
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Technology
- Technology Blogs by Members
- SAP Data Archiving Basic Guide for Beginner's
Technology Blogs by Members
Explore a vibrant mix of technical expertise, industry insights, and tech buzz in member blogs covering SAP products, technology, and events. Get in the mix!
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
P2004515579
Explorer
Options
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
11-21-2022
10:45 PM
Topics to be covered
- Introduction
- Benefits
- Programs
- Archiving object
- T-Codes Explain
- Archiving Development Kit
- Access to archived data
- Data Archiving Roadmap
- Storage system
- Conclusion
Introduction
Recently, I completed SAP Data Archiving Basic Training. Everyone has heard about archiving once in a lifetime. Let’s understand the basics of SAP data archiving in detail.
‘Archiving’ means the process associated with copying data and supporting documents from an active system to an external source for the purpose of deletion or storage for later retrieval.
In SAP, ‘Data archiving’ means selecting the huge volume of data that is no longer required in the database and that has not been used for a long time. Sap recommends this process of data archiving to clean up the SAP standard tables and improve the system's performance and usability.

Fig.1 A data archiving decision tree (Source: SAP)
Benefits of data archiving
- Reduce the cost of memory, disk, and administration costs.
- Improved system performance and response time.
- Reduce the cost of maintenance and run of growing application infrastructure.
Let’s understand the programs used in the data archiving process,
- Write :-
This program creates a new archive file and writes the data in it. At this point, no data has been deleted from the database. The write program can be executed in two processing models. (To create archive files)
- Test mode
- Production mode
In the test mode, no archive files will be created, whereas in the production mode, archive files will be created.

Fig.2 Write Program
Write session: -
- SARA - > Give archiving object name.
- Click on write button
- Now provide variant name and click on maintain button to create the variant for write session.
- Determine the user under which the session needs to be started.
- Specify the date and time.
- Define the spool parameter.
- Execute
- Delete: -
This program reads the data from the archived files and deletes the data from the database. The delete program can be executed in different processing modes.
- Test mode
- Production mode
In the test mode, the log after the execution shows the entries of the data to be deleted from the database, whereas in the production mode it shows the statistics of the deleted data from the database.
Delete session:-
- SARA- > Give archiving name.
- Click on delete action button
- Determine the user under which the archive files need to be deleted
- Select the archive files to be deleted
- Specify the start date and time.
- Define the spool parameter
- Execute
- Reload: -
This program is used to reload the archived data from the external storage system back into the respective SAP database tables. It is not available for all the archiving objects. (If need be, the archived objects can be restored.)
- Pre-processing: -
Before the write phase, some archiving objects undergo optional phase named pre-processing.
In pre-processing, the data for archiving is marked by the creation of a deletion flag, but the data is not deleted from the database.
On completion of pre-processing, the data marked for deletion will be archived by write program.

Fig.3 Preprocessing
- Post processing:-
It also operates on the database and does not require any archive files. This is the final program and can be executed asynchronously with the delete program.
If the data from the database is not deleted by the delete programs, it can be deleted by the post processing program.
- Index program:-
The program builds or deletes an index that allows individuals access. Infostructure created for archive objects acts as an index to the archived data.
Archiving session’s status:-
- Complete status:- Data archived and deleted.(Green)
- Incomplete status:- Data was only archived.(Yellow)
- Error status:- Error occurred while write program.(Red)

Fig.4 Status
Archiving object:-
- Archiving objects describe the structure and context of the data to be archived.
- An archiving object combines all the functions necessary to archive data that is linked through business process (Such as Orders, invoices etc.) and object linked to this data.
- Archiving objects are defined by the transaction AOBJ.

Fig.5 Archiving Object
Archive Administration:
The Archive administration enables you to all your archiving programs (read, write, delete, and restore) and also generates background jobs for them.
Residence period:
Amount of data that will be available online before it meets the achievability criteria.
Retention period: -
It is the entire time that the data spends in archive format before it gets deleted from the actual database.
T-Codes explain:-
SARA:-
- Central transaction for performing data archiving.
- From SARA, we can branch to other transactions in data archiving environment.
- SARA is an archive administration tool that is used to write, delete and manage all data archive in SAP system.

