
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Technology
- Technology Blogs by SAP
- The key to the future, to be discovered in the pas...
Technology Blogs by SAP
Learn how to extend and personalize SAP applications. Follow the SAP technology blog for insights into SAP BTP, ABAP, SAP Analytics Cloud, SAP HANA, and more.
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
Product and Topic Expert
Options
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
02-24-2020
9:10 PM
At SAP Co-Innovation Lab, we build things that matter to our partners and our customers. In this blog co-authored with Colin Devonport, Red Hat Partner Manager, we would like to share with you how SAP, Red Hat, Lenovo, and Inspired Intellect team up at the lab to seek new innovation and new business insights with SAP Data Intelligence.
Many companies are seeking to optimize their business processes with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML). SAP, with hundreds of thousands of clients [1], and supporting business processes from front-office client relationship management to Enterprise Resource Planning to Edge Computing may have the broadest business process portfolio of any software provider. SAP has announced a strategic approach to support Machine Learning capabilities across the SAP portfolio, and as Juergen Mueller (SAP Chief Technology Officer) announced at SAP TechEd in September 2019, SAP offers more than 200 cases of machine learning embedded into SAP applications [2].
SAP is adding its Machine Learning capabilities to its Data Hub (Cloud and/or on Premise) to deliver the SAP Data Intelligence solutions [3] which provide the capabilities to analyze existing data, whatever the source, and scale AI across the enterprise. These products enable an “AI assembly line”, and enhance collaboration between those innovating using AI. SAP Data Hub is validated by SAP to operate on the Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform, and SAP, Red Hat and mutual business partners are focused on achieving key business outcomes from the use of AI, such as higher profitability, higher client engagement and experience; and supporting “client stickiness”.
SAP offers its partners facilities to support project-based co-innovation, assisting clients to innovate. Key among these facilities is a network of Co-innovation Labs (COIL) [4] in 15 locations around the world. These labs provide capable and productive spaces where clients, SAP, and SAP’s partners can work together to address business challenges. The COILs provide facilities to pilot, test and benchmark new approaches. SAP and Red Hat recognize the pace of innovation and adoption of AI and ML is incredibly rapid [7], as Gartner noting “Between 2018 and 2019, organizations that have deployed artificial intelligence (AI) grew from 4% to 14%”, [5].
A closer look at SAP Data intelligence capabilities illustrates a wide array services in data management, data orchestration, with additional ML services, for example to train new models.
[Fig 1]

While these system capabilities are comprehensive, and Red Hat also has extensive project based experience in AI [8], innovation is also about “overcoming the known failure patterns”, which may be non-technological. The team considered several such challenges indicated by Gartner in FIG 2 [6]
[Fig 2]

To assist clients with the issues as described in Fig 2 around “skills of staff” and “understanding AI benefits and “use cases”, the team brought in Inspired Intellect [9], an SAP partner with deep experience in skills transfer, including business case creation, and data extraction and transformation. Inspired Intellect also has extensive knowledge of leading use cases and how to deploy them. With the support of Jerry Platz, VP of SAP solutions at Inspired Intellect, the project team helped implement example cases at the Co-Innovation Lab in California. Leveraging the COIL provided Inspired Intellect more tools to develop, train and test Machine Learning models. Platz shared, “We recognize the issues Gartner Identified in many of our client engagements, and we understand that solving them often requires innovation in both technology and organizational approach. That’s where the COIL partnership provides value. Clients can work shoulder-to-shoulder with SAP, Red Hat and ourselves on real-world problems, using the latest tools and methodologies.” Platz added, “Of course creating business outcomes is not just about accessing the latest tools, but creating a strategy that identifies the most valuable use-cases and enabling AI/ML throughout the organization. This COIL approach allows customers to reduce time-to-outcome by pre-packaging a wide variety of use-cases. Of course, each case must be tailored towards specific needs, but in our experience, the “prepackaged cases” we have developed provide a very good start”. Platz continued “I’d also like to comment further on Gartner’s “vendor strategy” / integration complexity challenge. By standardizing our approaches on the Red Hat portfolio with SAP, we can make significant strides to overcome this challenge. Our most advanced clients have previously had to deal with a piecemeal approach, often with costly self-built integrations. What they really want is a stable, modular and less complicated platform with all the functionality. That’s what we are delivering, using SAP Data Hub and the Red Hat software portfolio”.
The COIL lab has a suite of Red Hat software available to support SAP Data Hub and Data Intelligence and, among them Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform and Red Hat CEPH. The installation is built on Lenovo systems, and uses Lenovo’s reference architecture for SAP Data Hub [10]. In some circumstances, a client’s needs may extend beyond those for SAP Data Hub and SAP Data Intelligence and potentially beyond the existing Lenovo Reference Architecture. The Co-Innovation lab therefore has access to a broad suite of complementary Red Hat products. Examples are in Fig 3.
[Fig3]

