- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Technology
- Technology Blogs by Members
- 2024 SAP Cloud Identity Services & IAM Portfolio: ...
Technology Blogs by Members
Explore a vibrant mix of technical expertise, industry insights, and tech buzz in member blogs covering SAP products, technology, and events. Get in the mix!
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
Colt
Active Contributor
Options
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
02-28-2024
6:10 PM
This blog explores the latest 2024 updates in SAP's Identity and Access Management (IAM) portfolio derived from various early 2024 SAP events, particularly focusing on SAP Cloud Identity Services (SCI).
IAM 101: Identity Lifecycle, Authorization, and Authentication
In simple terms, Identity and Access Management (IAM) revolves around three core aspects:
- Identity Lifecycle: This encompasses the journey of user identities within a system, from creation to deletion.
- Authorization: Determining what actions users are allowed to perform within a system.
- Authentication: Ensuring that users are who they claim to be when accessing applications or services.
Identity Access Management Portfolio by SAP
SAP offers a Identity Access Management (IAM) portfolio that caters to both on-premises and public cloud solutions. Let's delve into each category - Identity Lifecycle, Authentication, and Authorization - highlighting the different components within SAP's Cloud Identity Services (SCI) suite.
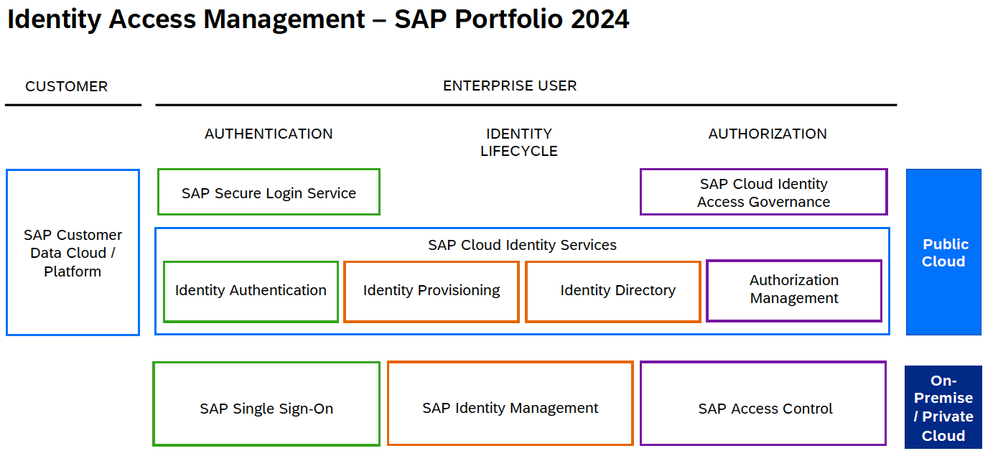
Source SAP SE: Image from the SAP presentation showcased at the DSAG Technology Days 2024 in Hamburg
Identity Lifecycle Management
For managing the lifecycle of identities, SAP provides several solutions:
- Identity Provisioning: Part of SCI. Facilitates seamless creation and management of user identities.
- Identity Directory: Part of SCI. Serves as a centralized repository for user and group information.
- SAP Identity Management: An on-premises product ensuring robust identity lifecycle management unitl the end of 2027/2030.
Authentication Solutions
SAP's authentication solutions ensure secure access to applications and services:
- Identity Authentication: Part of SCI. Provides seamless and secure authentication for users across applications.
- SAP Single Sign-On 3.0: An on-premises product offering single sign-on capabilities until the end of 2027.
- Secure Login Service: A standout addition to SAP's IAM lineup is the SAP Secure Login Service, heralded as the new star in the SAP Single Sign-On horizon. This service promises enhanced security and user experience in single sign-on scenarios.
Want to know more? Read here: https://community.sap.com/t5/technology-blogs-by-members/exploring-sap-secure-login-service-for-sap-...
Authorization Management
Authorization management is crucial for defining user permissions and access control:
- SAP Cloud Identity Access Governance: Symbiotically linked with SCI, it offers comprehensive authorization management and access governance.
- Authorization Management of SAP Cloud Identity Services: Streamlines authorization management for developers on SAP BTP. Define access policies with specified conditions, easily adjustable by administrators post-deployment. This centralizes access control, mitigating complexity and ensuring precise authorization levels.
Want to know more? Read here: https://community.sap.com/t5/technology-blogs-by-sap/sap-btp-innobytes-january-2024/ba-p/13584601
- SAP Access Control: An on-premises product offering that enables organizations to control access and prevent fraud across the enterprise, while minimizing the time and cost of compliance. An upcoming version (release 2026) will further enhance authorization capabilities within SAP's IAM portfolio.
While SAP's IAM portfolio boasts a comprehensive suite of solutions, it's worth noting that the SAP Customer Data Cloud is beyond the scope of this discussion due to the author's limited experience with it.
SAP Cloud Identity Services
Short Overview
SAP Cloud Identity Services (SCI) offer a suite of components tailored to address various facets of IAM:
- Identity Provisioning: Streamlining the process of creating and managing user identities.
- Identity Directory: Serving as a centralized repository for storing and accessing user and group information.
- Authorization Management: Facilitating the assignment and management of user permissions.
- Identity Authentication: Ensuring secure and seamless user authentication across applications.
Key Features of SCI
- Predefined Connectivity and Bundling: SCI seamlessly integrates with SAP cloud solutions, providing out-of-the-box configuration for user provisioning and authentication.
- Automated Service Enablement: Identity Services are automatically enabled as part of the product delivery process, simplifying setup for customers.
