
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Technology
- Technology Blogs by SAP
- Innovations in SAP Master Data Governance 6.1
Technology Blogs by SAP
Learn how to extend and personalize SAP applications. Follow the SAP technology blog for insights into SAP BTP, ABAP, SAP Analytics Cloud, SAP HANA, and more.
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
Advisor
Options
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-22-2012
5:21 PM
Introduction
 Precautionary statement: If you are new to SAP MDG, you might want to read my blog SAP Master Data Governance in SAP Business Suite 7 Innovations 2011 first. That other blog will provide you more of an overall introduction to SAP MDG. This blog here is focusing completely on additional value that the release 6.1 provides.
Precautionary statement: If you are new to SAP MDG, you might want to read my blog SAP Master Data Governance in SAP Business Suite 7 Innovations 2011 first. That other blog will provide you more of an overall introduction to SAP MDG. This blog here is focusing completely on additional value that the release 6.1 provides.SAP Master Data Governance (SAP MDG) offers governance applications for master data domains like financials, supplier, customer, and material, all tailored for centralized data maintenance. The applications allow for managing of master data that is ready to use within SAP environments, but also beyond.
Update: We have now released the newest version SAP MDG 6.1 into General Availability by December 14, 2012 after an extremely successfull ramp-up phase of three months. We have seen even higher than anticipated participation of customers and SAP partners in that ramp-up, and we got very good feedback with regards to product quality as well as on the new features. SAP MDG 6.1 is now openly available for all customers.
Like the last release of SAP MDG before, this release is also based on Enhancement Package 6 for SAP ERP 6.0. For existing installations, you do not need to upgrade to any higher Enhancement Package, but can just upgrade to SAP MDG 6.1 in that system.
SAP MDG 6.1 ships enhancements for SAP MDG for the mentioned master data domains. It also provides improvements for the MDG Application Foundation that allows for extending the standard content or building governance processes for your self-defined objects.
What is new in SAP MDG 6.1?
The new version of SAP MDG provides an even broader out-of-the-box data model, in particular for the master data domains of Material, Customer and Supplier. Based on the customer feedback we are already receiving via early customer validation and Ramp-Up projects, we are spot on with the new coverage. And it’s huge! See more below. It provides SAP MDG customers a jump start of their implementation projects, since most of the master data attributes they will want to put under central governance is already delivered in standard.

Figure 1: Create a new material using the wide-ranging master data model of SAP MDG 6.1
SAP MDG’s Application Foundation saw quite some enhancements with regards to integration improvements towards other SAP solutions or also 3rd party solutions via open web services. In addition, there are new capabilities to further ease the configuration of SAP MDG. This is particularly in order to support SAP MDG implementation projects with an even bigger scope, supported by the very broad data models now available in SAP MDG 6.1.
The combination of SAP Information Steward and SAP MDG now allows for data-quality monitoring, as well as integration with processes in SAP Master Data Governance to remediate the issues in the erroneous data.
Let me explain these focus areas of SAP MDG 6.1 in a little more detail.
Increased data model coverage for material, customer and supplier
In the Enhancement Package 6 version, SAP MDG covered identifying and descriptive attributes of material master including basic data and classification. We have extended this scope dramatically by extending the coverage of basic data, as well as by introducing many attributes that are dependent on organizational units like on plants, sales organizations, or distribution channels. Extensions also include data for valuation or tax classification as well as long texts.
As you might know, both data models for the supplier as well as for the customer domain are based on the so-called generic business partner. Until the last release, the focus for supplier and customer data was on generic business partner attributes, corporate, company and purchasing attributes of suppliers, as well as general customer data, and address information. SAP MDG 6.1 provides much broader data models, that now also include partner functions, dunning areas, and withholding tax types, as well as sales area data, tax indicators, and company code data for customers and additional purchasing organization data for suppliers. In addition, SAP MDG can now also handle business partner relationships, contact partners, as well as persons and groups – in addition to organizations that could already be handled before.
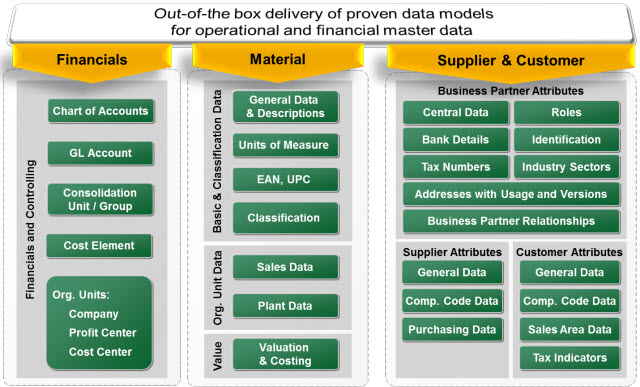
Figure 2: The broad out-of-the-box data model coverage in SAP Master Data Governance 6.1
Enhanced Application Foundation facilitating integration and configuration
As mentioned before, you will find improvements in the application foundation of SAP MDG 6.1 that will support easier integration of SAP MDG with other applications in the system landscape. For example, inbound processing of material master data is now supported via Enterprise Services that also support the enhanced data model. Through this you may want to connect SAP or non-SAP applications in order to trigger creation of or changes to material master data managed in SAP MDG.
