
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Supply Chain Management
- SCM Blogs by Members
- SCM Core Interface- Handbook (PART-2)
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
In continuation of PART-1
7. CIF Error Handling and Queue Management
7.1. Activate CIF Error Handling in SCM APO System
- Transaction code- /SAPAPO/C2

Here we choose the error handling method as Post-processing of errors. No splitting of LUW in order to activate the post-processing of the logical systems.
If you are transferring a large amount of data from SAP APO to SAP R/3, and you want to be ensure that an even system load is placed on SAP R/3, choose Inbound Queues.
Since we choose Inbound Queues in SAP APO, We did the necessary settings for the QIN Scheduler (Queue-In Scheduler) in the qRFC monitor in SAP R/3(As explained above). Queues that are to be processed automatically by SAP R/3 must be registered in the QIN Scheduler.
7.2. CIF Error Handling (Post Processing)
- Transaction code- /SAPAPO/CPP1
This functionality in APO will allow the CIF user to see all the logged CIF error messages centrally in APO. This process is independent of the queue type (inbound or outbound) and CIF errors in both the system (ECC and APO) can be handled from this one transaction in APO.
CIF error handling ensures that all CIF queue entries are processed during the data transfer. Faulty queues no longer lead to queue blocks. Instead, they are logged in post processing records in the relevant target system for the data transfer. You can then call these post processing records at a later point in time in CIF Post processing. Once the error has been corrected you can then send the objects to the relevant target system again.
If a change to transaction data cannot be posted in the target system due to an error, the system creates a post processing record with the error status Faulty for the object concerned.
CIF error handling is not available in the following situations, which means that CIF queues hang when errors occur:
- At the initial data transfer(Master Data and Transactional Data)
- At the transfer of master data (initial and change transfer)
- At short dumps or when liveCache is unavailable
- When the target system is unavailable
- When an object is locked in the target system (as before for the repetition of the transfer)
- If errors occur in customer exits or BAdIs that run in CIF inbound function modules during integration
You can find information about restrictions to CIF error handling when using certain applications and functions in SAP Note 602484.
Since not all errors are included in CIF error handling, faulty queue entries may continue to exist once CIF error handling has been activated. Faulty queue entries can also block objects that are resent by CIF post processing. Therefore, you still need to monitor CIF queues by using the qRFC monitors for inbound or outbound queues, or by using the SCM Queue Manager.
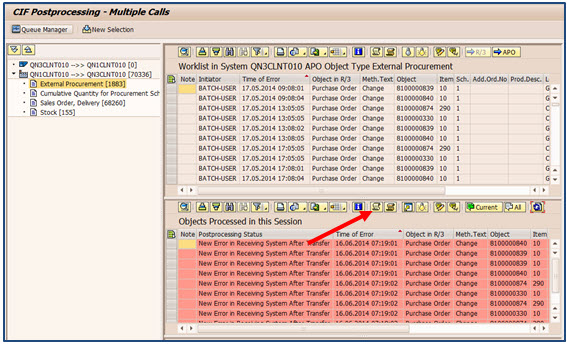
- Steps for CIF Post Processing
- Invoke transaction /SAPAPO/CPP1 in APO. Choose the target system and this should be the connected ECC system. Make sure that the indicator “Select Data from R3” is turned on. Processing status should be “1” for selecting the data which needs to be processed. However you can select the other statuses like processed, obsolete etc. depending upon the requirement.

- The navigation tree on the left side shows the system connection and the transfer directions; under each transfer direction, there are different order categories.
- Select and process the records for each group of the “order categories”, e.g. “In-House Production”, “External Procurement”, etc.
- These messages appear in detail on the right side of the screen and by double clicking on the rows for External procurement or In House Production.
- On the right side of the screen there are two sections. One is worklist of the inbound system (top) and second is objects processed in this session (bottom)

- Select the records to be processed. If there are too many records to be processed, you may sort them into different groups and process one group at a time. You may sort them by products and by location, and select a few product/location in a group.

- Depending upon the object types and the direction of the record, you can either select send to R/3 or Send to APO.

- Once the records are in process, they will be moved from the “Worklist” window to “Objects Process” window.

