
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Supply Chain Management
- SCM Blogs by SAP
- Recommendation - Blog Series Part 6
Supply Chain Management Blogs by SAP
Expand your SAP SCM knowledge and stay informed about supply chain management technology and solutions with blog posts by SAP. Follow and stay connected.
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
Employee
Options
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
06-20-2020
4:00 PM
In my previous blog I completed the FMEA and RCM assessment for the "Dewatering Pump" which is a critical equipment in my plant. The final outcome of the assessment is a list of recommendation which the reliability engineer creates and the maintenance planner will plan to execute it in the PMR application.
With this I move forward to the step 4 where the reliability engineer will create a set of recommendation during FMEA or RCM assessment.
Recommendation can be created from four different sources -
For the RCM assessment of "Dewatering pump", based on the Function, Functional Failure, Failure Modes & Effect, as a reliability engineer i want to propose three recommendation. Below are the recommendation types available in the system -
I will create the recommendation based out of placeholder instruction as a corrective-unplanned as it is breakdown scenario and as a reliability engineer i cannot predict the frequency.
Here on, the recommendation execution part is handed over to maintenance planner who will take a conscious decision on which recommendation should be implemented. Various factors are taken into consideration here like estimated cost, frequency, remaining risk etc.
In my next blog, I will give the overview of how a maintenance planner would take the recommendation forward.
Series 1: Brief Overview of ASPM and Master data setup
Series 2: Risk and Criticality (RC)
Series 3: Failure Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA)
Series 4: Checklist Assessment
Series 5: Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM)
Series 6: Recommendation
Series 7: Preventive Maintenance Review (PMR)
With this I move forward to the step 4 where the reliability engineer will create a set of recommendation during FMEA or RCM assessment.

Recommendation can be created from four different sources -
- Instruction - Manufacturer or the Operator would already have instruction with a set of steps using which reliability engineer can create a recommendation. The frequency given in the recommendation is considered in the PMR application by the maintenance planner
- Placeholder Instruction - It is possible that there is no detailed instruction available in the system and reliability engineer would create a placeholder instruction.
- Imported Task list (Maintenance Plan) - If a SAP PM system is connected with the ASPM system, then all the related task list with maintenance plan is replicated to ASPM system. The same information is also available in the context information.
- Imported Task list - If a SAP PM system is connected with the ASPM system, then all the task list which is not assigned to a maintenance plan is replicated to ASPM system. The same information is also available in the context information.
For the RCM assessment of "Dewatering pump", based on the Function, Functional Failure, Failure Modes & Effect, as a reliability engineer i want to propose three recommendation. Below are the recommendation types available in the system -
- Preventive - As the name suggests, it defines the recommendation which will help prevent a failure.
- Time Based - This recommendation has frequency based on time. Only single frequency is allowed
- Performance/Condition Based - This recommendation is based on an indicator which is available at the asset. Multiple frequency is allowed with a "AND"/"OR" operator.
- Corrective - As the name suggests, it defines the recommendation which will correct a failure which has already happened.
- Planned - Some times corrective measures are planned activities which you would do it at a frequency.
- Unplanned - This recommendation are complete breakdown scenario in which you cannot plan the frequency. If a breakdown happens, this set of recommendation needs to be preformed.
I will create the recommendation based out of placeholder instruction as a corrective-unplanned as it is breakdown scenario and as a reliability engineer i cannot predict the frequency.
- Create a placeholder instruction as I didnt find the instruction in the system. To give the recommendation I will create a placeholder instruction which the maintenance planner can convert to a instruction.

- I will proceed with recommendation creation after selecting the placeholder instruction

- Recommendation contains many vital information apart from recommendation type and sub-type.
- With applicable equipment phase, reliability engineer informs the maintenance planner when this recommendation should be executed. For example if the equipment is in partially operational, the recommendation need not be executed as it is marked for only fully operational phase.
- With priority, reliability engineer is able to give a direction on how to prioritize the recommendation in its execution mode.
- Estimated cost helps in evaluating how much cost it would take to execute the recommendation
- Risk Reduction and Risk remaining are other information which helps the maintenance planner to decide which recommendation should get executed.
- Few other details like line replacement unit (LRU)/shop replacement unit (SRU), role who will execute the recommendation are vital information which helps maintenance planner to take the next steps.
- Recommendation validity can also be mentioned, which would mean the recommendation should be executed only between those dates.
- You can also specify details on which spare parts and component the recommendation is to be executed

- For each recommendation, you get to see the hierarchy for which the recommendation is created.

