
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Supply Chain Management
- SCM Blogs by SAP
- 5 ways SAP Intelligent Asset Management embraces C...
Supply Chain Management Blogs by SAP
Expand your SAP SCM knowledge and stay informed about supply chain management technology and solutions with blog posts by SAP. Follow and stay connected.
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
former_member44
Member
Options
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
11-29-2019
2:43 PM
SAP is celebrating the 10th anniversary of its journey to help improve the economy, society and the environment.
SAP helps customers manage digital change. But today’s challenges go far beyond the confines of business. What will our lives be like as water, oil, and other key commodities become scarcer? More and more people live on this earth and strive for prosperity — how can we help them to address these challenges and reach for their dreams?
Initially, there were only a few solutions, such as the SAP Environment, Health, and Safety Management application focusing on risk and compliance. Now, purpose-led innovations are evolving across the entire portfolio: SAP solutions help eliminate slavery from supply chains, optimize resource productivity, predict and prevent disasters, eliminate gender inequality, and educate people who have never had the chance to enter a classroom.
Moving forward, an area of focus is SAP’s commitment to a world of zero waste. For example, within our Digital Supply Chain we are working to reduce raw material wastage and moving toward circular value creation. To spur related innovation and action, SAP launched the Circular Economy 2030 challenge with Google Cloud at the World Economic Forum in Davos earlier this year.
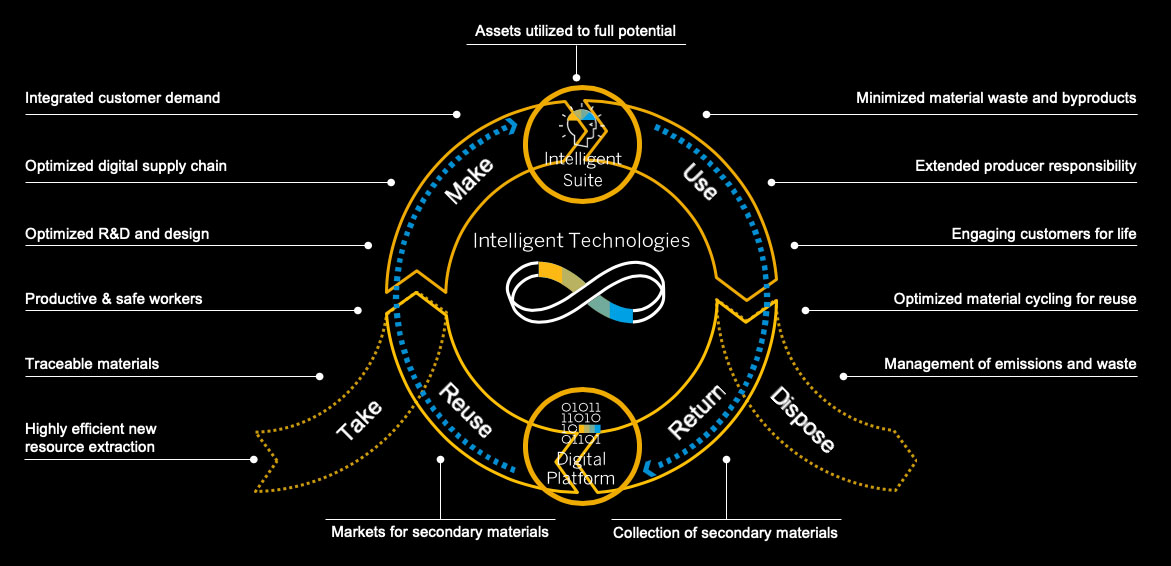 Image source: The Circularity Gap report (modified to illustrate the Intelligent Enterprise business context)
Image source: The Circularity Gap report (modified to illustrate the Intelligent Enterprise business context)
Some of the current linear processes in Manufacturing and Asset Management are:
The IAM suite brings a collaborative and data driven approach to provide a holistic coverage for utilizing Assets to their full potential. The goal being to evolve from a reactive to reliability-centered prescriptive maintenance.
Asset Central is the hub of our Intelligent Asset Management suite. It provides the next generation of Data model, that acts as a collaborative master data object of an Asset/Model required for all integration capabilities – bi-directional synch to ERP. This connects the single Asset master data object all the transactional processes up and downstream.