Let’s now take a look at an example use case - A manufacturing company experiencing lower yield than expected, more quality holds and more returned product. They believe that this is due to the need for improved maintenance and better operational settings in key fabrication assemblies. Over the years, their standard operating procedures have used historic data to optimize settings, predict and recommend maintenance. They have copious data from process sensors, they have fault data, and also correlating quality, orders, returns data. Are the data sufficient to learn more about optimizing the process, eliminating “faults” and improving high quality yield? Will a ML approach help? In some ways “business as usual”, but in this case they want to:
To provide a glimpse into the possibilities around Manufacturing, the team is implementing a use-case around a microchip / silicon manufacturing production process. Using pre-built models from Inspired Intellect, SAP Data Hub Pipeline Modeler is used to process and normalize sample data. The combined SAP and Red Hat software can be used to extract and transform the data in a workflow, and an example is shown in Fig 4.
[Fig 4]

Of course while these extraction and transformation capabilities are key to composing the right information, and to facilitating the analyses and learning, any company’s process experts also need a simple visualization approach, so these normalized data may be viewed, manipulated, understood. In the COIL, this can be done using SAP Analytics Cloud and other advanced visualization approaches [Fig5]
[Fig5]
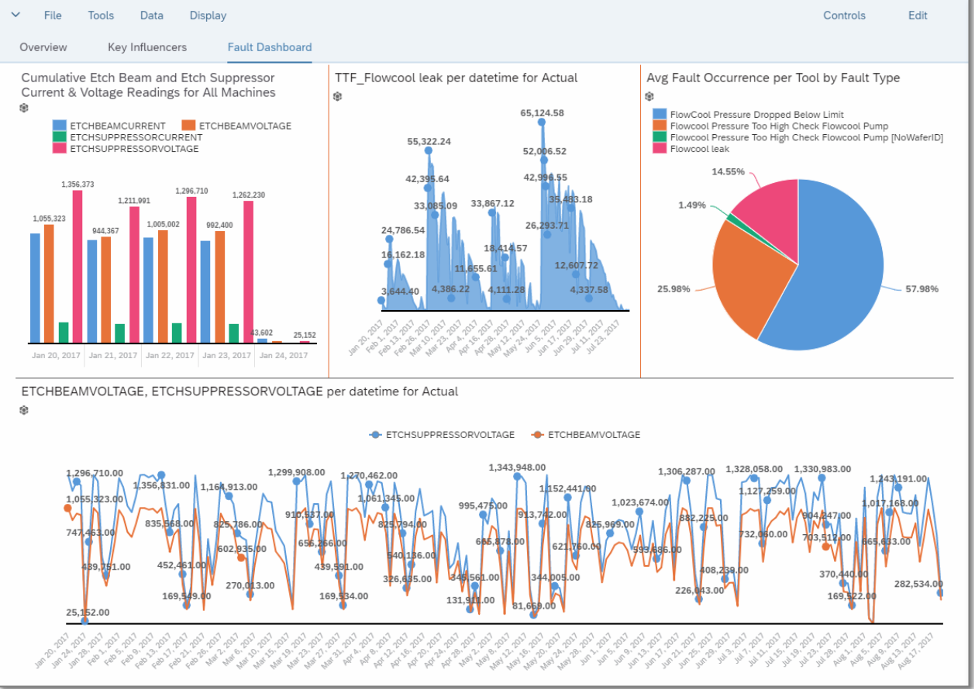
With this example scenario, the team is enabled to reason more deeply around the operational settings, recorded faults, and as above, perform “what ifs”. Of course SAP Data Hub and SAP Data Intelligence provide capabilities to use selected data sets to train ML algorithms, and with a platform approach such as this, further data, better training sets, and more business insight is facilitated.
This approach can go beyond demonstrations and discussions of this scenario. By agreement with SAP, this and other scenarios can also be used with a “Bring Your Own Data” (BYOD) pilot approach. BYOD is intended to assist companies (with suitably anonymized data) to work with the COIL team in a secure environment, to start gaining insights, to pilot use cases and gain company specific insights. To discover possible futures, hiding in the data from the past.
In the next edition of this SAP COIL blog, Kevin, Colin and Jerry will look in more detail at the further use cases by industry. Should you wish to contact the COIL team, please email coilsv@sap.com.
References
[1] https://www.sap.com/documents/2017/04/4666ecdd-b67c-0010-82c7-eda71af511fa.html
[2] https://sapinsider.wispubs.com/Assets/Blogs/2019/September/5-Important-Announcements-for-SAPinsiders...
[3] https://blogs.sap.com/2019/07/17/sap-data-hub-and-sap-data-intelligence-streamlining-data-driven-int...
