- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Supply Chain Management
- SCM Blogs by SAP
- SAP Asset Performance Management – FMEA (Failure M...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Introduction
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (abbreviated as “FMEA”) is one of the highly structured systematic techniques for failure analysis, which was known as developed by reliability engineers in the 1940s to study problems in the U.S. military systems.
IEC60812 states “Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA) is a systematic procedure for the analysis of a system to identify the potential failure modes, their causes and effects on system performance, performance of the immediate assembly and the entire system or a process”.
It is a widely adopted methodology which can contribute to risk identification, effects prediction, and potential cause analysis, which are all integral to minimize operational disruptions and overarching safety concerns in an industrial setting.
FMEA in SAP Asset Performance Management
SAP Asset Performance Management (abbreviated as “APM”) supports to develop maintenance strategies considering critical failure with the help of standard reliability methodologies such as Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM), Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) etc. and in recommending mitigation actions. You can read the Asset Strategy Overview blog for more details.
RPN method used by FMEA
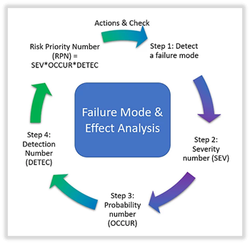
In this blog I will introduce how you can use FMEA, which is provided in SAP APM. It is essential to understand that FMEA uses RPN (Risk Priority Number) method for risk assessment. As depicted in a diagram below, it is required first to identify a failure mode, then define the severity number (SEV), the probability number(OCCUR), and the detection number (DETEC). When multiplying all three factors, SEV*OCCUR*DETEC, you get RPN (Risk Priority Number) score. This indicates that the higher the RPN value, the greater the risk.
Picture 1: Steps of calculating RPN (Risk Priority Number) in FMEA
How to use “Manage FMEA Assessments”
To begin, navigate to the "Manage FMEA Assessments" in SAP APM. This app resides under "Asset Reliability Engineering". I will go through the process step by step.
1. Prerequisite
In order to perform FMEA we need to have a technical object (abbreviated as “TO”, Equipment master data) replicated from SAP S/4HANA and this TO should include "Failure Data Profile", which is a failure catalog defined in SAP S/4HANA.
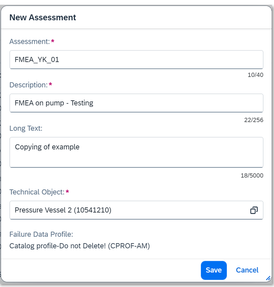
2. Create New Assessment
You can create a FMEA assessment with a technical object.
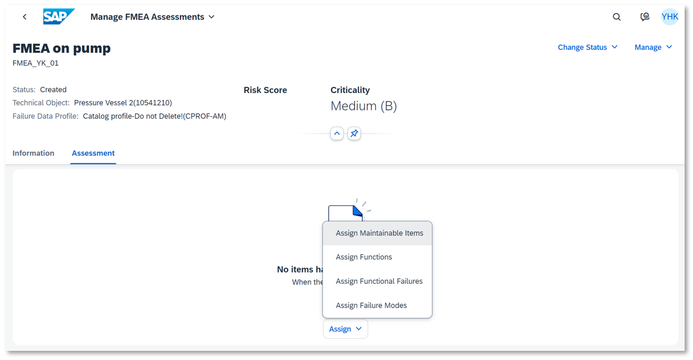
3. Assign Failure Mode
Here you have options to start with maintainable items or functions or functional failures for making the hierarchy if necessary. "Failure mode" is a term that describes the various ways something can fail.
