
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Enterprise Resource Planning
- ERP Blogs by Members
- Bank Reconciliation Accounts in S/4HANA 2020
Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by Members
Gain new perspectives and knowledge about enterprise resource planning in blog posts from community members. Share your own comments and ERP insights today!
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
former_member19
Contributor
Options
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-16-2020
2:33 PM
Introduction
With an intention of reducing the number of GL accounts and for simplifying the payment process and cash reporting, SAP has introduced a new way of mapping house banks with GL accounts. With this new method, it is possible to assign multiple house bank accounts to the same GL account.
To facilitate this, a new GL account type called ‘Cash Account’ is provided. When user creates a GL account with account type ‘Cash Account’ another field appears called ‘GL Account subtype’. The following values are possible in this field:
- B – Bank Reconciliation Account
Reconciliation account for house banks. You assign the required clearing accounts to this reconciliation account.
- S – Bank Subaccount
Clearing account of a bank reconciliation account for payments in transfer. When you create this subaccount, you need to enter the bank reconciliation account it is connected with.
- P – Petty Cash
Used for petty cash (accounts assigned in cash journal) accounts
A G/L account created with account type ‘Cash Account’ and subtype ‘B’ is called a bank reconciliation account and is the main account for carrying confirmed balances. A bank reconciliation account can be assigned to multiple house bank accounts. You can therefore, for example, decide to set one GL account each for domestic banks and foreign banks. In effect, therefore, bank account has become a sub-ledger of the main general ledger (similar to customer, vendor or asset sub-ledger).
A G/L account created with account type ‘Cash Account’ and subtype ‘S’ is called a bank clearing account. For each main bank reconciliation account created, it is possible to create one clearing bank account for each payment method. When account subtype ‘S’ is selected, you need to assign the clearing account to a main bank reconciliation account.
The new mapping is represented as shown below:

Note: It is still possible to use the previous method of managing banks and their GL accounts. In such cases the GL account type would continue to be created as ‘balance sheet account’ and not as ‘Cash Account’.
User Guidance
In the following section I will show a step-by-step user guidance to demonstrate how the system can be set up and the output expected at each step.
Step 1: Create G/L Account as bank reconciliation account
Note that new G/L Account type ‘Cash Account’ is now available. ‘Cash Account’ is specifically used for bank reconciliation account.
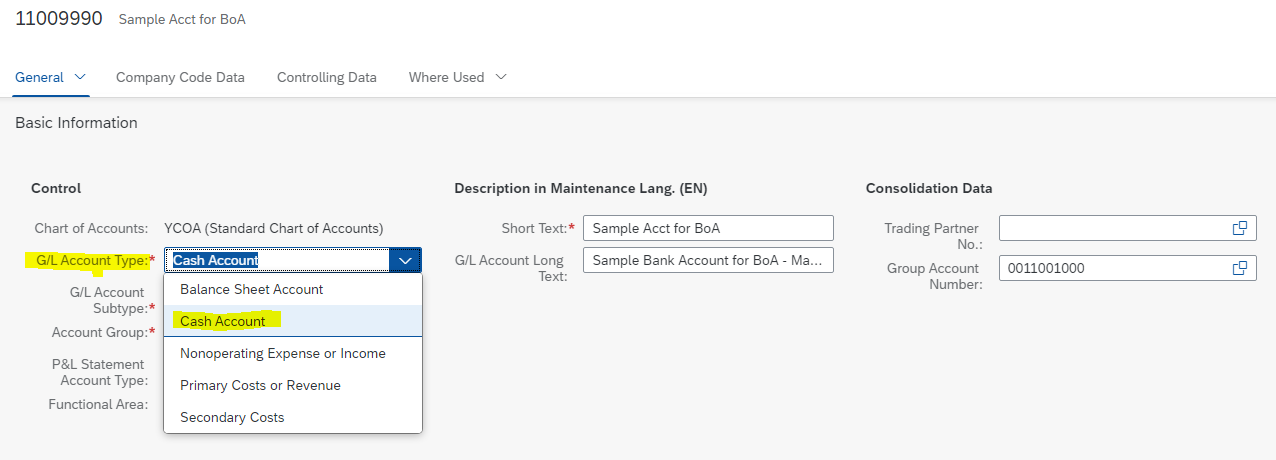
Also, a new field – GL Account Subtype appears when you select GL account type as ‘Cash Account’.
We select ‘B’ indicating that we are creating a main bank reconciliation account.

