
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Product Lifecycle Management
- PLM Blogs by Members
- Audit Management in SAP EHS Solution Portfolio
Product Lifecycle Management Blogs by Members
Get insider knowledge about product lifecycle management software from SAP. Tap into insights and real-world experiences with community member blog posts.
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
pardhreddyc
Active Contributor
Options
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
12-20-2022
5:11 AM
Hello everyone, Greetings!
The Majority of us mayn't have known about SAP Audit Management and its functions. May be, a few of us might have gone through it.
The Audit Management solution can be accessed using either via SAP GUI or Fiori Launch Pad (S/4 HANA On-Premise). In this blog, I would like to walk you all through the significance of SAP Audit Management and its positioning in overall SAP EHS solution portfolio in S/4 HANA On-Premise via SAP GUI.
To the best of my experience, as a SAP Consultant and Global Internal Auditor, I would say that Audit is one of the most crucial parts in organization`s growth. Audit ensures compliance with laws, regulations and internal controls, in fact, Audit also provides management with the tools necessary to improve operational efficiency by discovering and correcting inadmissible deviations with CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Action) in advance.
We all know very well that, every organization strives for the safety of the employee and Environment. This is where, SAP EHS Audit Management comes in and provides a comprehensive auditing solution to determine whether or not an object meets predefined requirements. It is a solution that can be used in the context of EHS processes (e.g. Safety Audits).
Let us look at SAP EHS-Audit Management positioning in overall SAP EHS Solution Portfolio.
Keynote:
Before I begin with the Audit Management Master and Transactional data, would like to highlight the overview of Components and Data Objects.
Depending upon organizational requirement, we can create "CODING MASK" for the audits. This mask simplifies the display of complex audit components and helps user to recognize the audit items easily. I have created coding mask for Audit Plan, Audit, Question List, Element and Question.
Note: In the Audit Management transaction, we can enter identification numbers without separators for all the audit components and then the system inserts the separators as per the coding mask that has been configured.
We have configured the coding mask for the audit components and now, let us create an Audit Plan for Q4 2022, Environmental Audit.
Audit Plan:
As part of Audit Plan, we have to enter Description, Dates, Search Criteria, Required Roles and High level Audit Scope, etc.
Now, let us create an AUDIT(s) for the current year as per the organizational audit plan. In this blog, I have created one Audit for Q4 2022 for Environmental Audit. However, we can have multiple audits under one Audit Plan.

Once Audit is created , we can create audit question list or else we could assign question list if one was already created it as a standard question list for an audit. The hierarchy profile in the question list can structure the questions and acts as a basis for the valuation of an audit object.
Now, let us create an element for the question list, which is a function list within the question list. We can have multiple elements under one question list.
As part of this walk through, I have created three elements, viz: General Walk Around, Air Emissions and Water Discharge.
Now let us create sequence of questions for each element in respective question list. We have to segregate the questions to assess each element function.
in similar fashion, let us create another question list to assess the "Policy Management" and create element , questions as well.
Note: Currently using coding mask, SAP system can deliver the new number for the question list from the superordinate question list, which means that, if we had created a question list as "AUD/004-3100-2022-01", then system would propose "AUD/004-3100-2022-02" for the second question list and it goes on in a sequence.
Once Audit components are defined and audit is "Approved" and "Released", the lead auditor prepares the execution of an audit. During the audit, the auditor records deviations and problems directly in the system online by providing valuation proposal.
The audit execution mainly consists of assessment, valuation of audit questions, determination of audit results, and rating of an audit.
System provides the overall Audit rating by consolidating individual assessment values of each audited areas. The grading of an Audit can be "Qualitative" or "Quantitative".

