
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Technology
- Technology Blogs by Members
- SAP Business Objects Dashboard (BCO6181, VUT)
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
SAP Business Objects Dashboard (BCO6181, VUT)
Definition
A dashboard is a collection of information that improves performance of the business and individual as well as easily accessible. The collection of information comes from different sources and in different formats.
“Dashboard design is a story-telling. A good story contains a beginning, an end and a point.”
There is a 5-step process that one can follow to be successful in their dashboard deployment.
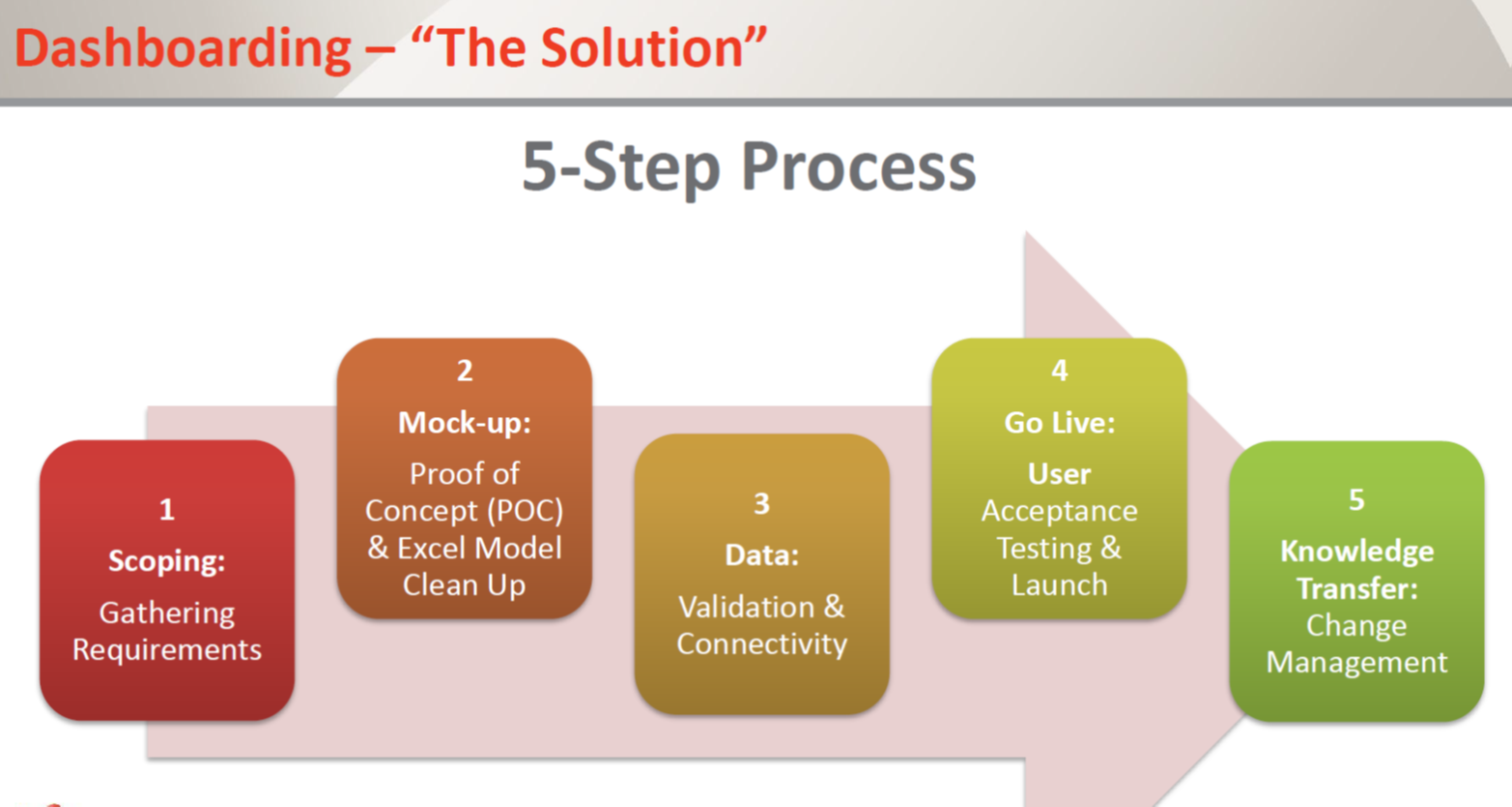
Step-1 Scoping
It includes various steps. Firstly, conduct scoping sessions and gather requirements such as data, design and functional. Who is the solution designed for? What decision will be made with the solution?
