
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Enterprise Resource Planning
- ERP Blogs by SAP
- S/4HANA and Machine Learning for Solution Architec...
Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
Get insights and updates about cloud ERP and RISE with SAP, SAP S/4HANA and SAP S/4HANA Cloud, and more enterprise management capabilities with SAP blog posts.
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
Advisor
Options
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
09-06-2019
11:22 AM
Last updated: March 24 2023
In my short blogs I try to provide an interesting overview on selected topics for SAP Solution Architects. This time it is Machine Learning (ML). I provide an overview of the SAP technology for Machine Learning, introduce some pre-built application-specific scenarios and show where to find more information. The blog does not cover implementation or technical details. I also do not cover conversational Artificial Intelligence or Robotic Process Automation (RPA).
Machine learning is a disruptive technology and is forecast to grow significantly and is one of the key innovations in digital transformation. It is a subset of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and predicts results using models that learn from large sets of sample data. In traditional solutions, humans create rules and solutions that work with clear requirements and structured data. Machine Learning can automate processes or decisions that are based on complex rules and structured data (e.g. database tables) or unstructured data (like natural language and images). An example is predicting supplier deliveries. The business benefit is to allow people to focus on tasks that add more value. The picture below shows possible ML scenarios in the Procure to Pay process.

There is a huge choice of software and solutions for ML. Whilst it is clear that incredibly complex problems can be solved by AI (e.g. self driving cars), the question for organisations using SAP enterprise software is can ML be applied to business scenarios with a clear return on investment. S/4HANA makes it easy to try simple ML scenarios and then allows you to expand into more ambitious solutions.
Analyst firm Omdia has ranked SAP 3 of 30 in its Embedded AI of The World’s Most AI-forward SaaS Companies' report
SAP provides four broad technology sets for ML:
These approaches provide pre-built application-specific business scenarios or allow you to build your own machine learning solutions. You can choose to run or build a whole end-to-end solution in SAP or you can choose to mix SAP data and tools with third party software and toolsets. SAP solutions can be consumed by:
1. ML in SAP S/4HANA powers specific features within standard SAP S/4HANA apps. Once configured, an administrator needs to train and activate the relevant ML scenario. Most (but not all) of the applications use a machine learning framework in S/4HANA called Intelligent Scenario Lifecyle Management (ILSM). There are two overall types of scenario:
2. Predictive Analytics in SAP Analytics Cloud (SAC): out-of-the-box predictive capabilities embedded into SAC stories with a simple user interface designed for analytical end-users. Examples include smart discovery, smart insights and smart predict (e.g. time series forecasting). These are powered by HANAs "APL" library. Customer specific analytics can be augmented with additional data fed from HANA CDS views, SAP Data Warehouse Cloud and/or non-SAP data sources.
3. ML services consumed side by side in SAP Business Technology Platform: AI business services are used by developers. Examples include libraries that help identify documents by their content or extract data fields from documents e.g. purchase orders. Some of these are used in pre-delivered S/4HANA apps.
4. SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP) solutions for data scientists and developers
BTP tends to be used for resource intensive scenarios such as neural networks that demand more memory (RAM) and more processing power (CPU). As stated above, side-by-side BTP is used in some out-of-the box standard SAP ML scenarios. For customer specific solutions, data scientists produce the ML models and work with developers to embed them into applications.
For more detail on all of these options see week 4 of the free OpenSAP training course SAP S/4HANA Embedded Analytics. Or refer to this blog.
SAP provides services to assist customer on their AI journey. Contact your Services Account Executive. Examples include "Explore Service for Intelligent ERP", "Quick-start service for embedded AI for SAP S/4HANA" and "Quick-start service for SAP Cash Application".
The ML scenarios available to you vary depending on whether you are using SAP S/4HANA on-premise or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition and SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP). Some e.g. SAP Cash Application require an additional license.
Here are some examples. In many of these, the machine learning is integrated into specific features and use cases of standard Fiori apps.
This blog by Venkata Raghu Banda describes how an embedded and side-by-side scenario are set up in S/4HANA. Or go straight to the configuration guides in these Best Practice scope items. For S/4HANA on-premise 5ZZ for embedded and 6AY for side-by-side. For S/4HANA Cloud, public edition 561 for embedded and 6AX for side-by-side.
See this ASUG presentation. It provides an overview of AI and ML and lists S/4HANA intelligent scenarios (many with links to more information). It also provides example of how ML can be combined with Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to provide intelligent end to end processes.
https://blog.asug.com/hubfs/Chapter%20Events/ASUG%20St%20Louis%20Leveraging%20SAP%20S4HANA%20AI%20+%...