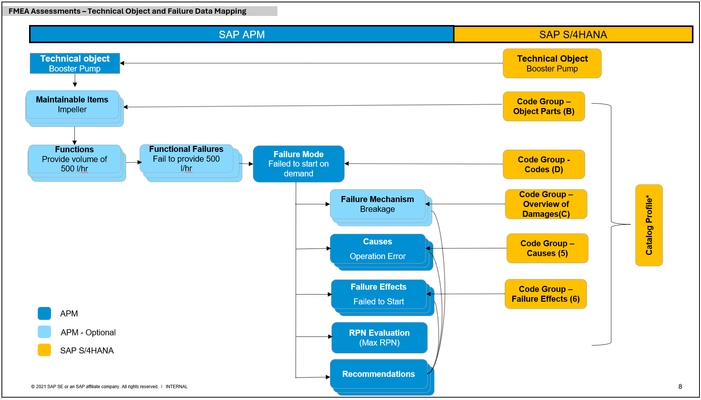
You can see the diagram below how a technical object (e.g. Booster pump) is structured with failure data and how this is mapped with catalog profile from SAP S/4HANA. “Functions” and “Functional Failures” are used only in APM and you can create the codes when not existing during FMEA process.
Picture 2: This diagram shows how a technical object is structured with failure data and how this is mapped with catalog profile from SAP S/4HANA.
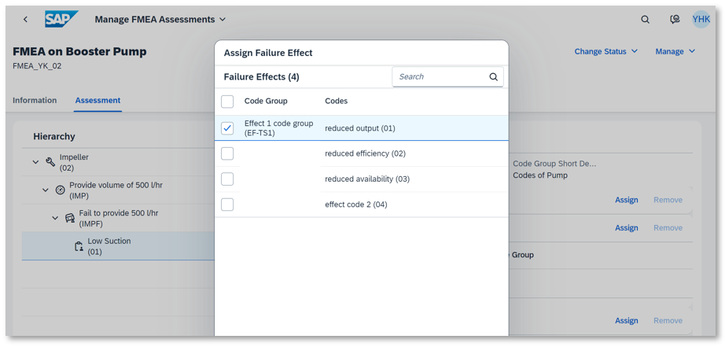
4. Assign Failure Effects
This step helps to predict what happens when the failure occurs.
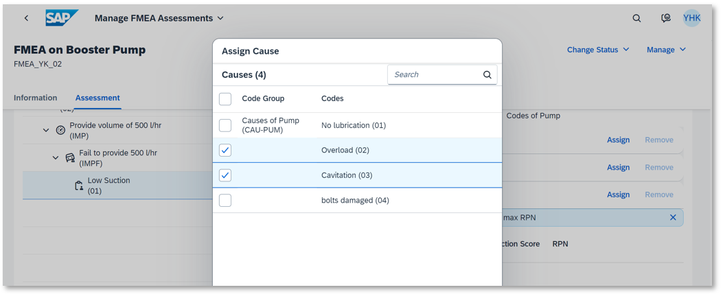
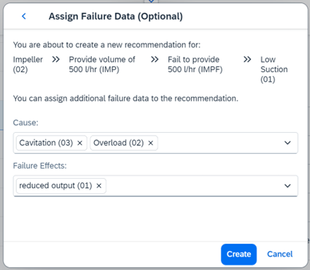
5. Assign Causes
In this step we need to identify what cause the failure and we will also determine the occurrence number and the detection number as I explained above in order to calculate RPN value.
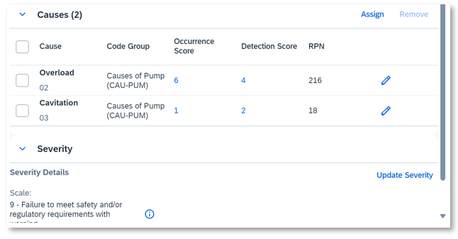
For example, you identified two causes for this failure. One is ‘Overload’, and the other is ‘Cavitation’. Then you determine how often it occurs and the likelihood of current control can detect the failure by using the pre-defined scale.
When you also determine the severity scale, the RPN is calculated by Occurrence score*Detection Score*Severity.