Fig.6 SARA
AOBJ:-
- Contains the programs offered by archiving object.
- Contains the tables from which the data is archived for a particular object, customizing settings for the object etc.
- AOBJ can be used to define custom archiving objects for the customer specific tables.
DB02:-
- A database table that is growing extremely fast could be the focal point of sharing.
- Database Monitoring done using transaction DB02.
- DB02 provides information about size and growth of tables, index files, table spaces etc.

Fig.7 DB02
DB15:-
- Transaction DB15 provides information about which database tables belongs to which archiving objects and vice versa.

Fig.8 DB15
TAANA:-
- TAANA transaction code is used to analyze how data is distributed across the fields of tables.(ex; time periods, organizational unit etc.)
- TAANA transactions will be used to determine how many records can be removed from the table using specific archiving object.

Fig.9 TAANA
Archiving Development Kit :- (ADK)
- Archive development kit is of central component for data archiving.
- ADK provides all data archiving functions and all necessary tools for developing new data archiving solution.
- With ADK, SAP provides an archiving solution for SAP standard tables in SAP applications. Also, we can write our own archiving objects that fit for specific tables and functions.
- ADK provides other features like data compression, connection to external storage, automatic structure conversion for data objects etc.
Access to archived data:-
Business Transaction:-
- SAP has delivered archive enabled transaction codes to retrieve the archived data.
Eg.FB03 for FI_DOCUMENT
- These transactions can directly be used to get access to data archive.
Document Relationship Browser(DRB):-
- Display of business processes across archive and database boundaries.
Using Archive Information System:-
- Archive information system is a cross application tool used to index archive files.
- The archive information system also offers an option for displaying archived data in a technical view.
Using archive read programs:-
- Application can offer programs that evaluate archived data and display it in a business view.

Fig.10 The three phases of the SAP data archiving procedure (Source: Mouritech)
Data Archiving Roadmap:-

