
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Technology
- Technology Blogs by SAP
- Intelligent Enterprise Data Management: the Symbio...
Technology Blogs by SAP
Learn how to extend and personalize SAP applications. Follow the SAP technology blog for insights into SAP BTP, ABAP, SAP Analytics Cloud, SAP HANA, and more.
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
christian86
Explorer
Options
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
08-14-2019
1:20 PM
Part 4 of 5 in the What Is Data Intelligence blog series.
Just imagine that you own the arterial road that leads to a small village in the middle of nowhere. You can easily manage the traffic on your road until a huge gusher in this small village is discovered by accident. As of now, a big oil company settles down in business and many more vehicles, including public transport and big trucks intend to use your road on a frequent basis. However, your road was not designed for managing heavy traffic caused by large vehicles.
So would you invest in establishing a new infrastructure to leverage the permanent road use for large vehicles (instead of letting them use the road rather restrictively)?
As a matter of fact, many companies find themselves in this situation. On one hand, there is a traditional IT enterprise architecture that is basically designed for taking care of structured enterprise data. On the other hand, there is a huge amount of unstructured data like audio files, video streams, and social media impressions that have been created and gathered over time.
This ‘Big Data’ commonly resides in object stores and data lakes scattered across the IT landscape which implies that it is already a challenge to even identify where a specific file or object has been stored. As outlined in this article, one can nevertheless state that using traditional enterprise information management solutions is not feasible when it comes to Big Data processing.
Nonetheless, as described in this article, most companies are convinced that applying intelligent technologies like Machine Learning (ML) to enterprise data and Big Data will help them gain smart, valuable insights to assist with making better, more confident decisions. However, when it comes down to operating with Big Data it is simply not feasible to replicate the entire pool of data into an application or a system.
In addition, as outlined in this article there are several pitfalls to consider when applying ML methods to merged data sets that might be both distributed across the IT landscape and ever-changing as well.
This is precisely why we have built SAP Data Intelligence, as it is aimed to tackle these exact obstacles. It comes with end-to-end coverage for the entire process of delivering intelligent enterprise applications through the use of core data management functionalities like:
as well as a comprehensive ML tooling support which wa discussed in this article as well.
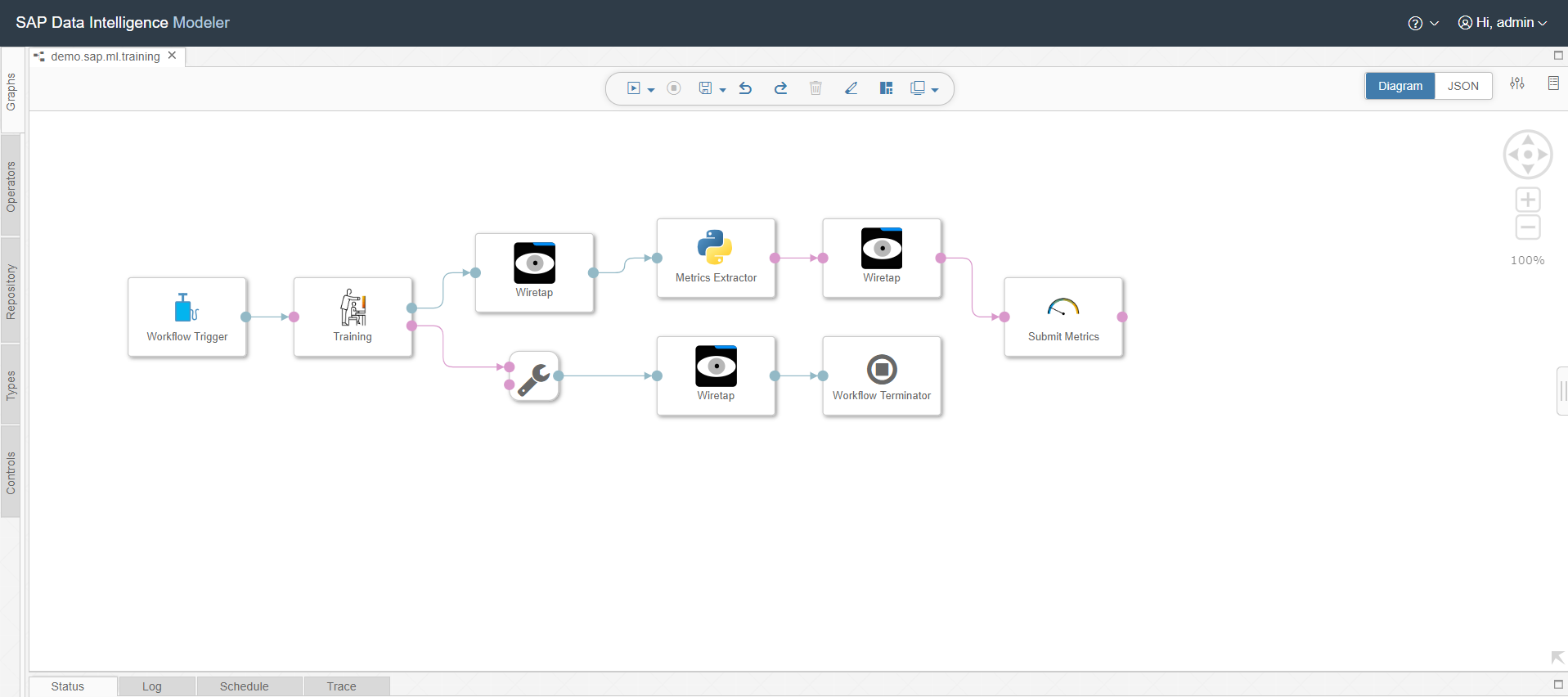