- Default Pre-Configuration: SAP cloud solutions come pre-configured with Identity Services, catering to common scenarios without the need for separate licensing.
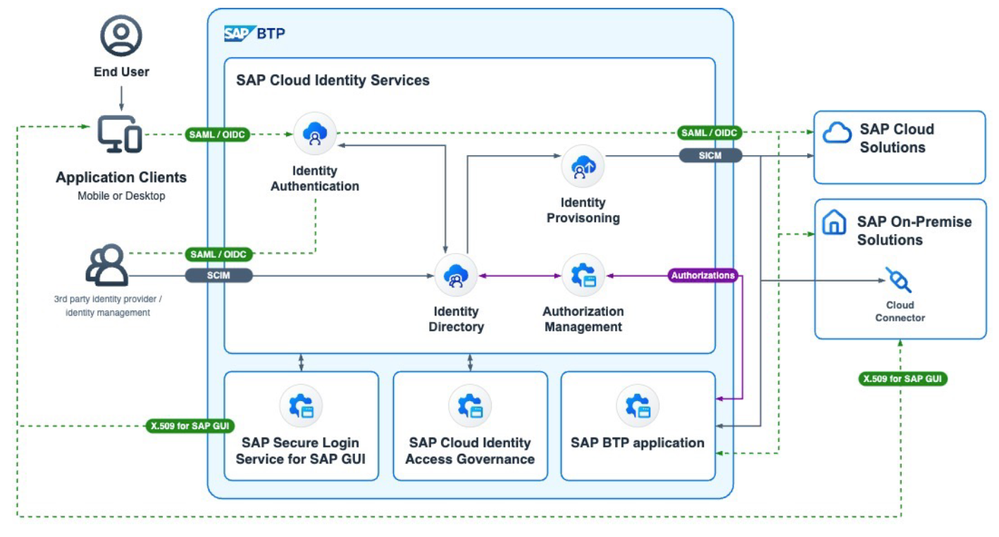
Source SAP SE: Image from the SAP presentation showcased at the DSAG Technology Days 2024 in Hamburg
Long story? Read here: https://xiting.com/en/downloads/download-sap-cloud-identity-services-e-book/
Cross-Enterprise Access Governance
Cross-enterprise identity management and access governance integration is set to be streamlined with the integration of Microsoft Entra ID and Microsoft Entra ID Governance alongside SAP Cloud Identity services and SAP Cloud Identity Access Governance. This integration will empower organizations to achieve single sign-on and provisioning capabilities across a range of SAP business applications, including SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud, SAP Ariba, SAP Concur, and SAP SuccessFactors. Furthermore, the linkage between Microsoft Entra ID and Microsoft Entra ID Governance with SAP Cloud Identity Access Governance will enable cohesive identity and access risk assessments, alongside monitoring and management of compliance controls.
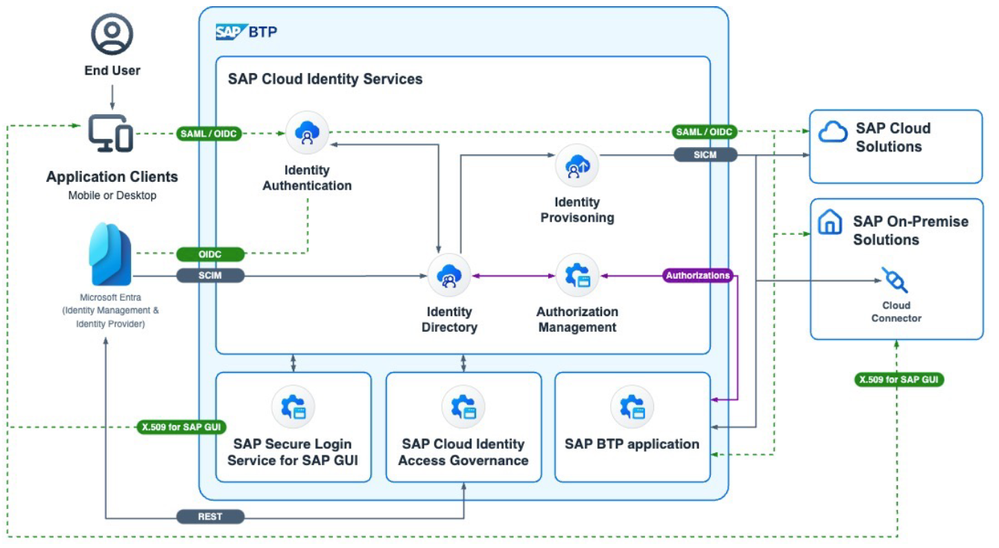
Source SAP SE: Image from the SAP presentation showcased at the DSAG Technology Days 2024 in Hamburg
Identity Lifecycle Management with SCI
SAP Cloud Identity Services facilitates efficient management of the employee lifecycle, from onboarding to offboarding, ensuring smooth transitions and access management throughout.
It plays a key role by centralizing Identity Access Management. They collect the derived identities and act as a single source of truth. The Identity Directory and Identity Provisioning components of SAP Cloud Identity Services work together to manage identities efficiently across systems.
Identity Directory: Centralized User Management
The Identity Directory serves as a central repository for user and group information, accessible via APIs and admin UI, simplifying connectivity and integration with SAP SaaS applications. It provides a System for Cross-domain Identity Management (SCIM) 2.0 REST API for managing resources (users, groups and custom schemas) with a set of attributes. Those attributes are defined in the SCIM 2.0 Core schema and the Enterprise user resource schema. Custom attributes are supported through a schema extension.
