
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Technology
- Technology Blogs by Members
- Hana scale out to scale up migration
Technology Blogs by Members
Explore a vibrant mix of technical expertise, industry insights, and tech buzz in member blogs covering SAP products, technology, and events. Get in the mix!
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
anikesh_jyotish
Participant
Options
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
03-20-2021
11:40 PM
Introduction:
SAP HANA Migration from scale-out to Scale-up architecture, Supported from SAP HANA Database Revision 80 (Support Package Stack SPS08).
Based on customer requirements opt for SAP HANA hardware architecture.
This provides fantastic flexibility – as a customer you can choose the vendor, storage, networking of your choice, and for non-production scenarios, it is possible to build systems that are much more cost-effective. The most important thing though is to get your production hardware correctly provisioned: it can be expensive.
DISCLAIMER
The content of this blog post is provided “AS IS”. This information could contain technical inaccuracies, typographical errors, and out-of-date information. This document may be updated or changed without notice at any time. Use of the information is therefore at your own risk. In no event shall SAP be liable for special, indirect, incidental, or consequential damages resulting from or related to the use of this document.
Overview
The first thing to remember is that HANA systems require a CPU to RAM ratio, which is fixed for production systems, at 256GB/socket for analytic use cases, and 768GB/socket for SAP Business Suite.

Infrastructure preparation: -
| HP Hardware details: - (From HP hardware site) | |
HPE Superdome X with BL920s Gen9 for SAP HANA TDI compute block using Intel E7-88X0v3 architecture for Scale-Up or Scale-Out Configurations | |
| Server | HPE Superdome X for SAP HANA TDI compute block 18U enclosure / 42U HPE 1075 mm shock intelligent rack 4-8 Two socket server blades, each with 2x FlexLOMs slots, 3x mezzanine slots, and up to 48 DIMM slots. Choice to flex the number of DIMMs per blade (16/32/48) to right-size the SAP HANA workload. For scale up, four to eight BL920s Gen9 8 blades that can be configured in 2/4/8/16- socket partitions, in a number of socket permutations that accommodate mixed workloads and multiple IT tiers. For scale out, up to 48 four blade 8 socket partitions are supported for large in memory analytic workloads. HPE nPartitions (nPars) technology offers electrically isolated hard partitions with 1, 2, 3, 4 or 8 nPars possible that can have mixed workloads, chipsets, and sizes. |
| Processors | A choice of processors are available in 2/4/8/16-socket configurations: Intel Xeon E7-8880 v3 processor (2.3 GHz/18-core/45MB/150 W) Intel Xeon E7-8890 v3 processor (2.5 GHz/18-core/45MB/165 W) |
| Memory | Up to 16 processors/288 cores possible Multiple flexible memory sizing Scale up RAM sizes: 8socket- 6/4/3/2TB and 16 socket- 12/8/4 offerings Scale out RAM sizes: 8 socket- 3/2TB offerings Maximum memory: 12TB DDR4 (384 x 32GB DIMMs) |
A list of all certified and supported hardware can be found in the SAP HANA Hardware Directory at https://www.sap.com/dmc/exp/2014-09-02-hana-hardware/enEN/index.html
All HWCCT tests of appliances (compute servers) certified with scenario HANA-HWC-AP SU 1.0 or HANA-HWC-AP RH 1.0 must use HWCCT of SAP HANA SPS08 or SAP HANA SPS09 or a related SAP HANA revision
All HWCCT tests of appliances (compute servers) certified with scenario HANA-HWC-AP SU 1.1 or HANA-HWC-AP RH 1.1 must use HWCCT of SAP HANA SPS10 or higher or a related SAP HANA revision
Setup all Suse Linux parameters based on the below SAP note, make sure to setup parameters based on your hardware details.
2205917 - SAP HANA DB: Recommended OS settings for SLES 12 / SLES for SAP Applications 12
Migration strategy and planning
As we are migrating HANA on BW or Business Suite on HANA, need to plan environment support during migration.
Here we always prefer to minimum impact on the current change management strategy, that’s why using a progressive system migration strategy.
