
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Technology
- Technology Blogs by SAP
- Data and Topology of SLD, LMDB, and Customer Profi...
Technology Blogs by SAP
Learn how to extend and personalize SAP applications. Follow the SAP technology blog for insights into SAP BTP, ABAP, SAP Analytics Cloud, SAP HANA, and more.
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
wolf_hengevoss
Active Participant
Options
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
04-30-2015
2:28 PM
Last update: September 2020
Landscape data is for some time being uploaded to SAP Support Portal - for example to enable for the Early Watch Alert. Now, landscape planning tools like Maintenance Planner emerge in the SAP Support Portal using that data, so its importance is increasing massively. With new use cases and high importance you have to take into account a valid topology of three layers of landscape data tools now: The System Landscape Directory (SLD), SAP Solution Manager Landscape Management Database (LMDB), and the SAP Support Portal Customer Profile. This blog describes how to avoid erroneous data in this highest layer. While the topology recommendations for SLD and LMDB systems have been described in detail, the connection to the top layer may need some investigation…
These are minimum pieces of information you need to understand why there are three levels of repositories containing data related to landscape management.
What is the “Customer Profile”? As System Landscape Directory and Landscape Management Database, the Customer Profile is a repository for landscape data. In contrast to SLD and LMDB the Customer Profile is hosted with several applications in the SAP Support Portal storing
By this, authorized access for users and tools is centrally possible, forming a source of truth making a joint approach to problem solving easier, for example in an incident.
The following figure shows the way, system data gets into the customer profile and are accessed by customers:

Figure 1a: Upload of data from customer landscapes into the SAP Support Portal Customer Profile: Data is sent to the SLD, synchronized with the LMDB and from there uploaded to the SAP Support Portal; (also see figure 5); access to system data in the Customer Profile is only possible through application using the customer number assigned to the technical system. The SID of the uploading SAP Solution Manager is also stored with the data.
Getting Data of the IT landscape hasn’t changed: SLD and LMDB gather the data from SLD Data Suppliers and host agents running on technical systems and the LMDB uploads it to the SAP Support Portal:
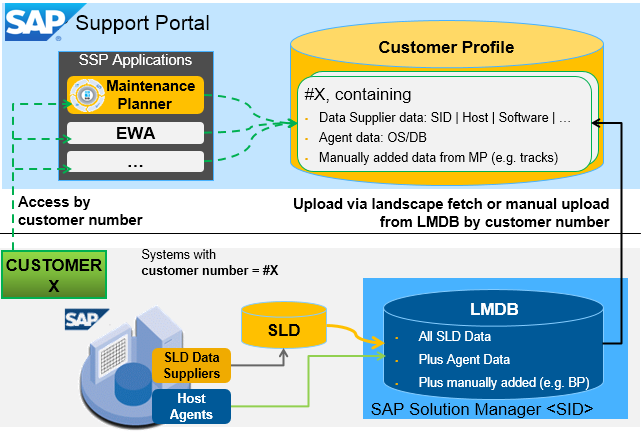
Figure 1b: Data flow from the technical system to the Customer Profile read by the Maintenance Planner in Detail.
In addition to data sent via SLD, LMDB, and Landscape Information Services (LIS), Maintenance Planner utilizes cloud tenants information from the Cloud Landscape Directory (CLD, hosted by SAP) as input for these 3 functionalities:
For more information on data handling, see
In such a case the technical system information for ABAP systems will be uploaded by generating a system_info.xml file from Support Package Manager (SPAM).
Prerequisite: This is supported on SPAM version 59 or latest. Please check and upgrade SPAM version to 59 before you proceed.Perform the following steps:
NOTE:
This works for AS ABAP based systems only.
It should be regarded being a work-around: Data uploaded this way will not be updated automatically, so uploading data via the LMDB is highly recommend.
There are new features available as of SAP Solution Manager 7.2 SPS09, which possibly affect the topology of SLD and LMDB and CIM/CR data handling in the IT landscape.
Note: All valid SLD/LMDB topologies stay valid.
Therefore, with SAP Solution Manager 7.2 SPS09, in case no SLD client applications are used – for example, SAP Process Integration, SAP NetWeaver Development Infrastructure, etc. – using an SLD becomes optional:
The following figure shows both options:

Figure 1c: SLD/LMDB topology options as of SAP Solution Manager 7.2 SPS09 with no SLD client apps.
In case, no SLD is available in the landscape, the LMDB needs to be updated with manual or automatic import of CIM/CR content to be configured in SAP Solution Manager transaction SolMan_Setup. For details see How to Reduce Manual Effort in CIM model and CR Content Update of SLD Systems.
The process of sending data to the customer profile, however, will only deliver good data quality, if the involved systems (SLD, LMDB, and their connections to the customer profile) are set up sensibly. This network of systems managing landscape data is what we call their topology.
Landscape Information Services (LIS) replaces the upload of system data to the SAP Support Portal - switch is planned for Q1 2020.
LIS scenarios available:

Figure 1d: SLD/LMDB topology with Landscape information Services.
For details and technical prerequisites, see:
System Data Upload to the SAP Support Portal via Landscape Information Services
Best practices for these tools are available since years. Obviously, still – or even increasing – this knowledge is absolutely necessary for having up-to-date
landscape data in SAP Support Portal (see figure 1). Therefore, if you’re not familiar with this topic, read the following blogs:
Being principles of handling data in repositories, all principles named in the topology blogs for SLD and LMDB apply to the customer profile. You only need to apply them to the last layer. The recommended landscape looks like the following figures. They will describe a scenario each. The following symbols are used to describe connections between SLD, LMDB, and SAP Support Portal:

One SAP Solution Manager system with role = productive uploads via scheduled automated or via manual direct upload to the SAP Support Portal. The following figure shows this scenario:
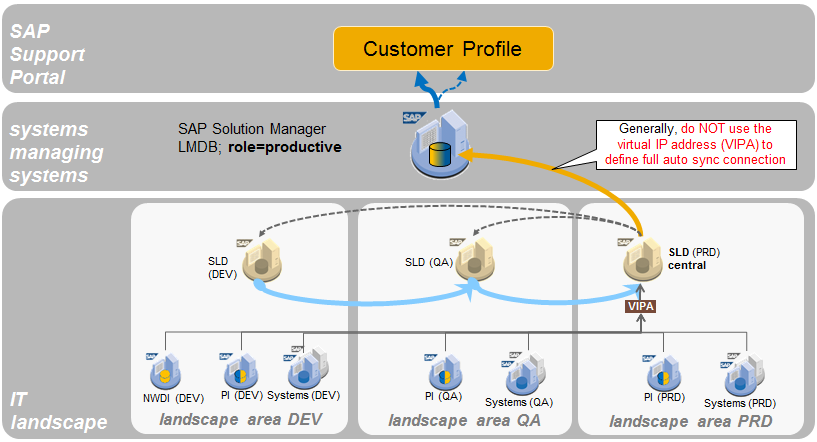
Figure 2a shows Scenario 1a – default setup: 1 SAP Solution Manager system uploading data. SAP Solution Manager in role = prod. uploads via
scheduled landscape fetch job or via manual direct upload to the SAP Support Portal.
Note: For SAP Solution Manager 7.2 –this versions is currently in ramp-up and not generally available until officially declared so – there is amn important requirement regarding the SAP NetWeaver version of the SLD. For details see:
Required SAP NW Version of the Source SLD for LMDB in SAP Solution Manager 7.2 & Options to Get ther...
1 SAP Solution Manager in role = prod., one = test: Only prod uploads via landscape fetch or via manual direct upload to SAP Support Portal.
Since Solution Manager system with role = test do not upload data to the SAP Support Portal, the handling is almost the same.
The following figure shows this scenario:

Figure 2b shows default setup with a test system of SAP Solution Manager: 1 SAP Solution Manager uploading data. SAP Solution Manager in role = productive uploads via scheduled landscape fetch or via manual direct upload to SAP Support Portal. Note, that one SLD provides data for both Solution Manager systems so that their input is identical.
There are new features available as of SAP Solution Manager 7.2 SPS09, which possibly affect the topology of SLD and LMDB and CIM/CR data handling in the IT landscape.
Note: All valid SLD/LMDB topologies stay valid.
Here, test systems of SAP Solution Manager are not shown. This scenario is only valid, if both SAP Solution Mangers get completely separated data: Separate SLD for each Solution Manager with no data exchange required plus unique SID/host name combinations (to be ensured by a naming convention) are required.
The reason is that otherwise, you would violate the unique-path-principle, sending data of the same system through different paths, so that contradicting versions of the same system would be shown: System data of the same system would turn up twice, separated by the Sap Solution Manager uploading the data: Such a setup can happen at value added re-sellers and big customers having separated IT landscapes.
The following figures shows this scenario in a valid and an invalid form:

Figure 2c: What may seem as being same scenario as in figure 3, is invalid: both are productive SAP Solution Manager systems get the same data being connected to the same SLD and both are productive, uploading data.
This scenario is shown in its valid form...

Figure 2d: Both SAP Solution Managers get completely separated data (from separated landscape areas) being connected to separate SLD for each SAP Solution Manager system with no data exchange required plus unique SID/host name combinations (to be ensured by a naming convention).
.
...and in an invalid form:
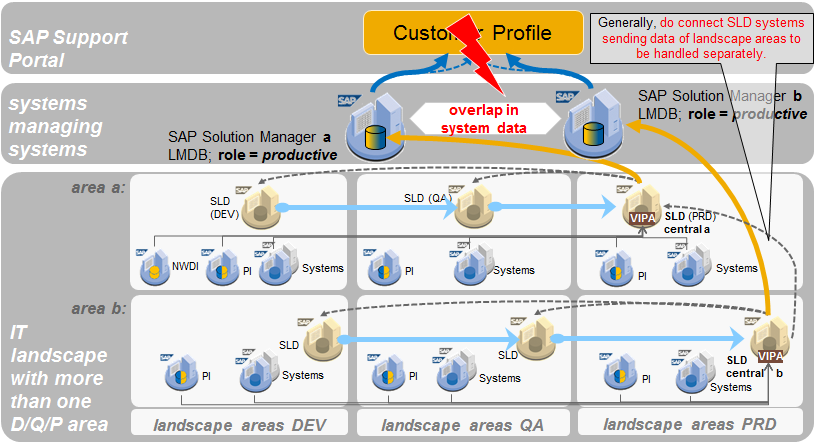
Figure 2e: Another invalid scenario would be using different SLD systems, which have connections by transport, forwarding, or sync.
If you cannot avoid all overlap of system data more than one productive SAP Solution Manager systems, you can still avoid compromising the data in the customer profile: Disable the automatic landscape fetch job for overlapping systems individually in all but one of the productive SAP Solution Manager systems. In LMDB, navigate to the technical systems in question, go to edit mode and on register card SAP Support Portal set System Synchronization to “Do Not Synchronize Selected Technical System”:
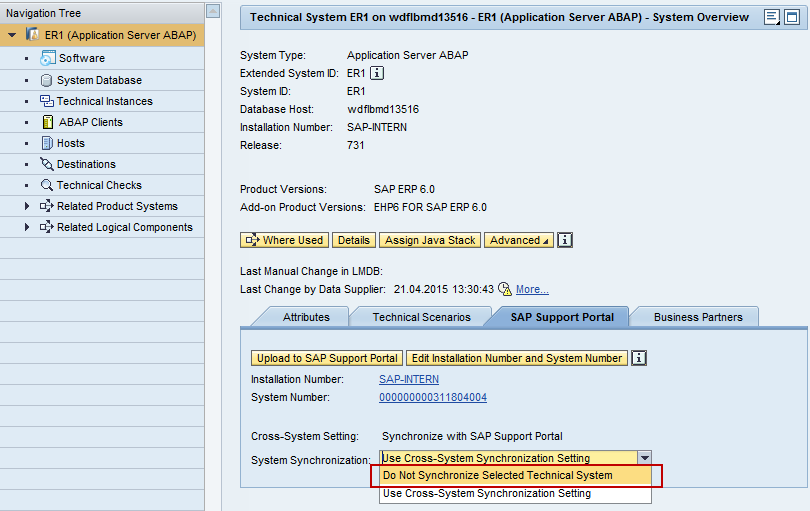
Figure 3a: Settings for the upload of technical systems data: The “cross system setting” can be deactivated for individual systems. (Example: LMDB in SAP Solution Manager 7.1.)
The setting can be done for the whole SAP Solution Manager. You'll find the description when you click the "i"-button on tab SAP Support Portal in the LMDB:

