
- SAP Community
- Groups
- Interest Groups
- Application Development
- Blog Posts
- Eight different sort algorithms implemented in ABA...
Application Development Blog Posts
Learn and share on deeper, cross technology development topics such as integration and connectivity, automation, cloud extensibility, developing at scale, and security.
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
Advisor
Options
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
04-30-2017
12:41 PM
- Bucket Sort
- Bubble Sort
- Merge Sort
- Quick Sort
- Selection Sort
- Insertion Sort
- Heap Sort
- Shell Sort
- A very draft performance comparison
- Sleep Sort in JavaScript
Some application developers think that it is enough to know SORT keyword and how to use sorted table in ABAP for their daily work without knowing how SORT is done internally. For me I can not say this assumption is wrong. I personal preference is to know something more thoroughly. We have learned various sort algorithms in the university, here I just list my implementation on some of them using ABAP for my personal study purpose.
For each sort algorithm I will create a static public class with a sort method which accepts an internal table with unsorted Integer and an output table which are sorted. For simplification reason the element in the internal table only consists of unsigned integers ( >= 0 )
Bucket Sort ( In China we prefer to call it Hash Sort )
In ABAP the internal table is a perfect choice for bucket collection 🙂 A small trap here is, array in most program language has start index as 0, however in ABAP for internal table it is 1. So be careful about the possibility that 0 appears in the input internal table.
And I also implement a version using JavaScript which can support negative integer in Bucket Sort as well. See source code here.
I have implemented two variants, the only difference between them:
- Variant 1 uses two nested DO LOOP, while variant 2 uses WHILE as inner LOOP.
- Variant 1 uses traditional keyword MODIFY itab FROM workarea INDEX index to swap the two adjacent element, while variant 2 uses new grammar itab[ index ].
Source code for both variants.
Merge Sort
Again I have implemented two variants.
Variant1 - use Recursive
Callstack could be found below:
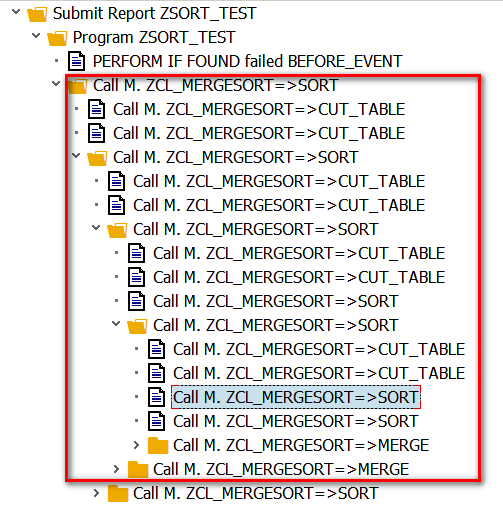
Variant 2 - non recursive version
This variant is implemented in a non-recursive way.

Source code of both variants.
Quick Sort
Selection Sort
Insertion Sort
Heap Sort
Shell Sort
A very draft performance comparison
Since each sort algorithm has different time complexity - best case, worst case and average case according to different data distribution, here below I only make a very draft comparison by generating some random integers in ABAP via cl_abap_random_int:
DATA: lv_seed TYPE i.
lv_seed = sy-timlo.
DATA(lo_ran) = cl_abap_random_int=>create( min = 1 max = 1000 seed = lv_seed ).
DO iv_num TIMES.
APPEND lo_ran->get_next( ) TO rv_table.
ENDDO.Meanwhile I am especially curious about how ABAP keyword SORT will behave against these eight sort algorithms, so I create another two sort approaches.
The ninth sort approach
Pretty simple, just use ABAP keyword SORT to sort the table.
method SORT.
rv_table = iv_table.
SORT rv_table.
endmethod.The tenth sort approach
I just loop the original table and put each element to a sorted table with line item as INT4.
DATA: lt_sorted TYPE ZTSORTED_INT4.
LOOP AT iv_table ASSIGNING FIELD-SYMBOL(<item>).
INSERT <item> INTO table lt_sorted.
ENDLOOP.
APPEND LINES OF lt_sorted TO rv_table.The table type ZTSORTED_INT4 has line type INT4 with sorted table type.

