
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Supply Chain Management
- SCM Blogs by SAP
- Unlock your supply chain potential with SAP Integ...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Last Update on February 6, 2024.
Looking to optimize your supply chain planning? Look no further than SAP Integrated Business Planning for Supply Chain. With a wide variety of embedded and side-by-side intelligent use cases, SAP IBP AI offers master data anomaly checks, machine learning forecasting, supply and inventory optimization, and more.
Continuous Monitoring
Alert Threshold Determination
Custom alerts are used to identify important or critical supply chain issues, such as inventory shortages, an imbalance of supply and demand, or any unexpected changes in the supply chain. You can specify the threshold values to be used to determine issues. For example, you can set threshold values for minimum stock levels for a specific location.
But what if you do not know what these thresholds should be? With machine learning rules, you can define custom alerts without knowing the exact thresholds. If the data changes, your custom alert definition is automatically adjusted. The DBSCAN and the k-means clustering-based algorithms can be used.
More information: Alert determination
Required license: SAP IBP Control Tower
Batch Job Anomaly Detection
Using machine learning for batch jobs can help you detect anomalies in job duration and allow you to review your job schedules. The Outlier Jobs Detection job template uses a machine learning algorithm, namely the density-based clustering algorithm (DBSCAN), to determine the outlier jobs.
The algorithm uses the job name and job duration and analyzes the logs of executed application jobs that are still available in the system.
It provides the best results if the same job name is used to schedule the same job type with the same parameters, and if multiple instances of the same job name have been already executed.
More information: Batch Job Anomaly detection
Required licenseany SAP IBP license

Master Data
Master Data Consistency Check
Machine learning for Master Data Consistency improves the master data quality for planning in SAP IBP by self-learning semantic rules to identify problems in master data and recommend values for correction.
Machine learning for data consistency is executed as an application job using the job template ML Master Data Consistency. It can identify the semantic relations and patterns in master data and derive association rules. From the derived rules, the algorithm identifies outliers with higher probability of confidence and recommends values for the outliers. Based on the generated rules and recommendations, you can decide if the rules match the business semantics, and if the generated outliers and recommendations are valid. You can then make appropriate changes to the master data, either in the source system or in SAP IBP. You can train the algorithm and test data once, or periodically.
More information: Master Data consistency check
Required license: any SAP IBP license


Discover Patterns in Master Data app
To identify patterns in the data (or data that don't fit the pattern), you can run pattern analyses in the Manage Master Data app, and make changes based on the results. The Manage Master Data app offers a machine learning-assisted feature to find patterns within master data records and highlight potential errors. To review the patterns, you must use the Discover Patterns in Master Data app.
The Discover Patterns in Master Data app enables you to do the following:
- List the pattern analyses that have been performed for master data types used in your planning areas.
Obtain detailed information about the pattern analyses. - Assess the recommended corrections listed in the app, and identify changes that should be applied to your master data.
- Assess if the patterns can be considered as applicable rules.
- Delete patterns.
More information: Discover Patterns in Master Data
Cross-application Topics
Segmentation
Segmentation helps you define more specific alerts and reports, and generate more accurate results for demand planning and inventory planning.
ABC segmentation is the prioritization of planning objects based on their relative importance, while XYZ segmentation is the classification of planning objects based on their demand volatility.
Among the segmentation methods, you can choose k-means. In this case, the system uses machine learning to create segments as homogenous as possible with regards to the values of the segmentation measure. This approach is particularly useful when you are unsure of what thresholds should be defined for the segments.
More information:
Required license: any SAP IBP license
Demand Planning
Demand Sensing
Demand sensing optimizes daily forecasts for multiple products in a highly automated way for a short period between 4-8 weeks. The forecasts are based on a review of the consensus demand and the most recent demand signals retrieved from internal sources such as sales orders and external sources. Demand sensing can drive better deployment and transportation decision, which leads to reduced stock-outs and less rush orders, by improving the short-term forecast and increase automation the following ways.
In particular, the xGBoost (eXtreme Gradient Boosting – i.e. Demand Sensing with Gradient Boosting) algorithm uses machine learning to forecast the weekly demand. Then, the pattern recognition disaggregates the sensed demand to daily demand taking into account working days, holidays and other variables.
More information: Demand Sensing
Required license: SAP IBP for Demand
Advanced Forecasting Algorithms
Statistical forecasting is used to create forecasts for a longer period such as 2–3 years for long-term forecasting or 12–18 months for mid-term forecasting.
The three algorithms Gradient Boosting of Decision Trees, (S)ARIMAX and Multiple Linear Regression use independent variables (business drivers – internal and external) to explain a target variable such as sales history and calculate a forecast based on the results. You can also analyze the impact of these drivers using the impact key figures.
More information:
Required license: SAP IBP for Demand
Curve-based Forecasting Method
This algorithm can be used to predict future demand for the entire lifecycle of planning objects with a sales history as short as two periods.