- Similarly, I created two preventive recommendation from source "instruction" for the effect

- The first recommendation has estimated cost of 30 USD where as second recommendation has it as 1000 USD

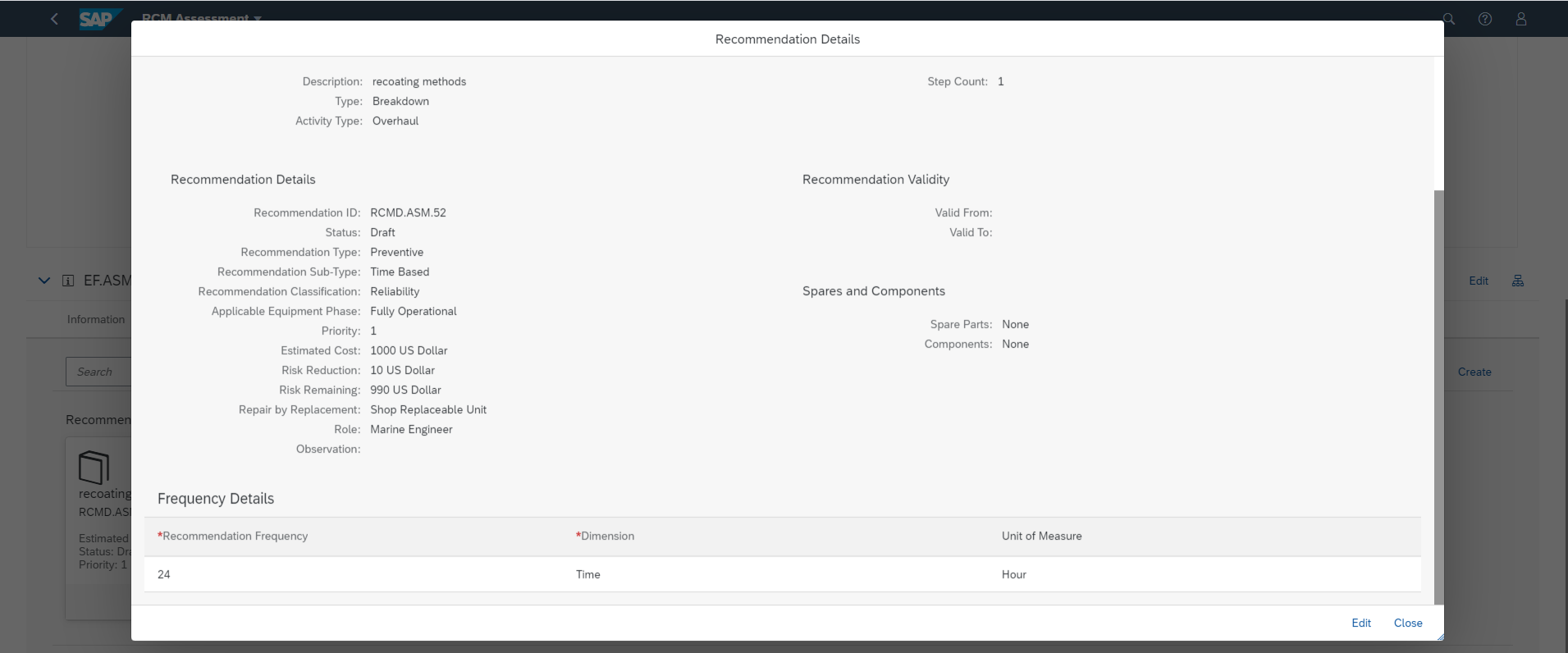
- Overall as a reliability engineer I created three recommendation for the effect.

- Recommendation created in the assessment are in status "Draft". I will publish the RCM assessment which I created earlier. Once the assessment is published, recommendation status is changed to "Open" and it is visible in the PMR tile.
Here on, the recommendation execution part is handed over to maintenance planner who will take a conscious decision on which recommendation should be implemented. Various factors are taken into consideration here like estimated cost, frequency, remaining risk etc.
In my next blog, I will give the overview of how a maintenance planner would take the recommendation forward.
Series 1: Brief Overview of ASPM and Master data setup
Series 2: Risk and Criticality (RC)
Series 3: Failure Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA)
Series 4: Checklist Assessment
Series 5: Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM)
Series 6: Recommendation
Series 7: Preventive Maintenance Review (PMR)
Note – For any abbreviations, please refer the blog series 1
- SAP Managed Tags:
- SAP Asset Strategy and Performance Management
Labels:
4 Comments
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
Labels in this area
-
Business Trends
169 -
Business Trends
24 -
Catalog Enablement
1 -
Event Information
47 -
Event Information
4 -
Expert Insights
12 -
Expert Insights
38 -
intelligent asset management
1 -
Life at SAP
63 -
Product Updates
500 -
Product Updates
66 -
Release Announcement
1 -
SAP Digital Manufacturing for execution
1 -
Super Bowl
1 -
Supply Chain
1 -
Sustainability
1 -
Swifties
1 -
Technology Updates
187 -
Technology Updates
17
Related Content
- SAP Business Network for Logistics 2404 Release – What’s New? in Supply Chain Management Blogs by SAP
- Adverse Media Monitoring: How to improve overall Supply Chain Management in Supply Chain Management Blogs by Members
- Best Practices for using current SAP APM Rules for Condition Monitoring in Supply Chain Management Blogs by SAP
- Understanding Network Partner Integration in SAP Business Network for Logistics in Supply Chain Management Blogs by SAP
- The Benefits of Applying Semantic Visions’ Screening and Monitoring Services in Supply Chain Management Blogs by Members
Top kudoed authors
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 10 | |
| 8 | |
| 5 | |
| 4 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 2 |