
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Technology
- Technology Blogs by Members
- Big Data and Data Science in Action - SAP Webcast ...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
SAP provided this webcast today, giving a background on data science.

Figure 1: Source: SAP
A data scientist uses mathematics and IT to solve business problems, asks the right questions, and use technical tools and programming languages

Figure 2: Source: SAP
How does data science differ from BI? The SAP speaker said BI defines standard reporting functionality while data science contains a math component
The maturity model shown in Figure 2 shows data mining, applying math standards to a dataset, algorithms, decisions trees, to find a pattern, to create clusters, or forecast a time series
Modeling comes in using a business process with a causal model, what are the driving factors, invent a math formula, or to use the data to fine-tune parameters
Optimization is looking at deviations, changing safety stocks.

Figure 3: Source: SAP
Figure 3 was a quiz – the numbers are in Euros
One set of numbers is true
The other set of Numbers is made up – invented by person
54% of the attendees thought the left column was false (including me). Wait until the end for the “final answer”.

Figure 4: Source: SAP
Figure 4 shows a retail example of how customers buy things
Retail generates data, measuring the impacts of sales promotions
Retail produces new products, need to be tested, problem is large # of products fail
Company puts two new products on shelf to sell products, which product has more or less
Figure 4 looks like product A is more successful, and it might leave Product A on shelf and remove B
First new flavor you may buy out of curiosity. The second effect – eaten it and like/not like, buy again
During the first month , the first effect is stronger, second effect is more important to keep customers in long term
You want to see how people buy product repeatedly to determine success and ask the right questions

Figure 5: Source: SAP
Figure 5 is a supply chain optimization example for a railway, where they manage a large supply chain of spare parts, with a complex set up, with different locations of serving trains, parts available, broken part.
Supply chains are managed in each location, replenishing policy – use spare parts until drop at reorder point and consume over time. Parameters are involved.
Who says reorder point is where it should be?
Solution looks at simulation in the future, using the historical information – statistical distribution for demand
They then optimize parameter to reduce reorder point so inventory is smaller to enable forecasting

Figure 6: Source: SAP
Next example of newspaper sales in Figure 6 provides forecasting with optimizing
If not send enough, lose sales, but if too much the newspaper incurs the cost of sending newspapers back
How many newspapers send each day is the model.
Look at history to forecast future sales; add safety stock
As an example, say Shop “B” in Figure 6 is a small shop next to football stadium, gameday sell a lot, others days not. It needs to take into effect special factors
More precise is the variability of demand
It uses model to optimize papers to print/sell

Figure 7: Source: SAP
Another use case covered was Utilities with sensor data analytics – power utilities – use for processes
“Before data science get the data quality in place” the speaker said.
Data record could have millions of entries – could be incomplete
Use data science to improve data quality:
- Look at & manually update- labor intensive
- Define business rules; business experts apply to dataset; takes time
- Use math algorithms to identify patterns in data
Combine all three approaches to improve data quality
A data science team consists of those with a math background and combines those with technical and visualization (to hide complexity) and the back end use big data. See http://readwrite.com/2014/07/21/data-scientist-income-skills-jobs