For more information on SAP Data Intelligence, see the SAP page: https://www.sap.com/products/data-intelligence.html
SAP help for the cloud version of SAP Data Intelligence is here: https://help.sap.com/viewer/product/SAP_DATA_INTELLIGENCE/Cloud/en-US
There are lots of new technology layers and Open Source terminology to understand. Here is a jargon buster to save SAP Solution Architects time in Google.
More about SAP's Artificial Intelligence ethical and trustworthiness standards can be found here: SAP Global AI Ethics Policy
I hope you found this blog informative. I would be happy to see your feedback on using SAP Machine Learning solutions.
Amin Hoque
Enterprise Architect at SAP Services UK
In my short blogs I try to provide an interesting overview on selected topics for SAP Solution Architects. This time it is Machine Learning (ML). I provide an overview of the SAP technology for Machine Learning, introduce some pre-built application-specific scenarios and show where to find more information. The blog does not cover implementation or technical details. I also do not cover conversational Artificial Intelligence or Robotic Process Automation (RPA).
What is Machine Learning?
Machine learning is a disruptive technology and is forecast to grow significantly and is one of the key innovations in digital transformation. It is a subset of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and predicts results using models that learn from large sets of sample data. In traditional solutions, humans create rules and solutions that work with clear requirements and structured data. Machine Learning can automate processes or decisions that are based on complex rules and structured data (e.g. database tables) or unstructured data (like natural language and images). An example is predicting supplier deliveries. The business benefit is to allow people to focus on tasks that add more value. The picture below shows possible ML scenarios in the Procure to Pay process.

There is a huge choice of software and solutions for ML. Whilst it is clear that incredibly complex problems can be solved by AI (e.g. self driving cars), the question for organisations using SAP enterprise software is can ML be applied to business scenarios with a clear return on investment. S/4HANA makes it easy to try simple ML scenarios and then allows you to expand into more ambitious solutions.
Analyst firm Omdia has ranked SAP 3 of 30 in its Embedded AI of The World’s Most AI-forward SaaS Companies' report
SAP Solutions for Machine Learning
SAP provides four broad technology sets for ML:
- ML in SAP S/4HANA apps for business users
- Predictive Analytics in SAP Analytics Cloud for business users
- ML services consumed side by side in SAP Business Technology Platform for developers
- SAP Business Technology Platform solutions for data scientists and developers
These approaches provide pre-built application-specific business scenarios or allow you to build your own machine learning solutions. You can choose to run or build a whole end-to-end solution in SAP or you can choose to mix SAP data and tools with third party software and toolsets. SAP solutions can be consumed by:
- Business Users: AI embedded into apps that need little or no knowledge of ML
- Developers: AI services that can be incorporated into new developments
- Data scientists: AI experts who want to use SAP data and tools to set up ML processes
1. ML in SAP S/4HANA powers specific features within standard SAP S/4HANA apps. Once configured, an administrator needs to train and activate the relevant ML scenario. Most (but not all) of the applications use a machine learning framework in S/4HANA called Intelligent Scenario Lifecyle Management (ILSM). There are two overall types of scenario:
- Embedded: some use embedded predictive analytics for simpler scenarios based mainly on SAP structured data. An example of an embedded S/4HANA ML solutions is “early detection of slow or non-moving goods”. These use functions in the HANA layer through Automated Predictive Library (APL) or Predictive Analysis Library (PAL).
- Side-by-side: others rely on integration to more complex side-by-side ML running in the Business Technology Platform (BTP). An example is Intelligent Intercompany Reconciliation.
2. Predictive Analytics in SAP Analytics Cloud (SAC): out-of-the-box predictive capabilities embedded into SAC stories with a simple user interface designed for analytical end-users. Examples include smart discovery, smart insights and smart predict (e.g. time series forecasting). These are powered by HANAs "APL" library. Customer specific analytics can be augmented with additional data fed from HANA CDS views, SAP Data Warehouse Cloud and/or non-SAP data sources.
3. ML services consumed side by side in SAP Business Technology Platform: AI business services are used by developers. Examples include libraries that help identify documents by their content or extract data fields from documents e.g. purchase orders. Some of these are used in pre-delivered S/4HANA apps.
4. SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP) solutions for data scientists and developers
BTP tends to be used for resource intensive scenarios such as neural networks that demand more memory (RAM) and more processing power (CPU). As stated above, side-by-side BTP is used in some out-of-the box standard SAP ML scenarios. For customer specific solutions, data scientists produce the ML models and work with developers to embed them into applications.