- Scan the KPI’s (Look for exceptions by scanning multiple reports daily)
- Isolate the problems(Look through several reports that contain detailed data to determine which specific area needs attention)
- Determine the root cause(Conduct OLAP analysis to analyse related dimension to determine root cause of the problem)
Step-2 Mock-up
Start with implement design requirements and functional requirements such as dashboard layout, dashboard look, and user interaction and navigation placement on dashboard.
Step-3 Data
This step includes validation and connectivity data sources, data output format, availability of data and SAP BW (BICS), Non-SAP (Flynet), BOBJ (Query browser, Live Office, BIWS, Antivia) respectively.
Step-4 Go-Live
Go-Live have user acceptance testing (UAT). Unit and performance testing is done to check the functionality and data quality. After that, in launch phase, adoption of high users is done and prepares it for next phase.
Step-5 Knowledge Transfer
This includes two steps- documentation (Technical and end user guide) and training (socialize dashboard with end users).
Dashboard Needs
Business needs
- Able to manage and monitor metrics
- High-impact interactive visualization of key metrics.
- Navigation and intuitive user interface
- Personalized content and display
Technology needs
- Scalable for growing organization
- Flexible because of changing needs of the organization
- Dashboard building capabilities are easy
- To leverage existing BI investments, integration is done.
- Security to ensure access by proper user.
Dashboard Use Cases
Executive Monitoring- It includes constant updates, task and action, view at a glance, drill down to detail and exception highlights. If an executive wants to review their critical information in an attractive and accessible format then executive monitoring is helpful.
Visualization Package- Visualization package have attractive evidence, highlight message, local data, limited interaction. It help analyst to create incredible output that impress people and they react to information.
Interactive Application- It helps to browse vast data, designed user experience, Interactive controls, action and process. Through this, people can change assumptions, make plans and review alternatives.
Information Wall- It gives constantly updates and provides information quickly about task. It has limited interaction and data, unattended operations and it also design user experience.
We are gladly thankful to our SAP mentors Paul Hawking and Tony de Thomasis.
Related Links
http://www.sdn.sap.com/irj/uac/library-bi#section8
http://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=xcelsius&aq=f
Group Members
Ravneet Kaur
Rajinder Kaur
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
"automatische backups"
1 -
"regelmäßige sicherung"
1 -
505 Technology Updates 53
1 -
ABAP
14 -
ABAP API
1 -
ABAP CDS Views
2 -
ABAP CDS Views - BW Extraction
1 -
ABAP CDS Views - CDC (Change Data Capture)
1 -
ABAP class
2 -
ABAP Cloud
2 -
ABAP Development
5 -
ABAP in Eclipse
1 -
ABAP Platform Trial
1 -
ABAP Programming
2 -
abap technical
1 -
absl
1 -
access data from SAP Datasphere directly from Snowflake
1 -
Access data from SAP datasphere to Qliksense
1 -
Accrual
1 -
action
1 -
adapter modules
1 -
Addon
1 -
Adobe Document Services
1 -
ADS
1 -
ADS Config
1 -
ADS with ABAP
1 -
ADS with Java
1 -
ADT
2 -
Advance Shipping and Receiving
1 -
Advanced Event Mesh
3 -
AEM
1 -
AI
7 -
AI Launchpad
1 -
AI Projects
1 -
AIML
9 -
Alert in Sap analytical cloud
1 -
Amazon S3
1 -
Analytical Dataset
1 -
Analytical Model
1 -
Analytics
1 -
Analyze Workload Data
1 -
annotations
1 -
API
1 -
API and Integration
3 -
API Call
2 -
Application Architecture
1 -
Application Development
5 -
Application Development for SAP HANA Cloud
3 -
Applications and Business Processes (AP)
1 -
Artificial Intelligence
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
4 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) 1 Business Trends 363 Business Trends 8 Digital Transformation with Cloud ERP (DT) 1 Event Information 462 Event Information 15 Expert Insights 114 Expert Insights 76 Life at SAP 418 Life at SAP 1 Product Updates 4
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise Oil Gas IoT Exploration Production