->

Figure 3b: Cross-System-Settings for the upload of technical systems data. (Example: LMDB in SAP Solution Manager 7.2.)

Figure 3c: SAP Note 2177157 related to the Cross-System-Settings.
In case of problems, see Uploading, Accessing, and Trouble-Shooting System Data in the Customer Profile Used for Planning Cha... for a comprehensive list of relevant SAP Notes.
SAP Notes specifically addressing data required for the planning with the Maintenance Planner:
Introduction
Landscape data is for some time being uploaded to SAP Support Portal - for example to enable for the Early Watch Alert. Now, landscape planning tools like Maintenance Planner emerge in the SAP Support Portal using that data, so its importance is increasing massively. With new use cases and high importance you have to take into account a valid topology of three layers of landscape data tools now: The System Landscape Directory (SLD), SAP Solution Manager Landscape Management Database (LMDB), and the SAP Support Portal Customer Profile. This blog describes how to avoid erroneous data in this highest layer. While the topology recommendations for SLD and LMDB systems have been described in detail, the connection to the top layer may need some investigation…
Tools, Entities, and Their Connections
These are minimum pieces of information you need to understand why there are three levels of repositories containing data related to landscape management.
- System Landscape Directory: This is where landscape data mgmt. starts. The SLD gets and gathers data from the technical systems and provides this information for several client applications such as SAP Process Integration (for this client, in the SLD business systems are created manually) and SAP Solution Manager.
- Landscape Management Database: The LMDB is seen in this blog mainly as a tool uploading data retrieved from the SLD to the Customer Profile. But there are two more things: The LMDB enriches SLD data in several ways - automatically by agents and manually by adding information that is not exposed to the Customer Profile, such as business partner information, so the LMDB is your source for detailed information on your landscape.
- Customer Profile: For the Maintenance Planner it provides (only) those data required to calculate update, upgrade, and conversion of systems.
Customer Profile
What is the “Customer Profile”? As System Landscape Directory and Landscape Management Database, the Customer Profile is a repository for landscape data. In contrast to SLD and LMDB the Customer Profile is hosted with several applications in the SAP Support Portal storing
- …system data of all customers, handling the access by customer numbers assigned to S-users
- …but selected parts, for example sensitive data such as business partner information are excluded
By this, authorized access for users and tools is centrally possible, forming a source of truth making a joint approach to problem solving easier, for example in an incident.
The following figure shows the way, system data gets into the customer profile and are accessed by customers:

Figure 1a: Upload of data from customer landscapes into the SAP Support Portal Customer Profile: Data is sent to the SLD, synchronized with the LMDB and from there uploaded to the SAP Support Portal; (also see figure 5); access to system data in the Customer Profile is only possible through application using the customer number assigned to the technical system. The SID of the uploading SAP Solution Manager is also stored with the data.
Getting Data of the IT Landscape
Getting Data of the IT landscape hasn’t changed: SLD and LMDB gather the data from SLD Data Suppliers and host agents running on technical systems and the LMDB uploads it to the SAP Support Portal:

Figure 1b: Data flow from the technical system to the Customer Profile read by the Maintenance Planner in Detail.
In addition to data sent via SLD, LMDB, and Landscape Information Services (LIS), Maintenance Planner utilizes cloud tenants information from the Cloud Landscape Directory (CLD, hosted by SAP) as input for these 3 functionalities:
- Cloud Integration Automation Service (CIAS😞 Here, it is used to present the list of cloud tenants available in the customer landscape.
This is required to plan for cloud integration scenarios. - Hybrid Landscape Visualization: Here, it is used to create landscape pictures using cloud tenants.
- Product Analytics: Here, it is used to analyze the products installed in the cloud systems of the customers landscape: PaaS (SCP) and SaaS systems (S/4HANA Cloud, SAP Successfactors, etc.), and SAP Hana Enterprise Cloud (HEC).
For more information on data handling, see
- the big picture in SAP Support Portal; Get the Status of Your IT Landscape - Data in SLD, LMDB, and SAP Support Portal, and Its Verificatio...
- For detailed information on handling data, which is provided via SLD and LMDB, see:
- Software Catalog Data aka CR CONTENT in SLD and LMDB
- Technical System Data Delivered by SLD Data Supplier and Agents
- Uploading, Accessing, and Trouble-Shooting System Data in the Customer Profile Used for Planning Cha...
- House-Keeping in the Customer Profile Data Used by the Maintenance Planner
Questions on connections between technical systems, SLD, and LMDB are discussed in the topology part.
Uploading AS ABAP Based Technical Systems' Data While Having Connection Problems
What should I do in case of problems with the connections described above? These could be
- Security policies in my organization prevent me from creating RFC connections to SAP Support Portal
- Problems in permissions or authentication, e.g. in a VAR scenario.
In such a case the technical system information for ABAP systems will be uploaded by generating a system_info.xml file from Support Package Manager (SPAM).
Prerequisite: This is supported on SPAM version 59 or latest. Please check and upgrade SPAM version to 59 before you proceed.Perform the following steps:
- In transaction SPAM, select Utilities -> Generate system info XML.
Logging in to client "000" may be required - Save the downloaded XML on your local system
- The systeminfo.xml file can be uploaded to the customer profile by choosing
"Add System" in the Explore Systems area.
NOTE:
This works for AS ABAP based systems only.
It should be regarded being a work-around: Data uploaded this way will not be updated automatically, so uploading data via the LMDB is highly recommend.
Topology of Tools Gathering Landscape Data
Topology Options Available as of SAP Solution Manager 7.2 SPS09
There are new features available as of SAP Solution Manager 7.2 SPS09, which possibly affect the topology of SLD and LMDB and CIM/CR data handling in the IT landscape.
- As of SAP Solution Manager 7.2 SPS09, SLD and LMDB can be a direct target for CIM model data and CR content. As of SAP Solution Manager 7.2 SPS06, the LMDB can act as a Data-Supplier target – this can now be combined with the new feature available as of SAP Solution Manager 7.2 SPS09 to allow direct CIM/CR Upload to the LMDB
- Furthermore, CIM/CR update in LMDB and SLD can automated
Note: All valid SLD/LMDB topologies stay valid.
Landscape without SLD Client Applications
Therefore, with SAP Solution Manager 7.2 SPS09, in case no SLD client applications are used – for example, SAP Process Integration, SAP NetWeaver Development Infrastructure, etc. – using an SLD becomes optional:
- You can still use it as a target for SLD Data Suppliers and as a CIM/CR source for the LMDB
- You can use the LMDB as a Data Supplier Target combining it with the new CIM/CR import to the LMDB
The following figure shows both options:

Figure 1c: SLD/LMDB topology options as of SAP Solution Manager 7.2 SPS09 with no SLD client apps.
In case, no SLD is available in the landscape, the LMDB needs to be updated with manual or automatic import of CIM/CR content to be configured in SAP Solution Manager transaction SolMan_Setup. For details see How to Reduce Manual Effort in CIM model and CR Content Update of SLD Systems.
The process of sending data to the customer profile, however, will only deliver good data quality, if the involved systems (SLD, LMDB, and their connections to the customer profile) are set up sensibly. This network of systems managing landscape data is what we call their topology.
Topology Options with Landscape Information Services
Landscape Information Services (LIS) replaces the upload of system data to the SAP Support Portal - switch is planned for Q1 2020.
LIS scenarios available:
- With SAP Solution Manager LMDB and SLD
- With SAP Solution Manager LMDB, but without SLD
- Exceptional case: Without SAP Solution Manager & without SLD