- Refresh the “Object Processed” window by click on the refresh button. If the errors are still persistent, it will be reflected in the status. Sometime this does not provide the actual error occurred.

- So To resolve the issue, you may select a desired entry and click on the application log button.
- The application log will be displayed

- Once the issue has been resolved, move the records back to the “Worklist” window to be processed again by selecting the record in “Object Processed” window and the “click on the icon. Then you can process the object once again.
- Resolve all the issues until the “Objects Processed” window is clear if it’s possible.
- You use the Set Entry as Obsolete indicator to set the processing status of the post processing record to Obsolete (Set Manually); for example, if you do not want an object to be sent again. The object itself is unaffected by this action.
- You use the Remove Obsolescence Indicator to reset the processing status to Still for Processing. As a result, the post processing record is displayed in yellow.
7.3. Queue Management
As mentioned in the restrictions of CIF post processing, all the errors did not get captured in the CIF post processing. We still need to monitor the CIF queues.
- CIF Queue Monitoring Steps and Procedure
Transactions to check for Errors (R/3 and APO)
SMQ1 - qRFC Monitor (Outbound Queue)
SMQ2 - qRFC Monitor (Inbound Queue)


- Click on Change View.
- This will show you only the error (SYSFAIL) queues with the error message.
- /SAPAPO/CQ - CIF queue manager

Note: The indicator for expand mode is performance incentive. The Transaction will take little bit longer time if you set this indicator.

- Double click on the error message on the left side box so that the details of the error will appear on the right side box:

Note:
- Please do not delete any queue from this screen as this will delete the error queue as well as the queues which are waiting for the error queue.
- Please select the queue and click on “ENGINE ICON”. This will take you to the same SMQ2 and SMQ1 screen where you can delete the single queue as well as you can reprocess the waiting queues once you delete the error queue.
- Evaluate CIF Application Log
Sometime the error message does not provide the detail information like product, location etc. The additional detail information can be seen in the CIF application log. Please proceed as following:
> In APO: Double click on the CIF error message within the CIF entry(Transaction SMQ2 and SMQ1) or execute transaction : /n/SAPAPO/C3
> In R/3:
In order to get the details of the Error message:
Transaction in R/3: CFG1 - Display CIF Application Log
- In both the cases copy the External or Transaction ID to get the details of the error message.

- Enter the External ID, From Date (Yesterday) and To date (Today) and Execute It.
It will give the details of the error message displayed in the SMQ2 or SMQ1 transaction.
- CIF Error Resolution Process
- Each CIF error should be evaluated against the list of errors and actions below. Any new errors should be investigated and resolved if possible with the list of known errors and actions updated.
- When the product, location and order number (if relevant) have been recorded along with the error message and necessary action then the CIF entry can be deleted.
- If there is any new error comes up and needs some time to investigate, the same queue can be saved by selecting the option edit à
- Once the saved queue is investigated and completed with the root cause analysis, then the saved queue can be restored (edit à
- An email should be sent to the Key User clearly detailing the product, location and order (if relevant) and the action(s) to be taken.
- When the Key User confirms that the action has been completed, an ad-hoc CIF reconciliation report should be run for the relevant product(s) to correct any differences between ECC and APO.
- If no confirmation from the Key User is received, then differences will be picked up in the weekly CIF reconciliation report.
8. Practical Challenges
There are various challenges which CIF admin or functional consultants will encounter while integrating the ECC & APO systems. Based on various project experiences, the following are some of the issues which are encountered.
8.1. Huge CIF queue build up in APO in-bound
If you are using the inbound queues both in ECC & APO system, then you might get into this issue.
When the data is transferred from ECC to APO the data is not visible in APO. Similarly, when the planning results from APO are transferred to ECC, the results are not visible in ECC & not returned to APO with ECC order number range. This is applicable for master & transaction data, both.
All the transferred data will be blocked in CIF inbound queue (SMQ2) with “Ready” status & you need to manually activate each LUW individually. This may take long time to clear all the queues
These queues will not be displayed in CIF queue manager (/SAPAPO/CQ). If you will run the reconciliation report (/SAPAPO/CCR) report, the differences between ECC & APO changes will reflect. But if will again transfer the differences from CCR report then it will again add one more record in the APO inbound. So it is always recommended to check the CIF blocks, clear them & then use the CCR for reconciliation.
.
Root Cause: - This issue mainly pops up when the inbound schedulers are either not registered in SMQR or if registered but inactive (Type= “U”, it should be “R”) in ECC & APO system.
Example: - Inbound scheduler is registered but inactive (Type-U) in APO.