Figure 8: Source: SAP
Figure 8 shows SAP UI5 front end with good user experience with functionality
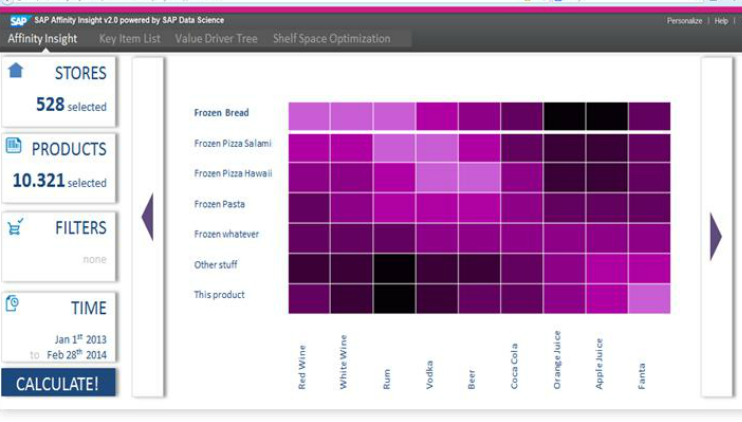
Figure 9: Source: SAP
Figure 9 shows how often customers buy 2 products at same time, to help promotions (does this mean orange juice is bought together with frozen bread)?
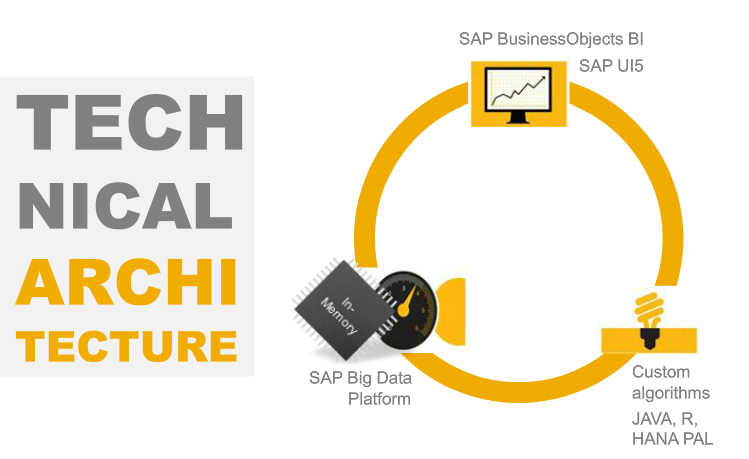
Figure 10: Source: SAP
Figure 10 shows the “Least common denominator”
BI and UI5 with UI5 combining transactions & analytical world, real-time, nice looking graphs with limited effort
SAP Big Data Platform includes HANA, Sybase portfolio
The algorithm side includes different tools with PAL in HANA or SQL algorithms, Java for specific coding
Spare parts simulator was built using Java
How to start a data science project:
Use cases workshop
Proof of concept project
Business case for full solution
Working with both business and IT
Data Science Quiz – Results