Figure 1d: SLD/LMDB topology with Landscape information Services.
For details and technical prerequisites, see:
System Data Upload to the SAP Support Portal via Landscape Information Services
Topology of SLD and LMDB in Detail
Best practices for these tools are available since years. Obviously, still – or even increasing – this knowledge is absolutely necessary for having up-to-date
landscape data in SAP Support Portal (see figure 1). Therefore, if you’re not familiar with this topic, read the following blogs:
- SLD Topology: How-To Gather and Distribute SLD-Data in Your IT-Landscape?
- SLD-LMDB Topology – Connections, Valid, and Invalid Data Exchange Between SLD and LMDB of SAP Soluti...
Enhancing SLD and LMDB Topology by the Connection to the Customer Profile
Being principles of handling data in repositories, all principles named in the topology blogs for SLD and LMDB apply to the customer profile. You only need to apply them to the last layer. The recommended landscape looks like the following figures. They will describe a scenario each. The following symbols are used to describe connections between SLD, LMDB, and SAP Support Portal:

Default Recommendation – 1 SAP Solution Manager System Uploading Data (no Test System)
One SAP Solution Manager system with role = productive uploads via scheduled automated or via manual direct upload to the SAP Support Portal. The following figure shows this scenario:

Figure 2a shows Scenario 1a – default setup: 1 SAP Solution Manager system uploading data. SAP Solution Manager in role = prod. uploads via
scheduled landscape fetch job or via manual direct upload to the SAP Support Portal.
Note: For SAP Solution Manager 7.2 –this versions is currently in ramp-up and not generally available until officially declared so – there is amn important requirement regarding the SAP NetWeaver version of the SLD. For details see:
Required SAP NW Version of the Source SLD for LMDB in SAP Solution Manager 7.2 & Options to Get ther...
Default Recommendation – 1 SAP Solution Manager System Uploading Data (with Test System)
1 SAP Solution Manager in role = prod., one = test: Only prod uploads via landscape fetch or via manual direct upload to SAP Support Portal.
Since Solution Manager system with role = test do not upload data to the SAP Support Portal, the handling is almost the same.
The following figure shows this scenario:

Figure 2b shows default setup with a test system of SAP Solution Manager: 1 SAP Solution Manager uploading data. SAP Solution Manager in role = productive uploads via scheduled landscape fetch or via manual direct upload to SAP Support Portal. Note, that one SLD provides data for both Solution Manager systems so that their input is identical.
Topology Options Available as of SAP Solution Manager 7.2 SPS09
There are new features available as of SAP Solution Manager 7.2 SPS09, which possibly affect the topology of SLD and LMDB and CIM/CR data handling in the IT landscape.
- As of SAP Solution Manager 7.2 SPS09, SLD and LMDB can be a direct target for CIM model data and CR content. As of SAP Solution Manager 7.2 SPS06, the LMDB can act as a Data-Supplier target – this can now be combined with the new feature available as of SAP Solution Manager 7.2 SPS09 to allow direct CIM/CR Upload to the LMDB
- Furthermore, CIM/CR update in LMDB and SLD can automated
Note: All valid SLD/LMDB topologies stay valid.
Alternative: 2 (or more) productive SAP Solution Manager Systems Uploading Data
Here, test systems of SAP Solution Manager are not shown. This scenario is only valid, if both SAP Solution Mangers get completely separated data: Separate SLD for each Solution Manager with no data exchange required plus unique SID/host name combinations (to be ensured by a naming convention) are required.
The reason is that otherwise, you would violate the unique-path-principle, sending data of the same system through different paths, so that contradicting versions of the same system would be shown: System data of the same system would turn up twice, separated by the Sap Solution Manager uploading the data: Such a setup can happen at value added re-sellers and big customers having separated IT landscapes.
The following figures shows this scenario in a valid and an invalid form:

Figure 2c: What may seem as being same scenario as in figure 3, is invalid: both are productive SAP Solution Manager systems get the same data being connected to the same SLD and both are productive, uploading data.
This scenario is shown in its valid form...