Identity Provisioning
Transformation Engine
Identity Provisioning Connectors play a crucial role in the Identity Lifecycle process. These connectors come in various types, including Source System Connectors, Target System Connectors, and Proxy System Connectors. They enable seamless integration between different systems, allowing for the provisioning and authentication of users.
The Identity Provisioning transformation engine offers several powerful capabilities:
- Assignment: Users can define rules for assignments based on input data. For instance, organizations can use the value of an identity's organizational unit to determine the roles required for that user.
- Mapping between identity models: The engine facilitates mapping between attributes in different models. For example, it can map the surname attribute to the family name attribute. Additionally, it allows for adjustments to data formats, such as converting time or number formats as needed.
- Filtering: Organizations can specify detailed criteria for determining which objects should be read or written. This enables fine-grained control over data synchronization and provisioning processes, ensuring that only relevant information is transferred between systems.
Various types of connectors to facilitate seamless integration
- Source System Connectors: These connectors enable the extraction of user data from source systems, such as SAP Cloud solutions, on-premise solutions, and third-party solutions.
- Target System Connectors: These connectors facilitate the transfer of user data to target systems, including SAP Cloud solutions, on-premise solutions, and third-party solutions.
- Proxy System Connectors: These connectors act as intermediaries between source and target systems, ensuring smooth data transfer and integration.
With support for over 20 SAP Cloud solutions, on-premise solutions, and third-party solutions, Identity Provisioning Connectors offer out-of-the-box configuration for user provisioning and authentication. This ensures quick and easy setup for organizations, enabling efficient management of user identities across diverse systems.
Authorization Management
Authorization plays a crucial role in ensuring secure access to applications and resources. Here's how SAP addresses authorization management:
- Internal Authorization Definition: Many applications define authorizations internally, tailored to their specific domain requirements.
- Central User Assignment: SAP Cloud Identity Services centralizes user assignment to roles and groups, streamlining access management.
- Authorization Management Service (AMS): This "new" service provides centralized management of end-user authorizations for applications on the SAP Business Technology Platform. AMS integrates seamlessly with SAP Cloud Identity Services, allowing for configuration and assignment of policies directly from the administration console.
- Policy Assignment: In SAP Cloud Identity, each policy corresponds to a group in the identity directory. Policies can be assigned to users by making them members of the respective policy group. Customers have the flexibility to assign SAP-provided or custom policies to users using the user-friendly UIs in the SAP Cloud Identity console or programmatically via the SCIM API of the Identity Directory.
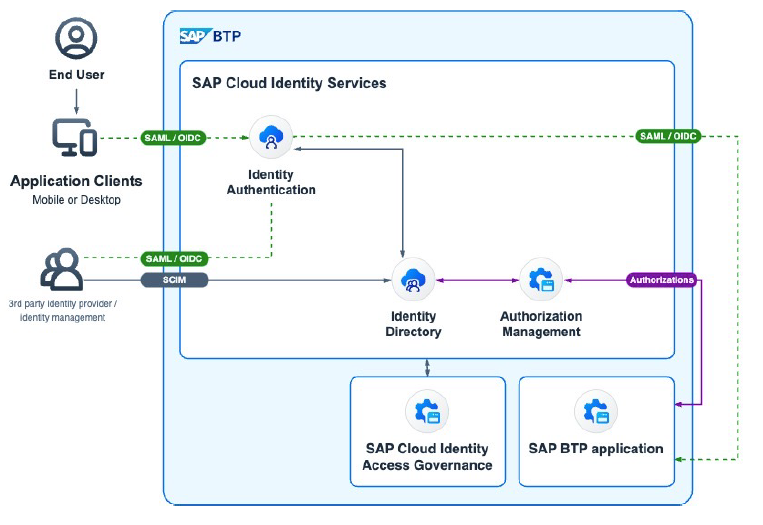
Source SAP SE: Image from the SAP presentation showcased at the DSAG Technology Days 2024 in Hamburg
Identity Access Governance
SAP Cloud Identity Access Governance (IAG) is already widely recognized, offering a comprehensive suite of features aimed at enhancing security and compliance.
Key Features:
- Privileged Access Management: Enables the management of super-user access, log consolidation, and automated log assessment to ensure stringent security measures.
- Access Certification: Facilitates the review of access, roles, risks, and mitigation controls to maintain compliance with regulatory standards.
- Access Analysis: Provides tools to analyze access, refine user assignments, and manage controls effectively.
- Access Request: Optimizes access by streamlining workflows, policy-based assignment, and processes to ensure efficient access provisioning.
- Role Design: Allows organizations to optimize role definition and governance processes, enhancing overall security posture.
Moreover, SAP Cloud Identity Access Governance offers HR-driven identity lifecycle management by integrating with SAP SuccessFactors. This integration enables automatic access requests triggered by changes in employee status within the HR system. The IAG Bridge Cloud facilitates the creation of access requests for cloud applications, with risk analysis and provisioning handled by SAP Cloud Identity Access Governance.
API-based integrations further enhance flexibility, allowing external applications to submit requests to SAP Cloud Identity Access Governance for processing. This enables efficient access provisioning and deprovisioning based on approval processes, with the option to retrieve request status periodically.
With support for over 16 SAP Cloud solutions, on-premises solutions, and third-party solutions, SAP Cloud Identity Access Governance provides a robust platform for organizations to maintain security, compliance, and efficient access management across their IT environment.