Another example could be that you want to manage the early lifecycle of supplier in SAP Supplier Lifecycle Collaboration (SLC) and hand over the master data creation or enrichment process to SAP MDG whenever you decide to do business with that particular supplier. While SAP SLC handles the supplier portfolio management of interested suppliers, bidders, and potential suppliers, SAP MDG handles the enrichment of the approved suppliers’ master data with all the attributes that are needed to run purchasing processes with them. SAP MDG 6.1 provides you with the interfaces to enable that integration between SAP SLC and SAP MDG.
As you have seen above, the data model coverage has increased a lot in SAP MDG 6.1. It has increased so much that it goes beyond the scope that some customers might want to cover in their first SAP MDG implementation project. So you might ask yourselves: How can I decrease the scope of the standard data model to what I need now? And can I extend that scope later? In SAP MDG 6.1, we provide a solution for that. The configuration environment has been enhanced by a feature called Governance Scope. Through this you can easy define which part of the data model shall be put under central governance. You can virtually remove or add complete entity types or also single attributes of the data model. The according master data attributes will then be ignored in your governance processes and cannot be maintained through SAP MDG. But they stay part of the data model and can easily be added to your governance scope in the next phase of your implementation or roll-out.
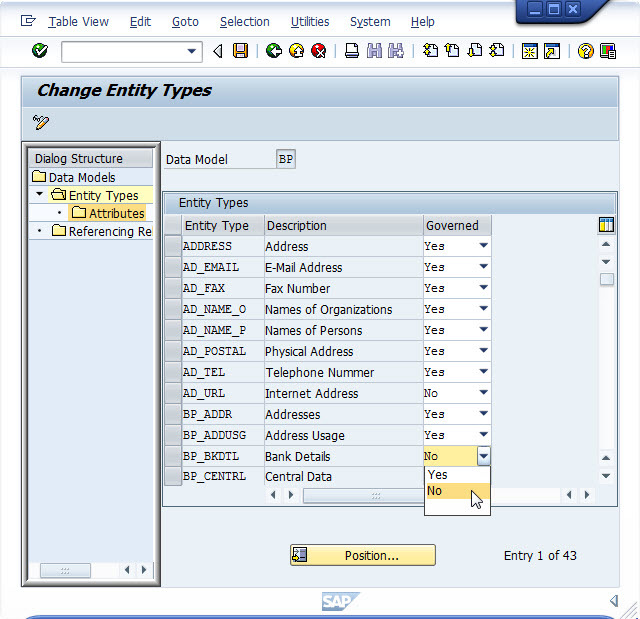
Figure 3: Simply switching the Governance Scope on or off in the SAP MDG data model
Improved data quality through seamless analytics and remediation
Whenever you access master data in a change request, SAP MDG will enforce data quality based on the configured validation rules. But what about the data that is currently not in a change request? Sometimes master data validation rules may change over time or some validations make only sense when combining master data with related transactional data, which you can obviously not do at time of master data creation. SAP Information Steward allows you to access all master data in your system regardless if it is currently in an change request or not. Based on validation rules and aggregation into data quality KPIs, it can visualize the data quality and allows drill-down to erroneous data. From the list of that bad data, you may want to start a remediation request to have the data corrected. SAP MDG 6.1 allows triggering correction processes to fix master data inconsistencies.
In order to help companies in setting up a seamless experience for their end-users, we are also offering a Rapid Deployment Solution (RDS) that focuses on providing pre-defined content in SAP Information Steward software for profiling and assessing the quality of master data in SAP ECC (table views, validation rules, and so on). It hence provides a data-quality monitoring cockpit for SAP Master Data Governance with direct and transparent insight into the current level of data quality, as well as integration with processes in SAP Master Data Governance to remediate the data issues.

Figure 4: Example UI integration between SAP Information Steward and SAP MDG for data quality remediation
For the next years to come, we plan to further extend the standard scope for SAP MDG’s master data domains and selected industry-specific master data models with the next releases of SAP MDG. We plan for additional investments in SAP MDG’s Application Foundation regarding extensibility, flexibility, usability, and ease of consumption. And we plan for further enabling of mobile access to SAP MDG, as well as native integration with SAP’s in-memory technology.