The prediction is based on the results of a previously executed Curve Clustering application job, which compared and typified the sales curves of other planning objects with a longer history. The algorithm compares the starting values of the identified curve types to the existing values of the sales history on which forecasting is running and uses the curve type with the most similar starting values as the forecast. The quality of the forecast is likely to improve over time as the calculations are performed on a continuously extending sales history.
Required license: SAP IBP for Demand
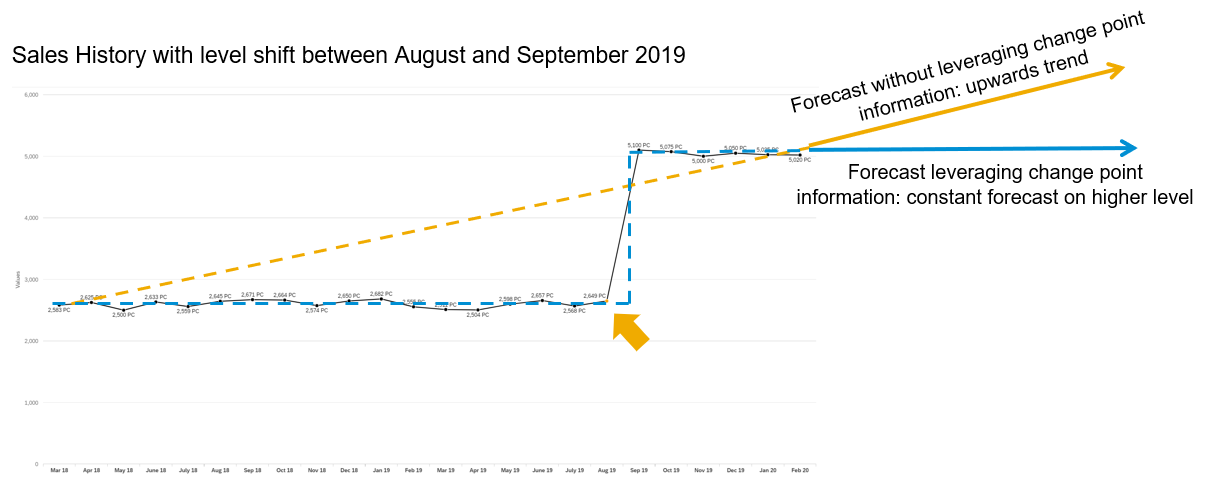
Change Point Detection
If you want to see what major changes occurred in the sales history that had long-term effects on the data, you can set the system to detect such changes based on predefined rules. This process is called change point detection. The changes can either be a level shift (when the mean of the time series values alters significantly) or a trend change (when the direction or slope of a trend alters significantly).
More information: Change Point Detection
Required license: SAP IBP for demand
Bring your own Machine Learning algorithm
You can boost the already existing forecasting capabilities of SAP IBP for demand by using custom-built forecasting algorithms in a tightly integrated process within IBP. SAP IBP takes care of the pre- processing (including reading and aggregation of relevant key figure data, applying Product Lifecycle settings in case of new product introduction) and post processing (including evaluation in a best fit model, applying Product Lifecycle settings and disaggregation), while the custom algorithm creates the forecast. This is done in a synchronous process, meaning that the external algorithm is called only if and when you trigger a forecast in SAP IBP, either through interactive forecasting in Excel or via a forecast job. The data exchange is done through an OData Service, and the external algorithm can be written in R, Python or any other suitable tools.
More information:
Required license: SAP IBP for demand, external system (SAP Data Intelligence)

Inventory Planning
Multi-stage Inventory Optimization
The Multi-stage inventory optimization recommends total inventory targets to maximize profit while buffering for uncertainty and maintaining customer service levels.
By using a set of stochastic mathematical algorithms, inventory optimization determines the lowest stocking cost possible for locations across an entire supply chain and provide stocking targets directly to planners at an item-location-time period level of granularity.
More information: Inventory optimization
Required license: SAP IBP for inventory
Customer Service Level Prediction
Situations may arise in which you want to determine how adjustments to safety stock values will impact service levels, such as when you want to limit your investment in inventory holdings at the end of a fiscal period. The Service Level Prediction operator enables planners to predict the customer service level by product-location, based on a predefined safety stock plan.
After creating a safety stock plan, planners can analyze predicted customer service levels in the plan’s future periods. Action may then be taken to minimize impact during anticipated periods of inadequate service, thus protecting customer service levels and minimizing revenue impacts.
Planners can run scenarios of potential future conditions and predict the customer service level and revenue impact. Scenario examples include unplanned events that increase lead time or reduces capacity, potential new market demand or unexpected surge in demand, inventory budget constraints directed by the Finance department, and so on.