Authentication
Authentication within SAP's ecosystem is facilitated through SAP Cloud Identity Services, serving as the interface for Identity Access Management. Here's how authentication in the overall hybrid SAP landscape idealy works:
- SAP Cloud Identity Services: This platform acts as the primary hub for authentication. SAP applications inherently trust SAP Cloud Identity Services for identity authentication, ensuring a secure login process.
- User Interaction: Users have the flexibility to interact with either Identity Authentication provided by SAP Cloud Identity Services or third-party Identity Providers. Regardless of the chosen method, users benefit from Single Sign-On capabilities, enhancing user experience and simplifying access to multiple applications.
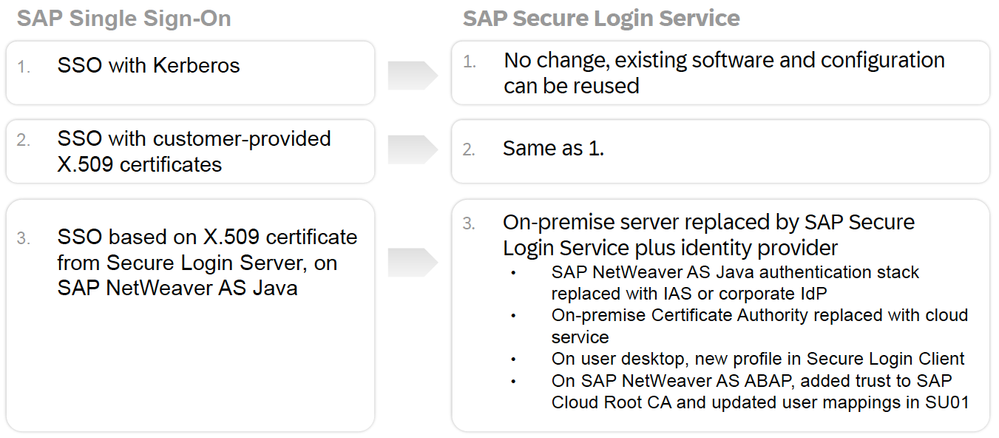
- Integration with SAP GUI: SAP GUI seamlessly integrates with short-term X.509 certificates from SAP Secure Login Service, further enhancing authentication security supporting MFA within SAP environments.
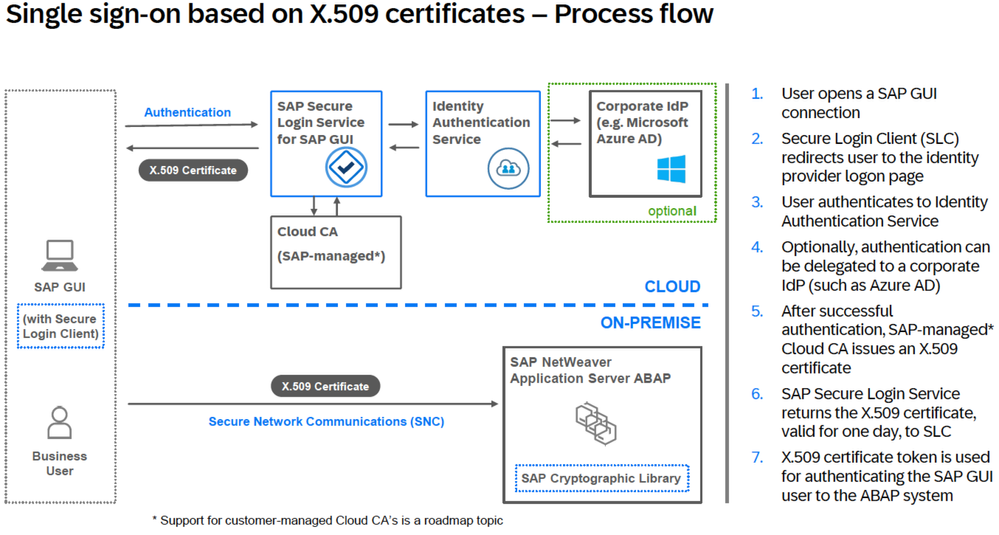
Source SAP SE: Image from the SAP presentation showcased at the DSAG Technology Days 2024 in Hamburg
Short Comparative Note: SAP Secure Login Service (SLS) for SAP GUI versus SAP Single Sign-On (SSO) 3.0. While SAP Single Sign-On 3.0 remains a viable solution for certain use cases, the emerging preference leans towards the new SLS for SAP GUI for most scenarios. The rationale behind this shift lies in the fact that SSO relies on capabilities like multi-factor authentication and CLM (Certificate Lifecycyle Management with NDES CA-Integration) on SAP NetWeaver Application Server Java, which is scheduled to exit mainstream maintenance by the end of 2027.Source SAP SE: Image from SAP
Contrarily, the new SLS does not depend on SAP NetWeaver AS Java; instead, it leverages a cloud-based service. It emphasizes seamless integration with cloud-centric identity providers, such as SAP Cloud Identity Services – Identity Authentication. Furthermore, it is offered as a cloud subscription, aligning with the contemporary preferences of software licensing among customers. However, it is important to note that currently, some features are still missing in direct comparison with the SAP SSO 3.0 Suite.
- Principal Propagation: SAP Cloud Identity Services facilitates principal propagation between applications, ensuring consistent authentication across various systems and enhancing interoperability.
Upcoming Developments and Enhancements
Upcoming: Simplified Principal Propagation for Authentication
SCI will act as a central token service, reducing complexity in system-to-system calls and enhancing trust between applications. In an upcoming development, SAP Cloud Identity Services is poised to introduce a significant enhancement aimed at simplifying principal propagation for authentication. Here's what to expect:
- Central Token Service: SAP Cloud Identity Services will transition into a central token service, streamlining the process of system-to-system calls. This move aims to reduce complexity and enhance efficiency in authentication workflows.