Output: The G/L account ‘11009990 – Sample Acct for BoA’ is created as bank reconciliation account and it is extended to company code 1710
Step 2: Create a bank clearing account
For bank clearing account also, you enter the account type as 'Cash Account'.
Note that when you create a GL account with type as ‘Cash Account’ and subtype as ‘S – Bank Subaccount’, another field appears where we need to assign the main bank reconciliation account with the bank clearing account.
We then assign 11009990 as the main bank reconciliation account.
Also note that for each main bank reconciliation account, you need to create one bank subaccount for each payment method.
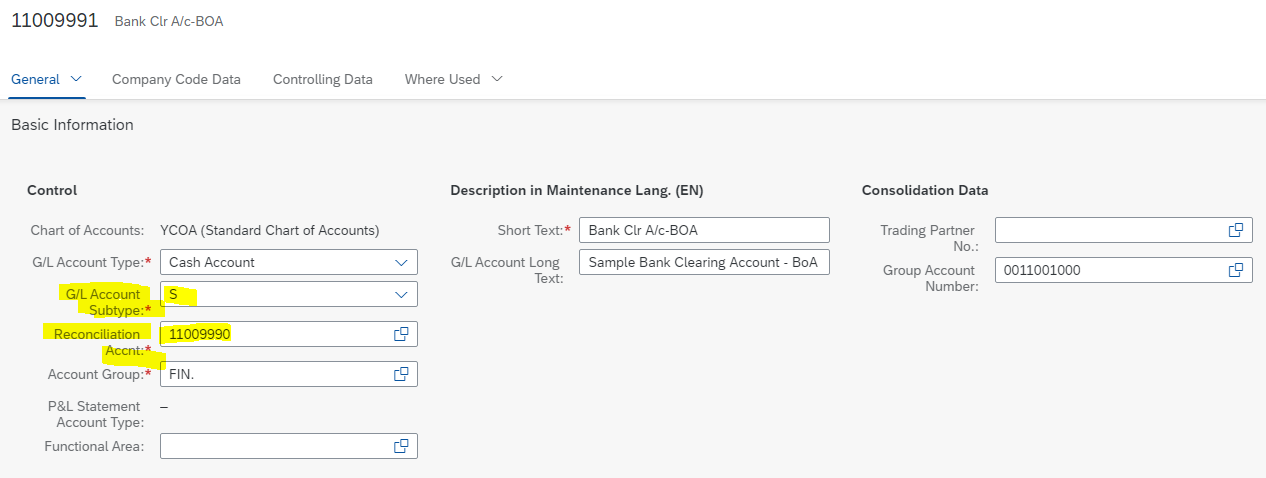
Output: Bank subaccount ‘11009991 – Bank Clr A/c-BOA’ is created which is assigned to bank reconciliation account 11009990. This account is extended to company code 1710.
Step 3: Create a bank
Create a bank using app ‘Manage Banks’
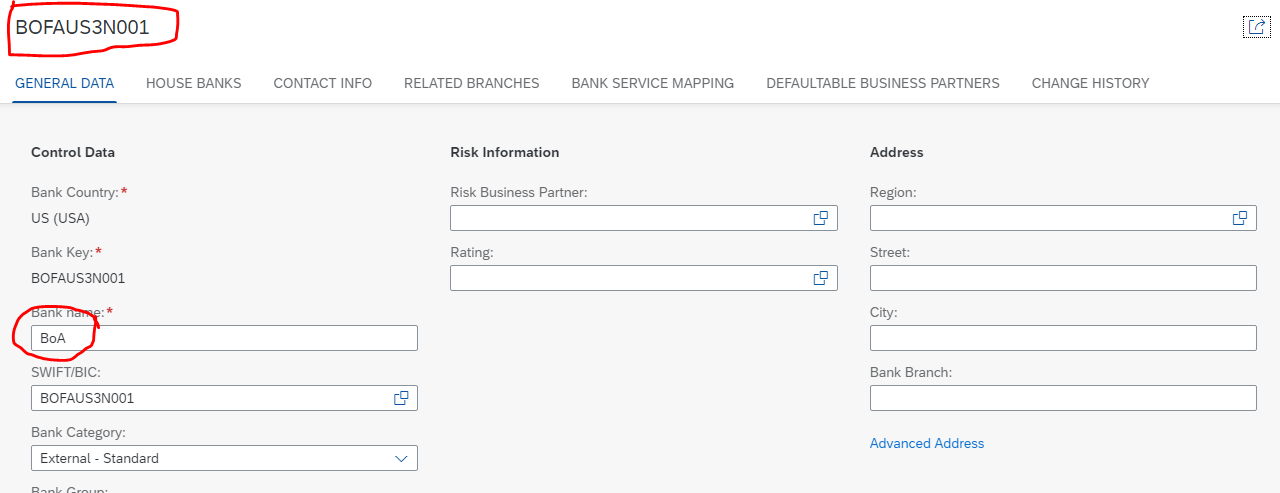
Output: Bank BoA is created with bank key BOFAUS3N001.
Step 4: Create a house bank
From the ‘House Banks’ section of the ‘Manage Bank’ app, click on ‘Create’ to create new house bank.

