
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Technology
- Technology Blogs by SAP
- SAP® Replication Server® Data Assurance
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Why Data Assurance?
We are in a data driven economy, where data drives business. Business agility depends on data availability, where it is needed, when it is needed. Accurate decisions depend on the consistency of the data. While SAP® Replication Server® delivers data in real-time, across boundaries, the SAP® Replication Server® Data Assurance insures the consistency of data where it is needed, when it is needed. SAP® Replication Server® Data Assurance is the data insurance protection for critical business data consistency.
What is Data Assurance?
SAP® Replication Server® Data Assurance compares row data and schema between two or more databases, and reports discrepancies, and helps reconcile inconsistencies. SAP Replication Server Data Assurance is a scalable, high-volume, and configurable data comparison product. It allows users to run comparison jobs even during replication by using a “wait and retry” strategy that eliminates any down time. SAP Replication Server Data Assurance is available as part of the SAP® Replication Server® Premium Edition in the 2015 Packaging.
Data Assurance Product Overview
Ensures data consistency between sources and targets
- Support different data type comparisons
- Usability
- Data Assurance can run as a Windows Service
- Supported databases:
- HANA, ASE, IQ
- Oracle, MS SQL, IBM DB2
Supported Topologies
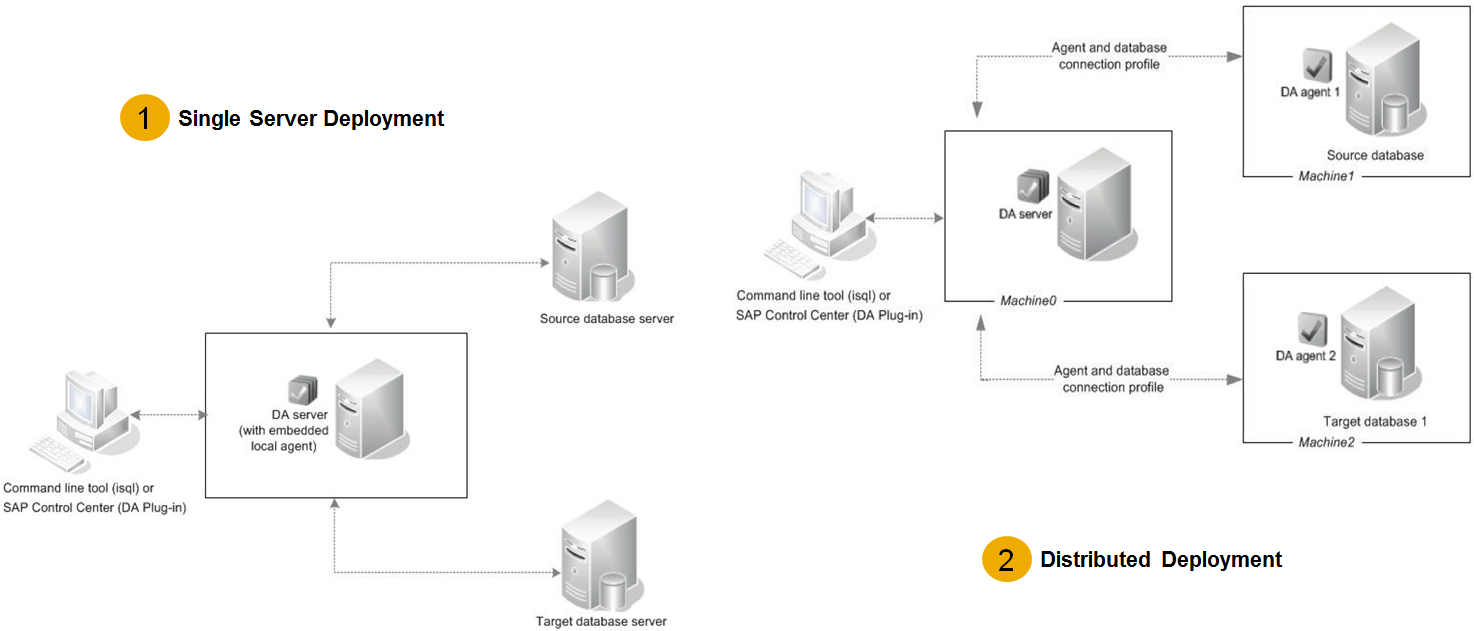
Figure 1
Figure 1 show the two topologies that are supported today. On the left is a single server topology with a local agent. Here the Data Assurance Server and Data Assurance agent co-exist on the same node. On the right is a distributed topology where the data agents reside independently and coexist with the source and target. Table 1 below provides the guidelines to consider these topologies.
Local Topology Use Case Scenario | Distributed Topology Use Case Scenario |
|
|
Table 1
Installation
Data Assurance can be installed in Command Line Interface (CLI), Graphical User Interface (GUI), or silent modes. Table 2 provides an installation checklist for the product.
Operating System checklist | Pre-install checklist |
|
|
Table 2
Successful deployment of the Data Assurance Server and Agent(s) will be similar to one of the two following sample summaries as shows in Figures 2 and 3.
Sample Local Topology Deployment Summary:

Figure 2
Sample Distributed Topology Deployment Summary

Figure 3
Data Assurance Operational Checklists
Successful Data Assurance Server and Agent Operation can be achieved with adherence to the following operational process checklists:
Row Comparison or Reconciliation Process
Process Steps |
|
Database Objects Schema Comparisons
Process Steps |
|
Import a Job based on Replication Definitions and Subscriptions
Process Steps |
|
Tune the Data Assurance Server for Better Performance
Process Steps |
|
Backup and Restore
Process Steps |
|
Delete Job History and Data Assurance System Database (DASD) backup
Process Steps |
|
Data Assurance Reconciliation
The strength of Server® Data Assurance lies in not only comparing data between the source and target systems but also reconciling them for consistency, insuring data quality. Data Assurance Jobs control reconciliation.

Figure 4
From the add clauses listed in Figure 4 above, reconciliation can be controlled as follows:
- The AUTO_RECONCILE argument helps enable automatic reconciliation, in that job.
- The CREATE_RECON_SCRIPT argument, when set to true creates a script for reconciliation.
- The show reconcile command shows the path of this script
- This argument can be combined with the AUTO_RECONCILE argument
Examples:
(1) DA applies reconciliation to the target (with optional difference rechecking phases):
COMPARE_MODE = ROW_COMPARE
CREATE_COL_LOG = TRUE
AUTO_RECONCILE = TRUE
(2) DA writes 0..3 INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE scripts to fix all differences manually (with optional rechecking phases):
COMPARE_MODE = ROW_COMPARE
CREATE_COL_LOG = TRUE
CREATE_RECON_SCRIPT = TRUE
(3) Both of the above together (not sure why you would, but you can):
COMPARE_MODE = ROW_COMPARE
CREATE_COL_LOG = TRUE
AUTO_RECONCILE = TRUE
CREATE_RECON_SCRIPT = TRUE
Notes (0..3😞
- If there are no differences, DA will write 0 scripts.
- If there are missing rows (only), DA will write 1 INSERT script.
- If there are missing and inconsistent rows (only), DA will write 1 INSERT script and 1 UPDATE script (2 in total).
- If there are missing, inconsistent and orphaned rows, DA will write all 3 scripts.
SAP Replication Server 15.7 SP300 Direct Reconciliation Enhancement
- A new compare mode called DIRECT_RECON has been added to improve below performances
- Materialization – populate/repopulate a target table using all source rows
- Reconcile the target table rows without replication latency. All differences presumed to be unchanging need to be reconciled as soon as possible
- Compare and reconcile rows in a single step, all in memory
- Reconcile with the appropriate insert, delete, or update statement directly to rows in the target table that are identified as being different.
- Do not save row values to disk
- No detailed text or XML report
- Enable multi-threaded reconciliation per comparison partition
Direct Reconciliation Example
This example shows how to create a job that uses direct reconcile:
1> create job job_direct_recon
2> add comparison cmp1
3> set compareset cs1
4> and set compare_mode to direct_recon
5> and set auto_recon_num_threads = 2
6> go
The two new changes are:
- new compare_mode “direct_recon”
- the job option “auto_recon_num_threads” /* determines how many threads are
created/partition* when performing the
direct reconciliation.*/
Notes:
The direct reconcile threads are managed internally and are only active for the duration of the “compare and reconcile” phase. (* internal DA partitions, not database partitions)
Figure 5 below shows a sample Direct Reconciliation Example Output:

Figure 5
Show Reconcile command
- The show reconcile command shows reconciliation information.
- show reconcile <job_name> {<history_id> | latest} [<comparison_name> <target_index> <script_type>]
- job_name the name of the job for which to show the reconciliation script.
- history_id the job history sequence ID of the reconcile script to be shown.
- comparison_name the name of the job comparison.
- target_index the index of the target. Use zero (0) for the first target.
- script_type the type of script to return: insert, update, or delete.
- Figure 6 below shows an example output of Show Reconcile command
Show reconciliation scripts for “job6” with history ID 29:
> show reconcile job6 29
> go

Figure 6
Data Assurance Security and Access Control
Security | Access Control |
|
|
Data Assurance Performance and Tuning Guidelines
Performance Settings | Tuning |
|
NOTE: Please read the Users guide for more details on hash types |
Data Assurance Resources
| Useful Links and Guides |
|---|
New Features Guide http://infocenter.sybase.com/help/topic/com.sybase.infocenter.dc60011.1571202/doc/pdf/da_nfg.pdf SAP Replication Server Data Assurance SAP Replication Server Data Assurance Installation Guide |
Acknowledgement: Thanks to Steve Jones (stev.jones@sap.com) and Carl Soane (carl.soane@sap.com) for their inputs.
- SAP Managed Tags:
- SAP Replication Server
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
ABAP CDS Views - CDC (Change Data Capture)
2 -
AI
1 -
Analyze Workload Data
1 -
BTP
1 -
Business and IT Integration
2 -
Business application stu
1 -
Business Technology Platform
1 -
Business Trends
1,661 -
Business Trends
87 -
CAP
1 -
cf
1 -
Cloud Foundry
1 -
Confluent
1 -
Customer COE Basics and Fundamentals
1 -
Customer COE Latest and Greatest
3 -
Customer Data Browser app
1 -
Data Analysis Tool
1 -
data migration
1 -
data transfer
1 -
Datasphere
2 -
Event Information
1,400 -
Event Information
64 -
Expert
1 -
Expert Insights
178 -
Expert Insights
273 -
General
1 -
Google cloud
1 -
Google Next'24
1 -
Kafka
1 -
Life at SAP
784 -
Life at SAP
11 -
Migrate your Data App
1 -
MTA
1 -
Network Performance Analysis
1 -
NodeJS
1 -
PDF
1 -
POC
1 -
Product Updates
4,577 -
Product Updates
326 -
Replication Flow
1 -
RisewithSAP
1 -
SAP BTP
1 -
SAP BTP Cloud Foundry
1 -
SAP Cloud ALM
1 -
SAP Cloud Application Programming Model
1 -
SAP Datasphere
2 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud
1 -
SAP S4HANA Migration Cockpit
1 -
Technology Updates
6,886 -
Technology Updates
403 -
Workload Fluctuations
1
- explore the business continuity recovery sap solutions on AWS DRS in Technology Blogs by Members
- How to test a Windows Failover cluster? in Technology Blogs by SAP
- Workload Analysis for HANA Platform Series - 2. Analyze the CPU, Threads and Numa Utilizations in Technology Blogs by SAP
- Taking Data Federation to the Next Level: Accessing Remote ABAP CDS View Entities in SAP HANA Cloud in Technology Blogs by SAP
- SAP Datasphere Connectivity With S/4 HANA System & SAP Analytics Cloud : Technical Configuration in Technology Blogs by Members
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 12 | |
| 10 | |
| 9 | |
| 7 | |
| 7 | |
| 7 | |
| 6 | |
| 6 | |
| 5 | |
| 4 |