Test code:
DATA(lt_test_data) = zcl_sort_helper=>generate_data( 3000 ).
zcl_sort_helper=>start_measure( ).
DATA(lt_bubble) = zcl_bubblesort=>sort( lt_test_data ).
WRITE: / 'Bubble Sort duration:' , zcl_sort_helper=>stop( ).
zcl_sort_helper=>start_measure( ).
DATA(lt_hashsort) = zcl_hashsort=>sort( lt_test_data ).
WRITE: / 'Hash Sort duration:' , zcl_sort_helper=>stop( ).
zcl_sort_helper=>start_measure( ).
DATA(lt_heapsort) = zcl_hashsort=>sort( lt_test_data ).
WRITE: / 'Heap Sort duration:' , zcl_sort_helper=>stop( ).
zcl_sort_helper=>start_measure( ).
DATA(lt_insertsort) = zcl_insertsort=>sort( lt_test_data ).
WRITE: / 'Insert Sort duration:' , zcl_sort_helper=>stop( ).
zcl_sort_helper=>start_measure( ).
DATA(lt_mergesort) = zcl_mergesort=>sort( lt_test_data ).
WRITE: / 'Merge Sort duration:' , zcl_sort_helper=>stop( ).
zcl_sort_helper=>start_measure( ).
DATA(lt_quicksort) = zcl_quicksort=>sort( lt_test_data ).
WRITE: / 'Quick Sort duration:' , zcl_sort_helper=>stop( ).
zcl_sort_helper=>start_measure( ).
DATA(lt_selectsort) = zcl_selectsort=>sort( lt_test_data ).
WRITE: / 'Select Sort duration:' , zcl_sort_helper=>stop( ).
zcl_sort_helper=>start_measure( ).
DATA(lt_shellsort) = zcl_shellsort=>sort( lt_test_data ).
WRITE: / 'Shell Sort duration:' , zcl_sort_helper=>stop( ).
zcl_sort_helper=>start_measure( ).
DATA(lt_sort_keyword) = zcl_sort_via_keyword=>sort( lt_test_data ).
WRITE: / 'ABAP Sort keyword duration:' , zcl_sort_helper=>stop( ).
zcl_sort_helper=>start_measure( ).
DATA(lt_sort_table) = zcl_abap_sorttable=>sort( lt_test_data ).
WRITE: / 'ABAP Sorted table duration:' , zcl_sort_helper=>stop( ).
ASSERT lt_bubble = lt_hashsort.
ASSERT lt_hashsort = lt_heapsort.
ASSERT lt_heapsort = lt_insertsort.
ASSERT lt_insertsort = lt_mergesort.
ASSERT lt_mergesort = lt_quicksort.
ASSERT lt_quicksort = lt_selectsort.
ASSERT lt_shellsort = lt_selectsort.
ASSERT lt_sort_keyword = lt_shellsort.
ASSERT lt_sort_table = lt_sort_keyword.The test result ( unit: microsecond )

The ABAP SORT keyword and SORTED TABLE did a really good job here 🙂
The complete source code for this blog could be found from my github.
Sleep Sort in JavaScript
Last but not least, the super cool "Sleep Sort" done in JavaScript, which does not need any comparison against two elements in the array.
const num = [1,5,6,11,2,3,4,8,7,14];
num.forEach( num => {
setTimeout( () => { console.log(num)}, num);
});Test output:

Happy coding 🙂
update on 2022-3-26
the latest url is here: https://github.com/wangzixi-diablo/ui5-tutorial/tree/main/abap/sort
- SAP Managed Tags:
- ABAP Development,
- ABAP Testing and Analysis,
- JavaScript
33 Comments
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
Labels in this area
-
A Dynamic Memory Allocation Tool
1 -
ABAP
8 -
abap cds
1 -
ABAP CDS Views
14 -
ABAP class
1 -
ABAP Cloud
1 -
ABAP Development
4 -
ABAP in Eclipse
1 -
ABAP Keyword Documentation
2 -
ABAP OOABAP
2 -
ABAP Programming
1 -
abap technical
1 -
ABAP test cockpit
7 -
ABAP test cokpit
1 -
ADT
1 -
Advanced Event Mesh
1 -
AEM
1 -
AI
1 -
API and Integration
1 -
APIs
8 -
APIs ABAP
1 -
App Dev and Integration
1 -
Application Development
2 -
application job
1 -
archivelinks
1 -
Automation
4 -
BTP
1 -
CAP
1 -
CAPM
1 -
Career Development
3 -
CL_GUI_FRONTEND_SERVICES
1 -
CL_SALV_TABLE
1 -
Cloud Extensibility
8 -
Cloud Native
7 -
Cloud Platform Integration
1 -
CloudEvents
2 -
CMIS
1 -
Connection
1 -
container
1 -
Debugging
2 -
Developer extensibility
1 -
Developing at Scale
3 -
DMS
1 -
dynamic logpoints
1 -
Eclipse ADT ABAP Development Tools
1 -
EDA
1 -
Event Mesh
1 -
Expert
1 -
Field Symbols in ABAP
1 -
Fiori
1 -
Fiori App Extension
1 -
Forms & Templates
1 -
General
1 -
Getting Started
1 -
IBM watsonx
1 -
Integration & Connectivity
9 -
Introduction
1 -
JavaScripts used by Adobe Forms
1 -
joule
1 -
NodeJS
1 -
ODATA
3 -
OOABAP
3 -
Outbound queue
1 -
Product Updates
1 -
Programming Models
14 -
Restful webservices Using POST MAN
1 -
RFC
1 -
RFFOEDI1
1 -
SAP BAS
1 -
SAP BTP
1 -
SAP Build
1 -
SAP Build apps
1 -
SAP Build CodeJam
1 -
SAP CodeTalk
1 -
SAP Odata
1 -
SAP UI5
1 -
SAP UI5 Custom Library
1 -
SAPEnhancements
1 -
SapMachine
1 -
security
3 -
text editor
1 -
Tools
17 -
User Experience
5
Top kudoed authors
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 5 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 1 | |
| 1 |