You have made some changes in the existing purchase requisition in ECC & saved. This change should transfer to APO immediately. But when you look into APO, the changes are not reflecting.
The changes are blocked in the APO inbound with “Ready” status & need manual intervention to clear them 
8.2. Master & Transaction Data change transfer to APO is not real time
This issue is applicable for all type of transaction data & only those master data objects which are configured as immediate transfer, e.g. material master, vendor & customer master, resource.
When there are any changes in the existing master data objects or transaction data which are integrated with APO & part of active integration model, still the changes are not reflecting in APO. You will not find any queue blocks for these changes. If you will run the reconciliation report in APO for transaction data consistency check (/SAPAPO/CCR), you will not find any record with differences. These changes will transfer to APO when the CIF job will run for respective integration model.
Root Cause: - This issue mainly pops up when you have not activated the online transfer using business transaction events for application “ND-APO” & NDI.
For master data, you can additionally check the “change pointers” are active or not, for the message type for the objects mentioned above.

8.3 Change pointers for master data changes are not recorded
This issue is applicable for all type of master data objects which are relevant to APO planning.
When there are any changes in the existing master data objects which are integrated with APO & part of active integration model, still the changes are not reflecting in APO. You will not find any CIF queue blocks for these changes. These changes will not even transfer to APO when the CIF job will run for respective integration model.
If you will check the table BDCP & BDCPS (for change pointer), you will not find the change pointer that you are looking for.
Root Cause: - This issue mainly pops up when you have not activated the “ALE change pointers” globally in the transaction code BD61, or the change pointer for specific message type for the master data object in the transaction code BD50 shown below.

8.4 Master Data Changes are not getting transferred to APO
This issue is applicable for all type of master data objects which are relevant to APO planning.
When there are any changes in the existing master data objects which are integrated with APO & part of active integration model, still the changes are not reflecting in APO. You will not find any CIF queue blocks for these changes. These changes will not even transfer to APO when the CIF job will run for respective integration model.
You have checked that the master the change pointers are active globally & for all the required master data message types.
Root Cause: - This issue mainly pops up when you have multiple integration models active for the same object. You should check the active integration model for the master data object by using the transaction code- CFM5 in ECC.
Conclusion: - you should have only one active integration model for any unique master data object.
8.5 Custom field value change in material master is not triggering change transfer to APO
This issue is applicable for all type of master data objects which are relevant to APO planning and enhanced by adding Z custom fields.
When there are any changes in the Z custom field value (Enhanced master data objects with Z fields relevant to APO planning) in the existing master data objects, the changes are not recorded & transferred to APO. The objects are integrated with APO & part of active integration model. There are no CIF queue blocks for these changes. These changes will only transfer to APO when there is an initial transfer for the respective master data objects.
You have checked that the change pointers are active globally (T.code-BD61) & for all the required master data message types (T.code-BD50).
Root Cause: - This issue mainly pops up when there is Z custom fields added in the APO relevant master data object but these tables & fields are not added in the transaction code BD62 for the specific message type.
Conclusion: - All fields of the required master data objects should be maintained in the transaction code- BD62, which should trigger the change transfer upon any change in ECC.
8.6 APO orders are not getting transferred from APO to ECC
This issue is only applicable to the transaction data which are planned in APO & to be sending back to ECC system.
Planning run has created procurement proposals in APO. These procurement proposals have to be send back to ECC. The new or changed proposals are not reflecting in ECC system. The transaction data is integrated with APO & part of active integration model. There are no CIF queue blocks for these changes. These changes are not reflecting even in the reconciliation report (/SAPAPO/CCR).
You have checked that the all the basic CIF configuration is maintained.
Root Cause: - This issue mainly pops up when the publication definition have not been maintained for the Plant & ECC logical system combination in APO. /SAPAPO/CP1
8.7 Poor performance of CIF background job
- First, check the setting in transaction CFC2. It is recommended to use the “Normal” logging to keep the system performance better. For administrator, who is responsible to resolve interface issues, can be given detailed logging access with “debugging on”.
- Second, schedule the performance improvement CIF batch jobs on regular basis, at least once in a week.
- Archive logs using t.code CFGD
- Configure the application log using t. code CFC6
- Third, check the block size settings of the filter objects using t.code CFC3. The size of the filter object improves system performance.
- The block size that should be used in each individual case is largely dependent upon the current data situation.
- There is no thumb rule to define the block size. It’s a judgmental, hit & trial method to find the optimum filter size. It is recommended to use the default settings as a starting point.
- Fourth, use Parallelized process wherever available.
8.8 Common configuration objects are not in sync between ECC & APO
There are various common configuration objects in ECC & APO which should in sync. This is one of the prerequisites before you initiate the master data transfer from ECC to APO. If the configuration is not in sync (object missing in APO) then there will be initial error in CIF data transfer.
Some of the common configuration objects are:
- Insert Regions
- Currencies
- Calendar
- Unit of Measure
- Time Zones
Root cause: Standard configuration has been changed in ECC for the UOM, Calendars, or new configuration objects have been added. These changes must be updated in APO.
Solution: - you can update the UOM, Currency & Calendars using the RSA1 transaction if the connected ECC system is created & active under the SAP source systems. You can use the “Transfer global settings” from the context.

