- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Enterprise Resource Planning
- ERP Q&A
- Creation of Outbound Delivery using VL01N in SAP
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Question as New
- Mark Question as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Creation of Outbound Delivery using VL01N in SAP
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Question as New
- Mark Question as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
4 weeks ago
Delivery Replication SAP to Salesforce
1. Introduction
Outbound Delivery in SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing) refers to the process of fulfilling customer orders by shipping goods or products from a company's warehouse or production facility to the customer's specified location. This documentation provides a comprehensive guide to understanding and executing Outbound Delivery processes within SAP.
2. Purpose
The purpose of Outbound Delivery in SAP is to streamline the logistics and shipping operations of a company, ensuring accurate and timely delivery of products to customers. By efficiently managing outbound deliveries, businesses can enhance customer satisfaction, optimize inventory management, and improve overall operational efficiency.
3. Key Features
- Creation of Outbound Delivery Orders (ODOs) based on sales orders or stock transport orders.
- Packing of goods into delivery packages or handling units.
- Generation of delivery documents such as delivery notes and shipping labels.
- Integration with transportation management systems for route optimization and carrier selection.
- Confirmation of goods issue to update inventory levels.
- Monitoring and tracking of delivery status in real-time.
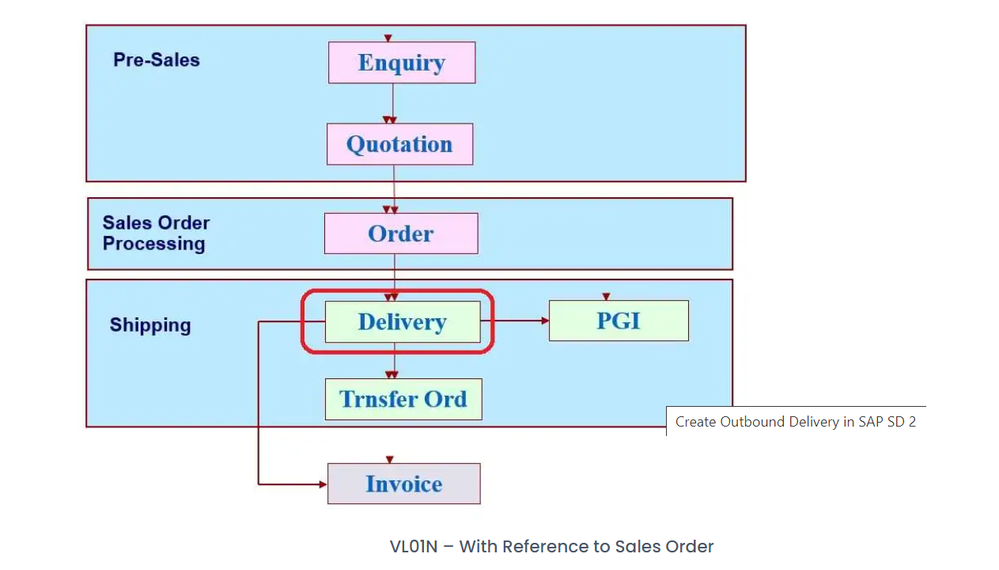
4. Process Flow
The typical process flow for Outbound Delivery in SAP involves the following steps:
- Sales Order Creation: Customer orders are received and entered into the SAP system as sales orders.
- Outbound Delivery Order Creation: Based on the sales orders, Outbound Delivery Orders (ODOs) are created in SAP. These ODOs contain information such as the items to be shipped, quantities, delivery dates, and customer shipping details.
- Packing: Goods are picked from the warehouse shelves or production lines and packed into delivery packages or handling units. The packing process involves assigning materials to specific delivery units and determining packaging materials.
- Goods Issue: Once the goods are packed and ready for shipment, a goods issue is posted in SAP to signify the removal of goods from inventory. This updates inventory levels and triggers the billing process.
- Delivery Document Printing: Delivery documents such as delivery notes and shipping labels are generated in SAP and printed for inclusion with the shipment.
- Shipment Execution: The goods are physically transported to the customer's location using selected carriers or transportation methods.
