- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Technology
- Technology Blogs by Members
- SAP Enterprise Architecture: Positioning Blockchai...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
This blog, which follows on from the previous one in the series, "Why I love SAP and Blockchain Databases and why you should too 🚀", will deliver an approach to positioning Blockchain Technology as a Technology Standard in our Companies.
The goal of the previous blog in this series was to get us thinking about Blockchain Databases in our Companies, in the Enterprise, and the goal of this blog is to get us thinking about how to position an Enterprise Blockchain Platform as a Technology Standard in our SAP Enterprise Architecture.
Why do we need to do this ? Why does Blockchain need to be a Technology Standard within the Enterprise Architecture in our Companies ?
In our SAP Enterprise Architecture we use Technology Standards as a way of framing where we use what software applications and why, what is the purpose of that software application.
So for each Technology that we have in the house, we have a box which describes what that Technology and do, what it's strengths are, and therefore where we should use it.
This all sounds very formal, but in our personal lives we do this at home every day. We possibly have more than one pair of shoes, perhaps one pair for going to the office and one pair for going running. I don't really want to get in to a debate about how many pairs of shoes people have and which ones they use for what but I imagine that you get the point.
Some shoes are more suited to different activities than others. Some have a hard sole some have a soft sole. These are capabilities of the shoe, soft sole leans towards capability for sport, thanks to this soft sole capability the shoe is more appropriate to be used for, to be applied to sport, You get the point.
And it's the same with software, some software is more suited to different activities than others, these are capabilities. And by keeping a list of what software we have in the company and what the capabilities of the software are, and where the software is encouraged to be used, helps to ensure that in our SAP Enterprise Architecture decision making processes we more consistently use the different types of software that we have for the purposes in which they are intended based upon what they can do.
To be more formal, there is a very nice description of Technology Standards here, 'At the most basic level, technology standards establish boundaries for technology usage, spec....
If we agree that to be able to consistently, repeatedly use Enterprise Blockchain Databases in our Companies we need to classify where we should use the Enterprise Blockchain Databases and why, then the first step is to write down all of the things that Enterprise Blockchain Databases is good for, what it can do, where it is strong, what the capabilities are.
Capabilities means what is it good for what is it good at ? What can it do ? Let's try to group the capabilities together where it makes sense. The most important capabilities and enablers of Enterprise Blockchain Databases and on a wider scale the Enterprise Blockchain Platforms, from the high level view, revolve around Data across the dimensions of:
Security / Privacy
Availability / Resilience
Collaboration / Sharing
Orchestration
Web3 / Tokenization / Wallet / SDK / Smart Contracts
Mobility / Edge
Integrations / Connectivity / Blockchain Bridges and Bridging
Types of Blockchain
Artificial Intelligence
Let's go through these capabilities one by one and think of all of the words we can around the dimension and picture what it actually means.
Enterprise Blockchain Database Capability - Security & Privacy
Capability/Enabler: Secure, Immutable, Trust, Cannot be modified, Tamperproof, Protect, Safe, Proof, Auditable, Confidentiality, Integrity, Originality, Transparency, Privacy
Why are Blockchain Databases so strong in this: As we discussed in the previous Blog in this series, Blockchain Databases have four special characteristics that make them a Blockchain Database, and those are, Immutable, Hash Mechanism, Distributed/Decentralised, Consensus Mechanism.
Regarding the Security & Privacy capability, it is the Immutable and Hash Mechanism and Consensus Mechanism which make the Blockchain Database so natively security hardened out of the box and in fact security hardened natively out of the box to a level which most conventional databases are not.
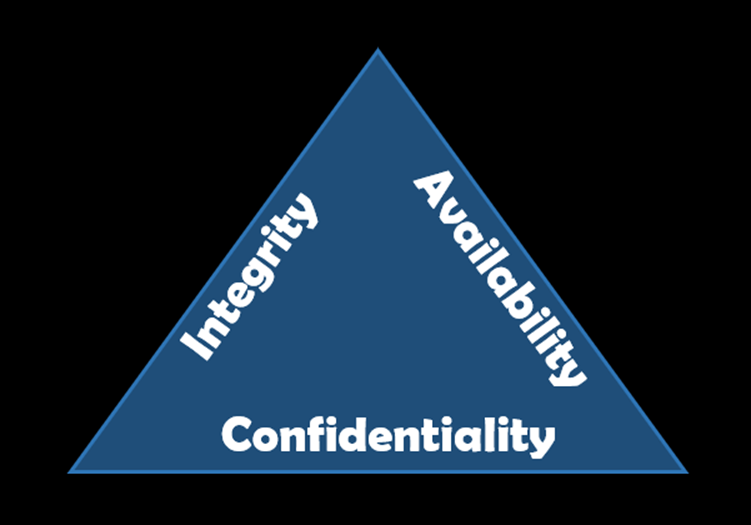
In terms of the NIST CIA Triad for Data Security, Criticality, Integrity, Availability, Enterprise Blockchain Databases comes in Very High across all three classifications.
Enterprise Blockchain Database Capability - Availability & Resilience
Capability/Enabler: Resilience, Distributed Multi Region, Distributed, Decentralised, Network Database, High Availability, Disaster Recovery, Business Continuity Planning
Why are Blockchain Databases so strong in this: Again, as we discussed in the previous Blog in this series, Blockchain Databases have four special characteristics that make them a Blockchain Database, and those are, Immutable, Hash Mechanism, Distributed/Decentralised, Consensus Mechanism.
Regarding the Availability & Resilience capability, it is the Distributed & Decentralised characteristics which make the Blockchain Database so natively resilient out of the box and in fact resilient natively out of the box to a level which most conventional databases are not.
An Enterprise Blockchain Database is a Network Database. When one of the Servers is down, the other Servers are up, A Server can go down and when it comes back up it will automatically synchronise with the rest of the Enterprise Blockchain Database Network. This is really suited to Business Continuity Planning.