Storage system in data archiving:-
- The archived files are saved in the content repository after the write program has created an archive file before the delete program starts. (OAC0)
- You can also use external storage system connected to sap system, SAP CMS or Archivelink interface stores the archive files to storage system automatically as instructed.
- You can write the archived files to local tapes or CD’s
Because data security is also important in data archiving, European countries have decided to implement the GDPR rule. GDPR stands for "General Data Protection Regulation." It gives individual the control and protection of their personal data.
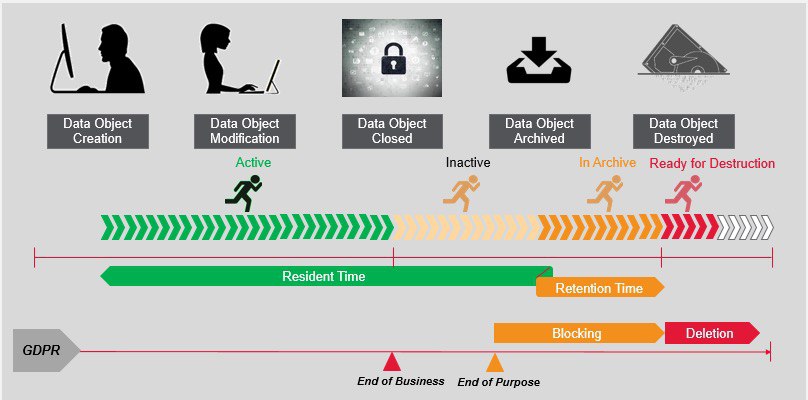
Fig.11 GDPR Rule(Source: SAP)
Conclusion:-
In this blog, I discussed some fundamental data archiving concepts. I understand that data archiving is a big topic. There are numerous topics, such as infostructure, logical path, and some technical stuff. I will try to cover the remaining topics in my next blog. The purpose of this blog post was to provide the basics of data archiving in a simpler format. Please correct me if I'm wrong somewhere, or leave a comment. I will appreciate your comments about this blog. You can expect to see many more blogs written by me about SAP functional modules. Make sure you follow me for more such articles.
Thank You.
You can use some references for additional information.
https://help.sap.com/docs/SAP_POLICY_MANAGEMENT/2f97c46b09a9420c998853f4b0187777/d269e2518fb9f261e10...
https://help.sap.com/docs/SAP_PRODUCTION_AND_REVENUE_ACCOUNTING/75bc5bb1955345c59bb53d3cc4db9ec2/4d8...
- SAP Managed Tags:
- NW ABAP Data Archiving
3 Comments
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
Labels in this area
-
"automatische backups"
1 -
"regelmäßige sicherung"
1 -
"TypeScript" "Development" "FeedBack"
1 -
505 Technology Updates 53
1 -
ABAP
14 -
ABAP API
1 -
ABAP CDS Views
2 -
ABAP CDS Views - BW Extraction
1 -
ABAP CDS Views - CDC (Change Data Capture)
1 -
ABAP class
2 -
ABAP Cloud
2 -
ABAP Development
5 -
ABAP in Eclipse
1 -
ABAP Platform Trial
1 -
ABAP Programming
2 -
abap technical
1 -
absl
2 -
access data from SAP Datasphere directly from Snowflake
1 -
Access data from SAP datasphere to Qliksense
1 -
Accrual
1 -
action
1 -
adapter modules
1 -
Addon
1 -
Adobe Document Services
1 -
ADS
1 -
ADS Config
1 -
ADS with ABAP
1 -
ADS with Java
1 -
ADT
2 -
Advance Shipping and Receiving
1 -
Advanced Event Mesh
3 -
AEM
1 -
AI
7 -
AI Launchpad
1 -
AI Projects
1 -
AIML
9 -
Alert in Sap analytical cloud
1 -
Amazon S3
1 -
Analytical Dataset
1 -
Analytical Model
1 -
Analytics
1 -
Analyze Workload Data
1 -
annotations
1 -
API
1 -
API and Integration
3 -
API Call
2 -
Application Architecture
1 -
Application Development
5 -
Application Development for SAP HANA Cloud
3 -
Applications and Business Processes (AP)
1 -
Artificial Intelligence
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
5 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) 1 Business Trends 363 Business Trends 8 Digital Transformation with Cloud ERP (DT) 1 Event Information 462 Event Information 15 Expert Insights 114 Expert Insights 76 Life at SAP 418 Life at SAP 1 Product Updates 4
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise Oil Gas IoT Exploration Production
