
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Enterprise Resource Planning
- ERP Blogs by Members
- Auxiliary Cost Component Structure with Primary Co...
Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by Members
Gain new perspectives and knowledge about enterprise resource planning in blog posts from community members. Share your own comments and ERP insights today!
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
mansoor_khan4
Active Participant
Options
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
06-22-2020
6:21 AM
Auxiliary Cost Component Structure with Primary Cost Component Split (Material Cost+ Processing Cost) in Product Cost Estimate- Part 1
The blog written titled “https://blogs.sap.com/2015/09/11/primary-cost-component-split-for-cost-estimation/” details some of the features of primary cost split and also espouses his views on the usability of the functionality.
And explained the “Understanding of Cost Component Structure” by Mr Hrusikesh Dalai “https://blogs.sap.com/2013/11/25/basics-of-standard-costing-understanding-the-cost-component-structu...
I would like to supplement his thoughts with certain other insights as well. But before that, a few generic impressions…
Introduction
Primary Cost component split for (Material + Activity (processing) Cost)
First I would like to add the feature of Material cost component split as “Raw Material Costing” for no BOMs or routings for raw materials in the system. You can, however,
The primary cost component split is an alternative way of showing the cost of goods manufactured of a product. This cost component split assigns the primary cost elements for the cost center or process to the cost components, which enables you to see the composition of the price for the activity type or the costs for the process.
The primary costs from Overhead Cost Controlling can either be transferred directly into the primary cost component split of the product or assigned to other cost components. In this way, you can explode the costs for specific internal activities partly by their primary costs, and combine them partly as secondary costs.
Benefits/Features of Cost Component Split – Auxiliary CCS
Controlling-> Product Cost Controlling-> Product Cost Planning-> Basic Settings for Material Costing-> Define Origin Group

``
Controlling-> Product Cost Controlling-> Product Cost Planning-> Basic Settings for Material Costing-> Define Cost Component Structure
Main Cost Component Structure
In Auxiliary cost component structure you can differentiate the “Cost component in detail w.r.f to Main CCS” whereas I took the example of Freight Cost component as created in first slight “Origin Groups”
Note: Ensure that do not assign any 43 category cost elements in the above step. Assign only all primary cost elements.
Assign the Material Consumption GL Accounts to cost components additionally with “Origin Groups” this enables to display the Raw Material Cost + Delivery (Freight) component in Auxiliary CCS.
The below detail explained the Main and Auxiliary CCS- Assignment of Primary Cost Elements with Origin Group
Transfer Structure
Controls the transfer of costs from the cost components of one cost component structure into the cost components of another cost component structure.
The transfer structure determines how the costs of the sending cost component split (such as the primary cost component split of an internal activity) are transferred to the receiving cost component split.
Through the transfer structure, a single cost component of the receiving cost component split can be assigned to every cost component of the sending cost component split.
If the cost component structure of the primary cost component split for the cost center activity prices is not the same as the cost component structure of the primary cost component split for the products, you can use the transfer structure to specify how the cost component split of an internal activity or process for a material cost estimate is transferred into the cost component splits of the material costed.
In contrast to the switching structure in Cost Center Accounting, which reassigns cost components within a single cost component structure, the transfer structure assigns cost components between two different cost component structures.

The above settings in Valuation variants for accessing the Material Valuation for Raw Materials ->
L- Price from info records & Sub strategy sequence A- Quotation price via condition table, you can
explore more as SAP provided possibilities as per business requirement.
Delivery Costs
Assign Condition Types to Origin Groups