Enterprise Blockchain Database Capability - Collaboration / Sharing
Capability/Enabler: Single Source of Truth, Shared Single Source of Truth, Multi-Party Collaboration, 3rd Party Collaboration, Common Store of Data, Sharing, Collaboration, Master Data Store, Distributed Data, Network Database, Track and Trace, Traceability, Audit, Auditability
Why are Blockchain Databases so strong in this: Again, as we discussed in the previous Blog in this series, Blockchain Databases have four special characteristics that make them a Blockchain Database, and those are, Immutable, Hash Mechanism, Distributed/Decentralised, Consensus Mechanism.
Regarding the Collaboration / Sharing capability, it is the Distributed & Decentralised characteristics which make the Blockchain Database so natively supporting Collaboration / Sharing out of the box and in fact supporting Collaboration / Sharing natively out of the box to a level which most conventional databases do not and can not, without additonal Clustering and Networking software.
An Enterprise Blockchain Database is a Network Database. This means the Database is running active on multiple Servers in multiple locations. As was described in the previous blog, McKinsey & Company, in their December 2023 Featured Insights Publication, gave a beautiful description of what is unique and special about Blockchain, "Blockchain is a secure database shared across a network of participants, where up-to-date information is available to all participants at the same time".
And this is what is so important and so special. When we install the Blockchain Database Server in two different Company's DataCenters (or as Blockchain as a Service in the Cloud) and establish a Database Ledger on the Servers we enable the two Company's to share Master and Transactional Data while knowing that neither can modify the Data which has been shared. This is really suited to sharing Data across the Enterprise or across Enterprises.

Enterprise Blockchain Database Capability - Orchestration
Capability/Enabler: Data Orchestration, Data Integration, Network Database, Instructions Communication, Data Delivery, Sending Data, Data Transfer, Data Connection
Why are Blockchain Databases so strong in this: Again, as we discussed in the previous Blog in this series, Blockchain Databases have four special characteristics that make them a Blockchain Database, and those are, Immutable, Hash Mechanism, Distributed/Decentralised, Consensus Mechanism.
Regarding the Data Orchestration, it is again the Distributed & Decentralised characteristics which make the Blockchain Database so natively supporting Data Orchestration out of the box and in fact supporting Data Orchestration natively out of the box to a level which most conventional databases do not and can not, without additonal Clustering and Networking software and all of the extra effort that that brings. An Enterprise Blockchain Database is a Network Database.
This means the Database is running active on multiple Servers in multiple locations. As was described in the previous blog, McKinsey & Company, in their December 2023 Featured Insights Publication, gave a beautiful description of what is unique and special about Blockchain, "Blockchain is a secure database shared across a network of participants, where up-to-date information is available to all participants at the same time". And this is what is so important and so special.
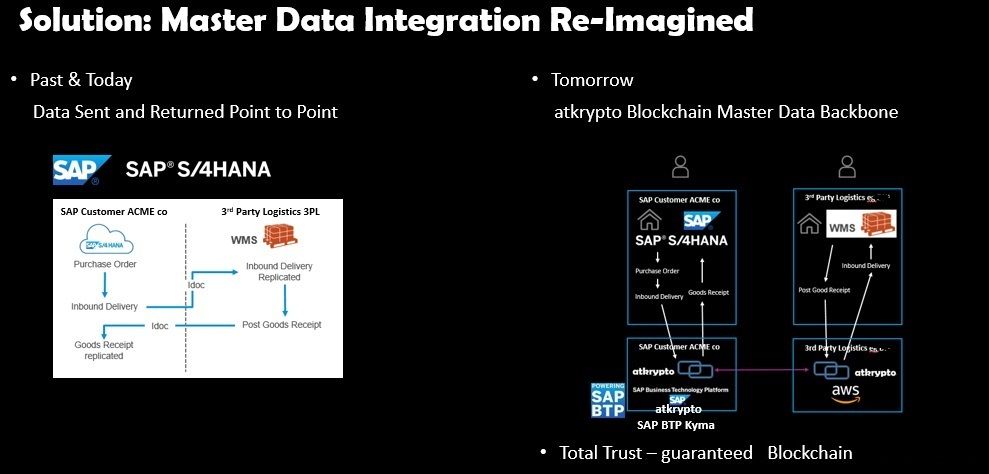
When we install the Blockchain Database Server in two different locations / DataCenters (or as Blockchain as a Service in the Cloud) and establish a Blockchain Database Ledger on the two or more locations' Servers we enable a situation where one Datacenter can put data onto the Blockchain, which is in fact an instruction for an action from an Application which is reading from the Blockchain in the other Datacenter. What this leads to is Data Integration at a level which is not possible with End to End Encryption and Encryption of Data at Rest alone.
Today Companies send Data to each other, with Blockchain Companies will write to and read from the same Blockchain Database Table. This is really suited to Orchestrating Data across the Enterprise or across Enterprises. In the following example we see how instructions to a Third Party Logistics company can be orchestrated across the Enterprise Blockchain running between the two companies.
Enterprise Blockchain Database Capability - Web3 / Tokenization / Wallet / SDK / Smart Contracts
Capability/Enabler: Web3 Foundation, Digital Asset Tokenization, Digital Wallet, Software Development Kit, Smart Contracts, Business Logic, Extension, Programming, Customisation
Why are Blockchain Databases so strong in this: As we discussed in the previous Blog in this series, Blockchain Databases have four special characteristics that make them a Blockchain Database, and those are, Immutable, Hash Mechanism, Distributed/Decentralised, Consensus Mechanism.
Tokenization is a combination of all of the Blockchain characteristics in one. Tokenization is the action of creating a Block on the Blockchain which is a Digital Token. The Digital Token is the digital representation of the information which has been stored on to the Blockchain.
With Tokenization comes a Wallet to store the Tokens in, it can be argued that the Wallet is not a classic capability of the Blockchain, but rather a capability of the Blockchain Platform.