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise sustainability responsibility esg social compliance cybersecurity risk
1 -
ASE
1 -
ASR
2 -
ASUG
1 -
Attachments
1 -
Authorisations
1 -
Automating Processes
1 -
Automation
2 -
aws
2 -
Azure
1 -
Azure AI Studio
1 -
B2B Integration
1 -
Backorder Processing
1 -
Backup
1 -
Backup and Recovery
1 -
Backup schedule
1 -
BADI_MATERIAL_CHECK error message
1 -
Bank
1 -
BAS
1 -
basis
2 -
Basis Monitoring & Tcodes with Key notes
2 -
Batch Management
1 -
BDC
1 -
Best Practice
1 -
bitcoin
1 -
Blockchain
3 -
bodl
1 -
BOP in aATP
1 -
BOP Segments
1 -
BOP Strategies
1 -
BOP Variant
1 -
BPC
1 -
BPC LIVE
1 -
BTP
12 -
BTP Destination
2 -
Business AI
1 -
Business and IT Integration
1 -
Business application stu
1 -
Business Application Studio
1 -
Business Architecture
1 -
Business Communication Services
1 -
Business Continuity
1 -
Business Data Fabric
3 -
Business Partner
12 -
Business Partner Master Data
10 -
Business Technology Platform
2 -
Business Trends
4 -
CA
1 -
calculation view
1 -
CAP
3 -
Capgemini
1 -
CAPM
1 -
Catalyst for Efficiency: Revolutionizing SAP Integration Suite with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and
1 -
CCMS
2 -
CDQ
12 -
CDS
2 -
Cental Finance
1 -
Certificates
1 -
CFL
1 -
Change Management
1 -
chatbot
1 -
chatgpt
3 -
CL_SALV_TABLE
2 -
Class Runner
1 -
Classrunner
1 -
Cloud ALM Monitoring
1 -
Cloud ALM Operations
1 -
cloud connector
1 -
Cloud Extensibility
1 -
Cloud Foundry
4 -
Cloud Integration
6 -
Cloud Platform Integration
2 -
cloudalm
1 -
communication
1 -
Compensation Information Management
1 -
Compensation Management
1 -
Compliance
1 -
Compound Employee API
1 -
Configuration
1 -
Connectors
1 -
Consolidation Extension for SAP Analytics Cloud
2 -
Control Indicators.
1 -
Controller-Service-Repository pattern
1 -
Conversion
1 -
Cosine similarity
1 -
cryptocurrency
1 -
CSI
1 -
ctms
1 -
Custom chatbot
3 -
Custom Destination Service
1 -
custom fields
1 -
Customer Experience
1 -
Customer Journey
1 -
Customizing
1 -
cyber security
3 -
Data
1 -
Data & Analytics
1 -
Data Aging
1 -
Data Analytics
2 -
Data and Analytics (DA)
1 -
Data Archiving
1 -
Data Back-up
1 -
Data Governance
5 -
Data Integration
2 -
Data Quality
12 -
Data Quality Management
12 -
Data Synchronization
1 -
data transfer
1 -
Data Unleashed
1 -
Data Value
8 -
database tables
1 -
Datasphere
2 -
datenbanksicherung
1 -
dba cockpit
1 -
dbacockpit
1 -
Debugging
2 -
Delimiting Pay Components
1 -
Delta Integrations
1 -
Destination
3 -
Destination Service
1 -
Developer extensibility
1 -
Developing with SAP Integration Suite
1 -
Devops
1 -
digital transformation
1 -
Documentation
1 -
Dot Product
1 -
DQM
1 -
dump database
1 -
dump transaction
1 -
e-Invoice
1 -
E4H Conversion
1 -
Eclipse ADT ABAP Development Tools
2 -
edoc
1 -
edocument
1 -
ELA
1 -
Embedded Consolidation
1 -
Embedding
1 -
Embeddings
1 -
Employee Central
1 -
Employee Central Payroll
1 -
Employee Central Time Off
1 -
Employee Information
1 -
Employee Rehires
1 -
Enable Now
1 -
Enable now manager
1 -
endpoint
1 -
Enhancement Request
1 -
Enterprise Architecture
1 -
ETL Business Analytics with SAP Signavio
1 -
Euclidean distance
1 -
Event Dates
1 -
Event Driven Architecture
1 -
Event Mesh
2 -
Event Reason
1 -
EventBasedIntegration
1 -
EWM
1 -