- Delivery Confirmation: Upon successful delivery, the delivery is confirmed in SAP to update the delivery status and trigger subsequent processes such as billing and customer invoicing.
T.code:-
- VL01N – With / Without Reference to Sales Order.
- VL02N – Single Document Change.
- Vl03N – Display Delivery Document.
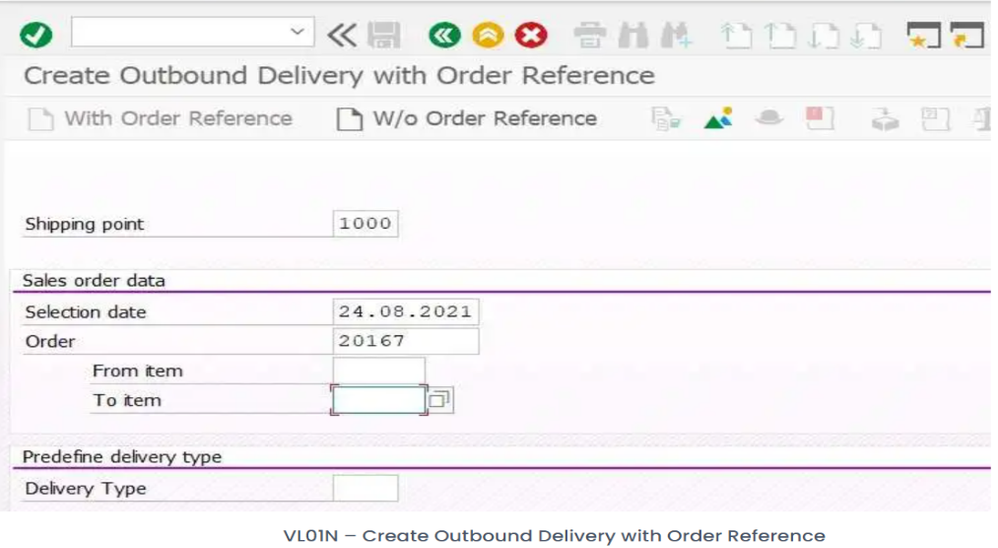
- In the initial Screen of Create Outbound Delivery Need to provide below information.
- Shipping Point: Get the shipping point from the shipping tab of sales order line item.
- Selection Date : It should be either the material availability date or the system copies the item into the delivery.
- Sales Order Number: The sales order number against which the delivery document needs to be created.