Enter the house bank details and assign the bank key just created

Output: House Bank BOA01 is created in company code 1710
Step 5: Create a house bank account
Create a new bank account using app ‘Manage Bank Accounts’

Output: House Bank Account BOA01 is created with account number 100001
Step 6: Assign the bank reconciliation account to house bank account.
In the ‘House Bank Account Connectivity’ tab, create a bank account connectivity by clicking on ‘Create’

Enter the bank reconciliation account created in step 1 in the field ‘G/L account’.
The indicator for ‘Bank Reconciliation Account’ turns to ‘Yes’

Output: House Bank Account BOA01 is assigned to GL account ‘11009990’ for house bank BOA01
Step 7: Assign the bank subaccount in ‘Bank Selection’ for bank customizing
When trying to assign bank subaccount in the customizing for ‘Bank Determination’, the field for Bank Subaccount is greyed out even after selection.

Note that this can be maintained in 'Bank Accounts (Enhanced)' tab

Output: Bank subaccount cannot be manually entered in classic ‘Bank Determination’ customizing anymore.
Step 8: Post a supplier invoice
Post a manual FI supplier invoice.

Output: Supplier invoice with document number 1900000001 is posted creating a liability line item.
Step 9: Post outgoing payment.
Use app ‘Post Outgoing Payment’ for posting invoice payment.
Enter house bank and bank account ID.
Enter the GL account. If a GL account other than 11009990 or 11009991 is entered here, the following error is shown.


Correct the GL account to 11009991

Simulate and post.

Output: Journal entry 1500000001 (2020, 1710) was saved successfully
Step 10: Assign the same bank reconciliation account to a different house bank
Create Bank Key
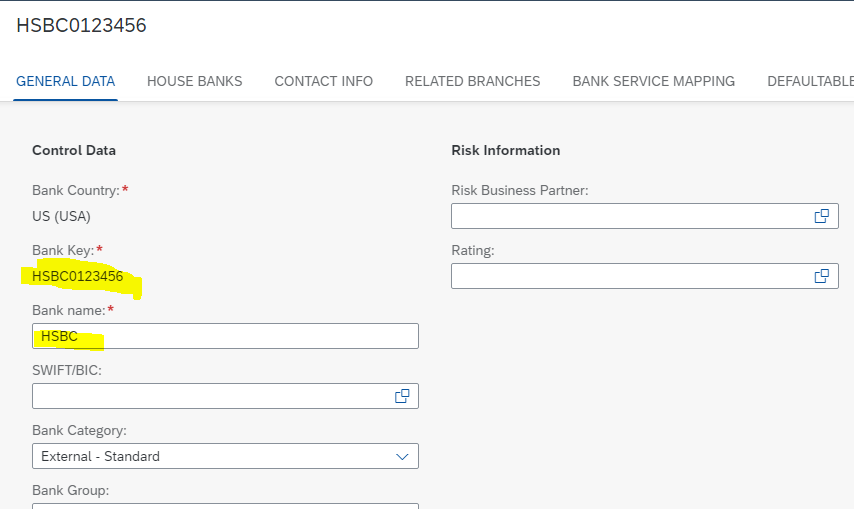
Create House Bank in company code 1710

Create a bank account for house bank HSB01 and assign the GL account 11009990 to it.