For other configuration object, either compares and maintains it manually, if missing, or use the compare tool under the Utility menu bar to compare the objects from concerned ECC system & update all differences in one shot.

9. CIF Housekeeping Job
- Report – RAPOKZFX
Detect and correct inconsistencies between material master and integration models with report RAPOKZFX. In rare cases, inconsistencies can occur between data in integration models and field APOKZ in table MARC. They may occur if you activate a model that refers to a material master that is being changed at the same time. In this case, the activation is finished successfully but the APOKZ is not set correctly, and an error message is displayed. The inconsistency can result in an error during the ATP check and when transferring production and planned orders
- Report – RCIFMAX
As of R/3 Plug-In 2002.1, report RCIFIMAX should be scheduled regularly to find Inconsistencies between the integration model sources and their runtime versions. This report must not be run in parallel with activations of integration models.
- Report – RSQOWKEX & RSQIWKEX – (Exceptional use only)
You can activate qRFC queues using the reports RSQOWKEX (outbound queues) and RSQIWKEX (inbound queues). In normal operation, however, it is not necessary to run these programs regularly because almost all queue entries are processed without errors. In case of queue errors, these should be detected by the procedures described below, and analyzed and corrected accordingly. The error analysis should suggest preventive measures to reduce the number of future exceptions. In exceptional cases, or, for example, on test systems, you can use reports RSQOWKEX and RSQIWKEX. If you start these reports at an inappropriate time or with too many queues selected, they may cause an excessive additional system load.
- Report - /SAPAPO/CIF_DELTAREPORT3
Detect and correct external inconsistencies between APO and R/3 with report /SAPAPO/CIF_DELTAREPORT3 (transaction /SAPAPO/CCR). To ensure that all relevant transaction data objects (such as purchase, production or sales orders, and stocks) for which there are active integration models exist in both APO and R/3, this report should be scheduled to run:
- Periodically, and preferably daily, to detect and reconcile possible inconsistencies as soon as possible. This is important because otherwise further inconsistencies can be generated and cause subsequent planning to be based on incorrect data.
- In case a recovery of your liveCache or your APO database had to be executed, but was incomplete (point-in-time recovery, loss of data,)
- In case you have evidence of inconsistencies between your APO and your R/3 OLTP system
- In case queue entries have been deleted.
- Report - /SAPAPO/OM17 - ( In case of Recovery only)
Internal consistency between APO DB and live-Cache is checked by transaction /SAPAPO/OM17. If it is necessary to reconcile the internal consistency, for example in case of a recovery, we recommend doing this first before checking and reconciling external consistency.
10. Performance Optimization Job
To optimize the performance of the data transfer between the APO and the connected R/3 OLTP system(s) and to prevent accumulation of useless data in the systems, several reorganization jobs must be scheduled to run regularly.
- Administration Jobs Related to Data Transfer (R/3)
- Delete application log with report RDELALOG. If writing of application logs is enabled in (R/3) transaction CFC2 or APO transactions /SAPAPO/C4 or /SAPAPO/C41) – and this should be done in a production system for certain users and for problem analysis only – old logs must be deleted regularly. It is recommended to run this job daily and delete logs older than 7 days.
- Delete ALE change pointers with report RBDCPCLR. If changes to master data are transferred periodically via ALE (as it is recommended), processed change pointers must be deleted regularly. After completing this, if your database system on the R/3 side is Oracle, run report RBDCPIDXRE to reorganize the Oracle indexes on tables BDCP and BCDPS. See SAP Note 328355.
