
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Enterprise Resource Planning
- ERP Blogs by Members
- Warranty Claim Management in SAP
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- It identifies the products/services under warranty
- Validate the authenticity of warranty claims
- Validates whether the product/service issue highlighted by customer falls under warranty
- Define the effects of warranties on pricing & invoicing
- Monitor expenses incurred under due to warranty issues
- Vehicle Consumer come into dealership
- Dealer determines if product/service defect is under valid warranty
- If yes, dealer files warranty claim
- Warranty assessors may review claim for accuracy
- Claim is either approved or rejected
- If approved, claim is processed through to Finance and dealer is reimbursed

SAP:
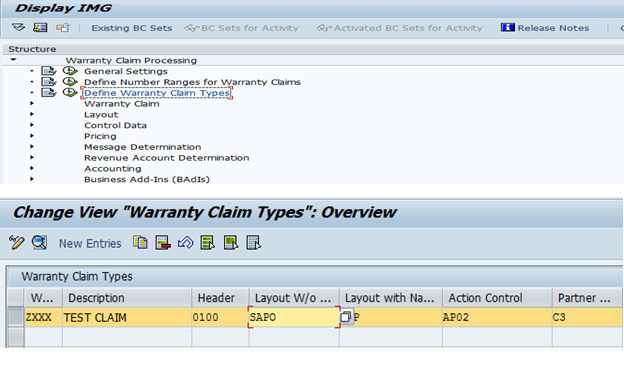
- Define Warranty Claim Type
- Assign Number Range for Claim Type
- Define Decision Codes
- Define Pricing for warranty claim
- Maintain Pricing Condition Records
- Define Action Matrix for Claim Processing
- Define GL Account Determination Procedure for Claim Processing
- Assign Pricing, action matrix and GL Account Determination Procedure to Claim Type
- Implement Validation/Substitution for claims (Optional)
- Define Output Determination for claim credit note
- Maintain Output Condition Records
path for configuring the same.





follows the same process.
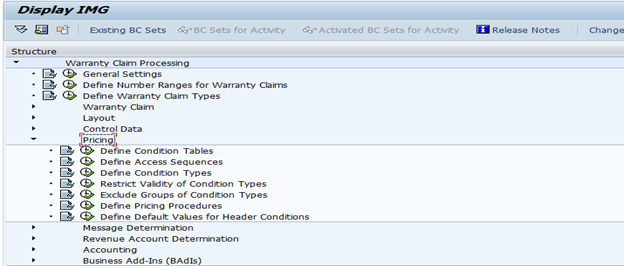

5. Maintain Pricing Condition Records
Similar to SD pricing condition records, warranty pricing condition records can be maintained via Transaction WYP1/WYP2/WYP3. To maintain conditions records
Please refer following SAP menu path.
SAP Menu ==> Logistics ==> Customer Service ==> Service Agreements ==> Warranty Claim Processing à Master Data ==>Condition Records for Pricing.

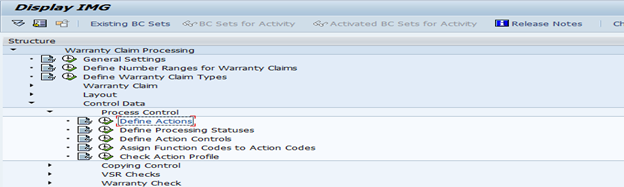
6. Define Action Matrix for Claim Processing
Action Matrix is a consolidated matrix of different actions/activities which can be carried out to a claim document at any given moment of time and also the consequences once any action is executed. Action matrix primarily consists of different actions and related status to it. Refer details about Action and Processing Status as mentioned below.
Action:
Every action does some processing and the processing logic is written is related Function Module attached to it. For example, standard action T041 has been defined as Elementary Action and Function Module WTY04_OC_POST_AC has been attached which would help to post credit memo for the claim amount.
To define action, follow below configuration path.
OWTY ==> Warranty Claim Processing ==> Control Data ==> Processing Control ==> Define Actions.
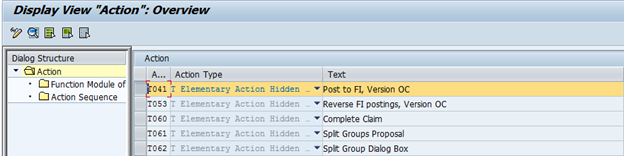
Refer Attached Function Module:

Processing Status:
After every action, claim gets a new status to identify every stage of the warranty claim. During definition of Action Matrix, these statuses would be used.
To define status, follow below configuration path.
OWTY ==> Warranty Claim Processing ==> Control Data ==> Processing Control ==> Define Processing Statuses.


