
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Enterprise Resource Planning
- ERP Blogs by SAP
- Integration of SAP Agricultural Contract Managemen...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Introduction
SAP Agricultural Contract Management provides enhanced contract capture screens that enable you to capture and maintain all the complex terms and conditions required to manage agricultural commodity contracts.
Pricing (Specifying price for a Contract Line item) is one of the key concepts while creating an SAP Agricultural Contract Management Trading Contract.
Pricing is established for a contract at the time of contract creation. The system retrieves this pricing to make the final settlement between the counter parties. If there is no pricing defined for a quantity on the lot, the system determines a provisional price for that portion of the quantity to settle a contract provisionally. You cannot make the final settlement unless all the pricing components are defined.
SAP Agricultural Contract Management uses Commodity Pricing Engine (CPE) to establish prices in a Trading Contract. CPE is a tool for calculating the prices of commodities. It retrieves pricing formulas in business documents and evaluates them to calculate final prices of commodities. The resulting price is then transferred to the condition types that are used in commodity pricing.
CPE enhances pricing by using complex rules to calculate a condition rate and a condition value. These rules define how market data from exchanges or other providers are considered.
More details on CPE can be found in the following blogs:
https://blogs.sap.com/2018/06/15/commodity-pricing-engine-cpe-introduction/
https://blogs.sap.com/2019/11/05/commodity-pricing-engine-cpe-formula/
https://blogs.sap.com/2019/11/06/commodity-pricing-engine-cpe-term/
Integration between SAP Agricultural Contract Management and CPE
Integration between SAP Agricultural Contract Management and CPE is achieved using Valuation Point provided in the Line item of SAP Agricultural Contract Management Trading Contract and BRF+ rules set up to determine following based on Valuation Point and other factors from Trading contract like Organization details, Material, Plant and Incoterms:
- Formula - It leads to determination of Condition Type and their Respective Formula Keys
- Basis ID - It leads to determination of Basis ID for Basis contract and Market condition types.
Please see more details below on how this is achieved.
Determination of Formula Key for SAP Agricultural Contract Management Trading Contracts
Determination of Formula Key for Condition Types is done using Valuation Point provided in the Agricultural Contract Management Trading Contract Line Item and BRF+ rules configured.
‘/ACCGO/FORMULA_ASSEMBLE’ is the name of the BRF+ application delivered by SAP Agricultural Contract Management for Formula Assembly determination.
As you can see from the screenshot below, following Functions are available in the Application.

Formula Assembly BRF+ Application
Let us take an Example for Purchasing Formula Function.

Purchasing Formula BRF+ Function
A ruleset has been assigned to the Function to determine Formula Key based on Purchasing Organization, Supplier, Plant, Material and Valuation Point.
Note: Data is maintained is similarly for Sales side as well.

Purchasing Formula BRF+ Ruleset
If we go inside the decision table, we can see how data is maintained to determine the Formula Key.
Note: Future price is the price for commodity at a future date against an exchange which includes Derivative Contract Specification, Market Identifier Code and Contract Maturity Code or Keydate.
Please refer blog below for more details.
https://blogs.sap.com/2018/06/20/commodity-pricing-engine-cpe-dcs-and-mic/
The basis is the price difference between the local cash price and the commodity futures price, and is commonly used in the agricultural, oil and gas, and energy sectors. The local cash price for a commodity is the futures price adjusted for characteristics such as freight, storage costs, quality factors, targeted margin, and the local supply and demand situation.
Contract conditions are entered manually by user in a Trading Contract. Market conditions are used for reporting purposes and their prices are determined from quotations. Difference between contract and market conditions drive the Mark-to-Market and Trader’s Profit and Loss Reports.
Sample Data in Decision Table
For this blog, let us take example of material ‘CO_SOYBEANS_01’.