Always using alias names for system build instead of a physical name, in this way we have achieved two goals one is safeguarding systems from vulnerabilities and second repointing virtual name DNS to migrated system minimize the impact no interface system and end-users.
Planning: -
- Migration of HANA DB from scale-out to scale-up architecture using Backup & Restore method
- Create the same topology in target DB
- The system built & Migration approach as below
- Dev à QAS à PPD à PRD
- SAP application HA/cluster set up for PPD and PRD system
- SAP DR set up for HANA DB using HSR
- HANA DB HA build on SUSE Linux Enterprise Server pacemaker clusters
Implantation Steps:
Build new landscape with current systems alias name in an isolated environment, BW on HANA or NW on HANA system always migrate by restore mythology instead of SWPM because SWPM is not taking care HANA specific functionality like HANA views, SDA and external configuration.
- Install the target system, the target SAP HANA Database can be of the same or higher revision compared to the source.
- Perform a backup of source SAP HANA Database (Multi-Node)
- Make sure that the statistics server on the target is the same as that of the source either stand-alone or embedded.
- Create the same topology in target HANA DB (Single Hana Box)
Created below table to compare topology difference between source and target,
services that have persistence data only need to create in a target.
Check persistence data by SQL or HANA studio.
SQL command:- SELECT * FROM M_VOLUMES
Service | Source Active services 1 Coordinator* + 1 Worker* + 1 Stand-by | Target Single Node (No Stand-by) |
| Nameserver | 3 | 1 |
| Indexserver | 3 | 1 |
| Compileserver | 3 | 1 |
| XSengine | 2 | 1 |
| Preprocessor | 3 | 1 |
| Daemon | 3 | 1 |
After comparing with the source system, it is evident that we would need to create additional 2 indexserver, 1 xsengine on the single-node target system.
Create additional index servers by below command:
ALTER SYSTEM ALTER CONFIGURATION('daemon.ini','host',’<hostname>’) SET('indexserver.c','instanceids')='<n>[,<n>+2]' WITH RECONFIGURE
EX :- ALTER SYSTEM ALTER CONFIGURATION ('daemon.ini', 'host', '<DB hostname>') SET('indexserver.c','instanceids') = '40,42' WITH RECONFIGURE;
Create additional XS by below command: -
ALTER SYSTEM ALTER CONFIGURATION('daemon.ini','host',’<hostname>’) SET('xsengine.c','instanceids')='<n>[,<n>+2]' WITH RECONFIGURE
EX:- ALTER SYSTEM ALTER CONFIGURATION ('daemon.ini', 'host', '<DB hostname>') SET('xsengine.c','instanceids') = '44' WITH RECONFIGURE;
Once source and target system services match start retore target DB by source backup.
- Copy the backup files from source system (multi-node) to the target system (single-node)
- Perform recovery using the backup files from the source
Points to Note before starting the recovery:
- Move or delete available data backups and log backups from the target system.
- Select Initialize log area.
Once DB recovery completed on target take a full backup and verify the backup catalog.
Post-migration steps
Need to delete all additional services from the target and before deletion performs reorg and data move.
- Mark the indexserver to be removed:
- call SYS.UPDATE_LANDSCAPE_CONFIGURATION('SET REMOVE','<hostname:port>');
In this example, call SYS.UPDATE_LANDSCAPE_CONFIGURATION('SET REMOVE','<DB hostname>:30040')
- Generate the plan for removing the indexserver:
- call REORG_GENERATE(2,'')
- Execute the generated plan:
- call REORG_EXECUTE(?)
Validate data consistency and repoint application to new migrated HANA DB.
backup:-
- Once the backup team confirms the installation of backing agent, we need to create one soft link as shown below
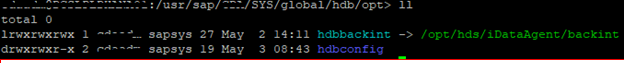
2.A user needs to be created which needs to have below mentioned roles
- Command:
CREATE USER COMMVAULT_USER PASSWORD <SET_YOUR_PASSWORD> NO FORCE_FIRST_PASSWORD_CHANGE;
GRANT BACKUP ADMIN, CATALOG READ, INIFILE ADMIN TO COMMVAULT_USER;
3. In HANA Studio backup catalog setting to be maintained as shown below:

4. Parameter to be configured as below

DR :-
Use below SAP NOTES for HANA DR setup.

