
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Technology
- Technology Blogs by SAP
- Through the Looking Glass: Requirements Management...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Requirements Management is a new standard process released by SAP Solution Manager 7.2. Note that there is also a requirements management for SAP Solution Manager in release 7.1 available. This is the so-called ST-OST, the focused solution. In addition, there is a Change Request Management add-on for SAP Solution Manager 7.1 provided by consulting.
This article tackles only the new SAP Solution Manager 7.2 standard Requirements Management. As the leading developer, I would like to give you a detailed overview of what you can expect in SAP Solution Manager 7.2.
Overview (Process and Architecture):
Requirements Management in release 7.2 consists of two new documents in the CRM Web UI: the Business Requirement and the IT Requirement.
The Business Requirement (SMBR) is used by the LoB for documenting and requesting new requirements. The IT Requirement is used by the IT department for evaluating requirements. There is an integration with Change Request Management, which means that you can create change documents via the IT Requirement and implement by using Change Request Management functionality. In many ways, the IT Requirement is with respect to its functionality an equivalent to the Request for Change. However, there are some differences, which we will explore later on. The full scenario runs now from the Business Requirement via the IT Requirement to the change documents. Normally, in larger companies, the LoB and the IT department are different departments with different cost centers. The LoB department pays the IT department for its services. In some scenarios, the IT department is outsourced and thus a separate company like a service provider.
That is why architecturally we decided to separate the process into two different documents, one for each department. It is a lot easier to differentiate authorities or other functionalities in CRM Web UI if you have two separate documents.
Yet if the LoB and the IT department are not separated or work very closely, you can as well use the IT Requirement standalone without the Business Requirement. This will simplify matters.
Currently, the relationship between the Business Requirement (BR) and IT Requirement (ITR) is 1:1. We are aware that this should be expanded and therefore are working towards a 1:N relationship for a future release.
Technically, Requirements Management builds upon the Change Request Management framework. For Change Request Management consultants, this makes Requirements Management a natural choice for expanding their consulting services.
For you to obtain an insight view into the Change Request Management framework, I provide some information
here.
Roles:
Standard Requirements Management is delivered with eight roles.
| Role | Document/Area | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Configuration user | SAP Solution Manager Configuration | Used to setup Requirements Management in SAP Solution Manager Configuration |
| Business process expert | Business Requirement | The business process expert knows the specific business process he is responsible for. He is the connection between business department and IT department. He is contacted for new requirements by the business department. He creates the Business Requirement and fills it with information on how it should work. |
| Business manager | Business Requirement | The business manager prioritizes Business Requirements and decides which requirements shall be evaluated by IT. He gives the final commitment from the business side so the implementation of the requirement can start. |
| BR admin | Business Requirement | The BR admin is the administrator for the Business Requirement document. He is able to set all user statuses, can view all document information, and searches and creates Business Requirements. He's the power user for the Business Requirement. |
| Solution architect | IT Requirement | The solution architect processes the IT Requirement in Change Request Management. He acts as a leading developer. He evaluates the requirement, which are requested by the LoB. He creates the high-level design. He knows the landscape and releases cycles. He knows the development team and the systems as well as techniques involved. He communicates with the development team to get an evaluation regarding capacity, cost, and feasibility. If the requirement gets implemented, he is authorized to create change documents as follow-up documents from the ITR. If there are questions, he communicates with the business process owner to clarify them. |
| Requirements manager | IT Requirement | The requirements manager is the manager of the IT Requirement. He prioritizes IT Requirements, hands the IT Requirements over to the solution architect so the requirements can be evaluated and analyzed. He approves the evaluation and commits from the IT side that the requirement can be implemented for a particular release and date at a specific expense and with a specific capacity and technique. |
| IT admin | IT Requirement | The IT admin is the administrator for the IT Requirement document. He is able to set all user statuses and access all its information. It’s a power user role for an IT Requirement. He can do everything that a solution architect and requirements manager can do combined. |
| Display user | Business Requirement and IT Requirement | The display user is able to search for and display the entire requirements process, meaning all IT Requirements, Business Requirements and Change Request Management documents. |
The General Process Flow:
The process starts with the business process expert who gets a requirement by an optional channel (e-mail, discussion, etc.). He creates a business requirement and defines it by describing the requirement, filling in the relevant business manager and possibly the requirements manager.