EWM Outbound configuration
1 -
EWM-TM-Integration
1 -
Existing Event Changes
1 -
Expand
1 -
Expert
2 -
Expert Insights
2 -
Fiori
14 -
Fiori Elements
2 -
Fiori SAPUI5
12 -
Flask
1 -
Full Stack
8 -
Funds Management
1 -
General
1 -
Generative AI
1 -
Getting Started
1 -
GitHub
8 -
Grants Management
1 -
groovy
1 -
GTP
1 -
HANA
6 -
HANA Cloud
2 -
Hana Cloud Database Integration
2 -
HANA DB
2 -
HANA XS Advanced
1 -
Historical Events
1 -
home labs
1 -
HowTo
1 -
HR Data Management
1 -
html5
8 -
HTML5 Application
1 -
Identity cards validation
1 -
idm
1 -
Implementation
1 -
input parameter
1 -
instant payments
1 -
Integration
3 -
Integration Advisor
1 -
Integration Architecture
1 -
Integration Center
1 -
Integration Suite
1 -
intelligent enterprise
1 -
iot
1 -
Java
1 -
job
1 -
Job Information Changes
1 -
Job-Related Events
1 -
Job_Event_Information
1 -
joule
4 -
Journal Entries
1 -
Just Ask
1 -
Kerberos for ABAP
8 -
Kerberos for JAVA
8 -
KNN
1 -
Launch Wizard
1 -
learning content
2 -
Life at SAP
5 -
lightning
1 -
Linear Regression SAP HANA Cloud
1 -
local tax regulations
1 -
LP
1 -
Machine Learning
2 -
Marketing
1 -
Master Data
3 -
Master Data Management
14 -
Maxdb
2 -
MDG
1 -
MDGM
1 -
MDM
1 -
Message box.
1 -
Messages on RF Device
1 -
Microservices Architecture
1 -
Microsoft Universal Print
1 -
Middleware Solutions
1 -
Migration
5 -
ML Model Development
1 -
Modeling in SAP HANA Cloud
8 -
Monitoring
3 -
MTA
1 -
Multi-Record Scenarios
1 -
Multiple Event Triggers
1 -
Neo
1 -
New Event Creation
1 -
New Feature
1 -
Newcomer
1 -
NodeJS
2 -
ODATA
2 -
OData APIs
1 -
odatav2
1 -
ODATAV4
1 -
ODBC
1 -
ODBC Connection
1 -
Onpremise
1 -
open source
2 -
OpenAI API
1 -
Oracle
1 -
PaPM
1 -
PaPM Dynamic Data Copy through Writer function
1 -
PaPM Remote Call
1 -
PAS-C01
1 -
Pay Component Management
1 -
PGP
1 -
Pickle
1 -
PLANNING ARCHITECTURE
1 -
Popup in Sap analytical cloud
1 -
PostgrSQL
1 -
POSTMAN
1 -
Process Automation
2 -
Product Updates
4 -
PSM
1 -
Public Cloud
1 -
Python
4 -
Qlik
1 -
Qualtrics
1 -
RAP
3 -
RAP BO
2 -
Record Deletion
1 -
Recovery
1 -
recurring payments
1 -
redeply
1 -
Release
1 -
Remote Consumption Model
1 -
Replication Flows
1 -
research
1 -
Resilience
1 -
REST
1 -
REST API
1 -
Retagging Required
1 -
Risk
1 -
Rolling Kernel Switch
1 -
route
1 -
rules
1 -
S4 HANA
1 -
S4 HANA Cloud
1 -
S4 HANA On-Premise
1 -
S4HANA
3 -
S4HANA_OP_2023
2 -
SAC
10 -
SAC PLANNING
9 -
SAP
4 -
SAP ABAP
1 -
SAP Advanced Event Mesh
1 -
SAP AI Core
8 -
SAP AI Launchpad
8 -
SAP Analytic Cloud Compass
1 -
Sap Analytical Cloud
1 -
SAP Analytics Cloud
4 -
SAP Analytics Cloud for Consolidation
3 -
SAP Analytics Cloud Story
1 -
SAP analytics clouds
1 -
SAP BAS
1 -
SAP Basis
6 -
SAP BODS
1 -
SAP BODS certification.
1 -
SAP BTP
21 -
SAP BTP Build Work Zone
2 -
SAP BTP Cloud Foundry
6 -
SAP BTP Costing
1 -
SAP BTP CTMS
1 -
SAP BTP Innovation
1 -
SAP BTP Migration Tool
1 -
SAP BTP SDK IOS
1 -
SAP Build
11 -
SAP Build App
1 -
SAP Build apps
1 -
SAP Build CodeJam
1 -
SAP Build Process Automation
3 -
SAP Build work zone
10 -
SAP Business Objects Platform
1 -
SAP Business Technology
2 -
SAP Business Technology Platform (XP)
1 -
sap bw
1 -
SAP CAP
2 -
SAP CDC
1 -
SAP CDP
1 -
SAP CDS VIEW
1 -
SAP Certification
1 -
SAP Cloud ALM
4 -
SAP Cloud Application Programming Model
1 -