A Software Development Kit is also not a classical characteristic or capability of the Blockchain, but rather a capability of the Enterprise Blockchain Platform. The SDK enables Developers to develop Decentralized Applications which run on top of the Blockchain.
And Web3 is the culmination or the whole of all of these capabilities and some more. The capabilities listed here go a long way to making up the core foundation of Web3. There is a nice overview of Web3 here in the SAP Community, including the following drawing:
Enterprise Blockchain Database Capability - Mobility / Edge
Capability/Enabler: Mobile, Mobility, Edge, IoT, Wireless, Move, Industry 4.0, Smart Everything, Connected Everything
Why are Blockchain Databases so strong in this: As we discussed in the previous Blog in this series, Blockchain Databases have four special characteristics that make them a Blockchain Database, and those are, Immutable, Hash Mechanism, Distributed/Decentralised, Consensus Mechanism.
The Distributed/Decentralised characteristic of the Blockchain Database Technology is what is so special here. As discussed above the Distributed characteristic of the Blockchain enables us to have a database which is networked between two locations.
It's this network database, and another fact which make Blockchain Databases so interesting for Edge/IoT/Mobile.
The other fact is the anologue to digital transformation of Things and the network getting closer to the Things at the Edge.
In the past Data was pretty much centralised to the DataCenter.
Things like Thermometers (in Pharmaceutical and Food Production), Maps & Compasses in Delivery Vehicles, Instructions on Paper, Locks on Doors, Photographs and Video, all of these Things were analogue. And now, all of these Things are going through a digital transformation, in two aspects, they are able to create digital representation of facts, and they are connected to the Network, and in some cases they even have larger computational power and can do business/processing logic and therefore are Smart Things. Thermometers are now connected to the Network, same for Maps and Compasses in Delivery Vehicles (GPS Location and navigation), Paper based Instructions are now electronic, Locks on Doors are now electronically monitored and controlled from the Network, Photographs and Video are now digital and connected to the network. And all of things Things are connected to the Network,the Edge of the Network, because they are the final point of the Network and together they make up the Internet of Things.
And so all of these Things are producing Data at the Edge of the Network. And this is where Blockchain comes in, Blockchain, for all of the reasons above is natively out of the box the most security hardened and resilient Database for protecting the integrity and confidentiality and originality of Data from the Edge.
The Capability and Enabler, Mobile / Edge / IoT comes in to play regarding having a Enterprise Blockchain Platform Server Node as close to the Edge as there is computational power, eg, on the Device, in the Connected Vehicle, or in the 5G Network IoT Gateway.
Do we take the Data from the Edge to the Blockchain or do we take the Blockchain to the Data at the Edge.
The most elegant is to take the Blockchain Mobile and to the Data at the Edge.
Surely the most secure way, is to protect the originality, integrity, confidentiality of the Data, at the Source, at the Edge, or as close to the Source as there is enough computational power to run a light Blockchain Database Server Node ? We will discuss this in detail in subsequent blogs.

Enterprise Blockchain Database Capability - Integrations / Connectivity / Blockchain Bridges and Bridging
Capability/Enabler: Integration, Integrator, Connection, Connectivity, Connector, Bridge, Blockchain Bridge, Bridging
Why are Blockchain Databases so strong in this: As we discussed in the previous Blog in this series, Blockchain Databases have four special characteristics that make them a Blockchain Database, and those are, Immutable, Hash Mechanism, Distributed/Decentralised, Consensus Mechanism.
This capability mainly revolves around the Distributed/Decentralised characteristic of the Blockchain.
This capability has a several different dimensions:
Getting Data in to the Blockchain
There are basically two clear leading options for getting Data in to the Enterprise Blockchain Platform, and those are:
API's
API's, there is nothing wrong with API's and there must always be API access to the Blockchain, for writing and for reading. For writing I see the API as more reactive than real time, and for reading data from the Blockchain API is the obvious choice.
There is a very nice blog in the SAP Community which favours Events over API's and personally I also lean that way for the majority of cases for writing data to the Blockchain. The blog is here: APIs: our flawed legacy from 1960’s thinking.[thanks to my friend Thomas Kaiser for finding that one]
Events
For me the biggest reason for using the Enterprise Blockchain Platform is the incredibly high level of security hardening and Data protection that it natively brings.
If we agree we will be more often positioning the Enterprise Blockchain Platform because of its security strengths, then next dimension is to write Data to the Enterprise Blockchain Platform as close to the source of that Data as possible no matter where the Data is, Edge or DataCenter.
The next dimension is that in the majority of cases, we will want to write the Data to the Enterprise Blockchain Platform as early as we can in the lifetime of the Data, ie, as soon as the Data was created.
If we want to write Data to an Enterprise Blockchain Platform as soon as the Data is created then the obvious technology for getting the Data to the Enterprise Blockchain Platform is Events, Event Driven Blockchain. I will be discussing this in detail in the later blogs which will deep dive in to individual use cases and reference architecture.
The Blockchain as a Data Integrator across the Organisation or Organisations
This capability crosses over with the Data Sharing capability. Basically the Enterprise Blockchain Platform becomes a Data Integrator within the Enterprise.
In a number of use cases the Enterprise Blockchain Platform could replace classical API based Integrations. In scenarios where there are Data Integrations between Applications, for example between Salesforce and SAP S/4HANA, instead of doing an API based Integration and only have security and protection to the level End to End Encryption, there could be an Enterprise Blockchain where Salesforce writes to the Enterprise Blockchain and SAP S/4HANA reads from the Enterprise Blockchain. This will be discussed in subsequent blogs which will deep dive in to use cases and reference architecture.
Bridging between Blockchains
This is a very important capability of Enterprise Blockchain Platforms and enables that Data can be bridged between Blockchains.