My recommendation for you is to attach a link to the Attachment assignment block to the document because the link is copied to the IT Requirement later. Then all people involved will see the working document in its latest version. Yet, you could as well use the solution documentation feature and assign the involved process and the document there.
After the Business Requirement is reviewed and was approved by the business manager, the requirement is handed over to IT. This means that automatically an IT Requirement is created as a follow-up document. The responsible requirements manager fills in a solution architect who checks the requirement in respect of capacity, cost, and feasibility.
After the analysis is approved by the requirements manager in the IT Requirement, this status is reflected in the Business Requirement by the specific user status. The business manager checks the proposal from IT again and approves that the requirement should be implemented in the proposed way.
After the approval has been done, the solution architect can now start implementing on the IT Requirement and create follow-up change documents as well as assign them to the relevant developers.
The implementations are done using Change Request Management functionality, which provides TMS integration. Later, all developments are done and the requirement has been tested successfully and is productive. This is reflected back to the IT and Business Requirement by the change documents. Now the IT Requirement and Business Requirement can be closed as well.
Status and their meaning
Business Requirement
| Status | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Define | Requirement is described by the business process expert. |
| Submitted for Validation | Requirement has been described and awaits review and priorization. It is similar to a queue status. |
| Being Checked | Requirement is priorized and reviewed by the business manager. |
| Rejected | Requirement will not be realized because for various reasons such as budget, company strategy. |
| Postponed | Requirement remains currently in focus but is kept for later. Parking queue. |
| Handed Over to IT | Business manager has decided that the requirement should be analyzed by the IT department because it is in focus. The IT Requirement will be created. |
| Requirement Rejected by IT | The IT department has rejected the IT Requirement. There are sound reasons why it cannot be done. There could be technical, budget, capacity or budget reasons. The solution architect and the business process expert should clarify if the requirement should be changed in a way that it fits. Otherwise, it should be rejected in the Business Requirement. This would set the IT requirement to Completed. |
| Postponed by IT | The IT department has set the IT Requirement to Postponed for various reasons such as capacity. |
Committed by IT | IT department has analyzed the requirement based on capacity, cost, and feasibility and they commit that they can execute it to the agreed terms. |
| Implemented | The requirement is productive. |
| Completed | The process is completed. |
IT Requirement
| Status | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Define | The requirement is handed over to the IT department so the evaluation can start. The requirements manager checks and identifies a solution architect. |
| Submitted for Validation | This is the working queue for the solution architect. He can check which requirements he needs to analyze. |
| Being Checked | The solution architect is working on the requirement and evaluates it with respect to capacity, cost, and feasibility. |
| Rejected | There are reasons why the requirement cannot be implemented. The business requirement is set to Rejected by IT so the business process expert knows that he has to speak to the solution architect. |
| Submitted for Approval | Evaluation is finished and the requirement is in the queue to be approved. |
| Postponed | The approval is postponed, maybe due to lack of capacity despite being ok with regard to function and expense. |
| Approval | The requirement is approved and committed by the requirements manager to be implemented based on capacity, cost, and feasibility. The Business Requirement is set to Committed by IT. |
| Submitted for Implementation | The business manager has accepted the commitment of the IT department. Implementation can start now. Technical information like change cycle, systems, and scope is maintained by the solution architect. |
| Implement | The requirement is implemented. Change documents are created and additional ones can be easily created by enhancing the scope. The implementation process continues with theocuments. |
| Implemented | The requirement is tested successfully and productively. The business requirement is set to Implemented. |
| Completed | The process in the IT requirement is completed. |
Here is a complete overview of the statuses that are available in the process and how you can set/reach them. There is more technical Information, for example, the name of the PPF actions. Setting the user status are listed as well.
Enhanced Change Request Management Framework:
Somebody who is familiar with the ChaRM framework and checking the status process overview above will notice that the Business Requirement pushes the status of the IT Requirement in same cases. The ChaRM Framework in release 7.10 has the so-called set predecessor functionality, which sets the status of a predecessor document depending on the status of all successor documents of the specific predecessor document.
Yet setting the status of a successor document is new in release 7.20. If you check the Customizing activity Make Settings for Change Transaction Types (also available in SAP Solution Manager Configuration), you find new Customizing for setting the predecessor status.
The screenshot displays the Customizing that defines that the Business Requirement which has status Accepted sets the status Submitted for Implementation in the IT Requirement.