- Delete old inactive integration model versions with report RIMODDEL. Every time an integration model is generated, a new version is created, distinguished by a timestamp. The old version is deactivated and the new one is activated. Old versions must be deleted regularly.
- Administration Jobs Related to Data Transfer (APO)
- Delete application log with report /SAPAPO/RDELLOG. Same as RDELALOG in R/3 (see above).
- Check processing of APO change pointers with report /SAPAPO/RDMCPPROCESS. To verify that all change pointers created are processed, after publishing of planning results to R/3 run report /SAPAPO/RDMCPPROCESS without restricting the selection of orders and confirm that message “No change pointers were selected” is displayed. If change pointers remain unprocessed, contact the application support team to clarify whether these change pointers are necessary and why they are not processed.
- Deletion of R/3 data those are no longer required in APO with report /SAPAPO/SDORDER_DEL.
- Delete old results of CIF delta report using report /SAPAPO/CIF_DELTAREPORT3_REORG. As it is now possible to save the results of a Delta report run, it is necessary to delete outdated results from the database. The spool list from this report contains the number of records deleted.
- Delete post-processing records with report /SAPAPO/CIF_POSTPROC_REORG. Processed and obsolete post-processing records are no longer required and should be deleted. This report is used to do so. Non-deletion of these records will have an increasingly negative impact on CIF performance over the time. The deletion is a two-step process. In a first run, outdated records that meet the selection criteria with the status still to be processed are set to status obsolete (set manually). In a second run, all processed and all obsolete records are deleted.
- Note:
a) Deleting change pointers may cause inconsistencies, as the corresponding order changes are not transferred to R/3.
In SAP APO database tables, the tables expand with data from SAP R/3 documents. However, this data is no longer required; no corresponding information exists in liveCache. In addition, the performance of the initial data supply or of other transfer processes with a high data volume is affected negatively. The obsolete records need to be deleted regularly to control the size of certain tables (e.g. /SAPAPO/SDFIELD and /SAPAPO/POSMAPN) and to improve the performance of the Sales order updates on SAP APO side. For details, see SAP Note 504620.\
11. Real CIF Error encountered in various project
- Error: CFEP000000043548 ED1CLNT120 @OJ@ Internal number assignment not defined
Cause:- There is no internal number range maintained for purchase requisition document type “NB”.
Solution:- Create pur req no range in ECC & enter it into the Document types under purchasingàPur Req for type NB “internal no rng”
- Error: CFEP000000043548 ED1CLNT120 @OJ@ Enter Purch. group
Cause:- Purchasing Group is not maintained in ECC system for the given material.
Solution:- Maintain the Purchasing group in the material master & reactivate the queue.
- Error: CFIP009000001374 ED1CLNT120 @OJ@ 21.12.2015 date comes after end of valid factory calendar
Cause:-The planning calendar validity is ending in 2010 while the orders dates are lying in 2013.
Solution:- Extend the planning calendar.
- Error: CFIP000100000896 ED1CLNT120 @OJ@ Messages for WM staging: Check order 100000896
Cause: The Production supply area has not maintained in the resource or in the BOM. System first picks the Prod Supply area from the resource master & if that is not maintained in the Resource then it will look in the BOM component.
This is used if the Warehouse management is active.
Note:- In the SPRO (Log Exe:--Wh mgmt àinterfaceàdefine production) production supply area is maintained or use trxn code OMK0.
Solution:-Maintain the Production supply area & should be assign to the Resource (for the master recipe for which component is assigned) or assign directly to the BOM component. Ensure that the storage location assigned in the Production supply area for a component should be assigned in the MMSC trxn.