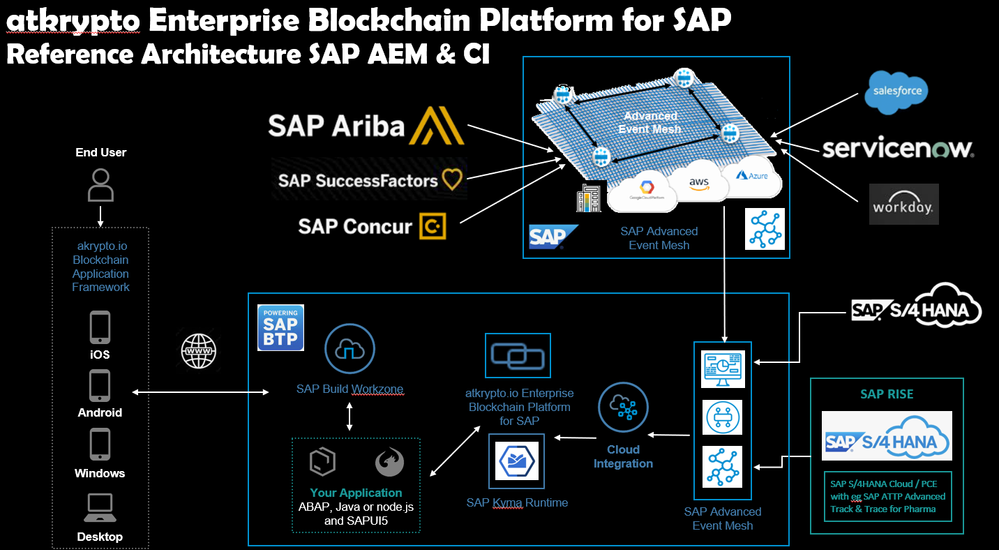
Enterprise Blockchain Database Capability - Types of Blockchain
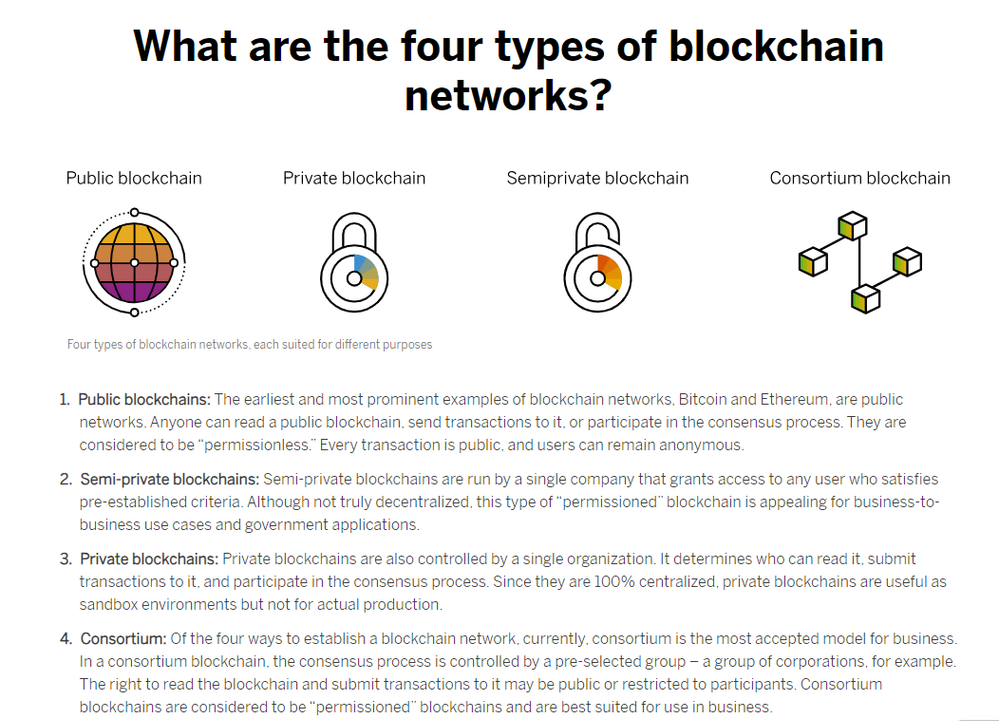
Capability/Enabler: Public, Private, Semi-Private, Consortium, Bridge
Why are Blockchain Databases so strong in this: As we discussed in the previous Blog in this series, Blockchain Databases have four special characteristics that make them a Blockchain Database, and those are, Immutable, Hash Mechanism, Distributed/Decentralised, Consensus Mechanism.
This capability mainly revolves around Layer 0 of the Blockchain Architecture, which is the Blockchain Network. An Enterprise Blockchain Platform which enables the Customer to create their own Blockchain Network will most likely have the best capability to enable the Customer create the Blockchain of their choice.
The main classifications of Blockchain Database are nicely described in this article from SAP, What is blockchain technology?.
Enterprise Blockchain Database Capability - Artificial Intelligence
Capability/Enabler: Integrity, Auditability, Traceability, Originality, Confidentiality, Protection, Safe, Treasure, Surety, Certainty, UnCompromised, Intelligent Technologies, Smart Technologies
Why are Blockchain Databases so strong in this: As we discussed in the previous Blog in this series, Blockchain Databases have four special characteristics that make them a Blockchain Database, and those are, Immutable, Hash Mechanism, Distributed/Decentralised, Consensus Mechanism.
This capability mainly revolves around Security characteristics of the Blockchain Platform and Database.
For Artificial Intelligence outcomes to be trustworthy, it must be certain that the Data used for the Artificial Intelligence can not have been altered.
That's it, it's as simple as that, if we want to trust what AI is telling us, then we need surety and certainty that the integrity and originality of the Data which the AI used cannot be or have been compromised.
Intelligent Technologies, for Intelligent Technologies to be intelligent, they cannot depend on stupid Data !
Smart Technologies, for Smart Technologies to be smart, they cannot depend on stupid Data !
That's where the Blockchain comes in.