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise sustainability responsibility esg social compliance cybersecurity risk
1 -
ASE
1 -
ASR
2 -
ASUG
1 -
Attachments
1 -
Authorisations
1 -
Automating Processes
1 -
Automation
1 -
aws
2 -
Azure
1 -
Azure AI Studio
1 -
B2B Integration
1 -
Backorder Processing
1 -
Backup
1 -
Backup and Recovery
1 -
Backup schedule
1 -
BADI_MATERIAL_CHECK error message
1 -
Bank
1 -
BAS
1 -
basis
2 -
Basis Monitoring & Tcodes with Key notes
2 -
Batch Management
1 -
BDC
1 -
Best Practice
1 -
bitcoin
1 -
Blockchain
3 -
BOP in aATP
1 -
BOP Segments
1 -
BOP Strategies
1 -
BOP Variant
1 -
BPC
1 -
BPC LIVE
1 -
BTP
11 -
BTP Destination
2 -
Business AI
1 -
Business and IT Integration
1 -
Business application stu
1 -
Business Architecture
1 -
Business Communication Services
1 -
Business Continuity
1 -
Business Data Fabric
3 -
Business Partner
12 -
Business Partner Master Data
10 -
Business Technology Platform
2 -
Business Trends
1 -
CA
1 -
calculation view
1 -
CAP
2 -
Capgemini
1 -
Catalyst for Efficiency: Revolutionizing SAP Integration Suite with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and
1 -
CCMS
2 -
CDQ
12 -
CDS
2 -
Cental Finance
1 -
Certificates
1 -
CFL
1 -
Change Management
1 -
chatbot
1 -
chatgpt
3 -
CL_SALV_TABLE
2 -
Class Runner
1 -
Classrunner
1 -
Cloud ALM Monitoring
1 -
Cloud ALM Operations
1 -
cloud connector
1 -
Cloud Extensibility
1 -
Cloud Foundry
3 -
Cloud Integration
6 -
Cloud Platform Integration
2 -
cloudalm
1 -
communication
1 -
Compensation Information Management
1 -
Compensation Management
1 -
Compliance
1 -
Compound Employee API
1 -
Configuration
1 -
Connectors
1 -
Consolidation Extension for SAP Analytics Cloud
1 -
Conversion
1 -
Cosine similarity
1 -
cryptocurrency
1 -
CSI
1 -
ctms
1 -
Custom chatbot
3 -
Custom Destination Service
1 -
custom fields
1 -
Customer Experience
1 -
Customer Journey
1 -
Customizing
1 -
Cyber Security
2 -
Data
1 -
Data & Analytics
1 -
Data Aging
1 -
Data Analytics
2 -
Data and Analytics (DA)
1 -
Data Archiving
1 -
Data Back-up
1 -
Data Governance
5 -
Data Integration
2 -
Data Quality
12 -
Data Quality Management
12 -
Data Synchronization
1 -
data transfer
1 -
Data Unleashed
1 -
Data Value
8 -
database tables
1 -
Datasphere
2 -
datenbanksicherung
1 -
dba cockpit
1 -
dbacockpit
1 -
Debugging
2 -
Delimiting Pay Components
1 -
Delta Integrations
1 -
Destination
3 -
Destination Service
1 -
Developer extensibility
1 -
Developing with SAP Integration Suite
1 -
Devops
1 -
digital transformation
1 -
Documentation
1 -
Dot Product
1 -
DQM
1 -
dump database
1 -
dump transaction
1 -
e-Invoice
1 -
E4H Conversion
1 -
Eclipse ADT ABAP Development Tools
2 -
edoc
1 -
edocument
1 -
ELA
1 -
Embedded Consolidation
1 -
Embedding
1 -
Embeddings
1 -
Employee Central
1 -
Employee Central Payroll
1 -
Employee Central Time Off
1 -
Employee Information
1 -
Employee Rehires
1 -
Enable Now
1 -
Enable now manager
1 -
endpoint
1 -
Enhancement Request
1 -
Enterprise Architecture
1 -
ETL Business Analytics with SAP Signavio
1 -
Euclidean distance
1 -
Event Dates
1 -
Event Driven Architecture
1 -
Event Mesh
2 -
Event Reason
1 -
EventBasedIntegration
1 -
EWM
1 -
EWM Outbound configuration
1 -
EWM-TM-Integration
1 -
Existing Event Changes
1 -
Expand
1 -
Expert
2 -
Expert Insights
1 -
Fiori
14 -
Fiori Elements
2 -
Fiori SAPUI5
12 -
Flask
1 -
Full Stack
8 -
Funds Management
1 -
General
1 -
Generative AI
1 -
Getting Started
1 -
GitHub
8 -
Grants Management
1 -
groovy
1 -
GTP
1 -
HANA
5 -
HANA Cloud
2 -
Hana Cloud Database Integration
2 -
HANA DB
1 -
HANA XS Advanced
1 -
Historical Events
1 -
home labs
1 -
HowTo
1 -
HR Data Management
1 -
html5
8 -
Identity cards validation
1 -
idm
1 -
Implementation
1 -
input parameter
1 -
instant payments
1 -
Integration
3 -
Integration Advisor
1 -
Integration Architecture
1 -
Integration Center
1 -
Integration Suite
1 -
intelligent enterprise
1 -
Java
1 -
job
1 -
Job Information Changes
1 -
Job-Related Events
1 -
Job_Event_Information
1 -
joule
4 -
Journal Entries
1 -
Just Ask
1 -
Kerberos for ABAP
8 -
Kerberos for JAVA
8 -
Launch Wizard
1 -
Learning Content
2 -
Life at SAP
1 -
lightning
1 -
Linear Regression SAP HANA Cloud
1 -
local tax regulations
1 -
LP
1 -
Machine Learning
2 -
Marketing
1 -
Master Data
3 -
Master Data Management
14 -
Maxdb
2 -
MDG
1 -
MDGM
1 -
MDM
1 -
Message box.
