
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Technology
- Technology Blogs by SAP
- Handling Temporal Data in SAP Cloud Application Pr...
Technology Blogs by SAP
Learn how to extend and personalize SAP applications. Follow the SAP technology blog for insights into SAP BTP, ABAP, SAP Analytics Cloud, SAP HANA, and more.
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
former_member73
Discoverer
Options
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
04-19-2021
7:51 AM
In this post I will explain how to handle temporal data in SAP Cloud Application Programming model with HANA native artifacts.
Temporal data is time dependent. We can say if there is any timestamp associated with any data set it can be called as temporal. SAP Cloud Application Programming model provides, out of the box support to for temporal entities.
Two ways we can declare entities as temporal.
1. With annotations
We can just add these annotations to the date fields to in an entity where temporal data needs to be handled.
2. Declare an entity using aspect
Using this predefined aspect temporal we can record changes in the database with valid from/to boundaries. Deploying this cds artefacts in the database will create validFrom and validTo timestamp fields in the respective tables.
Read requests on these entities will return valid data as of now without specifying any parameter.
With this approach we can see time slices are recorded in a single table. Many change requests with time, data size in single table will keep on increasing and cause performance issues.
We can consider the alternate approach to achieve this is by HANA System Versioned tables.=
System versioned tables support the tracking of changes on column store tables by capturing the validity period of each record.
System-versioned tables always consist of two physical tables:
The valid_from and valid_to columns are timestamps and are maintained by the system.
Below are the steps to achieve this.
Step 1:
Create a devspace in Business Application Studio selecting full stack cloud project including SAP HANA tools extension. Start the devspace.
Step 2:
Open terminal in the development space. Create an application by running the below command in the directory : /home/user/projects
It will download required maven libraries and create a project. Open created project in explorer.
File-> Open Workspace
Step 3:
Create the file schema.cds under db folder. Define two entities Product and Product_hist giving required field data.
Product entity is for original data where Product_hist is to capture the data which has been modified.
We can mark the fields validFrom and validTo with the annotations - @CDS.api.ignore and @assert.notNull in order to make sure these fields are not appeared in the metadata of entity’s odata and we don’t need to pass these fields in the payload while creating.
Step 4:
Create a HANA artifact for systemversioning.
ProductTableVersioning.hdbsystemversioning
The history entity has essentially the same structure as the main entity but must also meet a number of consistency requirements, specifically: the history entity does not have the key.
We need to make sure that in System Versioned HANA artifact file, the database tables and the columns we refer are in Uppercase.
Step 5:
Create corresponding service for the entity.
Deploy the code using MTA configurations giving HANA service instance details.
Once the code is deployed we could see that the tables are created in HANA DB. And we can have OData services to perform CRUD operations as well.
Create Request: POST
https://www.example.com/v4/TemporalCapService/Product
Request Payload:
Object is created with ValidFrom and ValidTo columns populated time details.
Update Request :PATCH
https://www.example.com/v4/TemporalCapService/Product('test1')
Request Payload:
We can see that, RDP_PRODUCT table is updated with new productname, where as RDP_PRODUCT_HISTORY has a record which was changed in the original table.
Delete Request:
Deletes the data from DB but the history table will get updated with the data present in the original table.
https://www.example.com/v4/TemporalCapService/Product('test1')
This is all from my side. I hope this article is useful. Thank you.
Temporal data is time dependent. We can say if there is any timestamp associated with any data set it can be called as temporal. SAP Cloud Application Programming model provides, out of the box support to for temporal entities.
Two ways we can declare entities as temporal.
1. With annotations @CDS.valid.from/to
We can just add these annotations to the date fields to in an entity where temporal data needs to be handled.
entity Product {
validFrom : Date @cds.valid.from;
validTo : Date @cds.valid.to;
}2. Declare an entity using aspect temporal
Using this predefined aspect temporal we can record changes in the database with valid from/to boundaries. Deploying this cds artefacts in the database will create validFrom and validTo timestamp fields in the respective tables.
using { temporal } from '@sap/cds/common';
entity Product : temporal {
key productId : String(20);
productName : String(20);
productCategory : String(20);
}
Read requests on these entities will return valid data as of now without specifying any parameter.
With this approach we can see time slices are recorded in a single table. Many change requests with time, data size in single table will keep on increasing and cause performance issues.
We can consider the alternate approach to achieve this is by HANA System Versioned tables.=
System versioned tables with SAP Cloud Application Programming model :
System versioned tables support the tracking of changes on column store tables by capturing the validity period of each record.
System-versioned tables always consist of two physical tables:
- The main table of records that are currently valid.
- A corresponding history table (a one-to-one correspondence) of archived records. A naming convention is not required but may be helpful, for example, to append "_history" to the name of the main table.
The valid_from and valid_to columns are timestamps and are maintained by the system.
Below are the steps to achieve this.
Step 1:
Create a devspace in Business Application Studio selecting full stack cloud project including SAP HANA tools extension. Start the devspace.
Step 2:
Open terminal in the development space. Create an application by running the below command in the directory : /home/user/projects
mvn -B archetype:generate -DarchetypeArtifactId=cds-services-archetype -DarchetypeGroupId=com.sap.cds \
-DarchetypeVersion=RELEASE \
-DgroupId=com.sap.cap -DartifactId=temporal-cap-service -Dpackage=com.sap.capIt will download required maven libraries and create a project. Open created project in explorer.
File-> Open Workspace
Step 3:
Create the file schema.cds under db folder. Define two entities Product and Product_hist giving required field data.
Product entity is for original data where Product_hist is to capture the data which has been modified.