Action Matrix:
Once Action and Processing Statuses are defined, action matrix can defined based on business requirement. This matrix would suggest what all activities (Claim Check, Claim Approval, Claim Reject etc.) can be done on a particular warranty claim and after completion of those action what would happen to the same claim document.
To define action matrix, please following below configuration path.
OWTY ==> Warranty Claim Processing ==> Control Data Processing Control ==> Define Action Controls.

Example of Standard Action Matrix is AP02.


Above given example (highlighted row), matrix suggests that for a claim document we can perform action T060 (via attached Function Module to it) only if the claim status is B002 and once we complete action T060, claim would have status B060.
7. Define GL Account Determination Procedure for Claim Processing
Every warranty claim should have account determination procedure attached to it to determine right GL account for posting claim expenses. Similar to configuration of Revenue Account Determination Procedure (e.g. definition of access sequence, condition type,
pricing procedure etc.) in the area of Finance, warranty GL Configuration procedure follows the same process.
To define GL determination procedure, refer following configuration path.
OWTY ==> Warranty Claim Processing ==> Revenue Account ==>Determination.

Example of Standard GL Determination procedure is KOFI00.

8. Assign Pricing, Action matrix and GL Account Determination Procedure to Claim Type
Pricing Procedure, Action Matrix and GL Account Determination procedure can be assigned to a claim type. To assign pricing procedure, action matrix and GL determination procedure, refer following configuration path.
OWTY ==> Warranty Claim Processing ==> Define Warranty Claim Types.

9. Implement Validation/Substitution for claims (Optional)
Validation and Substitution rules are similar functionality as available in the area of Finance. During warranty claim processing, if there is any business requirement to perform certain validation OR to substitute certain values as requested by business, these rules can be
implemented.
Implementation of Validation & Substitution is exactly similar to the functionality available in Finance Area. To implement validation and substitution please refer following configuration path.
OWTY ==> Warranty Claim Processing ==> Control Data ==> VSR Checks.

10. Define Output Determination for claim credit note
In case business has requirement to have an output (Print/Mail) for warranty credit notes, output determination procedure needs to be configure similar to output determination in SD area. Only difference here is, output type is assigned to FI documents generated for the claim. To implement output/message determination for warranty please refer following configuration path.
OWTY ==> Warranty Claim Processing ==> Message Determination.

11. Maintain Output Condition Records
Similar to SD output condition records, warranty message condition records can be maintained via Transaction WYN1/WYN2/WYN3. To
maintain conditions records please refer following SAP menu path.
SAP Menu ==> Logistics ==> Customer Service ==> Service Agreements ==> Warranty Claim ==> Processing ==> Master Data ==>
Condition Records for Message Determination.