Occurence score : frequency of the failure to occur
Detection score : likelihood of current control to detect the failure
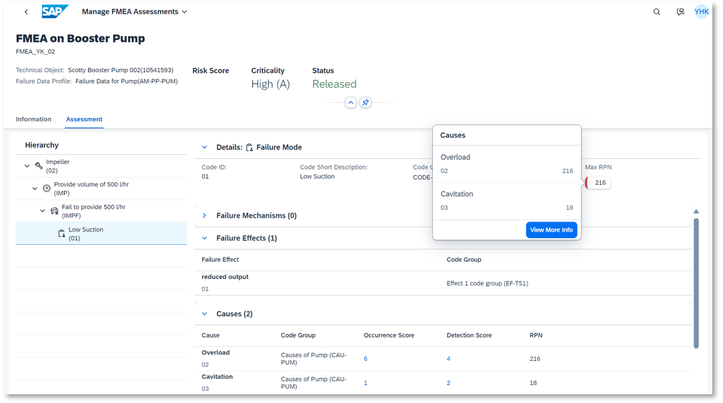
Max RPN will show up against this Failure Mode.
Based on this result, now you can create recommendations to mitigate risks.
6. Create Recommendations
These recommendations can include preventive measures, corrective actions, proposals for redesign or other actions aimed at mitigating risk. It is essential to prioritize based on their RPN scores to ensure that the most critical issues are addressed first.
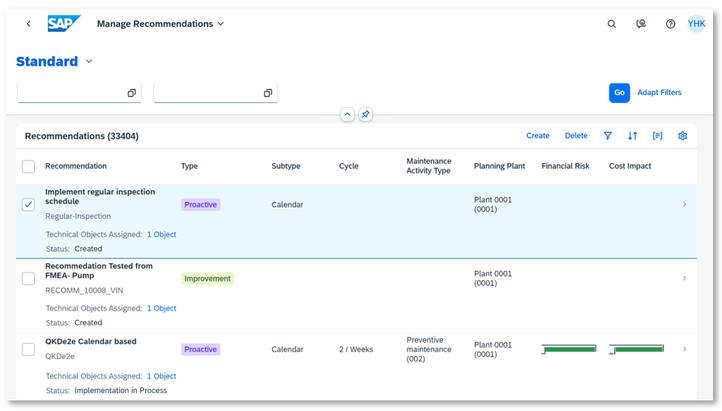
When creating a recommendation, you can also assign additional failure data to it to specify. You can have multiple recommendations and these recommendations will be listed in “Manage Recommendations” app. You can also add more information in the app.
Regarding more details of “Manage Recommendations”, I will recommend you to read this blog Recommendation Management.
You can also watch this video to see the explained process of FMEA.
What's more
FMEA can be extended to FMECA (Failure Mode, Effects and Criticality Analysis) to include a means of ranking the severity of the failure modes to allow prioritization of countermeasures. This is done by combining the severity measure and frequency of occurrence to produce a metric called criticality.
SAP Asset Performance Management is working to extend the feature of FMEA to FMECA in this year 2024. I will get back to you with another blog when FMECA is released.
For more info on SAP Asset Performance Management
- Check out all forthcoming webcasts here.
- Watch the replay of our recent webcasts
- Subscribe to What's New on the SAP Help Portal
- SAP Continuous Influence session
- The collection link blog
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
Business Trends
169 -
Business Trends
24 -
Catalog Enablement
1 -
Event Information
47 -
Event Information
4 -
Expert Insights
12 -
Expert Insights
39 -
intelligent asset management
1 -
Life at SAP
63 -
Product Updates
500 -
Product Updates
66 -
Release Announcement
1 -
SAP Digital Manufacturing for execution
1 -
Super Bowl
1 -
Supply Chain
1 -
Sustainability
1 -
Swifties
1 -
Technology Updates
187 -
Technology Updates
17
- SAP Business Network for Logistics 2404 Release – What’s New? in Supply Chain Management Blogs by SAP
- SAP Named a Leader in the 2024 Gartner Magic Quadrant for Transportation Management Systems in Supply Chain Management Blogs by SAP
- SAP Asset Performance Management Embedding Cumulocity IoT to Drive Innovations in IoT and AI in Supply Chain Management Blogs by SAP
- Adverse Media Monitoring: How to improve overall Supply Chain Management in Supply Chain Management Blogs by Members
- AI-powered supply chain solutions: Better decisions, better outcomes in Supply Chain Management Blogs by SAP
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 8 | |
| 7 | |
| 6 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 |