Materials Management-> Purchasing-> Conditions-> Define Price Determination Process-> Define Condition Types
Materials Management-> Purchasing-> Conditions-> Define Price Determination Process-> Set Calculation Schema – Purchasing
I summarized the splitting structure process steps in this explanation because one of our SAP former member/supporter explained in very excellent way on this context, please refer the below link
https://blogs.sap.com/2013/09/04/expense-analysis-and-splitting-in-manufacturing-cost-centers/
Activity Cost Analysis Summary for Fixed/Variable against production Cost Center
The below table content the plan activity calculation for all activities (Fixed/Variable) derived the same result as above in KSBT
Click on Price Details
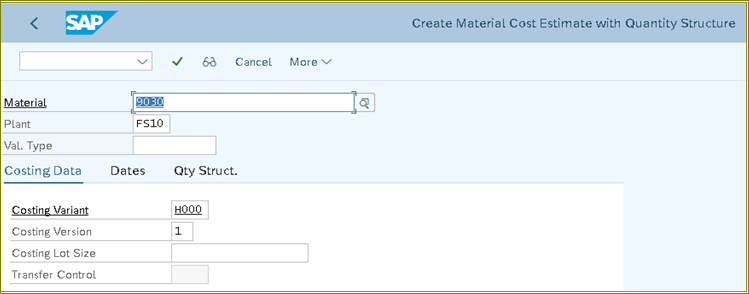
The below is Activity cost calculation explanation for (Power/Energy) as per cost planned and rate calculated above to Main & Auxiliary Cos Component Structure.
Conclusion
In this document in tried to explain the utilization of Auxiliary Cost Component structure with “Primary Cost Component Split” for Material Cost and Activities. In my next series of document I will explore for this scenario to Actual posting considering the S/4 HANA COML Actual Costing + COPA (Account based + Costing based) reporting.
Best Regards
Mansoor Khan
The blog written titled “https://blogs.sap.com/2015/09/11/primary-cost-component-split-for-cost-estimation/” details some of the features of primary cost split and also espouses his views on the usability of the functionality.
And explained the “Understanding of Cost Component Structure” by Mr Hrusikesh Dalai “https://blogs.sap.com/2013/11/25/basics-of-standard-costing-understanding-the-cost-component-structu...
I would like to supplement his thoughts with certain other insights as well. But before that, a few generic impressions…
Introduction
Primary Cost component split for (Material + Activity (processing) Cost)
First I would like to add the feature of Material cost component split as “Raw Material Costing” for no BOMs or routings for raw materials in the system. You can, however,
- Use these functions to create a cost estimate for raw materials enables you to include delivery costs.
- Access the purchasing data (MM_PUR), in order to include delivery costs such as freight charges and insurance costs
- Transfer structure for the “Primary cost component split” to Main Cost component
- Splitting the Main CCS to Aux CCS (Material Cost = Material Cost + Delivery Cost), Main activities cost in to various components with Primary Cost component split.
The primary cost component split is an alternative way of showing the cost of goods manufactured of a product. This cost component split assigns the primary cost elements for the cost center or process to the cost components, which enables you to see the composition of the price for the activity type or the costs for the process.
The primary costs from Overhead Cost Controlling can either be transferred directly into the primary cost component split of the product or assigned to other cost components. In this way, you can explode the costs for specific internal activities partly by their primary costs, and combine them partly as secondary costs.
Benefits/Features of Cost Component Split – Auxiliary CCS
- This can exist in addition to the main cost component split, and is not used in the standard cost estimate. It can be used for analysis purposes, in that it can be displayed with the cost estimate and passed on to Profitability Analysis.
- Synchronizing the Main Cost Component structure components like, Material Cost + Activities in various levels for better analysis and reporting purpose.
- This CCS analysis can explore in Material Ledger price analysis with different Cost Component structures
- Actual values will flow to COPA to the respective values fields’ mapped w.r.f to Auxiliary CCS.
- Define Origin Groups
Controlling-> Product Cost Controlling-> Product Cost Planning-> Basic Settings for Material Costing-> Define Origin Group

``

- Define Cost Component Structure
Controlling-> Product Cost Controlling-> Product Cost Planning-> Basic Settings for Material Costing-> Define Cost Component Structure
Main Cost Component Structure




- Auxiliary Cost Component Structure


In Auxiliary cost component structure you can differentiate the “Cost component in detail w.r.f to Main CCS” whereas I took the example of Freight Cost component as created in first slight “Origin Groups”
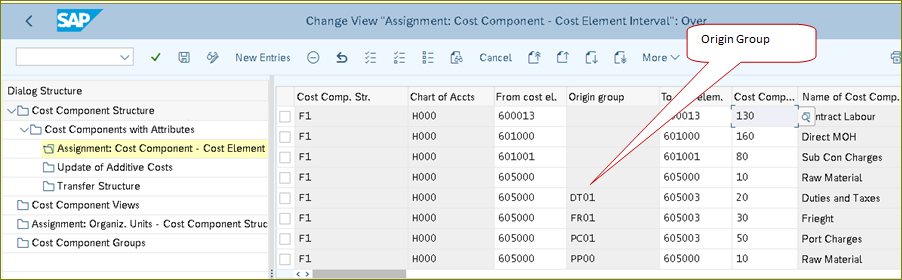
Note: Ensure that do not assign any 43 category cost elements in the above step. Assign only all primary cost elements.
Assign the Material Consumption GL Accounts to cost components additionally with “Origin Groups” this enables to display the Raw Material Cost + Delivery (Freight) component in Auxiliary CCS.
The below detail explained the Main and Auxiliary CCS- Assignment of Primary Cost Elements with Origin Group