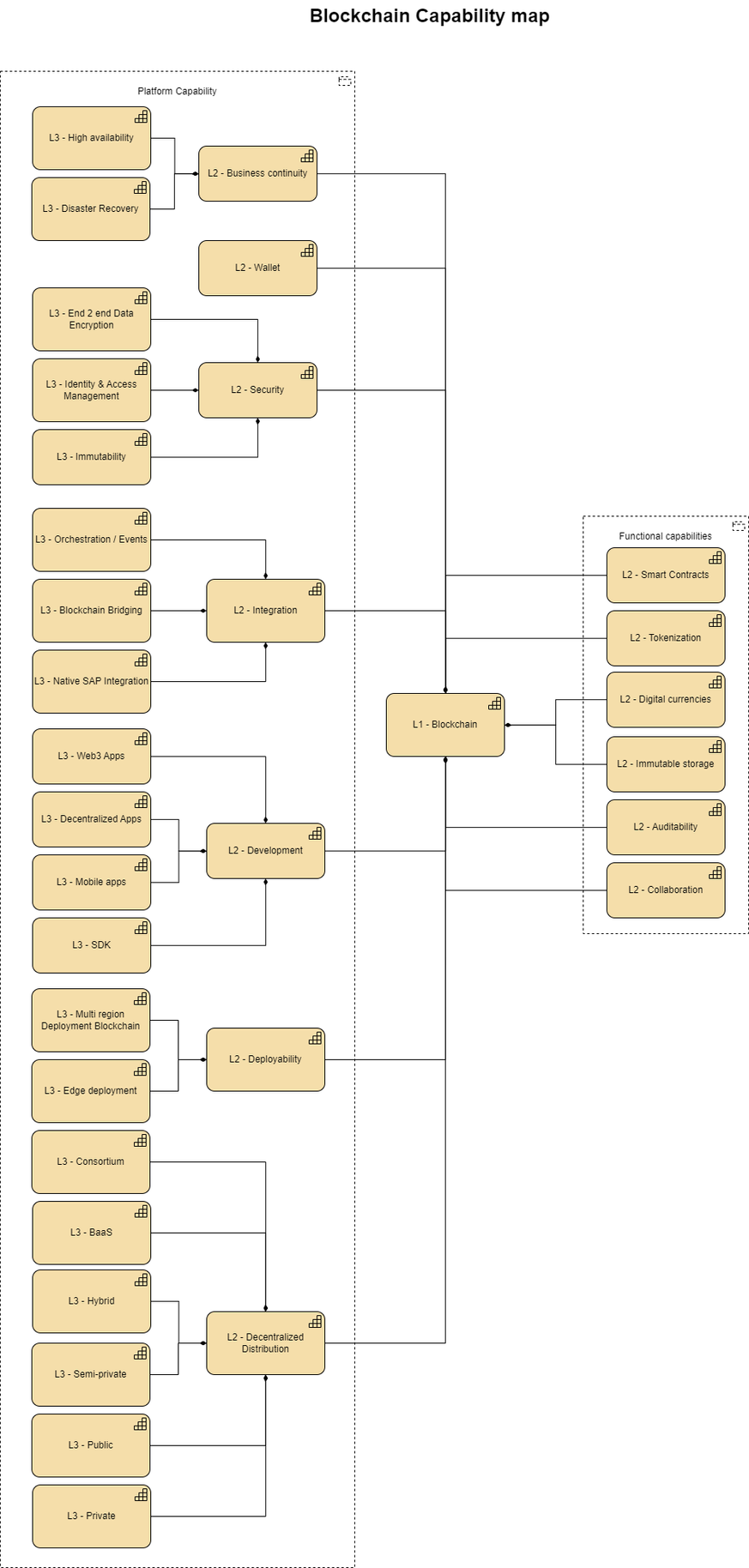
Now that we have elaborated on all of the capabilities and enablers of Enterprise Blockchain Databases and Enterprise Blockchain Platforms, let's get back to the goal of positioning Enterprise Blockchain Database and Platform as an Enterprise Technology Standard.
Before we do that, let's recap on the capabilities and enablers and summarise them:
In SAP Enterprise Architecture there is only one place to run the Enterprise Blockchain Platform, and that is, right next to the Digital Core S/4HANA in the "enabler", the SAP Business Technology Platform.
Why place the Enterprise Blockchain Platform in the SAP BTP ?
It's very very simple....
Proximity to the Data (of the Digital Core)
Ethnicity of the Data (in the Digital Core)
Proximity to the Process(es) (in the Digital Core)
Proximity to the Technology (of the Digital Core)
To wrap up, what we've done in this blog is identify all of the capabilities and enablers of Enterprise Blockchain Databases and the Enterprise Blockchain Platform, we've discussed why these capabilities are so important, and consequently how to position an Enterprise Blockchain Platform in the SAP Enterprise Architecture Technology Standards, where we use what and why.
We have also looked at where the Enterprise Blockchain Platform should reside, and the conclusion is in the "enabler", the SAP Business Technology Platform BTP, right next to the Digital Core S/4HANA, and enabling and leveraging all of the other Services in the SAP BTP and the native integration to the SAP Product Portfolio and other Enterprise Applications.
The good news is, as we discussed in the previous blog, this is no longer hype, we can do all of this today, and now, within the SAP Partner Edge Open EcoSystem there are enabling technology Blockchain Products designed and built by SAP Experts specifically for the needs of SAP Customers to make doing Blockchain and SAP easy, and so you can do SAP and Blockchain, today it's real and there's nothing stopping you.
So what are we waiting for ? Oh yeah, use cases, ok, that will be the next blog 😀 🚀
What do you think, are the words Blockchain, Web3, Distributed Ledger Technology, starting to appear in your Company's visions and technology visions ? What use cases are you looking at ? Let's chat about it in the comments.
For now, over and out.
Andy Silvey.
Independent SAP Technical Architect and CEO of atkrypto.io
Author Bio:
Andy Silvey is a 25 years SAP Technology veteran [15 years SAP Basis and 10 years SAP Tech Arch including Tech, Integration, Security, Data from 3.1H to S/4HANA PCE on RISE and the BTP and everything in between, and former SCN Moderator and Mentor alumni].