Inference: We can assign the same GL account 11009990 to two house bank accounts of different house banks.
Benefits (Point of View):
The new mapping architecture of bank and GL accounts is step forward in rationalizing the chart of account and simplifying the bank process as well. We can foresee several benefits of this new method:
- Number of GL accounts is greatly reduced without reducing the granularity of reports since individual bank reports can still be generated.
- Easier visibility of the cash balance at GL level without combining several accounts.
- Flexibility in displaying bank balance based on desired parameter set – example total balance in domestic banks, total balance in foreign banks.
- Since creation of house bank does not entail creation of GL account anymore, the process of creation and use of house bank can be faster especially where they are managed by different teams within an organization.
- Bank and payment configuration is simplified with the new setup.
We did not find any specific advantage of using the new account subtype ‘P’ in cash journal except that it is easier to identify in the classification of GL master data as ‘Cash Account’.
I hope this is useful in your conversations with clients on the latest S/4HANA features. Please share your opinion and feedback on this.
- SAP Managed Tags:
- SAP S/4HANA Finance
39 Comments
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
Labels in this area
-
"mm02"
1 -
A_PurchaseOrderItem additional fields
1 -
ABAP
1 -
ABAP Extensibility
1 -
ACCOSTRATE
1 -
ACDOCP
1 -
Adding your country in SPRO - Project Administration
1 -
Advance Return Management
1 -
AI and RPA in SAP Upgrades
1 -
Approval Workflows
1 -
ARM
1 -
ASN
1 -
Asset Management
1 -
Associations in CDS Views
1 -
auditlog
1 -
Authorization
1 -
Availability date
1 -
Azure Center for SAP Solutions
1 -
AzureSentinel
2 -
Bank
1 -
BAPI_SALESORDER_CREATEFROMDAT2
1 -
BRF+
1 -
BRFPLUS
1 -
Bundled Cloud Services
1 -
business participation
1 -
Business Processes
1 -
CAPM
1 -
Carbon
1 -
Cental Finance
1 -
CFIN
1 -
CFIN Document Splitting
1 -
Cloud ALM
1 -
Cloud Integration
1 -
condition contract management
1 -
Connection - The default connection string cannot be used.
1 -
Custom Table Creation
1 -
Customer Screen in Production Order
1 -
Data Quality Management
1 -
Date required
1 -
Decisions
1 -
desafios4hana
1 -
Developing with SAP Integration Suite
1 -
Direct Outbound Delivery
1 -
DMOVE2S4
1 -
EAM
1 -
EDI
2 -
EDI 850
1 -
EDI 856
1 -
EHS Product Structure
1 -
Emergency Access Management
1 -
Energy
1 -
EPC
1 -
Find
1 -
FINSSKF
1 -
Fiori
1 -
Flexible Workflow
1 -
Gas
1 -
Gen AI enabled SAP Upgrades
1 -
General
1 -
generate_xlsx_file
1 -
Getting Started
1 -
HomogeneousDMO
1 -
IDOC
2 -
integration
1 -
Learning Content
2 -
LogicApps
2 -
low touchproject
1 -
Maintenance
1 -
management
1 -
Material creation
1 -
Material Management
1 -
MD04
1 -
MD61
1 -
methodology
1 -
Microsoft
2 -
MicrosoftSentinel
2 -
Migration
1 -
MRP
1 -
MS Teams
2 -
MT940
1 -
Newcomer
1 -
Notifications
1 -
Oil
1 -
open connectors
1 -
Order Change Log
1 -
ORDERS
2 -
OSS Note 390635
1 -
outbound delivery
1 -
outsourcing
1 -
PCE
1 -
Permit to Work
1 -
PIR Consumption Mode
1 -
PIR's
1 -
PIRs
1 -
PIRs Consumption
1 -
PIRs Reduction
1 -
Plan Independent Requirement
1 -
Premium Plus
1 -
pricing
1 -
Primavera P6
1 -
Process Excellence
1 -
Process Management
1 -
Process Order Change Log
1 -
Process purchase requisitions
1 -
Product Information
1 -
Production Order Change Log
1 -
Purchase requisition
1 -
Purchasing Lead Time
1 -
Redwood for SAP Job execution Setup
1 -
RISE with SAP
1 -
RisewithSAP
1 -
Rizing
1 -
S4 Cost Center Planning
1 -
S4 HANA
1 -
S4HANA
3 -
Sales and Distribution
1 -
Sales Commission
1 -
sales order
1 -
SAP
2 -
SAP Best Practices
1 -
SAP Build
1 -
SAP Build apps
1 -
SAP Cloud ALM
1 -
SAP Data Quality Management
1 -
SAP Maintenance resource scheduling
2 -
SAP Note 390635
1 -
SAP S4HANA
2 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud private edition
1 -
SAP Upgrade Automation
1 -
SAP WCM
1 -
SAP Work Clearance Management
1 -
Schedule Agreement
1 -
SDM
1 -
security
2 -
Settlement Management
1 -
soar
2 -
SSIS
1 -
SU01
1 -
SUM2.0SP17
1 -
SUMDMO
1 -
Teams
2 -
User Administration
1 -
User Participation
1 -
Utilities
1 -
va01
1 -
vendor
1 -
vl01n
1 -
vl02n
1 -
WCM
1 -
X12 850
1 -
xlsx_file_abap
1 -
YTD|MTD|QTD in CDs views using Date Function
1
- « Previous
- Next »
Related Content
- Advanced WIP reporting in S/4HANA Cloud Public Edition in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
- S4 HANA Cost Center Activity Rate Calculation Hybrid Approach in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by Members
- Continuous Influence Session SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition: Results Review Cycle for Q4 2023 in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
- F0711-0712 Review of combined debtor/supplier invoices in Enterprise Resource Planning Q&A
- Alternative reconciliation account field for Supplier Invoice API in SAP Public Cloud in Enterprise Resource Planning Q&A
Top kudoed authors
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 1 | |
| 1 | |
| 1 | |
| 1 | |
| 1 |