Manage Corrective and Preventive Actions:
We may have certain CAPAs(Corrective Action & Preventive Action) to eliminate recurrence of certain errors and also to eliminate causes of errors.
SAP has a feature to assign persons responsible to complete the CAPA. Once user department executes auditor recommendations, CAPA can be updated with actual execution dates and level of completion, so that the auditor can re-assess the risk and verifies the effectiveness of actions during the follow-up audit.
Audit Report :
This is used to communicate all the audit findings and Corrective/Preventive Actions and over all audit results with the stakeholders of the organization.
CAPA Report:
Audit Monitor:
The audit monitor allows us to analyze and evaluate the entire audit program. For graphical representation the overview list can be exported to analytical tools or extracted to MS Excel. The example below shows the list of audits under the audit plan " AUDPL/3100-2022 Environmental, Health, and Safety Audit".
This is all about SAP Audit Management functions and I hope this blog proves useful to EHS/Audit team.
--
Yours Sincerely,
Pardhasaradhi Reddy. C
The Majority of us mayn't have known about SAP Audit Management and its functions. May be, a few of us might have gone through it.
The Audit Management solution can be accessed using either via SAP GUI or Fiori Launch Pad (S/4 HANA On-Premise). In this blog, I would like to walk you all through the significance of SAP Audit Management and its positioning in overall SAP EHS solution portfolio in S/4 HANA On-Premise via SAP GUI.
To the best of my experience, as a SAP Consultant and Global Internal Auditor, I would say that Audit is one of the most crucial parts in organization`s growth. Audit ensures compliance with laws, regulations and internal controls, in fact, Audit also provides management with the tools necessary to improve operational efficiency by discovering and correcting inadmissible deviations with CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Action) in advance.
We all know very well that, every organization strives for the safety of the employee and Environment. This is where, SAP EHS Audit Management comes in and provides a comprehensive auditing solution to determine whether or not an object meets predefined requirements. It is a solution that can be used in the context of EHS processes (e.g. Safety Audits).
Let us look at SAP EHS-Audit Management positioning in overall SAP EHS Solution Portfolio.

SAP EHS Solution Portfolio
Keynote:
- Audit Management is a complimentary with S/4 HANA Enterprise license.
- Using the Adobe Print Forms the solution supports customizing of report templates, but having said that, the interactive adobe forms are delivered with a separate consulting solution, which requires an additional cost - Adobe interactive forms (via consulting solution) is an alternative option for executing the process in the system.
- It has capability to comply with OSHA, ISO, API RP75 GMP, etc.
Before I begin with the Audit Management Master and Transactional data, would like to highlight the overview of Components and Data Objects.

- Audit Plan: It is used to keep an overview of audits in an organized and logical fashion. It describes the Audit program. It is the planning instrument for the administration of audits. The audit plan provides an organized overview of multiple audits and even contains subordinate plans. We can create annual plans for audits according to the organization`s requirement.
- Question List: It is a Master Data and serves to store the criteria according to which the audit assessments are being assessed. It contains set of questions in a determined hierarchy.
- Audit: It represents the Audit Type, Audit Trigger and Audit Object.
- Action: During an Audit, the auditor detects deviations or improvement areas and can notify the findings and can create CAPA(Corrective and Preventive Action).The data object type action contain fields for planned and actual execution dates, also the identification for the completion status.
Depending upon organizational requirement, we can create "CODING MASK" for the audits. This mask simplifies the display of complex audit components and helps user to recognize the audit items easily. I have created coding mask for Audit Plan, Audit, Question List, Element and Question.
Note: In the Audit Management transaction, we can enter identification numbers without separators for all the audit components and then the system inserts the separators as per the coding mask that has been configured.

Coding Mask for the Audit Components

Coding Mask Definition for Audit Plan

Coding Mask Definition for Audit

Coding Mask Definition for Audit Element

Coding Mask Definition for Audit Question
We have configured the coding mask for the audit components and now, let us create an Audit Plan for Q4 2022, Environmental Audit.
Audit Plan:
As part of Audit Plan, we have to enter Description, Dates, Search Criteria, Required Roles and High level Audit Scope, etc.