Andy is also co-Founder of atkrypto inc, an startup whose ambition is to make Blockchain easy for Enterprise.
atkrypto.io's flagship product is the atkrypto Enterprise Blockchain Platform for SAP, and atkrypto.io is a SAP Partner Edge Open EcoSystem Partner.
The atkrypto Enterprise Blockchain Platform for SAP has been designed by SAP Independent Experts for the needs of SAP Customers and to be deployed on the SAP BTP Kyma Runtime Service and leverage native integration to SAP Products.
atkrypto Enterprise Blockchain Platform for SAP has a number of unique qualities, including being the only Blockchain software in the world which has a DataCenter version and a light mobile version which can run on Edge/IoT/Mobile devices and enables data to be written to the Blockchain at the Edge where that same Blockchain is running on a Server in the DataCenter, protecting the integrity and originality of data from the Edge to Insights. Taking Blockchain to the Data at the Edge instead of taking the Data to the Blockchain.
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
"automatische backups"
1 -
"regelmäßige sicherung"
1 -
"TypeScript" "Development" "FeedBack"
1 -
505 Technology Updates 53
1 -
ABAP
14 -
ABAP API
1 -
ABAP CDS Views
2 -
ABAP CDS Views - BW Extraction
1 -
ABAP CDS Views - CDC (Change Data Capture)
1 -
ABAP class
2 -
ABAP Cloud
3 -
ABAP Development
5 -
ABAP in Eclipse
1 -
ABAP Platform Trial
1 -
ABAP Programming
2 -
abap technical
1 -
abapGit
1 -
absl
2 -
access data from SAP Datasphere directly from Snowflake
1 -
Access data from SAP datasphere to Qliksense
1 -
Accrual
1 -
action
1 -
adapter modules
1 -
Addon
1 -
Adobe Document Services
1 -
ADS
1 -
ADS Config
1 -
ADS with ABAP
1 -
ADS with Java
1 -
ADT
2 -
Advance Shipping and Receiving
1 -
Advanced Event Mesh
3 -
AEM
1 -
AI
7 -
AI Launchpad
1 -
AI Projects
1 -
AIML
9 -
Alert in Sap analytical cloud
1 -
Amazon S3
1 -
Analytical Dataset
1 -
Analytical Model
1 -
Analytics
1 -
Analyze Workload Data
1 -
annotations
1 -
API
1 -
API and Integration
3 -
API Call
2 -
API security
1 -
Application Architecture
1 -
Application Development
5 -
Application Development for SAP HANA Cloud
3 -
Applications and Business Processes (AP)
1 -
Artificial Intelligence
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
5 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) 1 Business Trends 363 Business Trends 8 Digital Transformation with Cloud ERP (DT) 1 Event Information 462 Event Information 15 Expert Insights 114 Expert Insights 76 Life at SAP 418 Life at SAP 1 Product Updates 4
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise Oil Gas IoT Exploration Production
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise sustainability responsibility esg social compliance cybersecurity risk
1 -
ASE
1 -
ASR
2 -
ASUG
1 -
Attachments
1 -
Authorisations
1 -
Automating Processes
1 -
Automation
2 -
aws
2 -
Azure
1 -
Azure AI Studio
1 -
Azure API Center
1 -
Azure API Management
1 -
B2B Integration
1 -
Backorder Processing
1 -
Backup
1 -
Backup and Recovery
1 -
Backup schedule
1 -
BADI_MATERIAL_CHECK error message
1 -
Bank
1 -
BAS
1 -
basis
2 -
Basis Monitoring & Tcodes with Key notes
2 -
Batch Management
1 -
BDC
1 -
Best Practice
1 -
bitcoin
1 -
Blockchain
3 -
bodl
1 -
BOP in aATP
1 -
BOP Segments
1 -
BOP Strategies
1 -
BOP Variant
1 -
BPC
1 -
BPC LIVE
1 -
BTP
13 -
BTP Destination
2 -
Business AI
1 -
Business and IT Integration
1 -
Business application stu
1 -
Business Application Studio
1 -
Business Architecture
1 -
Business Communication Services
1 -
Business Continuity
1 -
Business Data Fabric
3 -
Business Fabric
1 -
Business Partner
12 -
Business Partner Master Data
10 -
Business Technology Platform
2 -
Business Trends
4 -
BW4HANA
1 -
CA
1 -
calculation view
1 -
CAP
4 -
Capgemini
1 -
CAPM
1 -
Catalyst for Efficiency: Revolutionizing SAP Integration Suite with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and
1 -
CCMS
2 -
CDQ
12 -
CDS
2 -
Cental Finance
1 -
Certificates
1 -
CFL
1 -
Change Management
1 -
chatbot
1 -
chatgpt
3 -
CL_SALV_TABLE
2 -
Class Runner
1 -
Classrunner
1 -
Cloud ALM Monitoring
1 -
Cloud ALM Operations
1 -
cloud connector
1 -
Cloud Extensibility
1 -
Cloud Foundry
4 -
Cloud Integration
6 -
Cloud Platform Integration
2 -
cloudalm
1 -
communication
1 -
Compensation Information Management
1 -
Compensation Management
1 -
Compliance
1 -
Compound Employee API
1 -
Configuration
1 -
Connectors
1 -
Consolidation Extension for SAP Analytics Cloud
2 -
Control Indicators.