Decision Table to Determine Formula Key - 1

Decision Table to Determine Formula Key - 2
As we can see from the screenshots above, based on Valuation Point, Material, Purchase Org, and Plant we can define which condition types have to be determined and what will be the Formula Key for those condition type.
Example in System of how Formula Key is determined:
Note: I have used ‘QOI’ as the reference system – it is the Test system for S4 Infinity landscape and can be accessed easily by requesting user from DLM. Agricultural Contract Management is available on client 310.
I have created a Trading Contract in the system with Valuation Point ‘D_0001_SB’ and material ‘CO_SOYBEANS_01’ so that it satisfies the condition as above.

Valuation Point in SAP Agricultural Contract Management Trading Contract
The Condition Types and Formula Key is determined as maintained in the BRF+ Rules.
- ACFT - Contract Future Condition (Condition name is configurable by customer. This is just for example purpose)

Formula Key for Contract Future Condition Type
Formula Key, P_SB_F is determined as maintained for Condition type ACFT in the BRF+ rules.
- ACBS - Contract Basis Condition

Formula Key for Contract Basis Condition Type
Formula Key, P_SB_BC is determined as maintained for Condition type ACBS in the BRF+ rules.
- AMFT - Market Future Condition
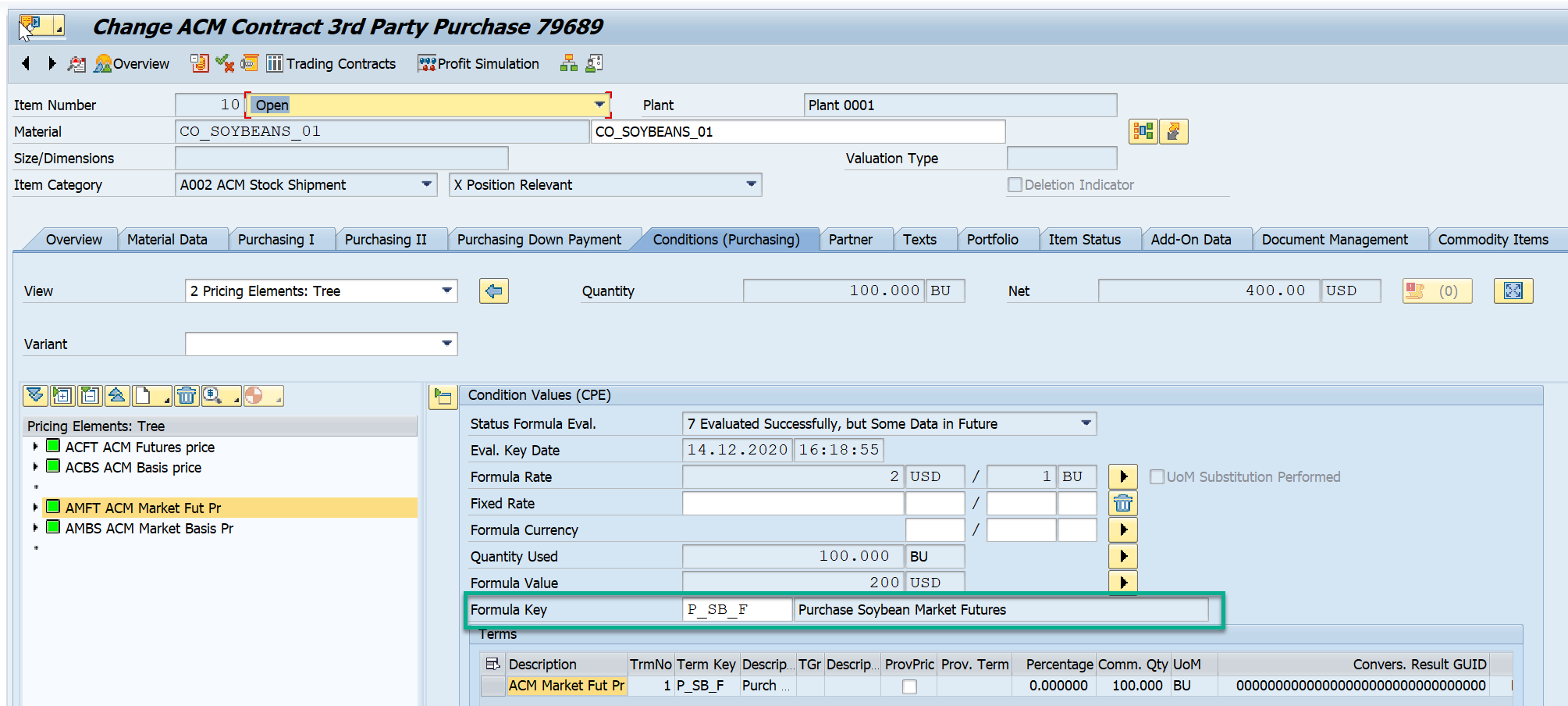
Formula Key for Market Future Condition Type
Formula Key, P_SB_F is determined as maintained for Condition type AMFT in the BRF+ rules.
- AMBS- Market Basis Condition