1 -
Messages on RF Device
1 -
Microservices Architecture
1 -
Microsoft Universal Print
1 -
Middleware Solutions
1 -
Migration
5 -
ML Model Development
1 -
Modeling in SAP HANA Cloud
8 -
Monitoring
3 -
MTA
1 -
Multi-Record Scenarios
1 -
Multiple Event Triggers
1 -
Neo
1 -
New Event Creation
1 -
New Feature
1 -
Newcomer
1 -
NodeJS
1 -
ODATA
2 -
OData APIs
1 -
odatav2
1 -
ODATAV4
1 -
ODBC
1 -
ODBC Connection
1 -
Onpremise
1 -
open source
2 -
OpenAI API
1 -
Oracle
1 -
PaPM
1 -
PaPM Dynamic Data Copy through Writer function
1 -
PaPM Remote Call
1 -
PAS-C01
1 -
Pay Component Management
1 -
PGP
1 -
Pickle
1 -
PLANNING ARCHITECTURE
1 -
Popup in Sap analytical cloud
1 -
PostgrSQL
1 -
POSTMAN
1 -
Process Automation
2 -
Product Updates
4 -
PSM
1 -
Public Cloud
1 -
Python
4 -
Qlik
1 -
Qualtrics
1 -
RAP
3 -
RAP BO
2 -
Record Deletion
1 -
Recovery
1 -
recurring payments
1 -
redeply
1 -
Release
1 -
Remote Consumption Model
1 -
Replication Flows
1 -
Research
1 -
Resilience
1 -
REST
1 -
REST API
1 -
Retagging Required
1 -
Risk
1 -
Rolling Kernel Switch
1 -
route
1 -
rules
1 -
S4 HANA
1 -
S4 HANA Cloud
1 -
S4 HANA On-Premise
1 -
S4HANA
3 -
S4HANA_OP_2023
2 -
SAC
10 -
SAC PLANNING
9 -
SAP
4 -
SAP ABAP
1 -
SAP Advanced Event Mesh
1 -
SAP AI Core
8 -
SAP AI Launchpad
8 -
SAP Analytic Cloud Compass
1 -
Sap Analytical Cloud
1 -
SAP Analytics Cloud
4 -
SAP Analytics Cloud for Consolidation
2 -
SAP Analytics Cloud Story
1 -
SAP analytics clouds
1 -
SAP BAS
1 -
SAP Basis
6 -
SAP BODS
1 -
SAP BODS certification.