Reference Documents: -
1943937 - Hardware Configuration Check Tool - Central Note
1944799 - SAP HANA Guidelines for SLES Operating System Installation
2093572 - SAP HANA Migration from Multi-Node to Single-Node
https://www.sap.com/dmc/exp/2014-09-02-hana-hardware/enEN/index.html
2205917 - SAP HANA DB: Recommended OS settings for SLES 12 / SLES for SAP Applications 12
Cheers!
Anikesh Jyotishi
- SAP Managed Tags:
- SAP HANA
6 Comments
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
Labels in this area
-
"automatische backups"
1 -
"regelmäßige sicherung"
1 -
505 Technology Updates 53
1 -
ABAP
14 -
ABAP API
1 -
ABAP CDS Views
2 -
ABAP CDS Views - BW Extraction
1 -
ABAP CDS Views - CDC (Change Data Capture)
1 -
ABAP class
2 -
ABAP Cloud
2 -
ABAP Development
5 -
ABAP in Eclipse
1 -
ABAP Platform Trial
1 -
ABAP Programming
2 -
abap technical
1 -
absl
1 -
access data from SAP Datasphere directly from Snowflake
1 -
Access data from SAP datasphere to Qliksense
1 -
Accrual
1 -
action
1 -
adapter modules
1 -
Addon
1 -
Adobe Document Services
1 -
ADS
1 -
ADS Config
1 -
ADS with ABAP
1 -
ADS with Java
1 -
ADT
2 -
Advance Shipping and Receiving
1 -
Advanced Event Mesh
3 -
AEM
1 -
AI
7 -
AI Launchpad
1 -
AI Projects
1 -
AIML
9 -
Alert in Sap analytical cloud
1 -
Amazon S3
1 -
Analytical Dataset
1 -
Analytical Model
1 -
Analytics
1 -
Analyze Workload Data
1 -
annotations
1 -
API
1 -
API and Integration
3 -
API Call
2 -
Application Architecture
1 -
Application Development
5 -
Application Development for SAP HANA Cloud
3 -
Applications and Business Processes (AP)
1 -
Artificial Intelligence
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
4 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) 1 Business Trends 363 Business Trends 8 Digital Transformation with Cloud ERP (DT) 1 Event Information 462 Event Information 15 Expert Insights 114 Expert Insights 76 Life at SAP 418 Life at SAP 1 Product Updates 4
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise Oil Gas IoT Exploration Production
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise sustainability responsibility esg social compliance cybersecurity risk
1 -
ASE
1 -
ASR
2 -
ASUG
1 -
Attachments
1 -
Authorisations
1 -
Automating Processes
1 -
Automation
1 -
aws
2 -
Azure
1 -
Azure AI Studio
1 -
B2B Integration
1 -
Backorder Processing
1 -
Backup
1 -
Backup and Recovery
1 -
Backup schedule
1 -
BADI_MATERIAL_CHECK error message
1 -
Bank
1 -
BAS
1 -
basis
2 -
Basis Monitoring & Tcodes with Key notes
2 -
Batch Management
1 -
BDC
1 -
Best Practice
1 -
bitcoin
1 -
Blockchain
3 -
BOP in aATP
1 -
BOP Segments
1 -
BOP Strategies
1 -
BOP Variant
1 -
BPC
1 -
BPC LIVE
1 -
BTP
11 -
BTP Destination
2 -
Business AI
1 -
Business and IT Integration
1 -
Business application stu
1 -
Business Architecture
1 -
Business Communication Services
1 -
Business Continuity
1 -
Business Data Fabric
3 -
Business Partner
12 -
Business Partner Master Data
10 -
Business Technology Platform
2 -
Business Trends
1 -
CA
1 -
calculation view
1 -
CAP
3 -
Capgemini
1 -
CAPM
1 -
Catalyst for Efficiency: Revolutionizing SAP Integration Suite with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and
1 -
CCMS
2 -
CDQ
12 -
CDS
2 -