- SAP AI Core and SAP AI Launchpad: services to manage AI assets, process data, train ML models and deploy them through web services or embed them in SAP solutions.
- SAP HANA ML: in-database ML including Predictive Analysis Library (PAL), Automated Predictive Library (APL) and APIs for Python and R scripts. External machine learning capabilities working with R, Python and Tensorflow.
- SAP Data Intelligence Cloud: provides a portfolio of deep learning that can work with vast quantities of structured and unstructured data from SAP and external cloud and on-premise sources such as Hadoop HDFS, AWS S3 and Azure Data Lake. It includes open source frameworks and algorithms familiar to data scientists such as the languages Python and R and libraries such as TensorFlow and Pandas.
For more detail on all of these options see week 4 of the free OpenSAP training course SAP S/4HANA Embedded Analytics. Or refer to this blog.
SAP provides services to assist customer on their AI journey. Contact your Services Account Executive. Examples include "Explore Service for Intelligent ERP", "Quick-start service for embedded AI for SAP S/4HANA" and "Quick-start service for SAP Cash Application".
SAP Machine Learning Scenarios
The ML scenarios available to you vary depending on whether you are using SAP S/4HANA on-premise or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition and SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP). Some e.g. SAP Cash Application require an additional license.
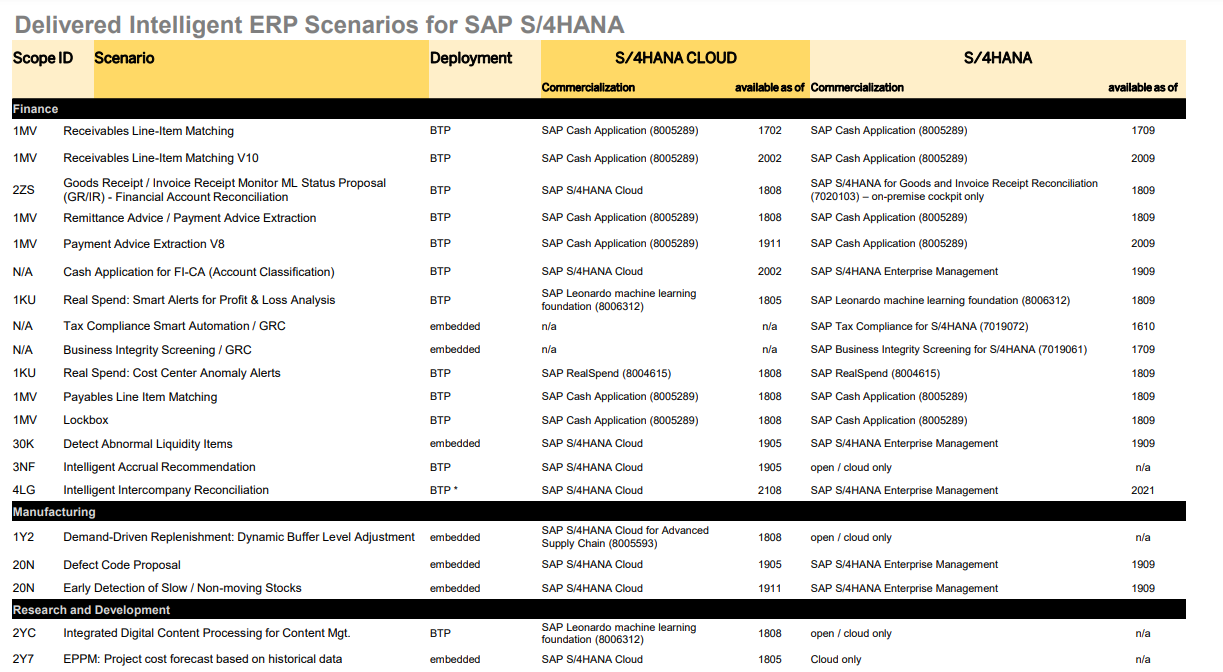
Here are some examples. In many of these, the machine learning is integrated into specific features and use cases of standard Fiori apps.
- Invoice and payment matching S/4HANA scope item 1MV in the SAP Cash application: look at a video and help.
- Invoice and Goods Receipt monitor in S/4HANA scope item 2ZS: see this video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FjA0KKJecpg
- Overdue Materials Stock In transit (Fiori app F2139) in S/4HANA scope item 20N: see this video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BQw8ADEbd48
- Create Sales Orders Automatic Extraction (Fiori app F4920) in S/4HANA scope item 4X9. Sales order can be created from a PDF order document.