- Token Request Flow: When a sender application needs to call an API of the receiver application on behalf of the current user, it will request a token from Identity Authentication within SAP Cloud Identity Services.
- Trust in Tokens: SAP applications, along with third-party applications, will trust tokens issued by SAP Cloud Identity Services for API calls. This trust ensures secure and seamless communication between applications, regardless of their origin.
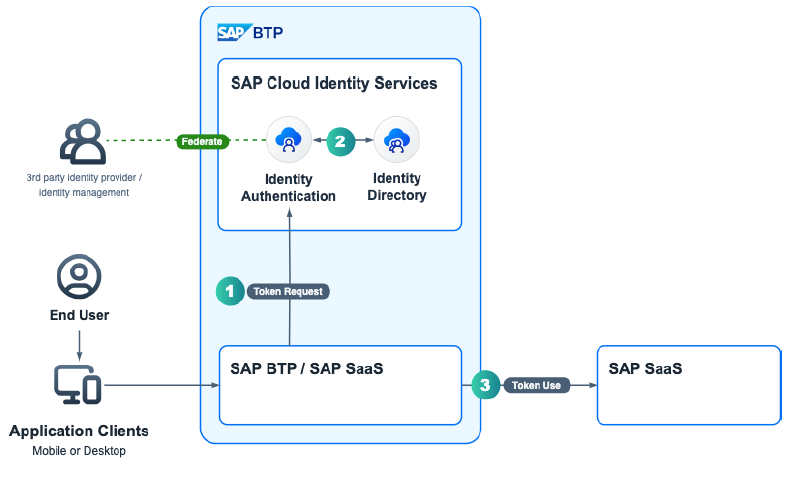
Source SAP SE: Image from the SAP presentation showcased at the DSAG Technology Days 2024 in Hamburg
SCIM & SAP: Updates for Improved Enterprise Readiness
SAP is working on enhancements to the SCIM protocol, including cursor-based pagination and additional schema support, to enhance user assignment processes and enterprise readiness.
Here's an overview of the recent developments:
- SCIM Adoption: SAP initially adopted SCIM as a product standard with the Identity Provisioning Service (IPS). SCIM2 was subsequently designated as the primary user and group replication protocol for SAP applications, outlining the implementation guidelines.
- SCIM User Lifecycle: SCIM includes the "active" flag to control authentication and app interactions. It mandates responding to GET requests after a DELETE request with no result. Applications have the autonomy to set users to a blocked status or create new user records as needed.
- Enterprise Readiness: SAP identified areas for improving SCIM's enterprise readiness, including the lack of delta-read processes and index-based pagination. To address these concerns, SAP is working on implementing cursor-based pagination for entities like Users and Groups, as well as multi-valued attributes.
- SCIM Groups and Schema Enhancements: SAP envisions SCIM Groups as the primary method for user assignments, offering transparent concepts for SCIM clients. SAP's group schemas introduce additional capabilities, such as defining group types and supported operations, providing more precise operations for SCIM clients.
- SAP User Extensions: SAP plans to introduce additional user extensions for business attributes derived from the One Domain Model (ODM). This extension aims to enable applications to create users with related business attributes. The schema will support legacy approaches and integration scenarios with the Master Data Integration Service.
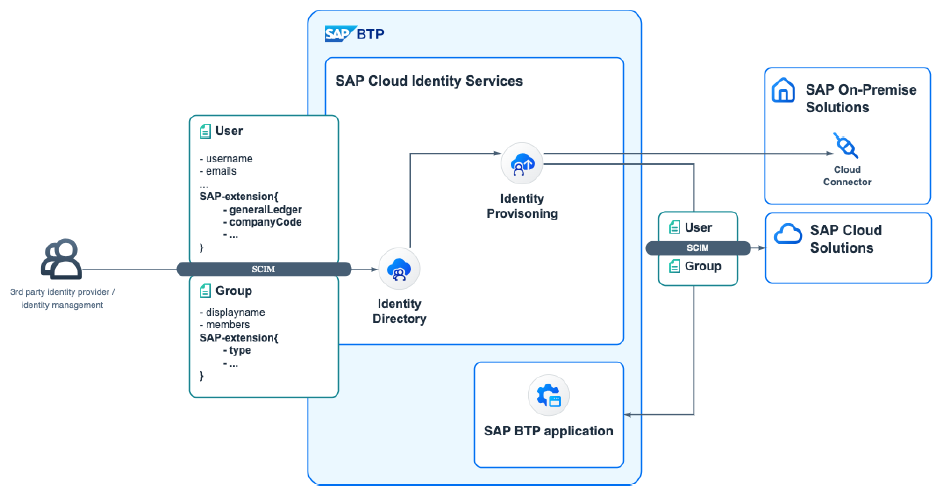
Source SAP SE: Image from the SAP presentation showcased at the DSAG Technology Days 2024 in Hamburg
SAP Cloud Identity Services continue to evolve, offering comprehensive IAM solutions for businesses. With features such as predefined connectivity, automated service enablement, and upcoming enhancements, SAP remains innovative, ensuring secure and efficient identity and access management for its customers.