Figure 11: Source: SAP
How first number of numbers distributed as shown in Figure 11
When you falsify tax statement, you make the numbers look random
Every digit has the same probability
The speaker said open Wikipedia – look at numbers that describe quantities count – length of wall, write the down – first digit of number, 1 often, 2, often, 3 less,
8 and 9 almost never appear – Benfords’ law
Digit 1 once on right, so the right side is not real
Left side is real
Question & Answer:
Q: Retail example – are there other data points beside repeat purchasing to determine whether products are more popular?
A: visibility of shelf space – not data points used, include them as influencing factors
Systematically test programs
Q: Data mining – use full or sample?
A: It depends on business problem
Q: When talking about data quality, when take out outlier, need to understand where outliers are coming from – how assess?
A: Depends on business problem
Q: Related to data quality, example had corrected sensor data, assumption is you’re not dropping wrong data, then how ensure single source of truth?
A: Sent uncleansed data, used data mining to cleanse, data cleansing proposition, and use field examinations, and compare datasets – where don’t agree, which means a method has failed
Q: How far can you use Hadoop for Data Science and analysis and with SAP HANA?
A: Connect Hadoop with HANA – smart query layer- see Adobe example from ASUG Annual Conference 0404 Adobe’s Story of Integrating Hadoop ... | ASUG
Q: How build Data Science skills? Reading list, training?
A: Depends on where start from – math, statistics, high performance computing – look at data mining tools (SAP Predictive Analysis, InfiniteInsight) – really meant to make Data Science for end user, see SAP training
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
For more information, SAP TechEd && d-code Las Vegas has 136 "Big Data" sessions and ASUG has 10 Big Data sessions
Monday, October 20th, ASUG will host a hands-on BI session - more to come soon.
ASUG has a Harness the Big Data Monster webcast on August 5 - register here
- SAP Managed Tags:
- SAP BusinessObjects Business Intelligence platform
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
"automatische backups"
1 -
"regelmäßige sicherung"
1 -
"TypeScript" "Development" "FeedBack"
1 -
505 Technology Updates 53
1 -
ABAP
14 -
ABAP API
1 -
ABAP CDS Views
2 -
ABAP CDS Views - BW Extraction
1 -
ABAP CDS Views - CDC (Change Data Capture)
1 -
ABAP class
2 -
ABAP Cloud
2 -
ABAP Development
5 -
ABAP in Eclipse
1 -
ABAP Platform Trial
1 -
ABAP Programming
2 -
abap technical
1 -
absl
1 -
access data from SAP Datasphere directly from Snowflake
1 -
Access data from SAP datasphere to Qliksense
1 -
Accrual
1 -
action
1 -
adapter modules
1 -
Addon
1 -
Adobe Document Services
1 -
ADS
1 -
ADS Config
1 -
ADS with ABAP
1 -
ADS with Java
1 -
ADT
2 -
Advance Shipping and Receiving
1 -
Advanced Event Mesh
3 -
AEM
1 -
AI
7 -
AI Launchpad
1 -
AI Projects
1 -
AIML
9 -
Alert in Sap analytical cloud
1 -
Amazon S3
1 -
Analytical Dataset
1 -
Analytical Model
1 -
Analytics
1 -
Analyze Workload Data
1 -
annotations
1 -
API
1 -
API and Integration
3 -
API Call
2 -
Application Architecture
1 -
Application Development
5 -
Application Development for SAP HANA Cloud
3 -
Applications and Business Processes (AP)
1 -
Artificial Intelligence
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
4 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) 1 Business Trends 363 Business Trends 8 Digital Transformation with Cloud ERP (DT) 1 Event Information 462 Event Information 15 Expert Insights 114 Expert Insights 76 Life at SAP 418 Life at SAP 1 Product Updates 4
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise Oil Gas IoT Exploration Production
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise sustainability responsibility esg social compliance cybersecurity risk
1 -
ASE
1 -
ASR
2 -
ASUG
1 -
Attachments
1 -
Authorisations
1 -
Automating Processes
1 -
Automation
1 -
aws
2 -
Azure
1 -
Azure AI Studio
1 -
B2B Integration
1 -
Backorder Processing
1 -
Backup
1 -
Backup and Recovery
1 -
Backup schedule
1 -
BADI_MATERIAL_CHECK error message
1 -
Bank
1 -
BAS
1 -
basis
2 -
Basis Monitoring & Tcodes with Key notes
2 -
Batch Management
1 -
BDC
1 -
Best Practice
1 -