- From and to Item Number: Line item number of sales order against which needs to be created delivery, if a user does not specify any line item then the system will consider all line items of sales order for delivery creation.
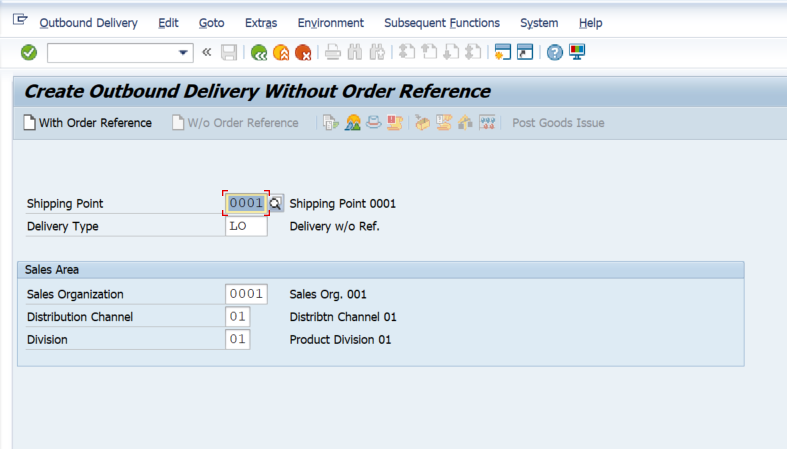
Create outbound delivery without order reference
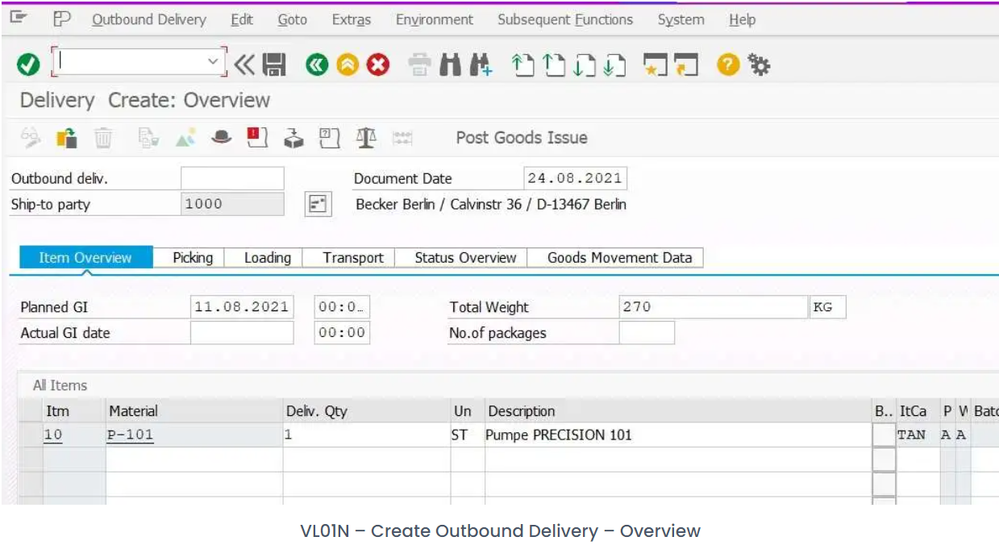
Then the system will land to the user on Create Delivery Overview screen like the below screenshot.
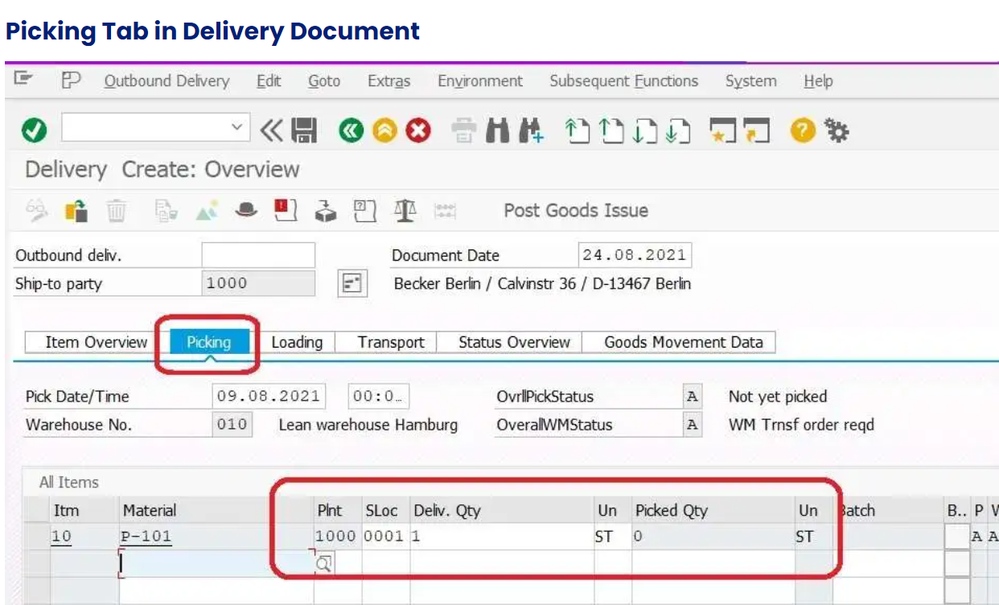
Picking Tab display
- Plant code: Delivery plant
- Storage location
- Delivery Quantity
- UoM
- Picked Quantity
The picked quantity is grey out mode that means we have to transfer the order to pick the material.