Asset Intelligence Network creates a platform for key stakeholders to collaborate with a Common Asset Taxonomy.

The collaborative mode brings all the Asset information in one place offering real-time, collaborative data integrity. This enables:
The combination of Asset Central and Asset Intelligence Network enables for the data integrity that is critical for data flow along the lifecycle of assets. This supports the end-to-end track and traceability of information about an asset – a key component for circular thinking.
The Use and Maintain phase of an Asset lifecycle plays a big role in the overall lifecycle of an Asset. In the Circular Economy context, it translates to keeping the Assets functioning for as long as possible.
Currently, a large percentage of maintenance happens on a time-based manner. Often this leads to over or under maintenance – overuse of materials for production/ under utilisation of assets or components or unexpected breakdowns. All of this can prove to be very expensive and wasteful.

The Asset Strategy and Performance Management and PdMS solutions of the IAM Suite helps optimise the usage and maintenance of Assets.
Indicators like these are highly dependent on industries and various other dimensions and operating set up of the assets.Indicators are extensible to support various other use cases in future. These could include other sustainability aspects – economic, environmental or social indicators.
We believe that the world economy is going to be increasingly circular and supply chains will play a key role in enabling this. We are just getting started.
We are constantly talking with our customers, partners and experts to learn and lead the way. We would love to hear from you.
SAP helps customers manage digital change. But today’s challenges go far beyond the confines of business. What will our lives be like as water, oil, and other key commodities become scarcer? More and more people live on this earth and strive for prosperity — how can we help them to address these challenges and reach for their dreams?
Initially, there were only a few solutions, such as the SAP Environment, Health, and Safety Management application focusing on risk and compliance. Now, purpose-led innovations are evolving across the entire portfolio: SAP solutions help eliminate slavery from supply chains, optimize resource productivity, predict and prevent disasters, eliminate gender inequality, and educate people who have never had the chance to enter a classroom.
Moving forward, an area of focus is SAP’s commitment to a world of zero waste. For example, within our Digital Supply Chain we are working to reduce raw material wastage and moving toward circular value creation. To spur related innovation and action, SAP launched the Circular Economy 2030 challenge with Google Cloud at the World Economic Forum in Davos earlier this year.
Intelligent Enterprise capitalises on the circular opportunity
 Image source: The Circularity Gap report (modified to illustrate the Intelligent Enterprise business context)
Image source: The Circularity Gap report (modified to illustrate the Intelligent Enterprise business context)Collaboration is key when moving to Circular Economies
Some of the current linear processes in Manufacturing and Asset Management are:
- No common Asset Taxonomy
- No business partner collaboration along the value chain
- Siloed Asset Data
- In-efficient Asset Data Maintenance
- Poor Asset Data integrity
- Inability to track usage of assets through the supply chain to assess how long an asset works if it is being replaced/if it is recycled in scenarios when it is failing too often.
The Intelligent Asset Management suite
The IAM suite brings a collaborative and data driven approach to provide a holistic coverage for utilizing Assets to their full potential. The goal being to evolve from a reactive to reliability-centered prescriptive maintenance.
 Siloed working mode
Siloed working mode
Asset Central is the hub of our Intelligent Asset Management suite. It provides the next generation of Data model, that acts as a collaborative master data object of an Asset/Model required for all integration capabilities – bi-directional synch to ERP. This connects the single Asset master data object all the transactional processes up and downstream.
Asset Intelligence Network creates a platform for key stakeholders to collaborate with a Common Asset Taxonomy.

The collaborative mode
The collaborative mode brings all the Asset information in one place offering real-time, collaborative data integrity. This enables:
- Creating preferred alliances with stakeholders within the ecosystem
- Sharing of best practices for optimal equipment availability
- Opportunities for new business models to monetize content and services
- Increased asset design/performance/engineering
- Enriching Asset Master data collaboratively through its lifecycle and beyond.
The combination of Asset Central and Asset Intelligence Network enables for the data integrity that is critical for data flow along the lifecycle of assets. This supports the end-to-end track and traceability of information about an asset – a key component for circular thinking.