More information: Service Level Prediction
Required license: SAP IBP for inventory
Probabilistic Inventory Planning – Demand Uncertainty
Buffer against forecast error and other demand-side uncertainty, to support your demand-driven supply chain. Improve customer service levels by planning the right inventory at the right place at the right time. Maximize the efficiency of inventory and working capital. Standardize and simplify the inventory target-setting process at each tier of the supply chain
More information: Forecast error calculations
Required license: SAP IBP for sales and operations, SAP IBP for inventory, SAP IBP for demand, SAP IBP for demand-driven replenishment
Probabilistic Inventory Planning - Supply Lead Time Calculation
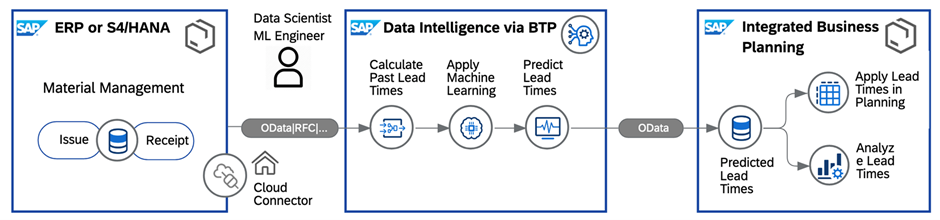
Few parameters have as significant an impact on supply chain planning as lead time. Lead time values used by the SAP IBP system can drift over time from actual execution times, or worse, reflect worst-case lead times. Supply Lead Time Recommendation keeps lead time values in SAP IBP current through a safe, automated process. By considering lead time variability, customers not only include the uncertainty at demand level (via the forecast error) but also get input on the uncertainty at the supply side. Inventory and supply planning accuracy improves and working capital is reduced by eliminating over-estimation of lead time.
Aggregated, time-phased lead times for transportation, production, and procurement are passed from SAP S/4HANA or SAP ECC to SAP IBP, where a new operator recommends values for lead time mean, variance, and confidence interval. After the operator runs, planners may compare new and old values, validate new values through scenario analysis, and where appropriate, explicitly promote new values to baseline.
Lead time values are most commonly used by inventory and supply optimizers. Planners may also use recommended values to create supplier score cards or compare recent execution trends to macro industry trends. A sophisticated ML “prediction” of future lead times may be configured in conjunction with an SAP IBP forecasting algorithm such as gradient boosting.
More information: Supply Lead Time Profiles
Required license: any SAP IBP license, SAP Data Intelligence
Supply Planning
Optimize your Supply Network
The supply optimizer allows you to create a demand and supply plan for your supply chain network which is cost-optimized. You can plan production, distribution, and procurement for the entire supply chain network, taking into account certain constraints. The algorithm can be configured to generate a plan that maximizes either profits or delivery.
Optimization aims at fulfilling the demands as far as possible under the given constraints (finite capacity planning). The optimizer enables cost-based planning: The approach of the optimizer is to make all decisions - what, when, where, and how much to transport, produce, or procure - based on the costs specified.
More information: TS-Based Supply Optimizer
Required license: SAP IBP for Response and Supply
Optimize your deployment
With the deployment optimizer you can create short-term distribution plans based on given supplies. You can distribute supply over the supply network of your organization, given its priorities and available-to-deploy elements. Cost parameters are considered by the optimizer to create the plan.
The optimizer takes all customer demand (sales orders), all confirmed component demands (for example, from production orders or stock transfer orders), all forecasted customer demands, and safety stock into account. It then tries to satisfy the demands with the existing supply elements. As an output, stock transfer requisitions are created. Those stock transfer requisitions that are pegged only to supply elements that are considered available to deploy become deployment stock transfer requisitions.
More information: Deployment run
Required license: SAP IBP for Response and Supply
Cloud Operations
Automatically allocate space using Machine Learning
With Hana Cloud the system can re-allocate hardware as needed. Artificial intelligence evaluates past job executions and decides automatically if the new job execution should run on an Elastic Compute Node (ECN) or on the main HANA DB. Then the needed size for the ECN is calculated automatically.
This means better performance due to more parallelization opportunities and and lower TCO: the total hardware capacity is increased but is only used when needed.
Required license: any SAP IBP license
Conclusion
Embedded and side-by-side artificial intelligence capabilities in SAP IBP significantly drive planning accuracy and automation, and ensure you get the most out of your supply chain. Jump on the AI train and try them out! And of course, do not hesitate to contact us for any questions.
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
Business Trends
169 -
Business Trends
23 -
Catalog Enablement
1 -
Event Information
47 -
Event Information
3 -
Expert Insights
12 -
Expert Insights
36 -
intelligent asset management
1 -
Life at SAP
63 -
Product Updates
500 -
Product Updates
60 -
Release Announcement
1 -
SAP Digital Manufacturing for execution
1 -
Super Bowl
1 -
Supply Chain
1 -
Sustainability
1 -
Swifties
1 -
Technology Updates
187 -
Technology Updates
15
- “Mind the Gap” – Improves ROI, Cost & Margin by Merging Planning Processes in Supply Chain Management Blogs by SAP
- RISE with SAP Advanced Logistics Package in Supply Chain Management Blogs by SAP
- SAP Field Logistics: Centralized Supplier Item Repository for an Optimized Rental Process in Supply Chain Management Blogs by SAP
- Drive productivity, safely and sustainably, with SAP manufacturing solutions in Supply Chain Management Blogs by SAP
- RISE with SAP advanced asset and service management package in Supply Chain Management Blogs by SAP
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 11 | |
| 7 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 |