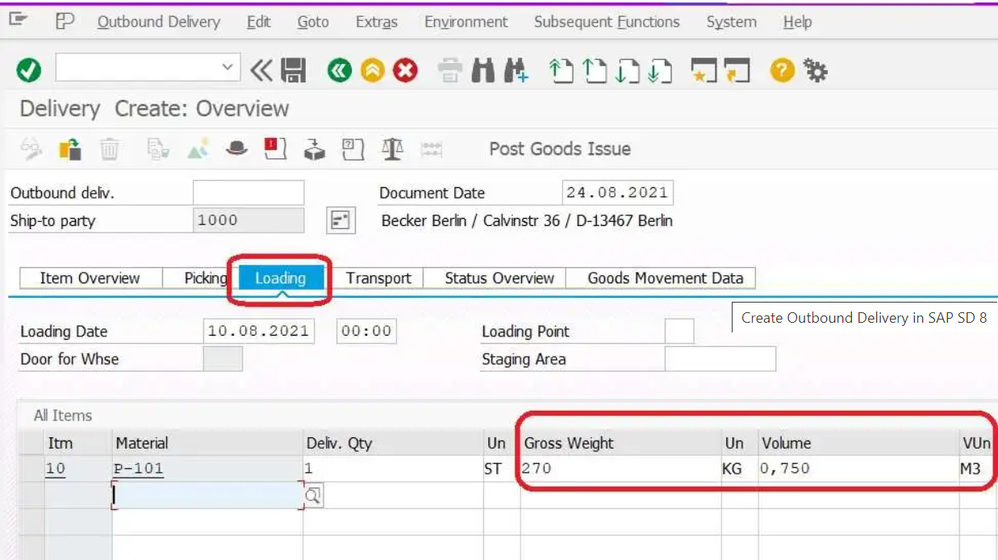
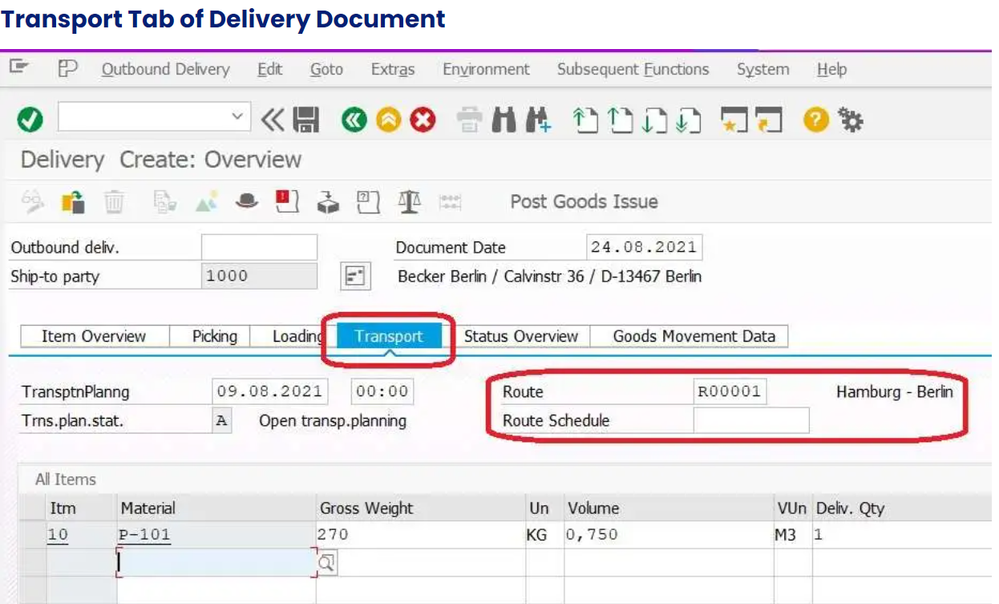
Transport tab provide information
- Transportation Planning date
- Transportation Planning status.