- SAP Managed Tags:
- SAP Cloud Identity Services,
- SAP Cloud Identity Access Governance,
- SAP Single Sign-On
1 Comment
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
Labels in this area
-
"automatische backups"
1 -
"regelmäßige sicherung"
1 -
"TypeScript" "Development" "FeedBack"
1 -
505 Technology Updates 53
1 -
ABAP
14 -
ABAP API
1 -
ABAP CDS Views
2 -
ABAP CDS Views - BW Extraction
1 -
ABAP CDS Views - CDC (Change Data Capture)
1 -
ABAP class
2 -
ABAP Cloud
3 -
ABAP Development
5 -
ABAP in Eclipse
1 -
ABAP Platform Trial
1 -
ABAP Programming
2 -
abap technical
1 -
abapGit
1 -
absl
2 -
access data from SAP Datasphere directly from Snowflake
1 -
Access data from SAP datasphere to Qliksense
1 -
Accrual
1 -
action
1 -
adapter modules
1 -
Addon
1 -
Adobe Document Services
1 -
ADS
1 -
ADS Config
1 -
ADS with ABAP
1 -
ADS with Java
1 -
ADT
2 -
Advance Shipping and Receiving
1 -
Advanced Event Mesh
3 -
AEM
1 -
AI
7 -
AI Launchpad
1 -
AI Projects
1 -
AIML
9 -
Alert in Sap analytical cloud
1 -
Amazon S3
1 -
Analytical Dataset
1 -
Analytical Model
1 -
Analytics
1 -
Analyze Workload Data
1 -
annotations
1 -
API
1 -
API and Integration
3 -
API Call
2 -
API security
1 -
Application Architecture
1 -
Application Development
5 -
Application Development for SAP HANA Cloud
3 -
Applications and Business Processes (AP)
1 -
Artificial Intelligence
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
5 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) 1 Business Trends 363 Business Trends 8 Digital Transformation with Cloud ERP (DT) 1 Event Information 462 Event Information 15 Expert Insights 114 Expert Insights 76 Life at SAP 418 Life at SAP 1 Product Updates 4
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise Oil Gas IoT Exploration Production
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise sustainability responsibility esg social compliance cybersecurity risk
1 -
ASE
1 -
ASR
2 -
ASUG
1 -
Attachments
1 -
Authorisations
1 -
Automating Processes
1 -
Automation
2 -
aws
2 -
Azure
1 -
Azure AI Studio
1 -
Azure API Center
1 -
Azure API Management
1 -
B2B Integration
1 -
Backorder Processing
1 -
Backup
1 -
Backup and Recovery
1 -
Backup schedule
1 -
BADI_MATERIAL_CHECK error message
1 -
Bank
1 -
BAS
1 -
basis
2 -
Basis Monitoring & Tcodes with Key notes
2 -
Batch Management
1 -
BDC
1 -
Best Practice
1 -
bitcoin
1 -
Blockchain
3 -
bodl
1 -
BOP in aATP
1 -
BOP Segments
1 -
BOP Strategies
1 -
BOP Variant
1 -
BPC
1 -
BPC LIVE
1 -
BTP
13 -
BTP Destination
2 -
Business AI
1 -
Business and IT Integration
1 -
Business application stu
1 -
Business Application Studio
1 -
Business Architecture
1 -
Business Communication Services
1 -
Business Continuity
1 -
Business Data Fabric
3 -
Business Fabric
1 -
Business Partner
12 -
Business Partner Master Data
10 -
Business Technology Platform
2 -
Business Trends
4 -
BW4HANA
1 -
CA
1 -
calculation view
1 -
CAP
4 -
Capgemini
1 -
CAPM
1 -
Catalyst for Efficiency: Revolutionizing SAP Integration Suite with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and
1 -
CCMS
2 -
CDQ
12 -
CDS
2 -
Cental Finance
1 -
Certificates
1 -
CFL
1 -
Change Management
1 -
chatbot
1 -
chatgpt
3 -
CL_SALV_TABLE
2 -
Class Runner
1 -
Classrunner
1 -
Cloud ALM Monitoring
1 -
Cloud ALM Operations
1 -
cloud connector
1 -
Cloud Extensibility
1 -
Cloud Foundry
4 -
Cloud Integration
6 -
Cloud Platform Integration
2 -
cloudalm
1 -
communication
1 -
Compensation Information Management
1 -
Compensation Management
1 -
Compliance
1 -
Compound Employee API
1 -
Configuration
1 -
Connectors
1 -
Consolidation Extension for SAP Analytics Cloud
2 -
Control Indicators.