Formula Key for Market Basis Condition Type
Formula Key, P_SB_BM is determined as maintained for Condition type AMBS in the BRF+ rules.
Note: Based on the Formula Key determined, Formula Evaluation takes place in CPE framework and further details of Terms and Quotation are determined as configured in transaction MCPE_WB or VCPE_WB. (In Agricultural Contract Management, we usually don’t maintain Term details in BRF+ rules. Term details are fetched from Formula only using formula evaluation of CPE.)
Formula Assembly Log
Formula Key determined can be viewed using following option as well.
- Select the condition type and click on Analysis button. Select ‘CPE Formula Assembly Log’ option from the dropdown.

CPE Formula Assembly Log - 1
The formula key determined is displayed in the logs.

CPE Formula Assembly Log - 2
Importance of Valuation Point and BRF+ for Formula Key determination
If we delete entry for ACFT from the BRF+ Ruleset, then it is not determined in the Contract at all.
User will not be able to price Future condition in that case.

Entry not maintained for ACFT in BRF+

ACFT is not determined in Trading Contract
Note: It might be possible that if ACFT Condition Type is maintained in Condition Types Access Sequence for a particular material then this condition type will be determined but Formula Key will not be determined as it is not maintained in BRF+.
It can be accessed using transaction – MEK3. (For sales side, transaction is VK13)
For example, entry is maintained for ACFT and material CO_SOYBEANS_01.

Condition Record Maintenance
As a result in the contract, Condition type is determined but is in error as Formula Key is not determined from the BRF+.

Future Condition In Error

Formula Assembly Log
Determination of Basis ID for Basis Condition Types
In the setup for CPE that we have in S4 systems, Basis ID (Basis ID is an important parameter for Basis condition types as it is used to identify and maintain quotation prices for basis conditions) is also determined via BRF+ rules based on Valuation Point and Incoterms.
We have Function available for both Purchase and Sales side in the BRF+ application.