Cental Finance
1 -
Certificates
1 -
CFL
1 -
Change Management
1 -
chatbot
1 -
chatgpt
3 -
CL_SALV_TABLE
2 -
Class Runner
1 -
Classrunner
1 -
Cloud ALM Monitoring
1 -
Cloud ALM Operations
1 -
cloud connector
1 -
Cloud Extensibility
1 -
Cloud Foundry
3 -
Cloud Integration
6 -
Cloud Platform Integration
2 -
cloudalm
1 -
communication
1 -
Compensation Information Management
1 -
Compensation Management
1 -
Compliance
1 -
Compound Employee API
1 -
Configuration
1 -
Connectors
1 -
Consolidation Extension for SAP Analytics Cloud
1 -
Controller-Service-Repository pattern
1 -
Conversion
1 -
Cosine similarity
1 -
cryptocurrency
1 -
CSI
1 -
ctms
1 -
Custom chatbot
3 -
Custom Destination Service
1 -
custom fields
1 -
Customer Experience
1 -
Customer Journey
1 -
Customizing
1 -
Cyber Security
2 -
Data
1 -
Data & Analytics
1 -
Data Aging
1 -
Data Analytics
2 -
Data and Analytics (DA)
1 -
Data Archiving
1 -
Data Back-up
1 -
Data Governance
5 -
Data Integration
2 -
Data Quality
12 -
Data Quality Management
12 -
Data Synchronization
1 -
data transfer
1 -
Data Unleashed
1 -
Data Value
8 -
database tables
1 -
Datasphere
2 -
datenbanksicherung
1 -
dba cockpit
1 -
dbacockpit
1 -
Debugging
2 -
Delimiting Pay Components
1 -
Delta Integrations
1 -
Destination
3 -
Destination Service
1 -
Developer extensibility
1 -
Developing with SAP Integration Suite
1 -
Devops
1 -
digital transformation
1 -
Documentation
1 -
Dot Product
1 -
DQM
1 -
dump database
1 -
dump transaction
1 -
e-Invoice
1 -
E4H Conversion
1 -
Eclipse ADT ABAP Development Tools
2 -
edoc
1 -
edocument
1 -
ELA
1 -
Embedded Consolidation
1 -
Embedding
1 -
Embeddings
1 -
Employee Central
1 -
Employee Central Payroll
1 -
Employee Central Time Off
1 -
Employee Information
1 -
Employee Rehires
1 -
Enable Now
1 -
Enable now manager
1 -
endpoint
1 -
Enhancement Request
1 -
Enterprise Architecture
1 -
ETL Business Analytics with SAP Signavio
1 -
Euclidean distance
1 -
Event Dates
1 -
Event Driven Architecture
1 -
Event Mesh
2 -
Event Reason
1 -
EventBasedIntegration
1 -
EWM
1 -
EWM Outbound configuration
1 -
EWM-TM-Integration
1 -
Existing Event Changes
1 -
Expand
1 -
Expert
2 -
Expert Insights
1 -
Fiori
14 -
Fiori Elements
2 -
Fiori SAPUI5
12 -
Flask
1 -
Full Stack
8 -
Funds Management
1 -
General
1 -
Generative AI
1 -
Getting Started
1 -
GitHub
8 -
Grants Management
1 -
groovy
1 -
GTP
1 -
HANA
5 -
HANA Cloud
2 -
Hana Cloud Database Integration
2 -
HANA DB
1 -
HANA XS Advanced
1 -
Historical Events
1 -
home labs
1 -
HowTo
1 -
HR Data Management
1 -
html5
8 -
Identity cards validation
1 -
idm
1 -
Implementation
1 -
input parameter
1 -
instant payments
1 -
Integration
3 -
Integration Advisor
1 -
Integration Architecture
1 -
Integration Center
1 -
Integration Suite
1 -
intelligent enterprise
1 -
Java
1 -
job
1 -
Job Information Changes
1 -
Job-Related Events
1 -
Job_Event_Information
1 -
joule
4 -
Journal Entries
1 -
Just Ask
1 -
Kerberos for ABAP
8 -
Kerberos for JAVA
8 -
Launch Wizard
1 -
Learning Content
2 -
Life at SAP
1 -
lightning
1 -
Linear Regression SAP HANA Cloud
1 -
local tax regulations
1 -
LP
1 -
Machine Learning
2 -
Marketing
1 -
Master Data
3 -
Master Data Management
14 -
Maxdb
2 -
MDG
1 -
MDGM
1 -
MDM
1 -
Message box.