- SAP Managed Tags:
- PLM Enterprise Asset Management (EAM)/Plant Maintenance (PM)
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
"mm02"
1 -
A_PurchaseOrderItem additional fields
1 -
ABAP
1 -
ABAP Extensibility
1 -
ACCOSTRATE
1 -
ACDOCP
1 -
Adding your country in SPRO - Project Administration
1 -
Advance Return Management
1 -
AI and RPA in SAP Upgrades
1 -
Approval Workflows
1 -
ARM
1 -
ASN
1 -
Asset Management
1 -
Associations in CDS Views
1 -
auditlog
1 -
Authorization
1 -
Availability date
1 -
Azure Center for SAP Solutions
1 -
AzureSentinel
2 -
Bank
1 -
BAPI_SALESORDER_CREATEFROMDAT2
1 -
BRF+
1 -
BRFPLUS
1 -
Bundled Cloud Services
1 -
business participation
1 -
Business Processes
1 -
CAPM
1 -
Carbon
1 -
Cental Finance
1 -
CFIN
1 -
CFIN Document Splitting
1 -
Cloud ALM
1 -
Cloud Integration
1 -
condition contract management
1 -
Connection - The default connection string cannot be used.
1 -
Custom Table Creation
1 -
Customer Screen in Production Order
1 -
Data Quality Management
1 -
Date required
1 -
Decisions
1 -
desafios4hana
1 -
Developing with SAP Integration Suite
1 -
Direct Outbound Delivery
1 -
DMOVE2S4
1 -
EAM
1 -
EDI
2 -
EDI 850
1 -
EDI 856
1 -
edocument
1 -
EHS Product Structure
1 -
Emergency Access Management
1 -
Energy
1 -
EPC
1 -
Financial Operations
1 -
Find
1 -
FINSSKF
1 -
Fiori
1 -
Flexible Workflow
1 -
Gas
1 -
Gen AI enabled SAP Upgrades
1 -
General
1 -
generate_xlsx_file
1 -
Getting Started
1 -
HomogeneousDMO
1 -
IDOC
2 -
Integration
1 -
learning content
2 -
LogicApps
2 -
low touchproject
1 -
Maintenance
1 -
management
1 -
Material creation
1 -
Material Management
1 -
MD04
1 -
MD61
1 -
methodology
1 -
Microsoft
2 -
MicrosoftSentinel
2 -
Migration
1 -
MRP
1 -
MS Teams
2 -
MT940
1 -
Newcomer
1 -
Notifications
1 -
Oil
1 -
open connectors
1 -
Order Change Log
1 -
ORDERS
2 -
OSS Note 390635
1 -
outbound delivery
1 -
outsourcing
1 -
PCE
1 -
Permit to Work
1 -
PIR Consumption Mode
1 -
PIR's
1 -
PIRs
1 -
PIRs Consumption
1 -
PIRs Reduction
1 -
Plan Independent Requirement
1 -
Premium Plus
1 -
pricing
1 -
Primavera P6
1 -
Process Excellence
1 -
Process Management
1 -
Process Order Change Log
1 -
Process purchase requisitions
1 -
Product Information
1 -
Production Order Change Log
1 -
Purchase requisition
1 -
Purchasing Lead Time
1 -
Redwood for SAP Job execution Setup
1 -
RISE with SAP
1 -
RisewithSAP
1 -
Rizing
1 -
S4 Cost Center Planning
1 -
S4 HANA
1 -
S4HANA
3 -
Sales and Distribution
1 -
Sales Commission
1 -
sales order
1 -
SAP
2 -
SAP Best Practices
1 -
SAP Build
1 -
SAP Build apps
1 -
SAP Cloud ALM
1 -
SAP Data Quality Management
1 -
SAP Maintenance resource scheduling
2 -
SAP Note 390635
1 -
SAP S4HANA
2 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud private edition
1 -
SAP Upgrade Automation
1 -
SAP WCM
1 -
SAP Work Clearance Management
1 -
Schedule Agreement
1 -
SDM
1 -
security
2 -
Settlement Management
1 -
soar
2 -
SSIS
1 -
SU01
1 -
SUM2.0SP17
1 -
SUMDMO
1 -
Teams
2 -
User Administration
1 -
User Participation
1 -
Utilities
1 -
va01
1 -
vendor
1 -
vl01n
1 -
vl02n
1 -
WCM
1 -
X12 850
1 -
xlsx_file_abap
1 -
YTD|MTD|QTD in CDs views using Date Function
1
- « Previous
- Next »
- Introducing the market standard of electronic invoicing for the United States in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
- Overview of the customer discount process (Skonto) in S/4HANA Cloud in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
- Continuous Influence Session SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition: Results Review Cycle for Q4 2023 in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
- SAP S/4HANA Cloud Private Edition | 2023 FPS01 Release – Part 2 in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
- Good to Know: SAP Travel Management for SAP S/4HANA in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 1 | |
| 1 | |
| 1 |