1 -
Controller-Service-Repository pattern
1 -
Conversion
1 -
Cosine similarity
1 -
cryptocurrency
1 -
CSI
1 -
ctms
1 -
Custom chatbot
3 -
Custom Destination Service
1 -
custom fields
1 -
Customer Experience
1 -
Customer Journey
1 -
Customizing
1 -
cyber security
3 -
cybersecurity
1 -
Data
1 -
Data & Analytics
1 -
Data Aging
1 -
Data Analytics
2 -
Data and Analytics (DA)
1 -
Data Archiving
1 -
Data Back-up
1 -
Data Flow
1 -
Data Governance
5 -
Data Integration
2 -
Data Quality
12 -
Data Quality Management
12 -
Data Synchronization
1 -
data transfer
1 -
Data Unleashed
1 -
Data Value
8 -
database tables
1 -
Datasphere
3 -
datenbanksicherung
1 -
dba cockpit
1 -
dbacockpit
1 -
Debugging
2 -
Defender
1 -
Delimiting Pay Components
1 -
Delta Integrations
1 -
Destination
3 -
Destination Service
1 -
Developer extensibility
1 -
Developing with SAP Integration Suite
1 -
Devops
1 -
digital transformation
1 -
Documentation
1 -
Dot Product
1 -
DQM
1 -
dump database
1 -
dump transaction
1 -
e-Invoice
1 -
E4H Conversion
1 -
Eclipse ADT ABAP Development Tools
2 -
edoc
1 -
edocument
1 -
ELA
1 -
Embedded Consolidation
1 -
Embedding
1 -
Embeddings
1 -
Employee Central
1 -
Employee Central Payroll
1 -
Employee Central Time Off
1 -
Employee Information
1 -
Employee Rehires
1 -
Enable Now
1 -
Enable now manager
1 -
endpoint
1 -
Enhancement Request
1 -
Enterprise Architecture
1 -
ESLint
1 -
ETL Business Analytics with SAP Signavio
1 -
Euclidean distance
1 -
Event Dates
1 -
Event Driven Architecture
1 -
Event Mesh
2 -
Event Reason
1 -
EventBasedIntegration
1 -
EWM
1 -
EWM Outbound configuration
1 -
EWM-TM-Integration
1 -
Existing Event Changes
1 -
Expand
1 -
Expert
2 -
Expert Insights
2 -
Exploits
1 -
Fiori
14 -
Fiori Elements
2 -
Fiori SAPUI5
12 -
first-guidance
1 -
Flask
1 -
FTC
1 -
Full Stack
8 -
Funds Management
1 -
gCTS
1 -
General
1 -
Generative AI
1 -
Getting Started
1 -
GitHub
9 -
Grants Management
1 -
groovy
1 -
GTP
1 -
HANA
6 -
HANA Cloud
2 -
Hana Cloud Database Integration
2 -
HANA DB
2 -
HANA XS Advanced
1 -
Historical Events
1 -
home labs
1 -
HowTo
1 -
HR Data Management
1 -
html5
8 -
HTML5 Application
1 -
Identity cards validation
1 -
idm
1 -
Implementation
1 -
input parameter
1 -
instant payments
1 -
Integration
3 -
Integration Advisor
1 -
Integration Architecture
1 -
Integration Center
1 -
Integration Suite
1 -
intelligent enterprise
1 -
iot
1 -
Java
1 -
job
1 -
Job Information Changes
1 -
Job-Related Events
1 -
Job_Event_Information
1 -
joule
4 -
Journal Entries
1 -
Just Ask
1 -
Kerberos for ABAP
8 -
Kerberos for JAVA
8 -
KNN
1 -
Launch Wizard
1 -
Learning Content
2 -
Life at SAP
5 -
lightning
1 -
Linear Regression SAP HANA Cloud
1 -
Loading Indicator
1 -
local tax regulations
1 -
LP
1 -
Machine Learning
2 -
Marketing
1 -
Master Data
3 -
Master Data Management
14 -
Maxdb
2 -
MDG
1 -
MDGM
1 -
MDM
1 -
Message box.
1 -
Messages on RF Device
1 -
Microservices Architecture
1 -
Microsoft Universal Print
1 -
Middleware Solutions
1 -
Migration
5 -
ML Model Development
1 -
Modeling in SAP HANA Cloud
8 -
Monitoring
3 -
MTA
1 -
Multi-Record Scenarios
1 -
Multiple Event Triggers
1 -
Myself Transformation
1 -
Neo
1 -
New Event Creation
1 -
New Feature
1 -
Newcomer
1 -
NodeJS
3 -
ODATA
2 -
OData APIs
1 -
odatav2
1 -
ODATAV4
1 -
ODBC
1 -
ODBC Connection
1 -
Onpremise
1 -
open source
2 -
OpenAI API
1 -
Oracle
1 -
PaPM
1 -
PaPM Dynamic Data Copy through Writer function
1 -
PaPM Remote Call
1 -
PAS-C01
1 -
Pay Component Management
1 -
PGP
1 -
Pickle
1 -
PLANNING ARCHITECTURE
1 -
Popup in Sap analytical cloud
1 -
PostgrSQL
1 -
POSTMAN
1 -
Prettier
1 -
Process Automation
2 -
Product Updates
5 -
PSM
1 -
Public Cloud
1 -
Python
4 -
python library - Document information extraction service
1 -
Qlik
1 -
Qualtrics
1 -
RAP
3 -
RAP BO
2 -
Record Deletion
1 -
Recovery
1 -
recurring payments
1 -
redeply
1 -
Release
1 -
Remote Consumption Model
1 -
Replication Flows
1 -
research
1 -
Resilience
1 -
REST
1 -
REST API
1 -
Retagging Required
1 -
Risk
1 -
Rolling Kernel Switch
1 -
route
1 -
rules
1 -
S4 HANA
1 -
S4 HANA Cloud
1 -
S4 HANA On-Premise
1 -
S4HANA
3 -
S4HANA_OP_2023
2 -
SAC
10 -
SAC PLANNING
9 -
SAP
4 -
SAP ABAP
1 -
SAP Advanced Event Mesh
1 -
SAP AI Core
8 -
SAP AI Launchpad
8 -
SAP Analytic Cloud Compass
1 -
Sap Analytical Cloud
1 -
SAP Analytics Cloud
4 -
SAP Analytics Cloud for Consolidation
3 -
SAP Analytics Cloud Story
1 -
SAP analytics clouds
1 -
SAP API Management
1 -
SAP BAS
1 -
SAP Basis
6 -
SAP BODS
1 -
SAP BODS certification.