[4] https://www.sap.com/corporate/en/company/innovation/sap-coil.html
[5] https://www.gartner.com/smarterwithgartner/top-trends-on-the-gartner-hype-cycle-for-artificial-intel...
[6] https://www.gartner.com/smarterwithgartner/3-barriers-to-ai-adoption/
[7] https://www.forbes.com/sites/cognitiveworld/2019/03/04/ai-economy-will-further-accelerate-the-pace-o...
[8] https://next.redhat.com/category/ai-machine-learning/
[9] https://www.linkedin.com/company/inspired-intellect/about/
Many companies are seeking to optimize their business processes with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML). SAP, with hundreds of thousands of clients [1], and supporting business processes from front-office client relationship management to Enterprise Resource Planning to Edge Computing may have the broadest business process portfolio of any software provider. SAP has announced a strategic approach to support Machine Learning capabilities across the SAP portfolio, and as Juergen Mueller (SAP Chief Technology Officer) announced at SAP TechEd in September 2019, SAP offers more than 200 cases of machine learning embedded into SAP applications [2].
SAP is adding its Machine Learning capabilities to its Data Hub (Cloud and/or on Premise) to deliver the SAP Data Intelligence solutions [3] which provide the capabilities to analyze existing data, whatever the source, and scale AI across the enterprise. These products enable an “AI assembly line”, and enhance collaboration between those innovating using AI. SAP Data Hub is validated by SAP to operate on the Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform, and SAP, Red Hat and mutual business partners are focused on achieving key business outcomes from the use of AI, such as higher profitability, higher client engagement and experience; and supporting “client stickiness”.
SAP offers its partners facilities to support project-based co-innovation, assisting clients to innovate. Key among these facilities is a network of Co-innovation Labs (COIL) [4] in 15 locations around the world. These labs provide capable and productive spaces where clients, SAP, and SAP’s partners can work together to address business challenges. The COILs provide facilities to pilot, test and benchmark new approaches. SAP and Red Hat recognize the pace of innovation and adoption of AI and ML is incredibly rapid [7], as Gartner noting “Between 2018 and 2019, organizations that have deployed artificial intelligence (AI) grew from 4% to 14%”, [5].
A closer look at SAP Data intelligence capabilities illustrates a wide array services in data management, data orchestration, with additional ML services, for example to train new models.
[Fig 1]

While these system capabilities are comprehensive, and Red Hat also has extensive project based experience in AI [8], innovation is also about “overcoming the known failure patterns”, which may be non-technological. The team considered several such challenges indicated by Gartner in FIG 2 [6]
[Fig 2]