SAP Cloud Integration for Data Services
1 -
SAP cloud platform
8 -
SAP Companion
1 -
SAP CPI
3 -
SAP CPI (Cloud Platform Integration)
2 -
SAP CPI Discover tab
1 -
sap credential store
1 -
SAP Customer Data Cloud
1 -
SAP Customer Data Platform
1 -
SAP Data Intelligence
1 -
SAP Data Migration in Retail Industry
1 -
SAP Data Services
1 -
SAP DATABASE
1 -
SAP Dataspher to Non SAP BI tools
1 -
SAP Datasphere
10 -
SAP DRC
1 -
SAP EWM
1 -
SAP Fiori
2 -
SAP Fiori App Embedding
1 -
Sap Fiori Extension Project Using BAS
1 -
SAP GRC
1 -
SAP HANA
1 -
SAP HCM (Human Capital Management)
1 -
SAP HR Solutions
1 -
SAP IDM
1 -
SAP Integration Suite
9 -
SAP Integrations
4 -
SAP iRPA
2 -
SAP Learning Class
1 -
SAP Learning Hub
1 -
SAP Odata
2 -
SAP on Azure
1 -
SAP PartnerEdge
1 -
sap partners
1 -
SAP Password Reset
1 -
SAP PO Migration
1 -
SAP Prepackaged Content
1 -
SAP Process Automation
2 -
SAP Process Integration
2 -
SAP Process Orchestration
1 -
SAP S4HANA
2 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud
1 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud for Finance
1 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud private edition
1 -
SAP Sandbox
1 -
SAP STMS
1 -
SAP successfactors
3 -
SAP SuccessFactors HXM Core
1 -
SAP Time
1 -
SAP TM
2 -
SAP Trading Partner Management
1 -
SAP UI5
1 -
SAP Upgrade
1 -
SAP Utilities
1 -
SAP-GUI
8 -
SAP_COM_0276
1 -
SAPBTP
1 -
SAPCPI
1 -
SAPEWM
1 -
sapmentors
1 -
saponaws
2 -
SAPS4HANA
1 -
SAPUI5
4 -
schedule
1 -
Secure Login Client Setup
8 -
security
9 -
Selenium Testing
1 -
SEN
1 -
SEN Manager
1 -
service
1 -
SET_CELL_TYPE
1 -
SET_CELL_TYPE_COLUMN
1 -
SFTP scenario
2 -
Simplex
1 -
Single Sign On
8 -
Singlesource
1 -
SKLearn
1 -
soap
1 -
Software Development
1 -
SOLMAN
1 -
solman 7.2
2 -
Solution Manager
3 -
sp_dumpdb
1 -
sp_dumptrans
1 -
SQL
1 -
sql script
1 -
SSL
8 -
SSO
8 -
Substring function
1 -
SuccessFactors
1 -
SuccessFactors Platform
1 -
SuccessFactors Time Tracking
1 -
Sybase
1 -
system copy method
1 -
System owner
1 -
Table splitting
1 -
Tax Integration
1 -
Technical article
1 -
Technical articles
1 -
Technology Updates
14 -
Technology Updates
1 -
Technology_Updates
1 -
terraform
1 -
Threats
1 -
Time Collectors
1 -
Time Off
2 -
Time Sheet
1 -
Time Sheet SAP SuccessFactors Time Tracking
1 -
Tips and tricks
2 -
toggle button
1 -
Tools
1 -
Trainings & Certifications
1 -
Transport in SAP BODS
1 -
Transport Management
1 -
TypeScript
2 -
ui designer
1 -
unbind
1 -
Unified Customer Profile
1 -
UPB
1 -
Use of Parameters for Data Copy in PaPM
1 -
User Unlock
1 -
VA02
1 -
Validations
1 -
Vector Database
2 -
Vector Engine
1 -
Visual Studio Code
1 -
VSCode
1 -
Web SDK
1 -
work zone
1 -
workload
1 -
xsa
1 -
XSA Refresh
1
- « Previous
- Next »
Related Content
- ABAP Cloud Developer Trial 2022 Available Now in Technology Blogs by SAP
- Deep dive into Q4 2023, What’s New in SAP Cloud ALM for Implementation Blog Series in Technology Blogs by SAP
- Part 1:- SAP Basis OS support on SUSE Linux for beginners in Technology Blogs by Members
- Exploring SAP Extensibility - Types of Extensibilities in Technology Blogs by SAP
- SAP Background Job Processing in Technology Q&A
Top kudoed authors
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 10 | |
| 9 | |
| 5 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 |