SAP MDG is an important part of SAP’s EIM portfolio
SAP MDG is a tool for central creation or change of master data. Based on your broader Information Governance initiatives, you will want to combine SAP MDG with other solutions of SAP’s Enterprise Information Management (EIM) portfolio.
 SAP has recently published a book “Enterprise Information Management with SAP” that is available at SAP Press. The book provides the big picture of SAP’s EIM offerings: what the different products are, how they work together, and how to get started using them. After the overview, you can dive into the details. The book provides very good explanations how to perform the most important tasks in SAP Master Data Governance, SAP Information Steward, SAP NetWeaver Information Lifecycle Management, and SAP Extended Content Management as well as step-by-step instructions for working with SAP Data Services. (Remark that I am actually one of the authors. But since all royalties are donated to Doctors without Borders, I do not feel bad at all promoting the book here.)
SAP has recently published a book “Enterprise Information Management with SAP” that is available at SAP Press. The book provides the big picture of SAP’s EIM offerings: what the different products are, how they work together, and how to get started using them. After the overview, you can dive into the details. The book provides very good explanations how to perform the most important tasks in SAP Master Data Governance, SAP Information Steward, SAP NetWeaver Information Lifecycle Management, and SAP Extended Content Management as well as step-by-step instructions for working with SAP Data Services. (Remark that I am actually one of the authors. But since all royalties are donated to Doctors without Borders, I do not feel bad at all promoting the book here.)I already mentioned SAP Information Steward for continuous monitoring of master data quality in all relevant systems and correction in SAP MDG. You will find additional information on the Information Steward site on SCN.
SAP Data Services supports SAP MDG with data quality services, duplicate prevention, validations and data enrichment. This helps to prevent creation of duplicates early and embedded in the process for increased effectiveness and efficiency. You can find more information on the Data Services site on SCN.
As briefly laid out in this blog and in more detail in my other blog mention above, SAP MDG focuses on comprehensive master data ready for use in SAP applications, through ready-to-run governance applications for specific master data domains. In addition, the MDG Application Foundation allows for custom-defined master data objects, processes, and user interfaces. SAP MDG provides pre-built validation against SAP business logic and customer's configuration settings, and can distribute master data to SAP and non-SAP systems. You can find more information on the SAP Master Data Governance site on SCN.
- SAP Managed Tags:
- SAP Master Data Governance
35 Comments
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
Labels in this area
-
ABAP CDS Views - CDC (Change Data Capture)
2 -
AI
1 -
Analyze Workload Data
1 -
BTP
1 -
Business and IT Integration
2 -
Business application stu
1 -
Business Technology Platform
1 -
Business Trends
1,661 -
Business Trends
87 -
CAP
1 -
cf
1 -
Cloud Foundry
1 -
Confluent
1 -
Customer COE Basics and Fundamentals
1 -
Customer COE Latest and Greatest
3 -
Customer Data Browser app
1 -
Data Analysis Tool
1 -
data migration
1 -
data transfer
1 -
Datasphere
2 -
Event Information
1,400 -
Event Information
64 -
Expert
1 -
Expert Insights
178 -
Expert Insights
273 -
General
1 -
Google cloud
1 -
Google Next'24
1 -
Kafka
1 -
Life at SAP
784 -
Life at SAP
11 -
Migrate your Data App
1 -
MTA
1 -
Network Performance Analysis
1 -
NodeJS
1 -
PDF
1 -
POC
1 -
Product Updates
4,577 -
Product Updates
325 -
Replication Flow
1 -
RisewithSAP
1 -
SAP BTP
1 -
SAP BTP Cloud Foundry
1 -
SAP Cloud ALM
1 -
SAP Cloud Application Programming Model
1 -
SAP Datasphere
2 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud
1 -
SAP S4HANA Migration Cockpit
1 -
Technology Updates
6,886 -
Technology Updates
403 -
Workload Fluctuations
1
Related Content
- Empowering Retail Business with a Seamless Data Migration to SAP S/4HANA in Technology Blogs by Members
- 10+ ways to reshape your SAP landscape with SAP Business Technology Platform - Blog 7 in Technology Blogs by SAP
- 10+ ways to reshape your SAP landscape with SAP Business Technology Platform – Blog 4 in Technology Blogs by SAP
- Top Picks: Innovations Highlights from SAP Business Technology Platform (Q1/2024) in Technology Blogs by SAP
- Dynamic Derivations using BADI in SAP MDG in Technology Blogs by Members
Top kudoed authors
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 12 | |
| 10 | |
| 9 | |
| 7 | |
| 7 | |
| 6 | |
| 6 | |
| 6 | |
| 6 | |
| 4 |