Basis ID BRF+ Function
Ruleset is assigned to the function, which has a rule to determine Basis ID based on Condition Type, Incoterms and Valuation Point.
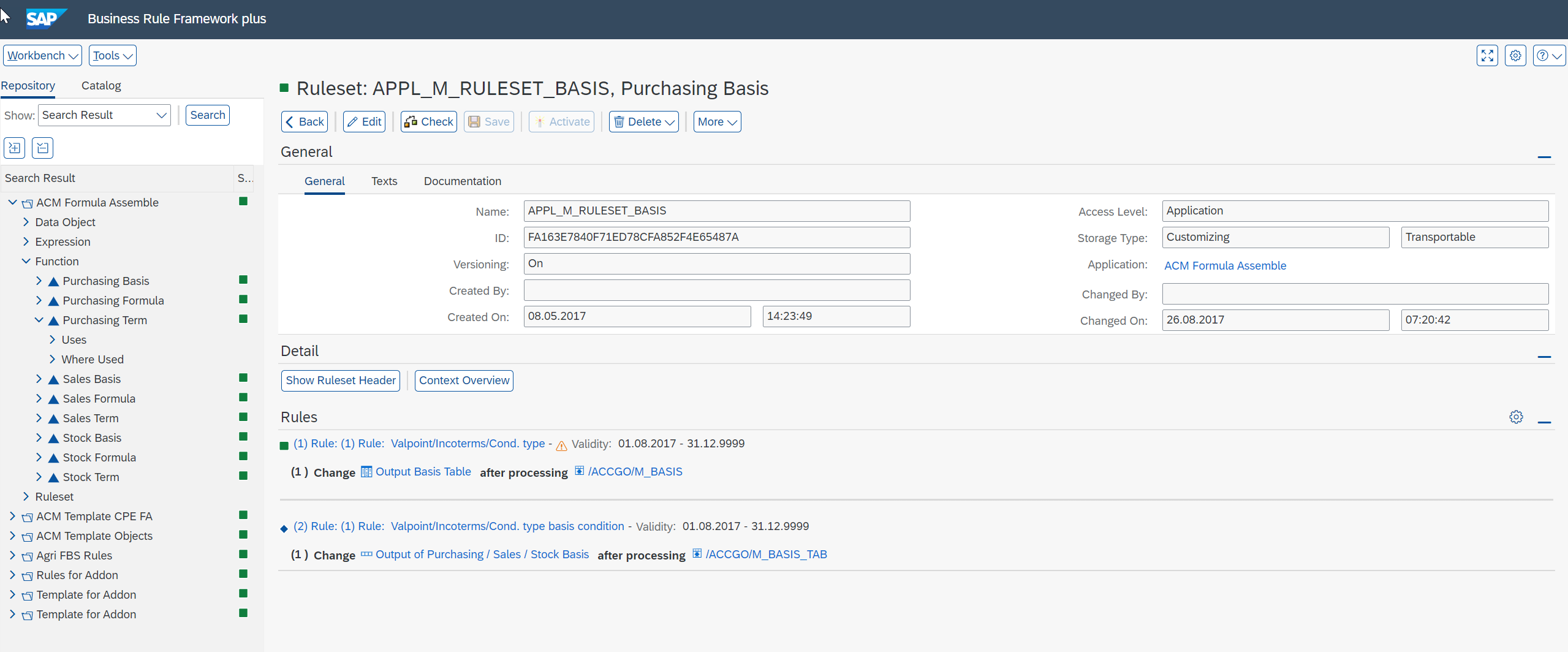
BRF+ Ruleset for Basis ID Determination
Taking example, for Valuation point ‘D_0001_SB’:

Sample Decision Table for Basis ID Determination
Basis ID can be viewed under Quotation details for basis condition types (more details of how and why Basis ID is used will be provided in subsequent blogs):

