
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- CRM and Customer Experience
- CRM and CX Blogs by Members
- SAP CAR - Transaction data change - Task status
CRM and CX Blogs by Members
Find insights on SAP customer relationship management and customer experience products in blog posts from community members. Post your own perspective today!
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
maciej_jarecki
Contributor
Options
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
04-08-2023
7:01 AM
Introduction:
Most of companies are exchanging huge amount of data between systems as data is an information and to execute any business process is more then mandatory. Connecting systems in SAP world is usually executed via SAP middleware like SAP PI/PO or any newer and renamed version of it like CPI. These systems are very powerful and sophisticated but not each industry needs it. Example of such an industry is Retail business that received number of data mainly from single source which is POS system. Increasing usability of SAP CAR system across companies and business processes that SAP CAR is involved in caused more effort spent on the maintenance and support.
Objective:
SAP CAR receives POS transactions related to number of processes mainly sales but as well good movements operations or finance transactions. Each POS transaction is a set of data that is processed by tasks. Tasks are processed independently but sometimes during the execution of any task error can occur due to the wrong data which needs to be changes and because the task dependency some of them need to be reversed first.
Selection of the task depends on the Customization of POS transactions and for here we use following assignment.
The focus of this article is to describe when you can do a change of POS transaction data based on task status and what is the procedure of reversing/ canceling the task.
Both configuration parameters are set on task definition level.
Cancelation procedure:
When checkbox is selected then reversal/cancelation means the task needs to get status ready to be cancelled first. Task is executed and same code of task is executed with information it’s reversed execution and as well system process values with opposite sign.
Changeability of data for task:
Describes when data can be changed.
Example:
For the purpose of this article I created four dummy tasks. Each of them has a different value in regards to mentioned before parameters and on top of it one is with “type of task” is set to manual trigger as it has special way of processing the cancelation.
Task 1 – No reverse required, and data is always changeable
Task 2 – No reverse required but data can only be changed if task status is ready
Task 3 – To cancel the task reversal process is required and changeability is the less restricted to status of ready or rejected.
Task 4 – it’s like Task 3 with the single difference of Type of task processing set to Manual Processing
Cancelation:
If reversal is required for a task as wrote before task needs to get first canceled. With cancelation system executes same piece of code as for regular task but with information it’s reversal and with values multiple by -1 to get opposite sign. Special feature is manual task that can be changed to canceled without request of cancelation.
Most of companies are exchanging huge amount of data between systems as data is an information and to execute any business process is more then mandatory. Connecting systems in SAP world is usually executed via SAP middleware like SAP PI/PO or any newer and renamed version of it like CPI. These systems are very powerful and sophisticated but not each industry needs it. Example of such an industry is Retail business that received number of data mainly from single source which is POS system. Increasing usability of SAP CAR system across companies and business processes that SAP CAR is involved in caused more effort spent on the maintenance and support.
Objective:
SAP CAR receives POS transactions related to number of processes mainly sales but as well good movements operations or finance transactions. Each POS transaction is a set of data that is processed by tasks. Tasks are processed independently but sometimes during the execution of any task error can occur due to the wrong data which needs to be changes and because the task dependency some of them need to be reversed first.
Selection of the task depends on the Customization of POS transactions and for here we use following assignment.

The focus of this article is to describe when you can do a change of POS transaction data based on task status and what is the procedure of reversing/ canceling the task.
Both configuration parameters are set on task definition level.
Cancelation procedure:

When checkbox is selected then reversal/cancelation means the task needs to get status ready to be cancelled first. Task is executed and same code of task is executed with information it’s reversed execution and as well system process values with opposite sign.
Changeability of data for task:

Describes when data can be changed.
- Always changeable – No restriction to change a data
- Only changeable if task has status ready – in this case we can change data only if task is in status ready neither rejected nor cancelled nor processed etc.
- Changeable if Task Not Processed or Canceled – data of POS transaction can be changed when task status is ready or rejected.
Example:
For the purpose of this article I created four dummy tasks. Each of them has a different value in regards to mentioned before parameters and on top of it one is with “type of task” is set to manual trigger as it has special way of processing the cancelation.
Task 1 – No reverse required, and data is always changeable
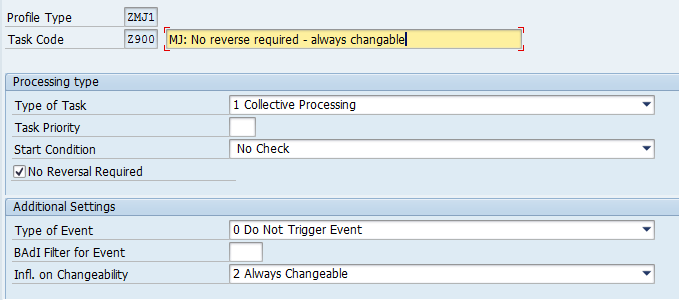
Task 2 – No reverse required but data can only be changed if task status is ready

Task 3 – To cancel the task reversal process is required and changeability is the less restricted to status of ready or rejected.

Task 4 – it’s like Task 3 with the single difference of Type of task processing set to Manual Processing

Cancelation:
If reversal is required for a task as wrote before task needs to get first canceled. With cancelation system executes same piece of code as for regular task but with information it’s reversal and with values multiple by -1 to get opposite sign. Special feature is manual task that can be changed to canceled without request of cancelation.

- SAP Managed Tags:
- SAP Customer Activity Repository,
- SAP Point-of-Sale
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
Labels in this area
-
ABAP
1 -
API Rules
1 -
c4c
1 -
CAP development
1 -
clean-core
1 -
CRM
1 -
Custom Key Metrics
1 -
Customer Data
1 -
Determination
1 -
Determinations
1 -
Introduction
1 -
KYMA
1 -
Kyma Functions
1 -
open SAP
1 -
RAP development
1 -
Sales and Service Cloud Version 2
1 -
Sales Cloud
1 -
Sales Cloud v2
1 -
SAP
1 -
SAP Community
1 -
SAP CPQ
1 -
SAP CRM Web UI
1 -
SAP Customer Data Cloud
1 -
SAP Customer Experience
1 -
SAP CX
1 -
SAP CX extensions
1 -
SAP Integration Suite
1 -
SAP Sales Cloud v2
1 -
SAP Service Cloud v2
1 -
SAP Service Cloud Version 2
1 -
Service and Social ticket configuration
1 -
Service Cloud v2
1 -
side-by-side extensions
1 -
Ticket configuration in SAP C4C
1 -
Validation
1 -
Validations
1
Related Content
- SAP Commerce Cloud Q1 ‘24 Release Highlights in CRM and CX Blogs by SAP
- Delete & Rename Contract Account Name from SAP Cloud for Customer (C4C) in CRM and CX Blogs by Members
- Account in Visit cannot be changed in CRM and CX Questions
- How to add action in custom workcenter in SAP C4C in CRM and CX Questions
- CRM Basic Technical Info for ABAPers in CRM and CX Blogs by Members