To assist clients with the issues as described in Fig 2 around “skills of staff” and “understanding AI benefits and “use cases”, the team brought in Inspired Intellect [9], an SAP partner with deep experience in skills transfer, including business case creation, and data extraction and transformation. Inspired Intellect also has extensive knowledge of leading use cases and how to deploy them. With the support of Jerry Platz, VP of SAP solutions at Inspired Intellect, the project team helped implement example cases at the Co-Innovation Lab in California. Leveraging the COIL provided Inspired Intellect more tools to develop, train and test Machine Learning models. Platz shared, “We recognize the issues Gartner Identified in many of our client engagements, and we understand that solving them often requires innovation in both technology and organizational approach. That’s where the COIL partnership provides value. Clients can work shoulder-to-shoulder with SAP, Red Hat and ourselves on real-world problems, using the latest tools and methodologies.” Platz added, “Of course creating business outcomes is not just about accessing the latest tools, but creating a strategy that identifies the most valuable use-cases and enabling AI/ML throughout the organization. This COIL approach allows customers to reduce time-to-outcome by pre-packaging a wide variety of use-cases. Of course, each case must be tailored towards specific needs, but in our experience, the “prepackaged cases” we have developed provide a very good start”. Platz continued “I’d also like to comment further on Gartner’s “vendor strategy” / integration complexity challenge. By standardizing our approaches on the Red Hat portfolio with SAP, we can make significant strides to overcome this challenge. Our most advanced clients have previously had to deal with a piecemeal approach, often with costly self-built integrations. What they really want is a stable, modular and less complicated platform with all the functionality. That’s what we are delivering, using SAP Data Hub and the Red Hat software portfolio”.
The COIL lab has a suite of Red Hat software available to support SAP Data Hub and Data Intelligence and, among them Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform and Red Hat CEPH. The installation is built on Lenovo systems, and uses Lenovo’s reference architecture for SAP Data Hub [10]. In some circumstances, a client’s needs may extend beyond those for SAP Data Hub and SAP Data Intelligence and potentially beyond the existing Lenovo Reference Architecture. The Co-Innovation lab therefore has access to a broad suite of complementary Red Hat products. Examples are in Fig 3.
[Fig3]

Let’s now take a look at an example use case - A manufacturing company experiencing lower yield than expected, more quality holds and more returned product. They believe that this is due to the need for improved maintenance and better operational settings in key fabrication assemblies. Over the years, their standard operating procedures have used historic data to optimize settings, predict and recommend maintenance. They have copious data from process sensors, they have fault data, and also correlating quality, orders, returns data. Are the data sufficient to learn more about optimizing the process, eliminating “faults” and improving high quality yield? Will a ML approach help? In some ways “business as usual”, but in this case they want to:
- Use historic batch data, over a longer period of measurements to validate “causality” (e.g. to influence a re-design).
- Process a wider set of data. New sensors, new data with different “post processing”
- Enable the process experts with simple to use “and manipulate” views to do “what if” or make automated recommendations
- With the data as available, validate how much an ML assisted or autonomous approach might save?
- Reduce complexity; avoid or eliminate costly “self-built integrations”
To provide a glimpse into the possibilities around Manufacturing, the team is implementing a use-case around a microchip / silicon manufacturing production process. Using pre-built models from Inspired Intellect, SAP Data Hub Pipeline Modeler is used to process and normalize sample data. The combined SAP and Red Hat software can be used to extract and transform the data in a workflow, and an example is shown in Fig 4.
[Fig 4]

Of course while these extraction and transformation capabilities are key to composing the right information, and to facilitating the analyses and learning, any company’s process experts also need a simple visualization approach, so these normalized data may be viewed, manipulated, understood. In the COIL, this can be done using SAP Analytics Cloud and other advanced visualization approaches [Fig5]
[Fig5]