- Route
- Gross weight
- Volume
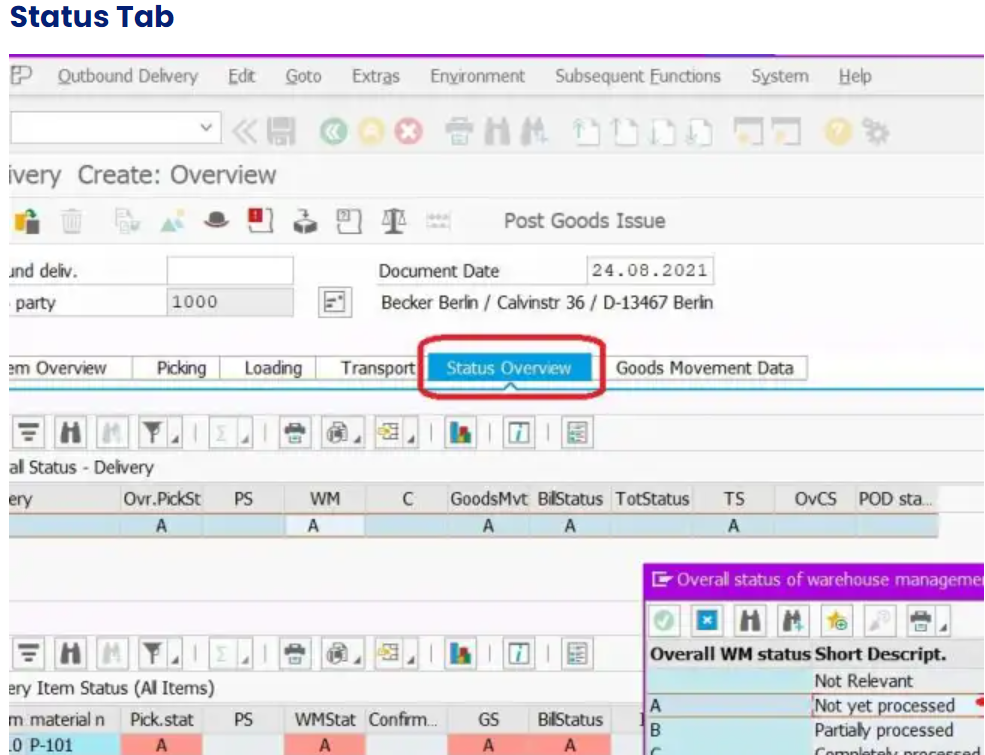
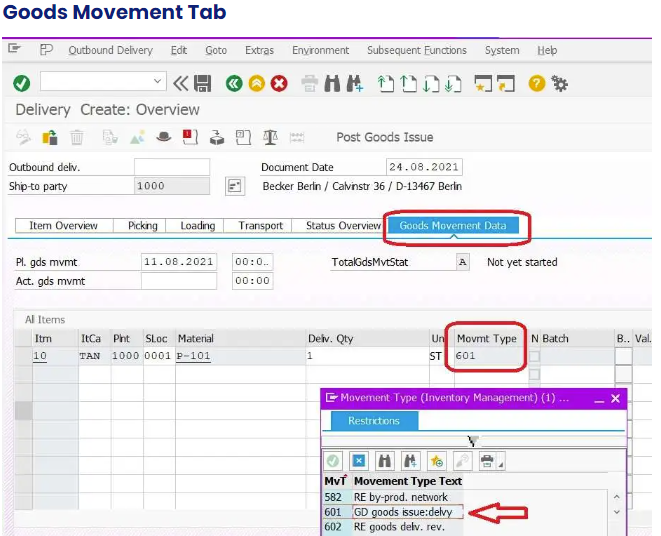
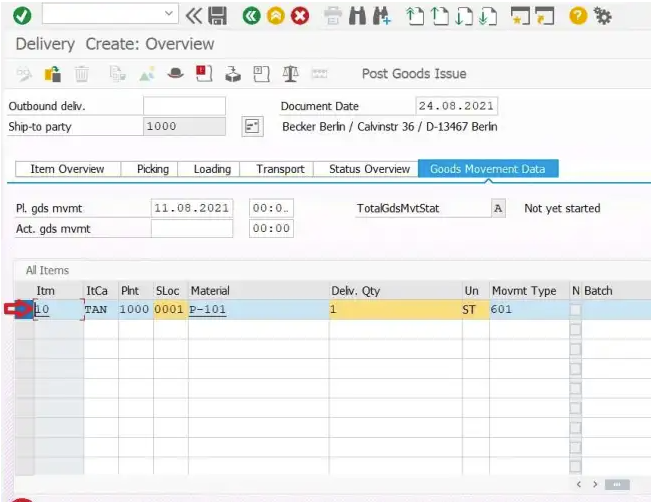
The goods movement tab provides information that which movement type is used for this delivery document.