- Error: CFIP0000072359 EQ1CLNT210 @OJ@ Backflushing only possible for materials kept in stock
Cause: The Backflush indicator in the material master is “1” always backflush. While the valuation class in the material master is WIPS – WIP inventory stock.
Hence while converting planned order into process order system reads the accounting view data to calculate the cost & determine the accounts using the valuation class. That time system is giving the CIF error.
Note:- The Qty & value updating field in the material type config is not relevant to this error.
Solution:-Either changes the Valuation class in the accounting view of material master or else change the back flush indicator from 1 to blank.
- Error: CFPLO000100000382 MQ1CLNT210 @OJ@ Two constraints that exclude each other or create unrealizable situation
Cause:
Process Order directly created in ECC system & sent to APO. In ECC Master Recipe is created but the production version is not created & also not CIFed to APO. Hence the error occurred.
Note: - Following observations:-
- Delete the queue.
- Create the production version in ECC but don’t CIF to APO.
- Now if you will create the Process order in ECC system then it will go to APO without any error. But there will not be source of supply in the process order in APO. The reason is that the PPM is still not CIFed to APO.
- All the operation will also appear in APO but without any operation description.
- You can also schedule the order in APO without PPM availability but the dates will calculate based on ECC master data not as per APO.
Resolution:-Create the Production version in ECC & send it to APO.
- Source of supply () not in source list (Material/Plant) despite source list requirement
- Vendor is not included in the source list (if it is purchase info record).
- Vendor /scheduling agreement is not included in the source list for the material plant.
- The validity dates are not in the range of the purchase requisition.
- The validity dates of the Pur Info record maintained in the info record is different then valid in the source list.
- The validity date of the source of supply in APO is inconsistent with the validity dates in ECC system.
- Source list indicator is set in the material master “Purchasing view”.
- Source list is maintenance is mandatory at plant level irrespective of the material type (In-house or External)
Solution:-
- Maintain the vendor or scheduling agreement in the source list with the consistent validity date in ECC & APO.
- The validity dates should be same in ECC & APO for the outline agreement & the purchase info record.
- If after removing the “Source list indicator” from the material master still the same error is reflecting that means in the source list configuration the ‘Source list indicator” is mandatory for that location.
- Not possible to determine shipping data for material MAT1 at YYYY
- Check the Sales organization data of Material master and it should be maintained with correct sales area which is maintained in customizing “Setup for Stock Transport Order”.
- Make sure that the Customizing for “Set Up for Stock Transport Order” is correctly maintained. Ask the user to check the same and if necessary take the help of R/3 Support team.
- In order to check the Customizing for “Set Up for Stock Transport Order” , follow the path : SPRO à Material Management à Purchasing à Purchase Order à Set Up for Stock Transfer Order.
Here please make sure that
- Receiving plant is assigned to correct customer Number created by the Sales area of supplying plant.
- Also check correct delivery document type (NL-Intra Company and NLCC-Inter Company) has been assigned to the supplying plant.
- A correct purchasing document type should be assigned to the combination of receiving plant and supplying plant.
- No sales area is assigned to sold-to party XXXXXXXXX and plant YYYY