The prerequisite to make it work is that you have assigned the relevant ChaRM framework actions and consistency checks for executing the Customizing.
The ChaRM consistency check is called SUCCDOC_CAN_BE_SET.
It should be called via regular execution.

The ChaRM action is called via SET_SUCCDOC.

It should be called as a late action.

My Business Requirement Fiori App:
The Fiori app was developed because the LoB is used on simple and up-to-date UIs. Fiori as the current state-of-the-art SAP UI is the best choice.
The My Business Requirements Fiori app is a classic master/detail Fiori app. Thanks to a tile you can see the number of Business Requirements to which your business partner is assigned and which of them are not completed.
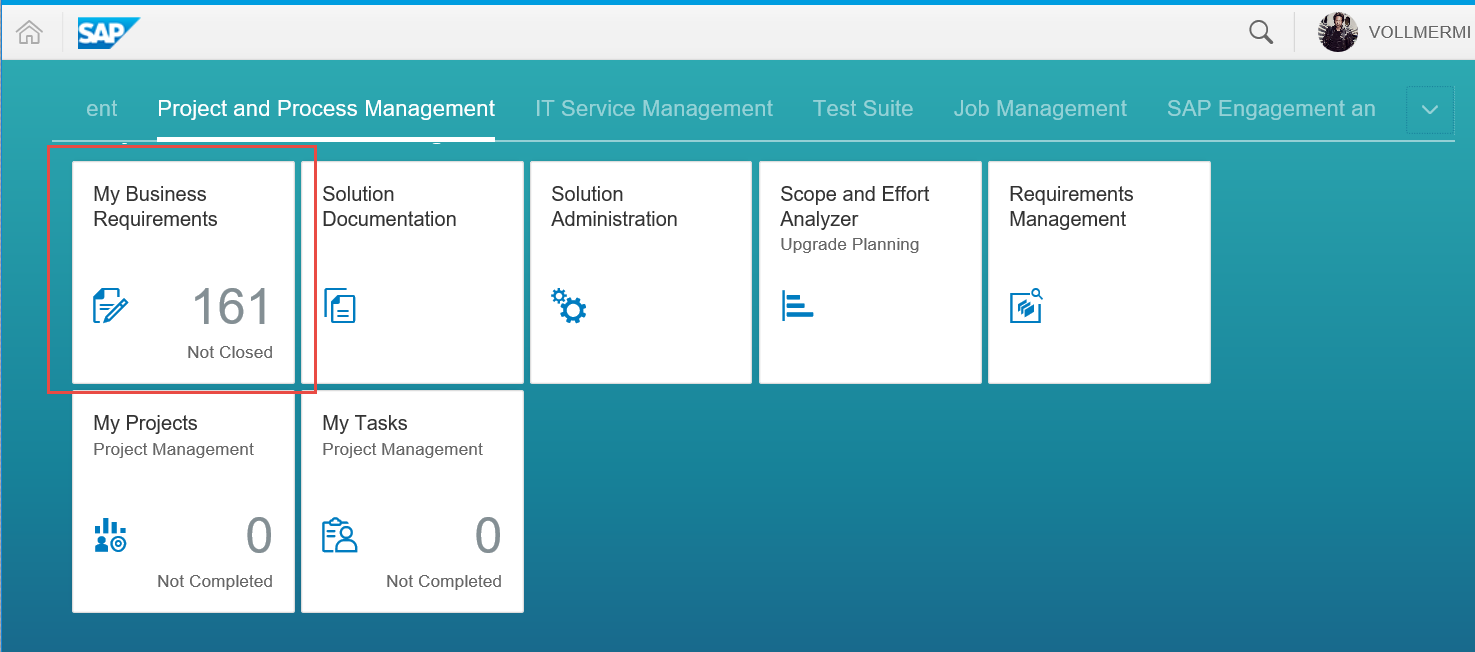