Figure 2d: Both SAP Solution Managers get completely separated data (from separated landscape areas) being connected to separate SLD for each SAP Solution Manager system with no data exchange required plus unique SID/host name combinations (to be ensured by a naming convention).
.
...and in an invalid form:

Figure 2e: Another invalid scenario would be using different SLD systems, which have connections by transport, forwarding, or sync.
Upload via the LMDB Technical System Editor & Settings Avoiding Duplicate Uploads
If you cannot avoid all overlap of system data more than one productive SAP Solution Manager systems, you can still avoid compromising the data in the customer profile: Disable the automatic landscape fetch job for overlapping systems individually in all but one of the productive SAP Solution Manager systems. In LMDB, navigate to the technical systems in question, go to edit mode and on register card SAP Support Portal set System Synchronization to “Do Not Synchronize Selected Technical System”:

Figure 3a: Settings for the upload of technical systems data: The “cross system setting” can be deactivated for individual systems. (Example: LMDB in SAP Solution Manager 7.1.)
The setting can be done for the whole SAP Solution Manager. You'll find the description when you click the "i"-button on tab SAP Support Portal in the LMDB:

->

Figure 3b: Cross-System-Settings for the upload of technical systems data. (Example: LMDB in SAP Solution Manager 7.2.)

Figure 3c: SAP Note 2177157 related to the Cross-System-Settings.
Further Information
Trouble Shooting and Relevant SAP Notes
In case of problems, see Uploading, Accessing, and Trouble-Shooting System Data in the Customer Profile Used for Planning Cha... for a comprehensive list of relevant SAP Notes.
SAP Notes specifically addressing data required for the planning with the Maintenance Planner:
- SAP Note 2382263 - RZ70: Switch Framework Status and Active Business Functions
- SAP Note 589800 - Extension of the ABAP Data Supplier (RZ70) for Maintenance Planner
Further Information @ the SCN
- SAP Managed Tags:
- SAP Solution Manager
Labels:
5 Comments
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
Labels in this area
-
ABAP CDS Views - CDC (Change Data Capture)
2 -
AI
1 -
Analyze Workload Data
1 -
BTP
1 -
Business and IT Integration
2 -
Business application stu
1 -
Business Technology Platform
1 -
Business Trends
1,661 -
Business Trends
91 -
CAP
1 -
cf
1 -
Cloud Foundry
1 -
Confluent
1 -
Customer COE Basics and Fundamentals
1 -
Customer COE Latest and Greatest
3 -
Customer Data Browser app
1 -
Data Analysis Tool
1 -
data migration
1 -
data transfer
1 -
Datasphere
2 -
Event Information
1,400 -
Event Information
66 -
Expert
1 -
Expert Insights
178 -
Expert Insights
293 -
General
1 -
Google cloud
1 -
Google Next'24
1 -
Kafka
1 -
Life at SAP
784 -
Life at SAP
12 -
Migrate your Data App
1 -
MTA
1 -
Network Performance Analysis
1 -
NodeJS
1 -
PDF
1 -
POC
1 -
Product Updates
4,577 -
Product Updates
338 -
Replication Flow
1 -
RisewithSAP
1 -
SAP BTP
1 -
SAP BTP Cloud Foundry
1 -
SAP Cloud ALM
1 -
SAP Cloud Application Programming Model
1 -
SAP Datasphere
2 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud
1 -
SAP S4HANA Migration Cockpit
1 -
Technology Updates
6,886 -
Technology Updates
415 -
Workload Fluctuations
1
Related Content
- Behind the compatibility - What are the compatibility means between GRC and the plugins in Technology Blogs by SAP
- Up Net Working Capital, Up Inventory and Down Efficiency. What to do? in Technology Blogs by SAP
- SAP Analytics Cloud - Performance statistics and zero records in Technology Blogs by SAP
- Switch on gCTS (for existing packages) in Technology Blogs by SAP
- 10+ ways to reshape your SAP landscape with SAP Business Technology Platform – Blog 4 in Technology Blogs by SAP
Top kudoed authors
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 29 | |
| 21 | |
| 10 | |
| 7 | |
| 6 | |
| 6 | |
| 6 | |
| 5 | |
| 5 | |
| 4 |