Select any one line item of the delivery document and click on the item Details button. It will display item data of that line item.
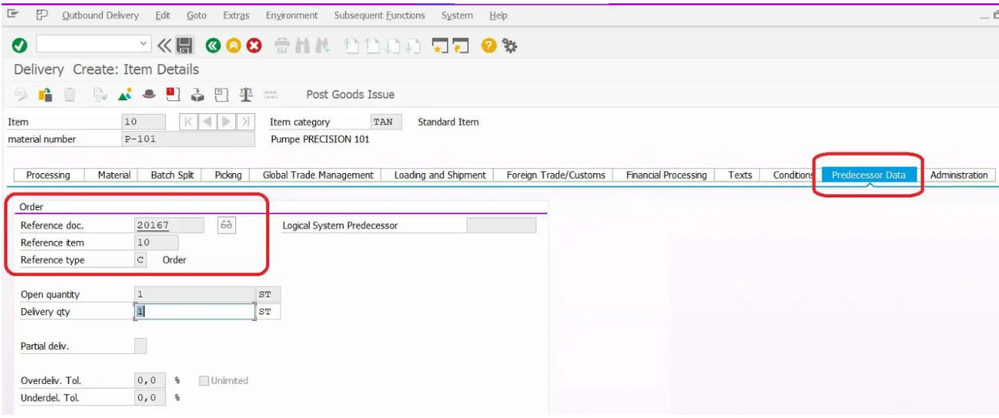
The predecessor data tab provides information about
- Reference Document number e.g. Sales order number.
- Reference Item: line item number of Sales order number.
- Reference Type: Document category.
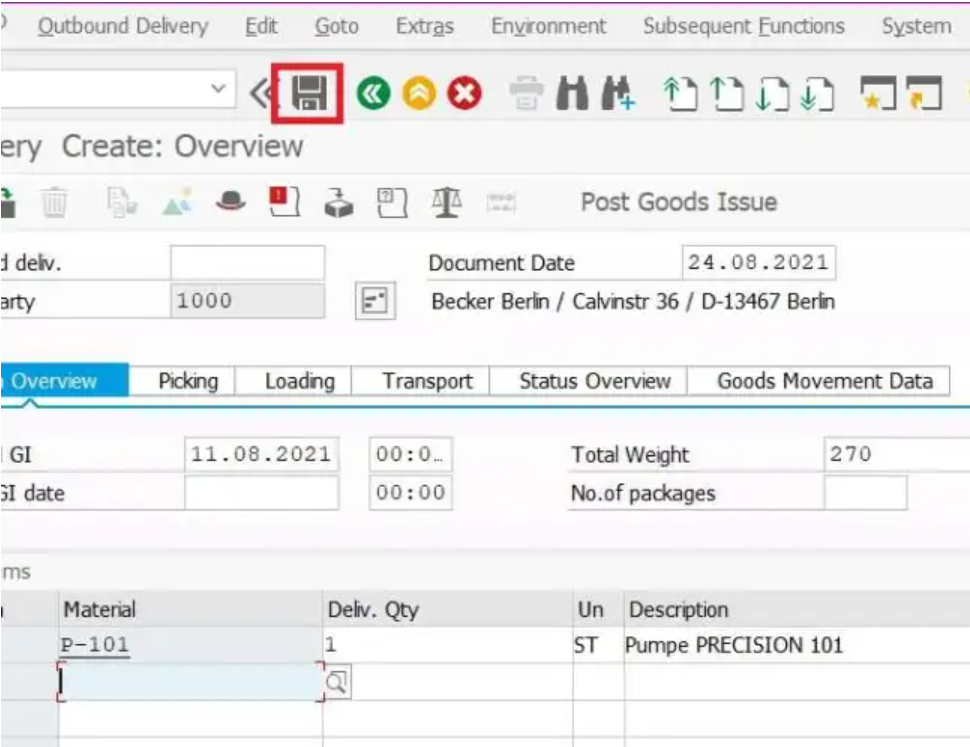
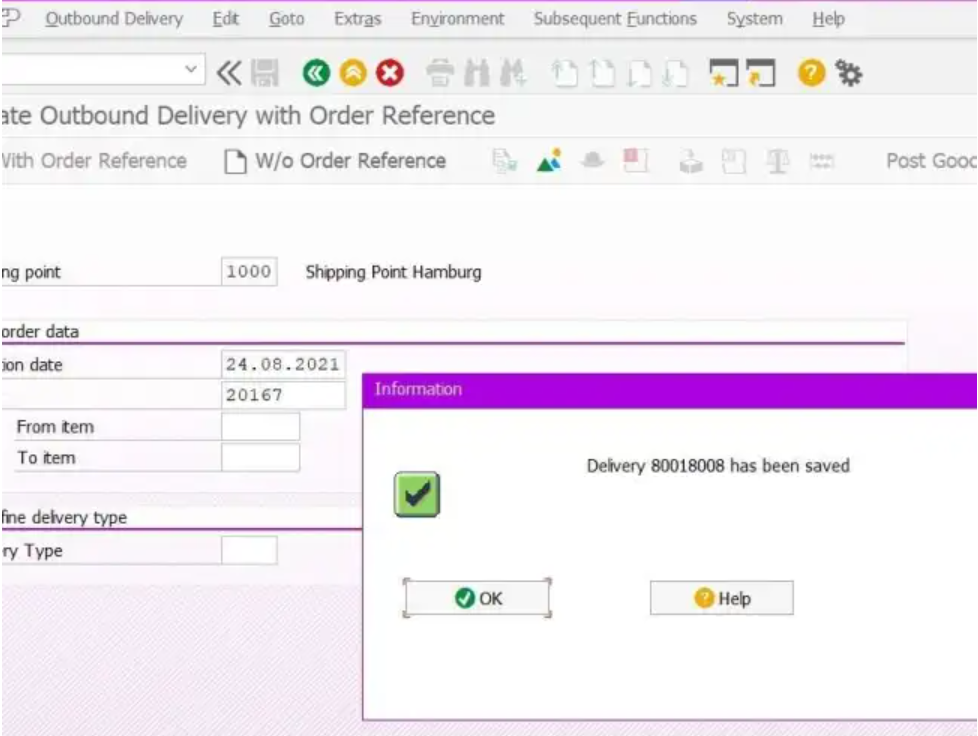
Click on SAVE button.
Now, the delivery document has been saved with the delivery number.
5. Benefits
- Improved order fulfilment accuracy and speed.
- Enhanced visibility and traceability of outbound shipments.
- Reduction in shipping errors and delays.
- Optimal utilization of warehouse resources.
- Better customer service and satisfaction.
6. Conclusion
Outbound Delivery in SAP plays a critical role in ensuring the smooth and efficient execution of logistics and shipping operations. By leveraging SAP's robust functionality and integration capabilities, businesses can effectively manage outbound deliveries, meet customer expectations, and drive operational excellence.
Accepted Solutions (0)
Answers (0)
- #CoE#JJTOOLS An error/warning message is issued during outbound delivery due to material shortage or in Enterprise Resource Planning Q&A
- Avoid new deliveries for a purchase order in Enterprise Resource Planning Q&A
- Material has status: Technical Defect (delivery is not allowed) in Enterprise Resource Planning Q&A
- Advance Return Management complete configuration(SAP ARM) in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by Members
- How to generate quality certificates for outbound deliveries? in Enterprise Resource Planning Q&A
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 106 | |
| 12 | |
| 10 | |
| 5 | |
| 4 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 2 |
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.