When you enter the app, you see the master/detail screen with the list of your Business Requirements. On the right side, you have the detail screen with further information. You can display and edit the data or create new Business Requirements.
The displayed data is visible on three tabs. The header information which is as well displayed on the master list consists of the description, the priority, and the user status.
The Conversation tab includes the texts which are entered. Additionally, it is possible to enter further text.
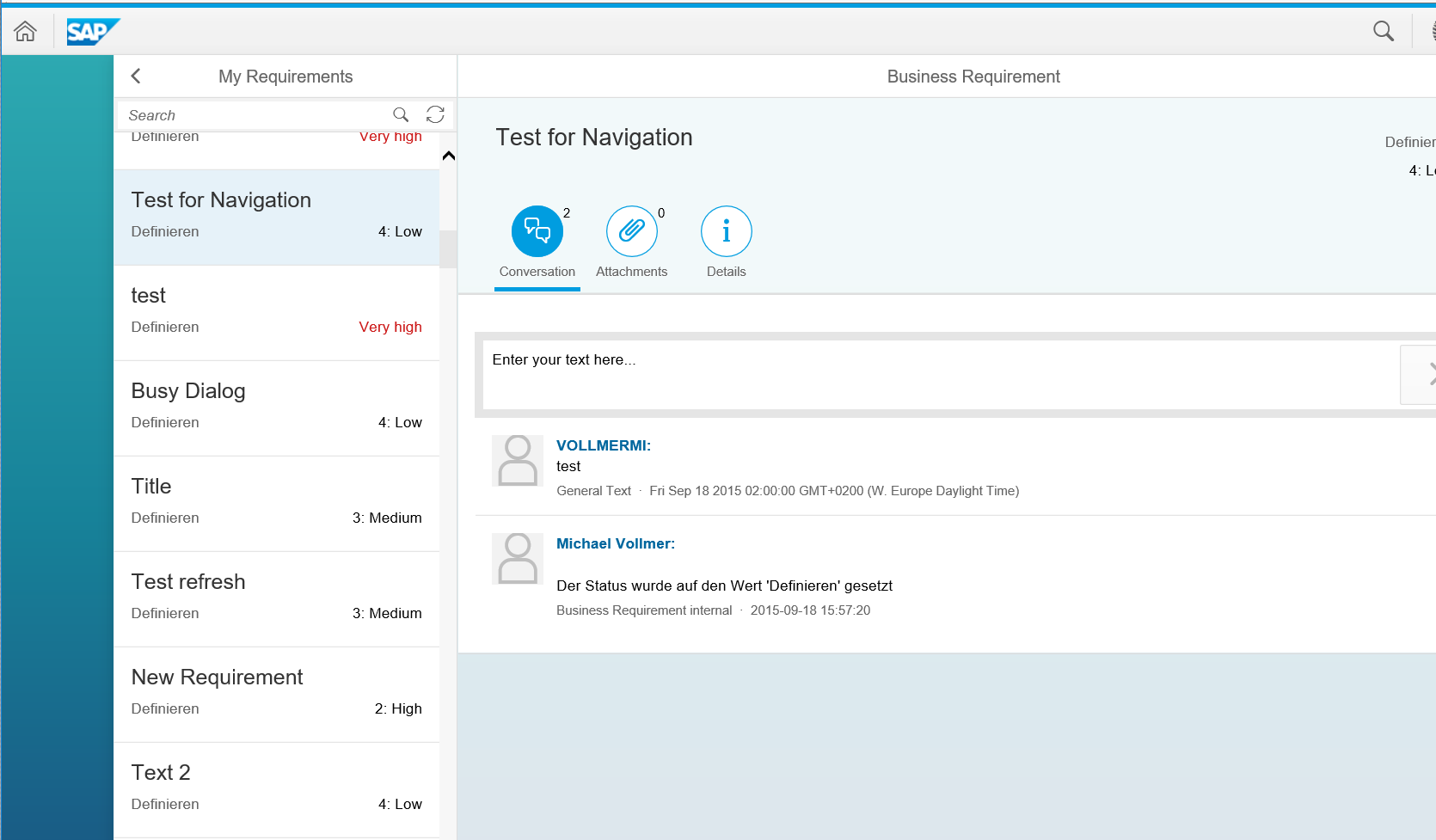
The Details tab includes the Business Requirement number (object ID), the creator and creation date, the first three business partners customized on the CRM Web UI, the priority and the category. The texts of the business partners are read dynamically from the backend which means that if you customize other first three business partners in the CRM Web UI, this is applied here automatically.