1 -
SAP BTP
21 -
SAP BTP Build Work Zone
2 -
SAP BTP Cloud Foundry
6 -
SAP BTP Costing
1 -
SAP BTP CTMS
1 -
SAP BTP Innovation
1 -
SAP BTP Migration Tool
1 -
SAP BTP SDK IOS
1 -
SAP BTPEA
1 -
SAP Build
11 -
SAP Build App
1 -
SAP Build apps
1 -
SAP Build CodeJam
1 -
SAP Build Process Automation
3 -
SAP Build work zone
10 -
SAP Business Objects Platform
1 -
SAP Business Technology
2 -
SAP Business Technology Platform (XP)
1 -
sap bw
1 -
SAP CAP
2 -
SAP CDC
1 -
SAP CDP
1 -
SAP CDS VIEW
1 -
SAP Certification
1 -
SAP Cloud ALM
4 -
SAP Cloud Application Programming Model
1 -
SAP Cloud Integration for Data Services
1 -
SAP cloud platform
8 -
SAP Companion
1 -
SAP CPI
3 -
SAP CPI (Cloud Platform Integration)
2 -
SAP CPI Discover tab
1 -
sap credential store
1 -
SAP Customer Data Cloud
1 -
SAP Customer Data Platform
1 -
SAP Data Intelligence
1 -
SAP Data Migration in Retail Industry
1 -
SAP Data Services
1 -
SAP DATABASE
1 -
SAP Dataspher to Non SAP BI tools
1 -
SAP Datasphere
9 -
SAP DRC
1 -
SAP EWM
1 -
SAP Fiori
3 -
SAP Fiori App Embedding
1 -
Sap Fiori Extension Project Using BAS
1 -
SAP GRC
1 -
SAP HANA
1 -
SAP HCM (Human Capital Management)
1 -
SAP HR Solutions
1 -
SAP IDM
1 -
SAP Integration Suite
9 -
SAP Integrations
4 -
SAP iRPA
2 -
SAP LAGGING AND SLOW
1 -
SAP Learning Class
1 -
SAP Learning Hub
1 -
SAP Master Data
1 -
SAP Odata
2 -
SAP on Azure
2 -
SAP PartnerEdge
1 -
sap partners
1 -
SAP Password Reset
1 -
SAP PO Migration
1 -
SAP Prepackaged Content
1 -
SAP Process Automation
2 -
SAP Process Integration
2 -
SAP Process Orchestration
1 -
SAP S4HANA
2 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud
1 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud for Finance
1 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud private edition
1 -
SAP Sandbox
1 -
SAP STMS
1 -
SAP successfactors
3 -
SAP SuccessFactors HXM Core
1 -
SAP Time
1 -
SAP TM
2 -
SAP Trading Partner Management
1 -
SAP UI5
1 -
SAP Upgrade
1 -
SAP Utilities
1 -
SAP-GUI
8 -
SAP_COM_0276
1 -
SAPBTP
1 -
SAPCPI
1 -
SAPEWM
1 -
sapfirstguidance
1 -
SAPHANAService
1 -
SAPIQ
1 -
sapmentors
1 -
saponaws
2 -
SAPS4HANA
1 -
SAPUI5
5 -
schedule
1 -
Script Operator
1 -
Secure Login Client Setup
8 -
security
9 -
Selenium Testing
1 -
Self Transformation
1 -
Self-Transformation
1 -
SEN
1 -
SEN Manager
1 -
service
1 -
SET_CELL_TYPE
1 -
SET_CELL_TYPE_COLUMN
1 -
SFTP scenario
2 -
Simplex
1 -
Single Sign On
8 -
Singlesource
1 -
SKLearn
1 -
Slow loading
1 -
soap
1 -
Software Development
1 -
SOLMAN
1 -
solman 7.2
2 -
Solution Manager
3 -
sp_dumpdb
1 -
sp_dumptrans
1 -
SQL
1 -
sql script
1 -
SSL
8 -
SSO
8 -
Substring function
1 -
SuccessFactors
1 -
SuccessFactors Platform
1 -
SuccessFactors Time Tracking
1 -
Sybase
1 -
system copy method
1 -
System owner
1 -
Table splitting
1 -
Tax Integration
1 -
Technical article
1 -
Technical articles
1 -
Technology Updates
15 -
Technology Updates
1 -
Technology_Updates
1 -
terraform
1 -
Threats
2 -
Time Collectors
1 -
Time Off
2 -
Time Sheet
1 -
Time Sheet SAP SuccessFactors Time Tracking
1 -
Tips and tricks
2 -
toggle button
1 -
Tools
1 -
Trainings & Certifications
1 -
Transformation Flow
1 -
Transport in SAP BODS
1 -
Transport Management
1 -
TypeScript
3 -
ui designer
1 -
unbind
1 -
Unified Customer Profile
1 -
UPB
1 -
Use of Parameters for Data Copy in PaPM
1 -
User Unlock
1 -
VA02
1 -
Validations
1 -
Vector Database
2 -
Vector Engine
1 -
Visual Studio Code
1 -
VSCode
2 -
VSCode extenions
1 -
Vulnerabilities
1 -
Web SDK
1 -
work zone
1 -
workload
1 -
xsa
1 -
XSA Refresh
1
- « Previous
- Next »
- Integrating Smart contracts with SAPUI5 in Technology Blogs by Members
- Enhance your SAP Datasphere Experience with API Access in Technology Blogs by SAP
- Supporting Multiple API Gateways with SAP API Management – using Azure API Management as example in Technology Blogs by SAP
- SAP Build Process Automation Pre-built content for Finance Use cases in Technology Blogs by SAP
- IoT - Ultimate Data Cyber Security - with Enterprise Blockchain and SAP BTP 🚀 in Technology Blogs by Members
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 8 | |
| 7 | |
| 5 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 |