SLOW
1 -
SAP Learning Class
1 -
SAP Learning Hub
1 -
SAP Master Data
1 -
SAP Odata
2 -
SAP on Azure
2 -
SAP PartnerEdge
1 -
sap partners
1 -
SAP Password Reset
1 -
SAP PO Migration
1 -
SAP Prepackaged Content
1 -
SAP Process Automation
2 -
SAP Process Integration
2 -
SAP Process Orchestration
1 -
SAP S4HANA
2 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud
1 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud for Finance
1 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud private edition
1 -
SAP Sandbox
1 -
SAP STMS
1 -
SAP successfactors
3 -
SAP SuccessFactors HXM Core
1 -
SAP Time
1 -
SAP TM
2 -
SAP Trading Partner Management
1 -
SAP UI5
1 -
SAP Upgrade
1 -
SAP Utilities
1 -
SAP-GUI
8 -
SAP_COM_0276
1 -
SAPBTP
1 -
SAPCPI
1 -
SAPEWM
1 -
sapfirstguidance
1 -
SAPHANAService
1 -
SAPIQ
1 -
sapmentors
1 -
saponaws
2 -
SAPS4HANA
1 -
SAPUI5
5 -
schedule
1 -
Script Operator
1 -
Secure Login Client Setup
8 -
security
9 -
Selenium Testing
1 -
Self Transformation
1 -
Self-Transformation
1 -
SEN
1 -
SEN Manager
1 -
service
1 -
SET_CELL_TYPE
1 -
SET_CELL_TYPE_COLUMN
1 -
SFTP scenario
2 -
Simplex
1 -
Single Sign On
8 -
Singlesource
1 -
SKLearn
1 -
Slow loading
1 -
soap
1 -
Software Development
1 -
SOLMAN
1 -
solman 7.2
2 -
Solution Manager
3 -
sp_dumpdb
1 -
sp_dumptrans
1 -
SQL
1 -
sql script
1 -
SSL
8 -
SSO
8 -
Substring function
1 -
SuccessFactors
1 -
SuccessFactors Platform
1 -
SuccessFactors Time Tracking
1 -
Sybase
1 -
system copy method
1 -
System owner
1 -
Table splitting
1 -
Tax Integration
1 -
Technical article
1 -
Technical articles
1 -
Technology Updates
15 -
Technology Updates
1 -
Technology_Updates
1 -
terraform
1 -
Threats
2 -
Time Collectors
1 -
Time Off
2 -
Time Sheet
1 -
Time Sheet SAP SuccessFactors Time Tracking
1 -
Tips and tricks
2 -
toggle button
1 -
Tools
1 -
Trainings & Certifications
1 -
Transformation Flow
1 -
Transport in SAP BODS
1 -
Transport Management
1 -
TypeScript
3 -
ui designer
1 -
unbind
1 -
Unified Customer Profile
1 -
UPB
1 -
Use of Parameters for Data Copy in PaPM
1 -
User Unlock
1 -
VA02
1 -
Validations
1 -
Vector Database
2 -
Vector Engine
1 -
Visual Studio Code
1 -
VSCode
2 -
VSCode extenions
1 -
Vulnerabilities
1 -
Web SDK
1 -
work zone
1 -
workload
1 -
xsa
1 -
XSA Refresh
1
- « Previous
- Next »
- Deployment of Seamless M4T v2 models on SAP AI Core in Technology Blogs by SAP
- SAP Datasphere's updated Pricing & Packaging: Lower Costs & More Flexibility in Technology Blogs by Members
- PM Notification Configuration from DMC to ERP in Technology Blogs by Members
- Govern SAP APIs living in various API Management gateways in a single place with Azure API Center in Technology Blogs by Members
- Supporting Multiple API Gateways with SAP API Management – using Azure API Management as example in Technology Blogs by SAP
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 8 | |
| 8 | |
| 5 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 3 |