The Attachments tab contains attachments and enables the user to display and upload them.

The master list can be grouped...

...and filtered by user status. Both status data is read from the backend. It shows in the screenshot where you can only see German status texts in the system. This means you add a new status to your process. This works automatically.
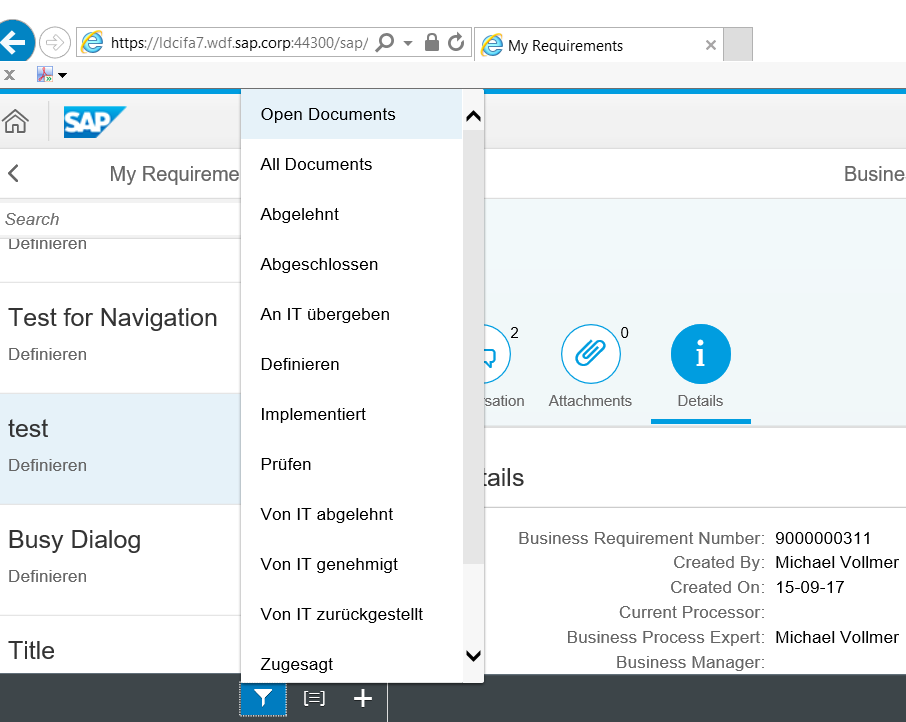
The app allows you to set a user status.
Technical background: As in Requirements Management the user status is changed by a PPF action using the
ChaRM framework, the relevant PPF actions are defined first. The customized PPF action container element USER_STATUS defines which status should be set. This technical user status is defined and the description is read from the technical user status. That's why you see here that the user status is to be set. In the screenshot further down, it is displayed by the German text Zur Prüfung eingereicht, which is equivalent to Submitted for Validation.

It is possible to edit nearly all Details fields (with the exception of Category).

You can create new Business Requirements. Both the edit and create mode support a live search of the business partners. In addition, you can search by the criteria Name or the Business Partner Number.