We can mark the fields validFrom and validTo with the annotations - @CDS.api.ignore and @assert.notNull in order to make sure these fields are not appeared in the metadata of entity’s odata and we don’t need to pass these fields in the payload while creating.
namespace rdp;
entity Product {
key productId : String(20);
productName : String(20);
productCategory : String(20);
productGroupId : String(20);
@cds.api.ignore
@assert.notNull: false
validFrom : Timestamp not null;
@cds.api.ignore
@assert.notNull: false
validTo : Timestamp not null;
}
entity Product_History {
productId : String(20);
productName : String(20);
productCategory : String(20);
productGroupId : String(20);
validFrom : Timestamp;
validTo : Timestamp;
}
Step 4:
Create a HANA artifact for systemversioning.
ProductTableVersioning.hdbsystemversioning
SYSTEM VERSIONING "RDP_PRODUCT"("VALIDFROM", "VALIDTO") HISTORY TABLE "RDP_PRODUCT_HISTORY" NOT VALIDATEDThe history entity has essentially the same structure as the main entity but must also meet a number of consistency requirements, specifically: the history entity does not have the key.
We need to make sure that in System Versioned HANA artifact file, the database tables and the columns we refer are in Uppercase.
Step 5:
Create corresponding service for the entity.
using rdp from '../db/schema';
service TemporalCapService {
entity Product as projection on rdp.Product;
}Deploy the code using MTA configurations giving HANA service instance details.
Once the code is deployed we could see that the tables are created in HANA DB. And we can have OData services to perform CRUD operations as well.
CRUD Operations on temporal entities:
Create Request: POST
https://www.example.com/v4/TemporalCapService/Product
Request Payload:
{"productId":"test1","productName":"testName1","productCategory":"testCat1","productGroupId":"123"}Object is created with ValidFrom and ValidTo columns populated time details.
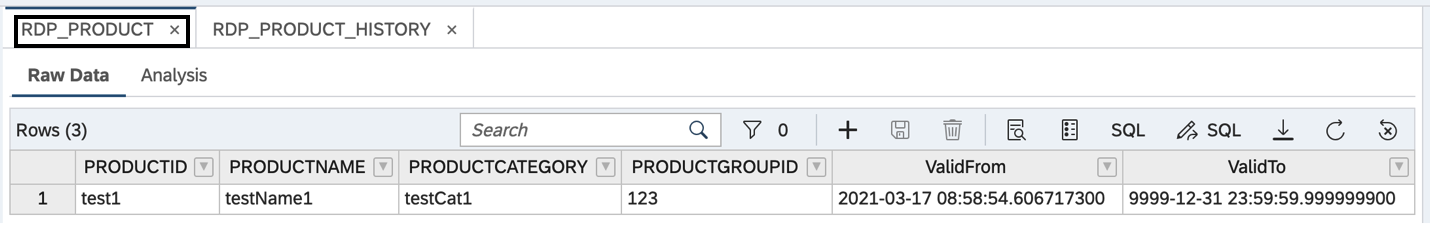
Update Request :PATCH
https://www.example.com/v4/TemporalCapService/Product('test1')
Request Payload:
{"productName":"testName123","productCategory":"testCat","productGroupId":"123"}We can see that, RDP_PRODUCT table is updated with new productname, where as RDP_PRODUCT_HISTORY has a record which was changed in the original table.


Delete Request:
Deletes the data from DB but the history table will get updated with the data present in the original table.
https://www.example.com/v4/TemporalCapService/Product('test1')


This is all from my side. I hope this article is useful. Thank you.
- SAP Managed Tags:
- SAP Cloud Application Programming Model
Labels:
6 Comments
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
Labels in this area
-
ABAP CDS Views - CDC (Change Data Capture)
2 -
AI
1 -
Analyze Workload Data
1 -
BTP
1 -
Business and IT Integration
2 -
Business application stu
1 -
Business Technology Platform
1 -
Business Trends
1,658 -
Business Trends
91 -
CAP
1 -
cf
1 -
Cloud Foundry
1 -
Confluent
1 -
Customer COE Basics and Fundamentals
1 -
Customer COE Latest and Greatest
3 -
Customer Data Browser app
1 -
Data Analysis Tool
1 -
data migration
1 -
data transfer
1 -
Datasphere
2 -
Event Information
1,400 -
Event Information
66 -
Expert
1 -
Expert Insights
177 -
Expert Insights
294 -
General
1 -
Google cloud
1 -
Google Next'24
1 -
Kafka
1 -
Life at SAP
780 -
Life at SAP
13 -
Migrate your Data App
1 -
MTA
1 -
Network Performance Analysis
1 -
NodeJS
1 -
PDF
1 -
POC
1 -
Product Updates
4,577 -
Product Updates
340 -
Replication Flow
1 -
RisewithSAP
1 -
SAP BTP
1 -
SAP BTP Cloud Foundry
1 -
SAP Cloud ALM
1 -
SAP Cloud Application Programming Model
1 -
SAP Datasphere
2 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud
1 -
SAP S4HANA Migration Cockpit
1 -
Technology Updates
6,873 -
Technology Updates
419 -
Workload Fluctuations
1
Related Content
- Improvising Time Management in SAP S/4HANA Cloud: A Co-Innovation Solution in Technology Blogs by SAP
- Embracing TypeScript in SAPUI5 Development in Technology Blogs by Members
- ABAP Cloud Developer Trial 2022 Available Now in Technology Blogs by SAP
- New Machine Learning features in SAP HANA Cloud in Technology Blogs by SAP
- SAP HANA Cloud Vector Engine: Quick FAQ Reference in Technology Blogs by SAP
Top kudoed authors
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 35 | |
| 25 | |
| 14 | |
| 7 | |
| 7 | |
| 6 | |
| 6 | |
| 5 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 |