Basis ID in Quotation Details
Basis ID determined can be viewed using following option as well.
- Select the condition type and click on Analysis button. Select ‘CPE Formula Assembly Log’ option from the dropdown.
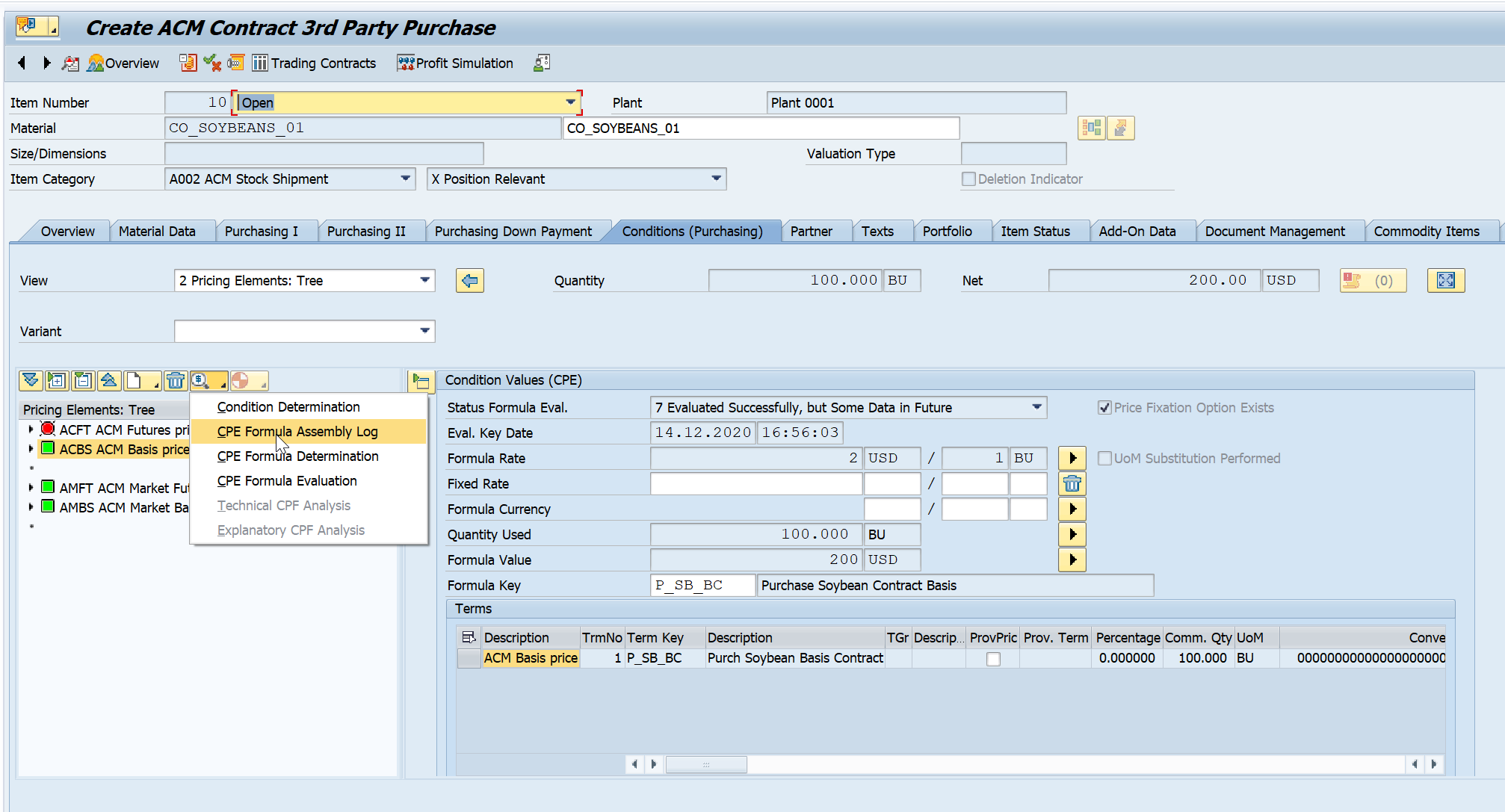
Formula Assembly Log for Basis ID Determination - 1
The Basis ID determined is displayed in the logs.

Formula Assembly Log for Basis ID Determination - 2
Conclusion
So, in this blog post I have explained how integration between SAP Agricultural Contract Management and Commodity Pricing Engine to maintain Prices for commodity in the Trading Contracts.
In my subsequent blog posts, I will explain more details regarding Various Pricing Approaches and most common errors from Commodity Pricing Engine while pricing a contract and how to resolve them.
- SAP Managed Tags:
- SAP S/4HANA,
- Global Trade Management
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
1 -
Business Trends
363 -
Business Trends
22 -
Customer COE Basics and Fundamentals
1 -
Digital Transformation with Cloud ERP (DT)
1 -
Event Information
461 -
Event Information
24 -
Expert Insights
114 -
Expert Insights
157 -
General
1 -
Governance and Organization
1 -
Introduction
1 -
Life at SAP
415 -
Life at SAP
2 -
Product Updates
4,685 -
Product Updates
217 -
Roadmap and Strategy
1 -
Technology Updates
1,502 -
Technology Updates
89
- Integration of SAP Service and Asset Manager(SSAM) with SAP FSM to support S/4HANA Service Processes in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
- Portfolio Management – Enhanced Financial Planning integration in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
- Enterprise Portfolio and Project Management in SAP S/4HANA Cloud, Private Edition 2023 FPS1 in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
- Quick Start guide for PLM system integration 3.0 Implementation/Installation in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
- Business Rule Framework Plus(BRF+) in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by Members
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 13 | |
| 11 | |
| 10 | |
| 8 | |
| 7 | |
| 6 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 3 |