1 -
Messages on RF Device
1 -
Microservices Architecture
1 -
Microsoft Universal Print
1 -
Middleware Solutions
1 -
Migration
5 -
ML Model Development
1 -
Modeling in SAP HANA Cloud
8 -
Monitoring
3 -
MTA
1 -
Multi-Record Scenarios
1 -
Multiple Event Triggers
1 -
Neo
1 -
New Event Creation
1 -
New Feature
1 -
Newcomer
1 -
NodeJS
2 -
ODATA
2 -
OData APIs
1 -
odatav2
1 -
ODATAV4
1 -
ODBC
1 -
ODBC Connection
1 -
Onpremise
1 -
open source
2 -
OpenAI API
1 -
Oracle
1 -
PaPM
1 -
PaPM Dynamic Data Copy through Writer function
1 -
PaPM Remote Call
1 -
PAS-C01
1 -
Pay Component Management
1 -
PGP
1 -
Pickle
1 -
PLANNING ARCHITECTURE
1 -
Popup in Sap analytical cloud
1 -
PostgrSQL
1 -
POSTMAN
1 -
Process Automation
2 -
Product Updates
4 -
PSM
1 -
Public Cloud
1 -
Python
4 -
Qlik
1 -
Qualtrics
1 -
RAP
3 -
RAP BO
2 -
Record Deletion
1 -
Recovery
1 -
recurring payments
1 -
redeply
1 -
Release
1 -
Remote Consumption Model
1 -
Replication Flows
1 -
Research
1 -
Resilience
1 -
REST
1 -
REST API
1 -
Retagging Required
1 -
Risk
1 -
Rolling Kernel Switch
1 -
route
1 -
rules
1 -
S4 HANA
1 -
S4 HANA Cloud
1 -
S4 HANA On-Premise
1 -
S4HANA
3 -
S4HANA_OP_2023
2 -
SAC
10 -
SAC PLANNING
9 -
SAP
4 -
SAP ABAP
1 -
SAP Advanced Event Mesh
1 -
SAP AI Core
8 -
SAP AI Launchpad
8 -
SAP Analytic Cloud Compass
1 -
Sap Analytical Cloud
1 -
SAP Analytics Cloud
4 -
SAP Analytics Cloud for Consolidation
2 -
SAP Analytics Cloud Story
1 -
SAP analytics clouds
1 -
SAP BAS
1 -
SAP Basis
6 -
SAP BODS
1 -
SAP BODS certification.
