
- SAP Community
- Groups
- Interest Groups
- Application Development
- Blog Posts
- Introduction - ABAP Programming on HANA
Application Development Blog Posts
Learn and share on deeper, cross technology development topics such as integration and connectivity, automation, cloud extensibility, developing at scale, and security.
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
Former Member
Options
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
06-24-2018
6:14 AM
What does this document have to offer?
The focus of this blog is to present an overview of the new programming techniques in ABAP after introduction of HANA database. The focus will be towards providing a guideline on why and how an ABAP developer should start transitioning its code to use the new coding techniques.
Who should be reading this?
Here the target audience would be ABAP developers who are looking forward to getting a basic understanding of ABAP on HANA programming and to understand why to opt for these new features.
Areas covered in this blog:
Code to Data Paradigm, OpenSQL, CDS Views, AMDPs.
Let us begin!
SAP ABAP has been rapidly evolving over the years. With introduction of S/4HANA it went to graduate to become a far more impressive and productive language. If you ask me how ABAP has improved then the answer is "Code-To-Data" Paradigm.
What is Code-To-Data Paradigm?
The traditional approach involves bringing data from database to our presentation server, doing the data intensive calculations & filtering and then presenting the filtered data to user.
The new HANA approach is to push our code to the database layer where all the data resides, do the calculations at database layer and bring only the relevant records to presentation server.

Because of C2D paradigm the delay caused due to latency of bringing large volumes of data to presentation layer is removed drastically resulting in high performance even with very large data sets.
To better understand this let me proceed using a basic scenario that any ABAP developer can easily relate to:
Example Scenario: An ALV report that returns the master data of “ALL” vendors and their addresses for vendors that are active, not marked for central deletion, not marked for deletion under “ALL” company code, not marked for deletion under “ALL” purchasing organization.
In this scenario, the performance would suffer because of fetching data for all vendors, for all company codes & for all Purchasing Organization. The resulting report will require a background run and the traditional ABAP report flow in this case would fetch data as follows:
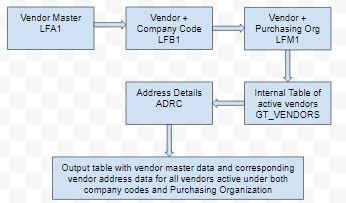
Here the presentation layer would interact with a couple of times if no joins are used under select statement. Moreover, using joins to fetch data from these tables would also be very slow because of large volumes of vendor data in system. So how must I improve the performance here?
Answer:- Code PushDown using
OpenSQL programming (though limited at this point)
CDS Views
ABAP Managed Database Procedures
Let us visit each of the above features and see how they work with HANA DB.
With OpenSQL programming you can write openSQL syntax in your ABAP code.
While writing code in OpenSQL the fields in select statement are comma separated, all the host variables are escaped using ‘@’ sign, the concatenation can be done in a single statement using ‘| |’ and so on and so forth.
The above scenario will be written as follows:
Result:

Here you can see that report ran for 1621 ms and returned us the desired results.
This is a very basic example that I took but in real time scenarios you may be doing some aggregations, or you may be translating some data during selection, or you may be grouping your result set based on some fields. Though the code push code opportunity is limited at the moment when using OpenSQL, the syntax for this has been enhanced since 7.4. release. SAP has many syntaxes that can be utilized in code to improve its performance. To start with you can find very descriptive examples and code snippets in the ABAP glossary itself.
SAP introduced a new data modeling infrastructure known as core data services or CDS. With CDS, data models are defined and consumed on database server rather than on application server. As a result, the table result view is created at the database level. CDS are completely compatible with openSQL and can be written using ABAP development tools like Eclipse Oxygen. These can be consumed by reports and AMDPs as well.
The above code will be created as a data definition in Eclipse and defined as follows:
Result:

The CDS view returned result in 39ms. Awesome? Yes it is.
Now CDS views could also be created with parameters or with associations. You may choose to create a CDS with parameters if you have a fixed result set and some input parameters to pass.
You could also create a CDS with association for a similar scenario if you have many tables to address in the view and if you want to keep the result set flexible.
AMDPs as the name says are database procedures that run on database directly and are written directly in ABAP. AMDPs are written using AMDP classes. Below is an example using the above scenario of how to create an AMDP class. The interface “IF_AMDP_MARKER_HDB” distinguishes an AMDP class from other classes.
Class definition:
Similarly, an AMDP class implementation will have methods define with a syntax “BY DATABASE PROCEDURE FOR <database> LANGUAGE <language>. In our case database will be HDB (HANA DB) and language will always be SQLSCRIPT.
This AMDP class can then be consumed in an ABAP program to achieve the code push down functionality.
Result:

What to choose OpenSQL or CDS or AMDP?
A question that would arise in any developers mind would be how to make a choice amongst the three programming techniques.
In the above example you can see that the performance was CDS > OpenSQL > AMDP.
Does that mean for the above scenario the best choice is to create a CDS? Not exactly!
If I do not reuse the CDS view then openSQL could be an equally effective choice.
Also note that CDS views and AMDP can only be created using ABAP Development Tools like Eclipse Oxygen. Refer the following link to understand on how to get eclipse on your system:
https://tools.hana.ondemand.com/#abap
There are no rules that can be adhered to when choosing from the above three programming techniques. It completely depends on the requirement and on what and how data needs to be handled. However, the points below can give an idea on how to proceed to making the most productive choice.
Choose Open SQL when:
Choose CDS views when:
Choose AMDPs When:
This blog was to give you a kick start on what HANA has to offer and what you can do with the new techniques. My advice to any beginner would be to get your hands on a system and just try.
The focus of this blog is to present an overview of the new programming techniques in ABAP after introduction of HANA database. The focus will be towards providing a guideline on why and how an ABAP developer should start transitioning its code to use the new coding techniques.
Who should be reading this?
Here the target audience would be ABAP developers who are looking forward to getting a basic understanding of ABAP on HANA programming and to understand why to opt for these new features.
Areas covered in this blog:
Code to Data Paradigm, OpenSQL, CDS Views, AMDPs.
Let us begin!
SAP ABAP has been rapidly evolving over the years. With introduction of S/4HANA it went to graduate to become a far more impressive and productive language. If you ask me how ABAP has improved then the answer is "Code-To-Data" Paradigm.
What is Code-To-Data Paradigm?
The traditional approach involves bringing data from database to our presentation server, doing the data intensive calculations & filtering and then presenting the filtered data to user.
The new HANA approach is to push our code to the database layer where all the data resides, do the calculations at database layer and bring only the relevant records to presentation server.

Because of C2D paradigm the delay caused due to latency of bringing large volumes of data to presentation layer is removed drastically resulting in high performance even with very large data sets.
To better understand this let me proceed using a basic scenario that any ABAP developer can easily relate to:
Example Scenario: An ALV report that returns the master data of “ALL” vendors and their addresses for vendors that are active, not marked for central deletion, not marked for deletion under “ALL” company code, not marked for deletion under “ALL” purchasing organization.
In this scenario, the performance would suffer because of fetching data for all vendors, for all company codes & for all Purchasing Organization. The resulting report will require a background run and the traditional ABAP report flow in this case would fetch data as follows:

Here the presentation layer would interact with a couple of times if no joins are used under select statement. Moreover, using joins to fetch data from these tables would also be very slow because of large volumes of vendor data in system. So how must I improve the performance here?
Answer:- Code PushDown using
OpenSQL programming (though limited at this point)
CDS Views
ABAP Managed Database Procedures
Let us visit each of the above features and see how they work with HANA DB.
- OpenSQL Programming
With OpenSQL programming you can write openSQL syntax in your ABAP code.
While writing code in OpenSQL the fields in select statement are comma separated, all the host variables are escaped using ‘@’ sign, the concatenation can be done in a single statement using ‘| |’ and so on and so forth.
The above scenario will be written as follows:
REPORT zact_vendor_osql.
SELECT a~lifnr,
b~bukrs,
c~ekorg,
d~name1,
d~city1,
d~region,
d~country,
d~post_code1
INTO TABLE @DATA(gt_vendor)
FROM lfa1 AS a
INNER JOIN lfb1 AS b ON b~lifnr = a~lifnr
INNER JOIN lfm1 AS c ON c~lifnr = a~lifnr
LEFT OUTER JOIN adrc AS d ON d~addrnumber = a~adrnr
WHERE a~loevm EQ @abap_false
AND a~sperr EQ @abap_false
AND a~sperm EQ @abap_false
AND a~node1 EQ @abap_false
AND b~sperr EQ @abap_false
AND c~loevm EQ @abap_false
AND c~sperm EQ @abap_false.
GET RUN TIME FIELD data(lv_end_time).
DATA(lv_time) = lv_end_time - lv_start_time.
cl_demo_output=>display_data(EXPORTING value = gt_vendor
name = |Duration { lv_time } ms|.
Result:

Here you can see that report ran for 1621 ms and returned us the desired results.
This is a very basic example that I took but in real time scenarios you may be doing some aggregations, or you may be translating some data during selection, or you may be grouping your result set based on some fields. Though the code push code opportunity is limited at the moment when using OpenSQL, the syntax for this has been enhanced since 7.4. release. SAP has many syntaxes that can be utilized in code to improve its performance. To start with you can find very descriptive examples and code snippets in the ABAP glossary itself.
- Core Data Services (CDS) Views
SAP introduced a new data modeling infrastructure known as core data services or CDS. With CDS, data models are defined and consumed on database server rather than on application server. As a result, the table result view is created at the database level. CDS are completely compatible with openSQL and can be written using ABAP development tools like Eclipse Oxygen. These can be consumed by reports and AMDPs as well.
The above code will be created as a data definition in Eclipse and defined as follows:
@AbapCatalog.sqlViewName: 'ZCDS_ACT_VEN' //SE11 SQL view name
@AbapCatalog.Complier.compareFilter: true
@AccessControl.authorizationCheck: #CHECK
@EndUserText.label: 'CDS View data definition'
define view ZCDS_ACT_VENDOR //CDS view name
as select from lfa1 as a
inner join lfb1 as b on a.lifnr = b.lifnr and b.sperr = ''
inner join lfm1 as c on a.lifnr = c.lifnr and c.sperm = ''
left outer join adrc as d on a.adrnr = d.addrnumber
{
key a.lifnr,
key b.bukrs,
key c.ekorg,
d.name1,
d.city1,
d.region,
d.country,
d.post_code1
} where a.loevm = '' and a.sperr = '' and a.sperm = ''
Result:

The CDS view returned result in 39ms. Awesome? Yes it is.
Now CDS views could also be created with parameters or with associations. You may choose to create a CDS with parameters if you have a fixed result set and some input parameters to pass.
You could also create a CDS with association for a similar scenario if you have many tables to address in the view and if you want to keep the result set flexible.
- ABAP Managed Database Procedures (AMDP)
AMDPs as the name says are database procedures that run on database directly and are written directly in ABAP. AMDPs are written using AMDP classes. Below is an example using the above scenario of how to create an AMDP class. The interface “IF_AMDP_MARKER_HDB” distinguishes an AMDP class from other classes.
Class definition:
CLASS zcl_act_vendor_amdp DEFINITION PUBLIC FINAL CREATE PUBLIC.
PUBLIC SECTION.
INTERFACES if_amdp_marker_hdb.
TYPES: BEGIN OF ty_vendor,
lifnr TYPE lifnr,
bukrs TYPE bukrs,
ekorg TYPE ekorg,
name1 TYPE name1,
city1 TYPE adrc-city1,
region TYPE adrc-region,
country TYPE adrc-country,
post_code1 TYPE adrc-post_code1,
END of ty_vendor,
tt_vendor TYPE SORTED TABLE OF ty_vendor WITH NON-UNIQUE KEY lifnr bukrs ekorg.
METHODS get_vendors_amdp IMPORTING VALUE(lv_clnt) type mandt
EXPORTING VALUE(lt_vendor) type tt_vendor.
ENDCLASS.
Similarly, an AMDP class implementation will have methods define with a syntax “BY DATABASE PROCEDURE FOR <database> LANGUAGE <language>. In our case database will be HDB (HANA DB) and language will always be SQLSCRIPT.
CLASS zcl_act_vendor_amdp IMPLEMENTATION.
METHOD get_vendors_amdp
BY DATABASE PROCEDURE FOR HDB LANGUAGE SQLSCRIPT
OPTIONS READ-ONLY USING lfa1 lfb1 lfm1 adrc.
lt_vendor = SELECT DISTINCT a.lifnr,
b.bukrs,
c.ekorg,
d.name1,
d.city1,
d.region,
d.country,
d.post_cdoe1
FROM lfa1 AS a
INNER JOIN lfb1 AS b
ON b.mandt = a.mandt AND b.lifnr = a.lifnr AND
b.loevm = '' AND b.sperr = ''
INNER JOIN lfm1 AS c
ON c.mandt = a.mandt AND c.lifnr = a.lifnr AND
c.loevm = '' AND c.sperm = ''
LEFT OUTER JOIN adrc AS d
ON d.client = a.mandt AND d.addrnumber = a.adrnr
WHERE a.mandt = lv_clnt
AND a.loevm = ''
AND a.sperr = ''
AND a.sperm = '';
ENDMETHOD.
ENDCLASS.
This AMDP class can then be consumed in an ABAP program to achieve the code push down functionality.
REPORT z_act_vendor_amdp.
TYPES: BEGIN OF ty_vendor,
lifnr TYPE lifnr,
bukrs TYPE bukrs,
ekorg TYPE ekorg,
name1 TYPE name1,
city1 TYPE adrc-city1,
region TYPE adrc-region,
country TYPE adrc-country,
post_code1 TYPE adrc-post_code1,
END OF ty_vendor.
DATA: gt_vendors TYPE SORTED TABLE OF ty_vendor WITH NON-UNIQUE KEY lifnr bukrs ekorg.
GET RUN TIME FIELD DATA(gv_start).
DATA(go_ref) = NEW zcl_act_vendor_amdp( ).
go_ref->get_vendors_amdp( EXPORTING lv_clnt = sy-mandt
IMPORTING lt_vendor = gt_vendors ).
GET RUN TIME FIELD DATA(gv_end).
DATA(gv_time) = gv_end - gv_start.
cl_demo_output=>display_data( value = gt_vendors
name = |Duration { gv_time }ms| ).
Result:

What to choose OpenSQL or CDS or AMDP?
A question that would arise in any developers mind would be how to make a choice amongst the three programming techniques.
In the above example you can see that the performance was CDS > OpenSQL > AMDP.
Does that mean for the above scenario the best choice is to create a CDS? Not exactly!
If I do not reuse the CDS view then openSQL could be an equally effective choice.
Also note that CDS views and AMDP can only be created using ABAP Development Tools like Eclipse Oxygen. Refer the following link to understand on how to get eclipse on your system:
https://tools.hana.ondemand.com/#abap
There are no rules that can be adhered to when choosing from the above three programming techniques. It completely depends on the requirement and on what and how data needs to be handled. However, the points below can give an idea on how to proceed to making the most productive choice.
Choose Open SQL when:
- The table selection is program specific and will not be reused
- When you do not have an ABAP Development Tool to create CDS or AMDP. The two can be consumed in GUI but cannot be created in GUI.
- When the data in question does not involve intensive calculations, and can be managed easily by OpenSQL.
- When you have a tricky selection screen with lot of select options that will be passed as single values too.
Choose CDS views when:
- The view can be reused among other views or programs.
- When a large volume of data is involved from various data sources.
- When you have good knowledge on how to write annotations to enhance your CDS view.
- Only single result set is required.
Choose AMDPs When:
- You are fluent with SQL scripting because your entire code will be written in SQL script and the compiler fails in determining the runtime SQL script errors like divide by zero.
- When you have to handle cross client data because AMDP does not do client handling on its own.
- When multiple result sets are required.
This blog was to give you a kick start on what HANA has to offer and what you can do with the new techniques. My advice to any beginner would be to get your hands on a system and just try.
- SAP Managed Tags:
- ABAP Development
22 Comments
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
Labels in this area
-
A Dynamic Memory Allocation Tool
1 -
ABAP
8 -
abap cds
1 -
ABAP CDS Views
14 -
ABAP class
1 -
ABAP Cloud
1 -
ABAP Development
4 -
ABAP in Eclipse
1 -
ABAP Keyword Documentation
2 -
ABAP OOABAP
2 -
ABAP Programming
1 -
abap technical
1 -
ABAP test cockpit
7 -
ABAP test cokpit
1 -
ADT
1 -
Advanced Event Mesh
1 -
AEM
1 -
AI
1 -
API and Integration
1 -
APIs
8 -
APIs ABAP
1 -
App Dev and Integration
1 -
Application Development
2 -
application job
1 -
archivelinks
1 -
Automation
4 -
BTP
1 -
CAP
1 -
CAPM
1 -
Career Development
3 -
CL_GUI_FRONTEND_SERVICES
1 -
CL_SALV_TABLE
1 -
Cloud Extensibility
8 -
Cloud Native
7 -
Cloud Platform Integration
1 -
CloudEvents
2 -
CMIS
1 -
Connection
1 -
container
1 -
Debugging
2 -
Developer extensibility
1 -
Developing at Scale
4 -
DMS
1 -
dynamic logpoints
1 -
Eclipse ADT ABAP Development Tools
1 -
EDA
1 -
Event Mesh
1 -
Expert
1 -
Field Symbols in ABAP
1 -
Fiori
1 -
Fiori App Extension
1 -
Forms & Templates
1 -
IBM watsonx
1 -
Integration & Connectivity
10 -
JavaScripts used by Adobe Forms
1 -
joule
1 -
NodeJS
1 -
ODATA
3 -
OOABAP
3 -
Outbound queue
1 -
Product Updates
1 -
Programming Models
13 -
Restful webservices Using POST MAN
1 -
RFC
1 -
RFFOEDI1
1 -
SAP BAS
1 -
SAP BTP
1 -
SAP Build
1 -
SAP Build apps
1 -
SAP Build CodeJam
1 -
SAP CodeTalk
1 -
SAP Odata
1 -
SAP UI5
1 -
SAP UI5 Custom Library
1 -
SAPEnhancements
1 -
SapMachine
1 -
security
3 -
text editor
1 -
Tools
16 -
User Experience
5
Top kudoed authors
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 5 | |
| 5 | |
| 3 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 1 |