But this certainly is not the end of the story. If you take a deeper look, the key concept behind an intelligent enterprise data management solution is leveraging the efficient use of extracted metadata assets. In SAP Data Intelligence, these metadata assets from the related source systems can be made available in the catalog of the SAP Data Intelligence Metadata Explorer for labeling, searching and data lineage functionalities.

Last, but not least, there is still another level of Intelligent Enterprise Information Management which consists of the real symbiosis of classical data management functionalities and intelligent technologies like ML. For example, one could use ML techniques to:
The establishment of a so-called “self-learning metadata governance” is stated on the roadmap of SAP Data Intelligence. This functionality boils down to the combination of metadata management and ML enriched with business semantics, which are extracted from SAP business systems and applications. It basically represents the metadata management of the future and is going to enhance the productivity of the involved subject matter experts.
Just imagine that you own the arterial road that leads to a small village in the middle of nowhere. You can easily manage the traffic on your road until a huge gusher in this small village is discovered by accident. As of now, a big oil company settles down in business and many more vehicles, including public transport and big trucks intend to use your road on a frequent basis. However, your road was not designed for managing heavy traffic caused by large vehicles.
So would you invest in establishing a new infrastructure to leverage the permanent road use for large vehicles (instead of letting them use the road rather restrictively)?
As a matter of fact, many companies find themselves in this situation. On one hand, there is a traditional IT enterprise architecture that is basically designed for taking care of structured enterprise data. On the other hand, there is a huge amount of unstructured data like audio files, video streams, and social media impressions that have been created and gathered over time.
This ‘Big Data’ commonly resides in object stores and data lakes scattered across the IT landscape which implies that it is already a challenge to even identify where a specific file or object has been stored. As outlined in this article, one can nevertheless state that using traditional enterprise information management solutions is not feasible when it comes to Big Data processing.
Nonetheless, as described in this article, most companies are convinced that applying intelligent technologies like Machine Learning (ML) to enterprise data and Big Data will help them gain smart, valuable insights to assist with making better, more confident decisions. However, when it comes down to operating with Big Data it is simply not feasible to replicate the entire pool of data into an application or a system.
In addition, as outlined in this article there are several pitfalls to consider when applying ML methods to merged data sets that might be both distributed across the IT landscape and ever-changing as well.
- How is it possible to leverage and automate Big Data and ML scenarios?
- How can we efficiently identify data assets distributed across the landscape?
- How can we establish a sustainable IT architecture?