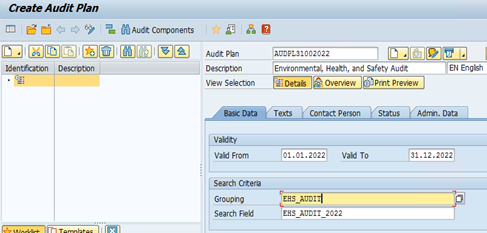


Now, let us create an AUDIT(s) for the current year as per the organizational audit plan. In this blog, I have created one Audit for Q4 2022 for Environmental Audit. However, we can have multiple audits under one Audit Plan.





Once Audit is created , we can create audit question list or else we could assign question list if one was already created it as a standard question list for an audit. The hierarchy profile in the question list can structure the questions and acts as a basis for the valuation of an audit object.



Now, let us create an element for the question list, which is a function list within the question list. We can have multiple elements under one question list.
As part of this walk through, I have created three elements, viz: General Walk Around, Air Emissions and Water Discharge.

Now let us create sequence of questions for each element in respective question list. We have to segregate the questions to assess each element function.







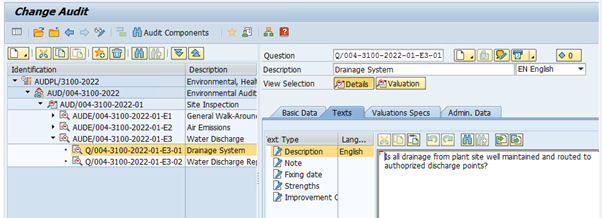

in similar fashion, let us create another question list to assess the "Policy Management" and create element , questions as well.
Note: Currently using coding mask, SAP system can deliver the new number for the question list from the superordinate question list, which means that, if we had created a question list as "AUD/004-3100-2022-01", then system would propose "AUD/004-3100-2022-02" for the second question list and it goes on in a sequence.





Once Audit components are defined and audit is "Approved" and "Released", the lead auditor prepares the execution of an audit. During the audit, the auditor records deviations and problems directly in the system online by providing valuation proposal.
The audit execution mainly consists of assessment, valuation of audit questions, determination of audit results, and rating of an audit.

System provides the overall Audit rating by consolidating individual assessment values of each audited areas. The grading of an Audit can be "Qualitative" or "Quantitative".

Audit Result
Manage Corrective and Preventive Actions:
We may have certain CAPAs(Corrective Action & Preventive Action) to eliminate recurrence of certain errors and also to eliminate causes of errors.
SAP has a feature to assign persons responsible to complete the CAPA. Once user department executes auditor recommendations, CAPA can be updated with actual execution dates and level of completion, so that the auditor can re-assess the risk and verifies the effectiveness of actions during the follow-up audit.

Audit Report :
This is used to communicate all the audit findings and Corrective/Preventive Actions and over all audit results with the stakeholders of the organization.


CAPA Report:

Audit Monitor:
The audit monitor allows us to analyze and evaluate the entire audit program. For graphical representation the overview list can be exported to analytical tools or extracted to MS Excel. The example below shows the list of audits under the audit plan " AUDPL/3100-2022 Environmental, Health, and Safety Audit".

This is all about SAP Audit Management functions and I hope this blog proves useful to EHS/Audit team.
--
Yours Sincerely,
Pardhasaradhi Reddy. C
- SAP Managed Tags:
- SAP Audit Management,
- SAP EHS Safety Issue,
- SAP Environment, Health, and Safety Management
11 Comments
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
Labels in this area
-
Automation
1 -
Billing plan
1 -
Milestone
1 -
Monitoring
1 -
PFAS
1 -
SAP DM
1 -
SAP DMC
1 -
SAP Production Connector
1 -
SPC Control Charts
1
Related Content
- Implementation journey of SAP ECTR at OSG EX-CELL-O Coldforming Technologies in Product Lifecycle Management Blogs by SAP
- LDPAS for Solution Manager in Product Lifecycle Management Q&A
- Quick Start guide for PLM system integration 3.0 Implementation in Product Lifecycle Management Blogs by SAP
- Transition from SAP Solution Manager to SAP Cloud ALM with help from SAP Enterprise Support in Product Lifecycle Management Q&A
- Striking the Perfect Balance in Product Lifecycle Management Blogs by SAP