1 -
Controller-Service-Repository pattern
1 -
Conversion
1 -
Cosine similarity
1 -
cryptocurrency
1 -
CSI
1 -
ctms
1 -
Custom chatbot
3 -
Custom Destination Service
1 -
custom fields
1 -
Customer Experience
1 -
Customer Journey
1 -
Customizing
1 -
cyber security
3 -
cybersecurity
1 -
Data
1 -
Data & Analytics
1 -
Data Aging
1 -
Data Analytics
2 -
Data and Analytics (DA)
1 -
Data Archiving
1 -
Data Back-up
1 -
Data Flow
1 -
Data Governance
5 -
Data Integration
2 -
Data Quality
12 -
Data Quality Management
12 -
Data Synchronization
1 -
data transfer
1 -
Data Unleashed
1 -
Data Value
8 -
database tables
1 -
Datasphere
3 -
datenbanksicherung
1 -
dba cockpit
1 -
dbacockpit
1 -
Debugging
2 -
Defender
1 -
Delimiting Pay Components
1 -
Delta Integrations
1 -
Destination
3 -
Destination Service
1 -
Developer extensibility
1 -
Developing with SAP Integration Suite
1 -
Devops
1 -
digital transformation
1 -
Documentation
1 -
Dot Product
1 -
DQM
1 -
dump database
1 -
dump transaction
1 -
e-Invoice
1 -
E4H Conversion
1 -
Eclipse ADT ABAP Development Tools
2 -
edoc
1 -
edocument
1 -
ELA
1 -
Embedded Consolidation
1 -
Embedding
1 -
Embeddings
1 -
Employee Central
1 -
Employee Central Payroll
1 -
Employee Central Time Off
1 -
Employee Information
1 -
Employee Rehires
1 -
Enable Now
1 -
Enable now manager
1 -
endpoint
1 -
Enhancement Request
1 -
Enterprise Architecture
1 -
ESLint
1 -
ETL Business Analytics with SAP Signavio
1 -
Euclidean distance
1 -
Event Dates
1 -
Event Driven Architecture
1 -
Event Mesh
2 -
Event Reason
1 -
EventBasedIntegration
1 -
EWM
1 -
EWM Outbound configuration
1 -
EWM-TM-Integration
1 -
Existing Event Changes
1 -
Expand
1 -
Expert
2 -
Expert Insights
2 -
Exploits
1 -
Fiori
14 -
Fiori Elements
2 -
Fiori SAPUI5
12 -
first-guidance
1 -
Flask
1 -
FTC
1 -
Full Stack
8 -
Funds Management
1 -
gCTS
1 -
General
1 -
Generative AI
1 -
Getting Started
1 -
GitHub
9 -
Grants Management
1 -
groovy
1 -
GTP
1 -
HANA
6 -
HANA Cloud
2 -
Hana Cloud Database Integration
2 -
HANA DB
2 -
HANA XS Advanced
1 -
Historical Events
1 -
home labs
1 -
HowTo
1 -
HR Data Management
1 -
html5
8 -
HTML5 Application
1 -
Identity cards validation
1 -
idm
1 -
Implementation
1 -
input parameter
1 -
instant payments
1 -
Integration
3 -
Integration Advisor
1 -
Integration Architecture
1 -
Integration Center
1 -
Integration Suite
1 -
intelligent enterprise
1 -
iot
1 -
Java
1 -
job
1 -
Job Information Changes
1 -
Job-Related Events
1 -
Job_Event_Information
1 -
joule
4 -
Journal Entries
1 -
Just Ask
1 -
Kerberos for ABAP
8 -
Kerberos for JAVA
8 -
KNN
1 -
Launch Wizard
1 -
Learning Content
2 -
Life at SAP
5 -
lightning
1 -
Linear Regression SAP HANA Cloud
1 -
Loading Indicator
1 -
local tax regulations
1 -
LP
1 -
Machine Learning
2 -
Marketing
1 -
Master Data
3 -
Master Data Management
14 -
Maxdb
2 -
MDG
1 -
MDGM
1 -
MDM
1 -
Message box.
1 -
Messages on RF Device
1 -
Microservices Architecture
1 -
Microsoft Universal Print
1 -
Middleware Solutions
1 -
Migration
5 -
ML Model Development
1 -
Modeling in SAP HANA Cloud
8 -
Monitoring
3 -
MTA
1 -
Multi-Record Scenarios
1 -
Multiple Event Triggers
1 -
Myself Transformation
1 -
Neo
1 -
New Event Creation
1 -
New Feature
1 -
Newcomer
1 -
NodeJS
3 -
ODATA
2 -
OData APIs
1 -
odatav2
1 -
ODATAV4
1 -
ODBC
1 -
ODBC Connection
1 -
Onpremise
1 -
open source
2 -
OpenAI API
1 -
Oracle
1 -
PaPM
1 -
PaPM Dynamic Data Copy through Writer function
1 -
PaPM Remote Call
1 -
PAS-C01
1 -
Pay Component Management
1 -
PGP
1 -
Pickle
1 -
PLANNING ARCHITECTURE
1 -
Popup in Sap analytical cloud
1 -
PostgrSQL
1 -
POSTMAN
1 -
Prettier
1 -
Process Automation
2 -
Product Updates
5 -
PSM
1 -
Public Cloud
1 -
Python
4 -
python library - Document information extraction service
1 -
Qlik
1 -
Qualtrics
1 -
RAP
3 -
RAP BO
2 -
Record Deletion
1 -
Recovery
1 -
recurring payments
1 -
redeply
1 -
Release
1 -
Remote Consumption Model
1 -
Replication Flows
1 -
research
1 -
Resilience
1 -
REST
1 -
REST API
1 -
Retagging Required
1 -
Risk
1 -
Rolling Kernel Switch
1 -
route
1 -
rules
1 -
S4 HANA
1 -
S4 HANA Cloud
1 -
S4 HANA On-Premise
1 -
S4HANA
3 -
S4HANA_OP_2023
2 -
SAC
10 -
SAC PLANNING
9 -
SAP
4 -
SAP ABAP
1 -
SAP Advanced Event Mesh
1 -
SAP AI Core
8 -
SAP AI Launchpad
8 -
SAP Analytic Cloud Compass
1 -
Sap Analytical Cloud
1 -
SAP Analytics Cloud
4 -
SAP Analytics Cloud for Consolidation
3 -
SAP Analytics Cloud Story
1 -
SAP analytics clouds
1 -
SAP API Management
1 -
SAP BAS
1 -
SAP Basis
6 -
SAP BODS
1 -
SAP BODS certification.