1 -
SAP BTP
20 -
SAP BTP Build Work Zone
2 -
SAP BTP Cloud Foundry
5 -
SAP BTP Costing
1 -
SAP BTP CTMS
1 -
SAP BTP Innovation
1 -
SAP BTP Migration Tool
1 -
SAP BTP SDK IOS
1 -
SAP Build
11 -
SAP Build App
1 -
SAP Build apps
1 -
SAP Build CodeJam
1 -
SAP Build Process Automation
3 -
SAP Build work zone
10 -
SAP Business Objects Platform
1 -
SAP Business Technology
2 -
SAP Business Technology Platform (XP)
1 -
sap bw
1 -
SAP CAP
2 -
SAP CDC
1 -
SAP CDP
1 -
SAP Certification
1 -
SAP Cloud ALM
4 -
SAP Cloud Application Programming Model
1 -
SAP Cloud Integration for Data Services
1 -
SAP cloud platform
8 -
SAP Companion
1 -
SAP CPI
3 -
SAP CPI (Cloud Platform Integration)
2 -
SAP CPI Discover tab
1 -
sap credential store
1 -
SAP Customer Data Cloud
1 -
SAP Customer Data Platform
1 -
SAP Data Intelligence
1 -
SAP Data Migration in Retail Industry
1 -
SAP Data Services
1 -
SAP DATABASE
1 -
SAP Dataspher to Non SAP BI tools
1 -
SAP Datasphere
9 -
SAP DRC
1 -
SAP EWM
1 -
SAP Fiori
2 -
SAP Fiori App Embedding
1 -
Sap Fiori Extension Project Using BAS
1 -
SAP GRC
1 -
SAP HANA
1 -
SAP HCM (Human Capital Management)
1 -
SAP HR Solutions
1 -
SAP IDM
1 -
SAP Integration Suite
9 -
SAP Integrations
4 -
SAP iRPA
2 -
SAP Learning Class
1 -
SAP Learning Hub
1 -
SAP Odata
2 -
SAP on Azure
1 -
SAP PartnerEdge
1 -
sap partners
1 -
SAP Password Reset
1 -
SAP PO Migration
1 -
SAP Prepackaged Content
1 -
SAP Process Automation
2 -
SAP Process Integration
2 -
SAP Process Orchestration
1 -
SAP S4HANA
2 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud
1 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud for Finance
1 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud private edition
1 -
SAP Sandbox
1 -
SAP STMS
1 -
SAP SuccessFactors
2 -
SAP SuccessFactors HXM Core
1 -
SAP Time
1 -
SAP TM
2 -
SAP Trading Partner Management
1 -
SAP UI5
1 -
SAP Upgrade
1 -
SAP-GUI
8 -
SAP_COM_0276
1 -
SAPBTP
1 -
SAPCPI
1 -
SAPEWM
1 -
sapmentors
1 -
saponaws
2 -
SAPUI5
4 -
schedule
1 -
Secure Login Client Setup
8 -
security
9 -
Selenium Testing
1 -
SEN
1 -
SEN Manager
1 -
service
1 -
SET_CELL_TYPE
1 -
SET_CELL_TYPE_COLUMN
1 -
SFTP scenario
2 -
Simplex
1 -
Single Sign On
8 -
Singlesource
1 -
SKLearn
1 -
soap
1 -
Software Development
1 -
SOLMAN
1 -
solman 7.2
2 -
Solution Manager
3 -
sp_dumpdb
1 -
sp_dumptrans
1 -
SQL
1 -
sql script
1 -
SSL
8 -
SSO
8 -
Substring function
1 -
SuccessFactors
1 -
SuccessFactors Time Tracking
1 -
Sybase
1 -
system copy method
1 -
System owner
1 -
Table splitting
1 -
Tax Integration
1 -
Technical article
1 -
Technical articles
1 -
Technology Updates
1 -
Technology Updates
1 -
Technology_Updates
1 -
Threats
1 -
Time Collectors
1 -
Time Off
2 -
Tips and tricks
2 -
Tools
1 -
Trainings & Certifications
1 -
Transport in SAP BODS
1 -
Transport Management
1 -
TypeScript
2 -
unbind
1 -
Unified Customer Profile
1 -
UPB
1 -
Use of Parameters for Data Copy in PaPM
1 -
User Unlock
1 -
VA02
1 -
Validations
1 -
Vector Database
1 -
Vector Engine
1 -
Visual Studio Code
1 -
VSCode
1 -
Web SDK
1 -
work zone
1 -
workload
1 -
xsa
1 -
XSA Refresh
1
- « Previous
- Next »
Related Content
- Empowering Retail Business with a Seamless Data Migration to SAP S/4HANA in Technology Blogs by Members
- 10+ ways to reshape your SAP landscape with SAP Business Technology Platform – Blog 4 in Technology Blogs by SAP
- Data Flows - The Python Script Operator and why you should avoid it in Technology Blogs by Members
- Recap - SAP ALM at SAP Insider Las Vegas 2024 in Technology Blogs by SAP
- See you at Google Cloud Next '24 in Technology Blogs by SAP
Top kudoed authors
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 9 | |
| 9 | |
| 7 | |
| 6 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 |