With this example scenario, the team is enabled to reason more deeply around the operational settings, recorded faults, and as above, perform “what ifs”. Of course SAP Data Hub and SAP Data Intelligence provide capabilities to use selected data sets to train ML algorithms, and with a platform approach such as this, further data, better training sets, and more business insight is facilitated.
This approach can go beyond demonstrations and discussions of this scenario. By agreement with SAP, this and other scenarios can also be used with a “Bring Your Own Data” (BYOD) pilot approach. BYOD is intended to assist companies (with suitably anonymized data) to work with the COIL team in a secure environment, to start gaining insights, to pilot use cases and gain company specific insights. To discover possible futures, hiding in the data from the past.
In the next edition of this SAP COIL blog, Kevin, Colin and Jerry will look in more detail at the further use cases by industry. Should you wish to contact the COIL team, please email coilsv@sap.com.
References
[1] https://www.sap.com/documents/2017/04/4666ecdd-b67c-0010-82c7-eda71af511fa.html
[2] https://sapinsider.wispubs.com/Assets/Blogs/2019/September/5-Important-Announcements-for-SAPinsiders...
[3] https://blogs.sap.com/2019/07/17/sap-data-hub-and-sap-data-intelligence-streamlining-data-driven-int...
[4] https://www.sap.com/corporate/en/company/innovation/sap-coil.html
[5] https://www.gartner.com/smarterwithgartner/top-trends-on-the-gartner-hype-cycle-for-artificial-intel...
[6] https://www.gartner.com/smarterwithgartner/3-barriers-to-ai-adoption/
[7] https://www.forbes.com/sites/cognitiveworld/2019/03/04/ai-economy-will-further-accelerate-the-pace-o...
[8] https://next.redhat.com/category/ai-machine-learning/
[9] https://www.linkedin.com/company/inspired-intellect/about/
- SAP Managed Tags:
- Machine Learning,
- SAP Data Intelligence,
- Co-Innovation Lab,
- SAP Business Technology Platform
Labels:
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
Labels in this area
-
ABAP CDS Views - CDC (Change Data Capture)
2 -
AI
1 -
Analyze Workload Data
1 -
BTP
1 -
Business and IT Integration
2 -
Business application stu
1 -
Business Technology Platform
1 -
Business Trends
1,658 -
Business Trends
92 -
CAP
1 -
cf
1 -
Cloud Foundry
1 -
Confluent
1 -
Customer COE Basics and Fundamentals
1 -
Customer COE Latest and Greatest
3 -
Customer Data Browser app
1 -
Data Analysis Tool
1 -
data migration
1 -
data transfer
1 -
Datasphere
2 -
Event Information
1,400 -
Event Information
66 -
Expert
1 -
Expert Insights
177 -
Expert Insights
294 -
General
1 -
Google cloud
1 -
Google Next'24
1 -
Kafka
1 -
Life at SAP
780 -
Life at SAP
13 -
Migrate your Data App
1 -
MTA
1 -
Network Performance Analysis
1 -
NodeJS
1 -
PDF
1 -
POC
1 -
Product Updates
4,577 -
Product Updates
341 -
Replication Flow
1 -
RisewithSAP
1 -
SAP BTP
1 -
SAP BTP Cloud Foundry
1 -
SAP Cloud ALM
1 -
SAP Cloud Application Programming Model
1 -
SAP Datasphere
2 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud
1 -
SAP S4HANA Migration Cockpit
1 -
Technology Updates
6,873 -
Technology Updates
419 -
Workload Fluctuations
1
Related Content
- 10+ ways to reshape your SAP landscape with SAP BTP - Blog 4 Interview in Technology Blogs by SAP
- 10+ ways to reshape your SAP landscape with SAP Business Technology Platform – Blog 4 in Technology Blogs by SAP
- Harnessing the Power of SAP HANA Cloud Vector Engine for Context-Aware LLM Architecture in Technology Blogs by SAP
- UNVEILING THE INNOVATIONS OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE in Technology Q&A
- Partner-2-Partner Collaboration in Manufacturing in Technology Blogs by SAP
Top kudoed authors
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 36 | |
| 25 | |
| 16 | |
| 13 | |
| 7 | |
| 7 | |
| 6 | |
| 6 | |
| 6 | |
| 6 |