1 -
SAP BTP
20 -
SAP BTP Build Work Zone
2 -
SAP BTP Cloud Foundry
5 -
SAP BTP Costing
1 -
SAP BTP CTMS
1 -
SAP BTP Innovation
1 -
SAP BTP Migration Tool
1 -
SAP BTP SDK IOS
1 -
SAP Build
11 -
SAP Build App
1 -
SAP Build apps
1 -
SAP Build CodeJam
1 -
SAP Build Process Automation
3 -
SAP Build work zone
10 -
SAP Business Objects Platform
1 -
SAP Business Technology
2 -
SAP Business Technology Platform (XP)
1 -
sap bw
1 -
SAP CAP
1 -
SAP CDC
1 -
SAP CDP
1 -
SAP Certification
1 -
SAP Cloud ALM
4 -
SAP Cloud Application Programming Model
1 -
SAP Cloud Integration for Data Services
1 -
SAP cloud platform
8 -
SAP Companion
1 -
SAP CPI
3 -
SAP CPI (Cloud Platform Integration)
2 -
SAP CPI Discover tab
1 -
sap credential store
1 -
SAP Customer Data Cloud
1 -
SAP Customer Data Platform
1 -
SAP Data Intelligence
1 -
SAP Data Migration in Retail Industry
1 -
SAP Data Services
1 -
SAP DATABASE
1 -
SAP Dataspher to Non SAP BI tools
1 -
SAP Datasphere
9 -
SAP DRC
1 -
SAP EWM
1 -
SAP Fiori
2 -
SAP Fiori App Embedding
1 -
Sap Fiori Extension Project Using BAS
1 -
SAP GRC
1 -
SAP HANA
1 -
SAP HCM (Human Capital Management)
1 -
SAP HR Solutions
1 -
SAP IDM
1 -
SAP Integration Suite
9 -
SAP Integrations
4 -
SAP iRPA
2 -
SAP Learning Class
1 -
SAP Learning Hub
1 -
SAP Odata
2 -
SAP on Azure
1 -
SAP PartnerEdge
1 -
sap partners
1 -
SAP Password Reset
1 -
SAP PO Migration
1 -
SAP Prepackaged Content
1 -
SAP Process Automation
2 -
SAP Process Integration
2 -
SAP Process Orchestration
1 -
SAP S4HANA
2 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud
1 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud for Finance
1 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud private edition
1 -
SAP Sandbox
1 -
SAP STMS
1 -
SAP SuccessFactors
2 -
SAP SuccessFactors HXM Core
1 -
SAP Time
1 -
SAP TM
2 -
SAP Trading Partner Management
1 -
SAP UI5
1 -
SAP Upgrade
1 -
SAP-GUI
8 -
SAP_COM_0276
1 -
SAPBTP
1 -
SAPCPI
1 -
SAPEWM
1 -
sapmentors
1 -
saponaws
2 -
SAPUI5
4 -
schedule
1 -
Secure Login Client Setup
8 -
security
9 -
Selenium Testing
1 -
SEN
1 -
SEN Manager
1 -
service
1 -
SET_CELL_TYPE
1 -
SET_CELL_TYPE_COLUMN
1 -
SFTP scenario
2 -
Simplex
1 -
Single Sign On
8 -
Singlesource
1 -
SKLearn
1 -
soap
1 -
Software Development
1 -
SOLMAN
1 -
solman 7.2
2 -
Solution Manager
3 -
sp_dumpdb
1 -
sp_dumptrans
1 -
SQL
1 -
sql script
1 -
SSL
8 -
SSO
8 -
Substring function
1 -
SuccessFactors
1 -
SuccessFactors Time Tracking
1 -
Sybase
1 -
system copy method
1 -
System owner
1 -
Table splitting
1 -
Tax Integration
1 -
Technical article
1 -
Technical articles
1 -
Technology Updates
1 -
Technology Updates
1 -
Technology_Updates
1 -
Threats
1 -
Time Collectors
1 -
Time Off
2 -
Tips and tricks
2 -
Tools
1 -
Trainings & Certifications
1 -
Transport in SAP BODS
1 -
Transport Management
1 -
TypeScript
1 -
unbind
1 -
Unified Customer Profile
1 -
UPB
1 -
Use of Parameters for Data Copy in PaPM
1 -
User Unlock
1 -
VA02
1 -
Validations
1 -
Vector Database
1 -
Vector Engine
1 -
Visual Studio Code
1 -
VSCode
1 -
Web SDK
1 -
work zone
1 -
workload
1 -
xsa
1 -
XSA Refresh
1
- « Previous
- Next »
- Setup of Synthetic User Monitoring in SAP Cloud ALM in Technology Blogs by Members
- Streamline the updates for SAP HANA Cloud with SAP Automation Pilot in Technology Blogs by SAP
- Exploring SAP Cloud ALM and its functionalities in Technology Blogs by Members
- Language Code for SAP Business Warehouse Application Server Power BI Connector in Technology Q&A
- Integrating IBM Security Verify with SAP Cloud Identity Services in SAP BTP in Technology Blogs by Members
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 9 | |
| 8 | |
| 7 | |
| 5 | |
| 5 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 |