- Is it possible to orchestrate external data flows?
This is precisely why we have built SAP Data Intelligence, as it is aimed to tackle these exact obstacles. It comes with end-to-end coverage for the entire process of delivering intelligent enterprise applications through the use of core data management functionalities like:
- metadata governance
- data quality processing
- data discovery and data lineage
- data preparation and data transformation
- data integration and (orchestration of) data pipelining
as well as a comprehensive ML tooling support which wa discussed in this article as well.

SAP Data Intelligence Modeler to design and create data-driven pipelines
But this certainly is not the end of the story. If you take a deeper look, the key concept behind an intelligent enterprise data management solution is leveraging the efficient use of extracted metadata assets. In SAP Data Intelligence, these metadata assets from the related source systems can be made available in the catalog of the SAP Data Intelligence Metadata Explorer for labeling, searching and data lineage functionalities.

SAP Data Intelligence Metadata Explorer to manage the metadata assets across the IT landscape
Last, but not least, there is still another level of Intelligent Enterprise Information Management which consists of the real symbiosis of classical data management functionalities and intelligent technologies like ML. For example, one could use ML techniques to:
- automatically classify extracted metadata assets based on text analysis, image processing or natural language processing.
- automate the mapping of predefined entities (like sales orders or customer industries) as well as establish and maintain the relationships of extracted entities originating from the various connected systems.
The establishment of a so-called “self-learning metadata governance” is stated on the roadmap of SAP Data Intelligence. This functionality boils down to the combination of metadata management and ML enriched with business semantics, which are extracted from SAP business systems and applications. It basically represents the metadata management of the future and is going to enhance the productivity of the involved subject matter experts.
Learn More
- Start your free trial
of SAP Data Intelligence today.
- This article is part 4 of 5 in the What Is Data Intelligence blog series. Stay tuned for future Data Intelligence blog posts.
- SAP Managed Tags:
- Machine Learning,
- SAP Data Intelligence,
- SAP Datasphere
Labels:
1 Comment
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
Labels in this area
-
ABAP CDS Views - CDC (Change Data Capture)
2 -
AI
1 -
Analyze Workload Data
1 -
BTP
1 -
Business and IT Integration
2 -
Business application stu
1 -
Business Technology Platform
1 -
Business Trends
1,658 -
Business Trends
91 -
CAP
1 -
cf
1 -
Cloud Foundry
1 -
Confluent
1 -
Customer COE Basics and Fundamentals
1 -
Customer COE Latest and Greatest
3 -
Customer Data Browser app
1 -
Data Analysis Tool
1 -
data migration
1 -
data transfer
1 -
Datasphere
2 -
Event Information
1,400 -
Event Information
66 -
Expert
1 -
Expert Insights
177 -
Expert Insights
293 -
General
1 -
Google cloud
1 -
Google Next'24
1 -
Kafka
1 -
Life at SAP
780 -
Life at SAP
13 -
Migrate your Data App
1 -
MTA
1 -
Network Performance Analysis
1 -
NodeJS
1 -
PDF
1 -
POC
1 -
Product Updates
4,577 -
Product Updates
340 -
Replication Flow
1 -
RisewithSAP
1 -
SAP BTP
1 -
SAP BTP Cloud Foundry
1 -
SAP Cloud ALM
1 -
SAP Cloud Application Programming Model
1 -
SAP Datasphere
2 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud
1 -
SAP S4HANA Migration Cockpit
1 -
Technology Updates
6,873 -
Technology Updates
417 -
Workload Fluctuations
1
Related Content
- Cloud Transport Management configuration between spaces in Technology Q&A
- Onboarding Users in SAP Quality Issue Resolution in Technology Blogs by SAP
- How to add Create Git-enabled change link in custom Business Role? in Technology Q&A
- How to host static webpages through SAP CPI-Iflow in Technology Blogs by Members
- BRF+ outbound delivery in Technology Q&A
Top kudoed authors
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 34 | |
| 25 | |
| 13 | |
| 7 | |
| 7 | |
| 6 | |
| 6 | |
| 6 | |
| 5 | |
| 4 |