1 -
SAP BTP
21 -
SAP BTP Build Work Zone
2 -
SAP BTP Cloud Foundry
6 -
SAP BTP Costing
1 -
SAP BTP CTMS
1 -
SAP BTP Innovation
1 -
SAP BTP Migration Tool
1 -
SAP BTP SDK IOS
1 -
SAP BTPEA
1 -
SAP Build
11 -
SAP Build App
1 -
SAP Build apps
1 -
SAP Build CodeJam
1 -
SAP Build Process Automation
3 -
SAP Build work zone
10 -
SAP Business Objects Platform
1 -
SAP Business Technology
2 -
SAP Business Technology Platform (XP)
1 -
sap bw
1 -
SAP CAP
2 -
SAP CDC
1 -
SAP CDP
1 -
SAP CDS VIEW
1 -
SAP Certification
1 -
SAP Cloud ALM
4 -
SAP Cloud Application Programming Model
1 -
SAP Cloud Integration for Data Services
1 -
SAP cloud platform
8 -
SAP Companion
1 -
SAP CPI
3 -
SAP CPI (Cloud Platform Integration)
2 -
SAP CPI Discover tab
1 -
sap credential store
1 -
SAP Customer Data Cloud
1 -
SAP Customer Data Platform
1 -
SAP Data Intelligence
1 -
SAP Data Migration in Retail Industry
1 -
SAP Data Services
1 -
SAP DATABASE
1 -
SAP Dataspher to Non SAP BI tools
1 -
SAP Datasphere
9 -
SAP DRC
1 -
SAP EWM
1 -
SAP Fiori
3 -
SAP Fiori App Embedding
1 -
Sap Fiori Extension Project Using BAS
1 -
SAP GRC
1 -
SAP HANA
1 -
SAP HCM (Human Capital Management)
1 -
SAP HR Solutions
1 -
SAP IDM
1 -
SAP Integration Suite
9 -
SAP Integrations
4 -
SAP iRPA
2 -
SAP LAGGING AND SLOW
1 -
SAP Learning Class
1 -
SAP Learning Hub
1 -
SAP Master Data
1 -
SAP Odata
2 -
SAP on Azure
2 -
SAP PartnerEdge
1 -
sap partners
1 -
SAP Password Reset
1 -
SAP PO Migration
1 -
SAP Prepackaged Content
1 -
SAP Process Automation
2 -
SAP Process Integration
2 -
SAP Process Orchestration
1 -
SAP S4HANA
2 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud
1 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud for Finance
1 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud private edition
1 -
SAP Sandbox
1 -
SAP STMS
1 -
SAP successfactors
3 -
SAP SuccessFactors HXM Core
1 -
SAP Time
1 -
SAP TM
2 -
SAP Trading Partner Management
1 -
SAP UI5
1 -
SAP Upgrade
1 -
SAP Utilities
1 -
SAP-GUI
8 -
SAP_COM_0276
1 -
SAPBTP
1 -
SAPCPI
1 -
SAPEWM
1 -
sapfirstguidance
1 -
SAPHANAService
1 -
SAPIQ
1 -
sapmentors
1 -
saponaws
2 -
SAPS4HANA
1 -
SAPUI5
5 -
schedule
1 -
Script Operator
1 -
Secure Login Client Setup
8 -
security
9 -
Selenium Testing
1 -
Self Transformation
1 -
Self-Transformation
1 -
SEN
1 -
SEN Manager
1 -
service
1 -
SET_CELL_TYPE
1 -
SET_CELL_TYPE_COLUMN
1 -
SFTP scenario
2 -
Simplex
1 -
Single Sign On
8 -
Singlesource
1 -
SKLearn
1 -
Slow loading
1 -
soap
1 -
Software Development
1 -
SOLMAN
1 -
solman 7.2
2 -
Solution Manager
3 -
sp_dumpdb
1 -
sp_dumptrans
1 -
SQL
1 -
sql script
1 -
SSL
8 -
SSO
8 -
Substring function
1 -
SuccessFactors
1 -
SuccessFactors Platform
1 -
SuccessFactors Time Tracking
1 -
Sybase
1 -
system copy method
1 -
System owner
1 -
Table splitting
1 -
Tax Integration
1 -
Technical article
1 -
Technical articles
1 -
Technology Updates
15 -
Technology Updates
1 -
Technology_Updates
1 -
terraform
1 -
Threats
2 -
Time Collectors
1 -
Time Off
2 -
Time Sheet
1 -
Time Sheet SAP SuccessFactors Time Tracking
1 -
Tips and tricks
2 -
toggle button
1 -
Tools
1 -
Trainings & Certifications
1 -
Transformation Flow
1 -
Transport in SAP BODS
1 -
Transport Management
1 -
TypeScript
3 -
ui designer
1 -
unbind
1 -
Unified Customer Profile
1 -
UPB
1 -
Use of Parameters for Data Copy in PaPM
1 -
User Unlock
1 -
VA02
1 -
Validations
1 -
Vector Database
2 -
Vector Engine
1 -
Visual Studio Code
1 -
VSCode
2 -
VSCode extenions
1 -
Vulnerabilities
1 -
Web SDK
1 -
work zone
1 -
workload
1 -
xsa
1 -
XSA Refresh
1
- « Previous
- Next »
Related Content
- SAP Cloud ALM and Identity Authentication Service (IAS) in Technology Blogs by SAP
- Configuring SAP CI/CD pipeline for Deploying ReactJS application in Cloud Foundry in Technology Q&A
- SAP Cloud Identity Services - Identity Authentication with sap ecc in Technology Q&A
- Consuming SAP with SAP Build Apps - Mobile Apps for iOS and Android in Technology Blogs by SAP
- Demystifying the Common Super Domain for SAP Mobile Start in Technology Blogs by SAP
Top kudoed authors
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 8 | |
| 7 | |
| 5 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 |