Transfer Structure
Controls the transfer of costs from the cost components of one cost component structure into the cost components of another cost component structure.
The transfer structure determines how the costs of the sending cost component split (such as the primary cost component split of an internal activity) are transferred to the receiving cost component split.
Through the transfer structure, a single cost component of the receiving cost component split can be assigned to every cost component of the sending cost component split.
If the cost component structure of the primary cost component split for the cost center activity prices is not the same as the cost component structure of the primary cost component split for the products, you can use the transfer structure to specify how the cost component split of an internal activity or process for a material cost estimate is transferred into the cost component splits of the material costed.
In contrast to the switching structure in Cost Center Accounting, which reassigns cost components within a single cost component structure, the transfer structure assigns cost components between two different cost component structures.
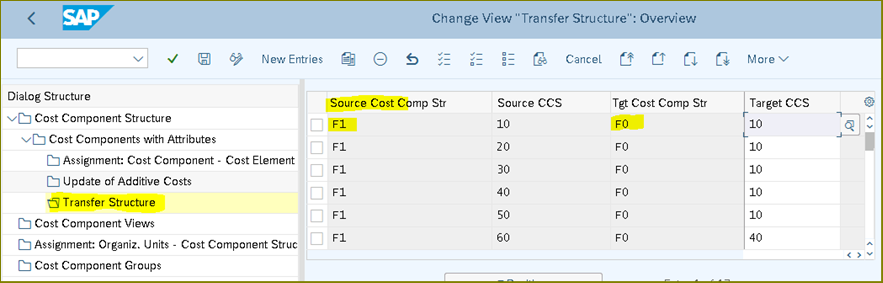

- Assignment: Organize. Units - Cost Component Structure

- Assignment of Auxiliary CCS to Controlling Area- OKEQ

- Costing Variant – OKKN


The above settings in Valuation variants for accessing the Material Valuation for Raw Materials ->
L- Price from info records & Sub strategy sequence A- Quotation price via condition table, you can
explore more as SAP provided possibilities as per business requirement.
- Purchasing : Assignment of Condition to Cost Components -> Raw Material Cost Estimate
Delivery Costs
Assign Condition Types to Origin Groups

- Define Condition Types in Material Management
Materials Management-> Purchasing-> Conditions-> Define Price Determination Process-> Define Condition Types

- Set Calculation Schema - Purchasing
Materials Management-> Purchasing-> Conditions-> Define Price Determination Process-> Set Calculation Schema – Purchasing

- Define Plan Activity – KP26

- Define Activity input Planning Cost Element – KP06



- Define Splitting Structure
- Assign Splitting Structure to Production Cost Center
- Plan Cost Splitting
I summarized the splitting structure process steps in this explanation because one of our SAP former member/supporter explained in very excellent way on this context, please refer the below link
https://blogs.sap.com/2013/09/04/expense-analysis-and-splitting-in-manufacturing-cost-centers/
- Plan Activity Calculation- KSPI


- Plan Activity Rate Report - KSBT


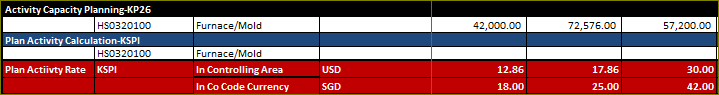
Activity Cost Analysis Summary for Fixed/Variable against production Cost Center
The below table content the plan activity calculation for all activities (Fixed/Variable) derived the same result as above in KSBT

- Purchase Info Record for RM – ME11/ME12


- Info Record History – ME1E


Click on Price Details

- Creation of Standard Cost Estimate – CK11N






The below is Activity cost calculation explanation for (Power/Energy) as per cost planned and rate calculated above to Main & Auxiliary Cos Component Structure.