- Quotation conversion rates (Fiori app F1904): see S/4HANA scope item 2YJ
This blog by Venkata Raghu Banda describes how an embedded and side-by-side scenario are set up in S/4HANA. Or go straight to the configuration guides in these Best Practice scope items. For S/4HANA on-premise 5ZZ for embedded and 6AY for side-by-side. For S/4HANA Cloud, public edition 561 for embedded and 6AX for side-by-side.
See this ASUG presentation. It provides an overview of AI and ML and lists S/4HANA intelligent scenarios (many with links to more information). It also provides example of how ML can be combined with Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to provide intelligent end to end processes.
https://blog.asug.com/hubfs/Chapter%20Events/ASUG%20St%20Louis%20Leveraging%20SAP%20S4HANA%20AI%20+%...
SAP Data Intelligence
For more information on SAP Data Intelligence, see the SAP page: https://www.sap.com/products/data-intelligence.html
SAP help for the cloud version of SAP Data Intelligence is here: https://help.sap.com/viewer/product/SAP_DATA_INTELLIGENCE/Cloud/en-US
ML Jargon Buster
There are lots of new technology layers and Open Source terminology to understand. Here is a jargon buster to save SAP Solution Architects time in Google.
- Apache Spark: platform for high volume distributed processing of big data. Often used with Hadoop HDFS. Processing includes SQL, batch processing, stream feeds and machine learning.
- Azure Data Lake: Microsoft's big data analytics solution. Often encountered when using ML for big data.
- Docker: used to create, deploy, and run applications using "containers". Docker containers are lightweight and fast. Containers build on Virtual Machine technology by allowing each container to share a common host Operating System making them fast to start. An application is made up a number of containers linked together. Docker is open-source. This technology is used in SAP Data Hub.
- Hadoop: provides massive distributed storage for structured and unstructured data with massive processing power. It is an open-source clustered file system called HDFS often managed on-premise.
- Jupyter Notebook: a tool used by data scientists to integrate code and its data output into a single document. Commonly used with Python for ML work. Jupyter Notebook is an open-source web application. Used for data cleaning, statistical modeling and simulations, data visualization and machine learning.
- Kafka: an open-source software platform for handling high through-put real time data feeds. Originally developed by LinkedIn but then became part of the Apache Software Foundation open-source. Can be used in SAP Data Hub operators.
- Kubernetes: system for managing containerized applications across a group of Virtual Machines. Kubernetes is open-source based on Google's Borg solution. It provides massive scaleability. This technology is used in SAP Data Intelligence.
- MQTT: Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) is a commonly used protocols in IoT (Internet of Things) projects. Can be used in SAP Data Hub operators.
- Python: open-source language used in many Artificial Intelligence (AI) projects with a huge library for machine learning. Libraries include Keras, TensorFlow and Pandas. Can be used in SAP Data Hub operators.
- R: open-source language used to analyze and manipulate data for statistical purposes. Can be used in SAP Data Intelligence.
- S3: Amazon Web Services (AWS) scaleable, high-speed, web-based cloud storage. Often encountered when using ML for big data.
More about SAP's Artificial Intelligence ethical and trustworthiness standards can be found here: SAP Global AI Ethics Policy
I hope you found this blog informative. I would be happy to see your feedback on using SAP Machine Learning solutions.
Amin Hoque
Enterprise Architect at SAP Services UK
- SAP Managed Tags:
- Machine Learning,
- SAP S/4HANA,
- SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud
Labels:
1 Comment
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
Labels in this area
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
1 -
Business Trends
363 -
Business Trends
21 -
Customer COE Basics and Fundamentals
1 -
Digital Transformation with Cloud ERP (DT)
1 -
Event Information
461 -
Event Information
23 -
Expert Insights
114 -
Expert Insights
151 -
General
1 -
Governance and Organization
1 -
Introduction
1 -
Life at SAP
415 -
Life at SAP
2 -
Product Updates
4,685 -
Product Updates
205 -
Roadmap and Strategy
1 -
Technology Updates
1,502 -
Technology Updates
85
Related Content
- The Role of SAP Business AI in the Chemical Industry. Overview in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
- Learn about Localization with SAP’s Experts at the DSAG-SAP Globalization Symposium 2024 in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
- Five Key assessments for a Smooth ECC to S/4HANA Transformation in Enterprise Resource Planning Q&A
- Release Assessment and Scope Dependency for SAP S/4HANA Cloud Public Edition(RASD): 2024 Edition in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
- SAP S/4HANA Cloud Extensions with SAP Build Best Practices: An Expert Roundtable in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
Top kudoed authors
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 5 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 |