- Check in the customizing of R/3 that whether any sales area is assigned to this VMI customer and plant combination. The Path to check this is SPRO àIntegration with Other SAP Components à Advanced Planning and Optimization à Application Specific Settings and Enhancements à Settings and Enhancements for Sales Order à Settings for Vendor Managed Inventory à Assign Sales Area and Order Type to Ordering Party/Plant.
- This setting is required if the customer is a VMI customer for one plant for some products without which the sales orders will not get any numbers from R/3.
12. CIF- Important T-codes
R/3: | |
Transaction code | Description |
CFM1 | Create integration model |
CFM2 | Activate/deactivate integration models |
CFG1 | View CIF application log |
CFC2 | User parameters for CIF |
CFC3 | Block sizes for initial transfer |
CFM5 | Filter object search in integration models |
CFC1 | Define logical systems as APO systems |
NDV2 | Setting of release level of APO systems |
SMQ1/SMQ2 | qRFC monitor incl. functions start, stop, execute |
SM59 | Definition of RFC destinations |
SALE | Definition of logical systems |
APO: | |
Transaction code | Description |
/SAPAPO/C3 | View CIF application log |
/SAPAPO/C4 | Setting of user parameters CIF |
/SAPAPO/C5 | Send planning results to R/3 |
/SAPAPO/C1 | Create business system group |
/SAPAPO/C2 | Assign logical systems to a business system group |
/SAPAPO/CQ | SCM Queue Manager |
/SAPAPO/CCR | Comparison/reconciliation tool |
SMQ1/SMQ2 | qRFC monitor incl. functions start, stop, execute |
SM59 | Definition of RFC destinations |
SALE | Definition of logical systems |
/SAPAPO/CPP | CIF Post processing |
References
- SAP Note: 563806
- SAP Note: 369007
- SAP note: 786446
- SDN: www.sdn.sap.com
- SAP Help: www.help.sap.com
- For more information, visit the Supply Chain Management homepage
- SAP Managed Tags:
- SAP Advanced Planning and Optimization
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
aATP
1 -
ABAP Programming
1 -
Activate Credit Management Basic Steps
1 -
Adverse media monitoring
1 -
Alerts
1 -
Ausnahmehandling
1 -
bank statements
1 -
Bin Sorting sequence deletion
1 -
Bin Sorting upload
1 -
BP NUMBER RANGE
1 -
Brazil
1 -
Business partner creation failed for organizational unit
1 -
Business Technology Platform
1 -
Central Purchasing
1 -
Charge Calculation
2 -
Cloud Extensibility
1 -
Compliance
1 -
Controlling
1 -
Controlling Area
1 -
Data Enrichment
1 -
DIGITAL MANUFACTURING
1 -
digital transformation
1 -
Dimensional Weight
1 -
Direct Outbound Delivery
1 -
E-Mail
1 -
ETA
1 -
EWM
6 -
EWM - Delivery Processing
2 -
EWM - Goods Movement
4 -
EWM Outbound configuration
1 -
EWM-RF
1 -
EWM-TM-Integration
1 -
Extended Warehouse Management (EWM)
3 -
Extended Warehouse Management(EWM)
7 -
Finance
1 -
Freight Settlement
1 -
Geo-coordinates
1 -
Geo-routing
1 -
Geocoding
1 -
Geographic Information System
1 -
GIS
1 -
Goods Issue
2 -
GTT
2 -
IBP inventory optimization
1 -
inbound delivery printing
1 -
Incoterm
1 -
Innovation
1 -
Inspection lot
1 -
intraday
1 -
Introduction
1 -
Inventory Management
1 -
Localization
1 -
Logistics Optimization
1 -
Map Integration
1 -
Material Management
1 -
Materials Management
1 -
MFS
1 -
New Feature
1 -
Outbound with LOSC and POSC
1 -
Packaging
1 -
PPF
1 -
PPOCE
1 -
PPOME
1 -
print profile
1 -
Process Controllers
1 -
Production process
1 -
QM
1 -
QM in procurement
1 -
Real-time Geopositioning
1 -
Risk management
1 -
S4 HANA
1 -
S4 HANA 2022
1 -
S4-FSCM-Custom Credit Check Rule and Custom Credit Check Step
1 -
S4SCSD
1 -
Sales and Distribution
1 -
SAP DMC
1 -
SAP ERP
1 -
SAP Extended Warehouse Management
2 -
SAP Hana Spatial Services
1 -
SAP IBP IO
1 -
SAP MM
1 -
sap production planning
1 -
SAP QM
1 -
SAP REM
1 -
SAP repetiative
1 -
SAP S4HANA
1 -
SAP TM
1 -
SAP Transportation Management
3 -
SAP Variant configuration (LO-VC)
1 -
SD (Sales and Distribution)
1 -
Source inspection
1 -
Storage bin Capacity
1 -
Supply Chain
1 -
Supply Chain Disruption
1 -
Supply Chain for Secondary Distribution
1 -
Technology Updates
1 -
TMS
1 -
Transportation Cockpit
1 -
Transportation Management
2 -
Visibility
2 -
warehouse door
1 -
WOCR
1
- « Previous
- Next »
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 3 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 1 | |
| 1 | |
| 1 | |
| 1 |