Waste reduction with optimisation in Circular Economies
The Use and Maintain phase of an Asset lifecycle plays a big role in the overall lifecycle of an Asset. In the Circular Economy context, it translates to keeping the Assets functioning for as long as possible.
Currently, a large percentage of maintenance happens on a time-based manner. Often this leads to over or under maintenance – overuse of materials for production/ under utilisation of assets or components or unexpected breakdowns. All of this can prove to be very expensive and wasteful.

The Asset Strategy and Performance Management and PdMS solutions of the IAM Suite helps optimise the usage and maintenance of Assets.
Some key features that contribute towards Circular Economies are:
- Emerging Issues Detection and Improvement requests closes the loop for design improvements : Continuous improvement of design of assets for Circular Economy. Improvements can be for various aspects – design for disassembly/re-manufacturing or design for optimum usage/new Failure conditions etc.Condition Monitoring’ in the PdMS solution helps in identifying patters and evidences of potential large-scale issues. This can be detected early.The ‘Improvement Request’ functionality can then help close the loop to provide such grassroots – usage/mis-use data upstream to enhance designs of the Assets.
- IndicatorsIndicator provide a lot of insights about assets during their Use and Maintain phase. Some examples being:
- Risk and criticality-based indicators
- Machine learning based, Asset health indicators – Health Scores, Remaining Useful Life
- Usage based Indicators – Mean Time to Failure (MMTF), Environmental hazards and risk indicators etc.
We are currently working on concepts for indicators that could be specifically relevant to Circular Economy. It is a long way to go for a standard set of indicators in this context, but some examples are:
- Design for recyclability rating
- Refactoring/refurbishment rating
- Disposability cost
- % of material purity – for end of life products
- Co2 rating of an Asset/ModelIndicators like
Indicators like these are highly dependent on industries and various other dimensions and operating set up of the assets.Indicators are extensible to support various other use cases in future. These could include other sustainability aspects – economic, environmental or social indicators.
- Risk and criticality assessments – This assessment provides Asset rating based on criticality for the business.
- Root Cause Analysis (RCA) – identifies the key issue faced in an Asset/Model to be able to improve the design/configuration of an Asset and prevent future issues. This is something that we are still working on.
- Obsolescence management – Another aspect we are still defining based on inputs from our customers. We are looking at (a) Obsolescence Rules, (b) Obsolescence Register (c) Obsolescence Review template, and (d) Obsolescence Review/Assessment.The review/assessment would potentially look at aspects like:
- Impact matrix
- Mitigation strategy
- Initiating de-commission process
- Re-assignment
- Cannibalization etc.
Join us in creating circles
We believe that the world economy is going to be increasingly circular and supply chains will play a key role in enabling this. We are just getting started.
We are constantly talking with our customers, partners and experts to learn and lead the way. We would love to hear from you.
Labels:
1 Comment
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
Labels in this area
-
Business Trends
169 -
Business Trends
23 -
Catalog Enablement
1 -
Event Information
47 -
Event Information
4 -
Expert Insights
12 -
Expert Insights
38 -
intelligent asset management
1 -
Life at SAP
63 -
Product Updates
500 -
Product Updates
64 -
Release Announcement
1 -
SAP Digital Manufacturing for execution
1 -
Super Bowl
1 -
Supply Chain
1 -
Sustainability
1 -
Swifties
1 -
Technology Updates
187 -
Technology Updates
17
Related Content
- Adverse Media Monitoring: How to improve overall Supply Chain Management in Supply Chain Management Blogs by Members
- SAP Intelligent Clinical Supply Management goes CTS Europe 2024 – our key insights in Supply Chain Management Blogs by SAP
- RISE with SAP Advanced Logistics Package in Supply Chain Management Blogs by SAP
- RISE with SAP advanced asset and service management package in Supply Chain Management Blogs by SAP
- 5 Reasons why Planners Should Consider the RISE with SAP Advanced Supply Chain Planning Package in Supply Chain Management Blogs by SAP
Top kudoed authors
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 8 | |
| 8 | |
| 8 | |
| 4 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 |