IT Requirement vs Request for Change: Similarities and Differences
Primarily the IT requirement as it is created from a business requirement is used in the field of innovations, the request for change is used for maintenance purposes.
Approval Procedure
The standard IT Requirement does not require an approval procedure like the Request for Change. Also, it has a different status flow. Therefore, you do not need the 'Extend Scope' process part like you would for the Request for Change.
Requirements Management provides a mutual commitment.
I see strong similarities between this process and a bid invitation, bid and purchase.
When we compare them, it looks like this: First the LoB 'creates a bid invitation', which refers to the Business Requirement changing to status Handed Over to IT. On the IT Requirement side, the IT department analyzes and 'commits the bid' by setting the status Approved. The LoB checks the additional cost for roll-out, etc., and commits itself by 'purchasing' the implementation service.
Remark: It is possible to use the approval procedure functionality for the IT Requirement (as well as for the Business Requirement). It just has to be customized.
Checklist
For evaluation of the requirement, the standard IT Requirement has a Checklist assignment block delivered by SAP. Via this assignment block, a standard checklist can be selected which supports the solution architect by validating the requirement. We just deliver an example checklist as we assume each customer customizes one of his own.

Creating Change documents
If the IT Requirement has status Submitted for Implementation or Implement, it is generally considered to be approved by LoB. As it is a new requirement and will mainly be implemented by running a project, the creation of change documents is only a technical procedure to process the implementation. Therefore, you can just add additional scope items and create the change documents by choosing the Actions pushbutton at these statuses.
Dependency on Business Requirement
The IT Requirement has a Business Requirement as a predecessor document. The Request for Change normally has an incident as a predecessor document.
ITPPM Integration
Naturally, as new requirements are innovative and are handled by projects, there is a strong ITPPM integration equivalent to the Request for Change.
BPCA Integration
There is no difference between an IT Requirement and a Request for Change. It is possible to perform a BPCA integration for both documents.
Solution Documentation Integration
The IT Requirement has the same full support for solution documentation as the Request for Change.

In the branch, you are able to see related Business and IT Requirements for a solution documentation element.

If you choose the link of a specific related document type, you can view more details and assign further documents. In addition, you can delete existing ones or jump directly to the CRM Web UI to create a specific new document of this particular type (a business requirement as you can see below).

That's basically all that comes to my mind. I hope I was able to provide an update. If you find errors or want to give feedback, feel free to get in contact with me.
Best regards, Michael
- SAP Managed Tags:
- SAP Solution Manager
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
ABAP CDS Views - CDC (Change Data Capture)
2 -
AI
1 -
Analyze Workload Data
1 -
BTP
1 -
Business and IT Integration
2 -
Business application stu
1 -
Business Technology Platform
1 -
Business Trends
1,658 -
Business Trends
93 -
CAP
1 -
cf
1 -
Cloud Foundry
1 -
Confluent
1 -
Customer COE Basics and Fundamentals
1 -
Customer COE Latest and Greatest
3 -
Customer Data Browser app
1 -
Data Analysis Tool
1 -
data migration
1 -
data transfer
1 -
Datasphere
2 -
Event Information
1,400 -
Event Information
66 -
Expert
1 -
Expert Insights
177 -
Expert Insights
299 -
General
1 -
Google cloud
1 -
Google Next'24
1 -
Kafka
1 -
Life at SAP
780 -
Life at SAP
13 -
Migrate your Data App
1 -
MTA
1 -
Network Performance Analysis
1 -
NodeJS
1 -
PDF
1 -
POC
1 -
Product Updates
4,577 -
Product Updates
345 -
Replication Flow
1 -
RisewithSAP
1 -
SAP BTP
1 -
SAP BTP Cloud Foundry
1 -
SAP Cloud ALM
1 -
SAP Cloud Application Programming Model
1 -
SAP Datasphere
2 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud
1 -
SAP S4HANA Migration Cockpit
1 -
Technology Updates
6,873 -
Technology Updates
427 -
Workload Fluctuations
1
- Supporting Multiple API Gateways with SAP API Management – using Azure API Management as example in Technology Blogs by SAP
- SAP Build Process Automation Pre-built content for Finance Use cases in Technology Blogs by SAP
- Consuming SAP with SAP Build Apps - Mobile Apps for iOS and Android in Technology Blogs by SAP
- Onboarding Users in SAP Quality Issue Resolution in Technology Blogs by SAP
- How to host static webpages through SAP CPI-Iflow in Technology Blogs by Members
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 40 | |
| 25 | |
| 17 | |
| 14 | |
| 8 | |
| 7 | |
| 7 | |
| 7 | |
| 6 | |
| 6 |