- Release Standard Cost Estimate- CK24/CK40N




Conclusion
In this document in tried to explain the utilization of Auxiliary Cost Component structure with “Primary Cost Component Split” for Material Cost and Activities. In my next series of document I will explore for this scenario to Actual posting considering the S/4 HANA COML Actual Costing + COPA (Account based + Costing based) reporting.
Best Regards
Mansoor Khan
- SAP Managed Tags:
- FIN Cost Object Controlling,
- FIN Product Cost Planning
19 Comments
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
Labels in this area
-
"mm02"
1 -
A_PurchaseOrderItem additional fields
1 -
ABAP
1 -
ABAP Extensibility
1 -
ACCOSTRATE
1 -
ACDOCP
1 -
Adding your country in SPRO - Project Administration
1 -
Advance Return Management
1 -
AI and RPA in SAP Upgrades
1 -
Approval Workflows
1 -
ARM
1 -
ASN
1 -
Asset Management
1 -
Associations in CDS Views
1 -
auditlog
1 -
Authorization
1 -
Availability date
1 -
Azure Center for SAP Solutions
1 -
AzureSentinel
2 -
Bank
1 -
BAPI_SALESORDER_CREATEFROMDAT2
1 -
BRF+
1 -
BRFPLUS
1 -
Bundled Cloud Services
1 -
business participation
1 -
Business Processes
1 -
CAPM
1 -
Carbon
1 -
Cental Finance
1 -
CFIN
1 -
CFIN Document Splitting
1 -
Cloud ALM
1 -
Cloud Integration
1 -
condition contract management
1 -
Connection - The default connection string cannot be used.
1 -
Custom Table Creation
1 -
Customer Screen in Production Order
1 -
Data Quality Management
1 -
Date required
1 -
Decisions
1 -
desafios4hana
1 -
Developing with SAP Integration Suite
1 -
Direct Outbound Delivery
1 -
DMOVE2S4
1 -
EAM
1 -
EDI
2 -
EDI 850
1 -
EDI 856
1 -
EHS Product Structure
1 -
Emergency Access Management
1 -
Energy
1 -
EPC
1 -
Find
1 -
FINSSKF
1 -
Fiori
1 -
Flexible Workflow
1 -
Gas
1 -
Gen AI enabled SAP Upgrades
1 -
General
1 -
generate_xlsx_file
1 -
Getting Started
1 -
HomogeneousDMO
1 -
IDOC
2 -
Integration
1 -
Learning Content
2 -
LogicApps
2 -
low touchproject
1 -
Maintenance
1 -
management
1 -
Material creation
1 -
Material Management
1 -
MD04
1 -
MD61
1 -
methodology
1 -
Microsoft
2 -
MicrosoftSentinel
2 -
Migration
1 -
MRP
1 -
MS Teams
2 -
MT940
1 -
Newcomer
1 -
Notifications
1 -
Oil
1 -
open connectors
1 -
Order Change Log
1 -
ORDERS
2 -
OSS Note 390635
1 -
outbound delivery
1 -
outsourcing
1 -
PCE
1 -
Permit to Work
1 -
PIR Consumption Mode
1 -
PIR's
1 -
PIRs
1 -
PIRs Consumption
1 -
PIRs Reduction
1 -
Plan Independent Requirement
1 -
Premium Plus
1 -
pricing
1 -
Primavera P6
1 -
Process Excellence
1 -
Process Management
1 -
Process Order Change Log
1 -
Process purchase requisitions
1 -
Product Information
1 -
Production Order Change Log
1 -
Purchase requisition
1 -
Purchasing Lead Time
1 -
Redwood for SAP Job execution Setup
1 -
RISE with SAP
1 -
RisewithSAP
1 -
Rizing
1 -
S4 Cost Center Planning
1 -
S4 HANA
1 -
S4HANA
3 -
Sales and Distribution
1 -
Sales Commission
1 -
sales order
1 -
SAP
2 -
SAP Best Practices
1 -
SAP Build
1 -
SAP Build apps
1 -
SAP Cloud ALM
1 -
SAP Data Quality Management
1 -
SAP Maintenance resource scheduling
2 -
SAP Note 390635
1 -
SAP S4HANA
2 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud private edition
1 -
SAP Upgrade Automation
1 -
SAP WCM
1 -
SAP Work Clearance Management
1 -
Schedule Agreement
1 -
SDM
1 -
security
2 -
Settlement Management
1 -
soar
2 -
SSIS
1 -
SU01
1 -
SUM2.0SP17
1 -
SUMDMO
1 -
Teams
2 -
User Administration
1 -
User Participation
1 -
Utilities
1 -
va01
1 -
vendor
1 -
vl01n
1 -
vl02n
1 -
WCM
1 -
X12 850
1 -
xlsx_file_abap
1 -
YTD|MTD|QTD in CDs views using Date Function
1
- « Previous
- Next »
Related Content
- Enterprise Portfolio and Project Management in SAP S/4HANA Cloud, Private Edition 2023 FPS1 in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
- Quick Start guide for PLM system integration 3.0 Implementation/Installation in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
- Add components to production order using FM bapi_alm_order_maintain. in Enterprise Resource Planning Q&A
- Business Rule Framework Plus(BRF+) in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by Members
- BOM component not showing in PI Sheet but shows on process order in Enterprise Resource Planning Q&A
Top kudoed authors
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 1 | |
| 1 |