bitcoin
1 -
Blockchain
3 -
BOP in aATP
1 -
BOP Segments
1 -
BOP Strategies
1 -
BOP Variant
1 -
BPC
1 -
BPC LIVE
1 -
BTP
11 -
BTP Destination
2 -
Business AI
1 -
Business and IT Integration
1 -
Business application stu
1 -
Business Application Studio
1 -
Business Architecture
1 -
Business Communication Services
1 -
Business Continuity
1 -
Business Data Fabric
3 -
Business Partner
12 -
Business Partner Master Data
10 -
Business Technology Platform
2 -
Business Trends
1 -
CA
1 -
calculation view
1 -
CAP
3 -
Capgemini
1 -
CAPM
1 -
Catalyst for Efficiency: Revolutionizing SAP Integration Suite with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and
1 -
CCMS
2 -
CDQ
12 -
CDS
2 -
Cental Finance
1 -
Certificates
1 -
CFL
1 -
Change Management
1 -
chatbot
1 -
chatgpt
3 -
CL_SALV_TABLE
2 -
Class Runner
1 -
Classrunner
1 -
Cloud ALM Monitoring
1 -
Cloud ALM Operations
1 -
cloud connector
1 -
Cloud Extensibility
1 -
Cloud Foundry
4 -
Cloud Integration
6 -
Cloud Platform Integration
2 -
cloudalm
1 -
communication
1 -
Compensation Information Management
1 -
Compensation Management
1 -
Compliance
1 -
Compound Employee API
1 -
Configuration
1 -
Connectors
1 -
Consolidation Extension for SAP Analytics Cloud
1 -
Controller-Service-Repository pattern
1 -
Conversion
1 -
Cosine similarity
1 -
cryptocurrency
1 -
CSI
1 -
ctms
1 -
Custom chatbot
3 -
Custom Destination Service
1 -
custom fields
1 -
Customer Experience
1 -
Customer Journey
1 -
Customizing
1 -
cyber security
2 -
Data
1 -
Data & Analytics
1 -
Data Aging
1 -
Data Analytics
2 -
Data and Analytics (DA)
1 -
Data Archiving
1 -
Data Back-up
1 -
Data Governance
5 -
Data Integration
2 -
Data Quality
12 -
Data Quality Management
12 -
Data Synchronization
1 -
data transfer
1 -
Data Unleashed
1 -
Data Value
8 -
database tables
1 -
Datasphere
2 -
datenbanksicherung
1 -
dba cockpit
1 -
dbacockpit
1 -
Debugging
2 -
Delimiting Pay Components
1 -
Delta Integrations
1 -
Destination
3 -
Destination Service
1 -
Developer extensibility
1 -
Developing with SAP Integration Suite
1 -
Devops
1 -
digital transformation
1 -
Documentation
1 -
Dot Product
1 -
DQM
1 -
dump database
1 -
dump transaction
1 -
e-Invoice
1 -
E4H Conversion
1 -
Eclipse ADT ABAP Development Tools
2 -
edoc
1 -
edocument
1 -
ELA
1 -
Embedded Consolidation
1 -
Embedding
1 -
Embeddings
1 -
Employee Central
1 -
Employee Central Payroll
1 -
Employee Central Time Off
1 -
Employee Information
1 -
Employee Rehires
1 -
Enable Now
1 -
Enable now manager
1 -
endpoint
1 -
Enhancement Request
1 -
Enterprise Architecture
1 -
ETL Business Analytics with SAP Signavio
1 -
Euclidean distance
1 -
Event Dates
1 -
Event Driven Architecture
1 -
Event Mesh
2 -
Event Reason
1 -
EventBasedIntegration
1 -
EWM
1 -
EWM Outbound configuration
1 -
EWM-TM-Integration
1 -
Existing Event Changes
1 -
Expand
1 -
Expert
2 -
Expert Insights
1 -
Fiori
14 -
Fiori Elements
2 -
Fiori SAPUI5
12 -
Flask
1 -
Full Stack
8 -
Funds Management
1 -
General
1 -
Generative AI
1 -
Getting Started
1 -
GitHub
8 -
Grants Management
1 -
groovy
1 -
GTP
1 -
HANA
5 -
HANA Cloud
2 -
Hana Cloud Database Integration
2 -
HANA DB
1 -
HANA XS Advanced
1 -
Historical Events
1 -
home labs
1 -
HowTo
1 -
HR Data Management
1 -
html5
8 -
HTML5 Application
1 -
Identity cards validation
1 -
idm
1 -
Implementation
1 -
input parameter
1 -
instant payments
1 -
Integration
3 -
Integration Advisor
1 -
Integration Architecture
1 -
Integration Center
1 -
Integration Suite
1 -
intelligent enterprise
1 -
Java
1 -
job
1 -
Job Information Changes
1 -
Job-Related Events
1 -
Job_Event_Information
1 -
joule
4 -
Journal Entries
1 -
Just Ask
1 -
Kerberos for ABAP
8 -
Kerberos for JAVA
8 -
Launch Wizard
1 -
Learning Content
2 -
Life at SAP
1 -
lightning
1 -
Linear Regression SAP HANA Cloud
1 -
local tax regulations
1 -
LP
1 -
Machine Learning
2 -
Marketing
1 -
Master Data
3 -
Master Data Management
14 -
Maxdb
2 -
MDG
1 -
MDGM
1 -
MDM
1 -
Message box.
1 -
Messages on RF Device
1 -
Microservices Architecture
1 -
Microsoft Universal Print
1 -
Middleware Solutions
1 -
Migration
5 -
ML Model Development
1 -
Modeling in SAP HANA Cloud
8 -
Monitoring
3 -
MTA
1 -
Multi-Record Scenarios
1 -
Multiple Event Triggers
1 -
Neo
1 -
New Event Creation
1 -
New Feature
1 -
Newcomer
1 -
NodeJS
2 -
ODATA
2 -
OData APIs
1 -
odatav2
1 -
ODATAV4
1 -
ODBC
1 -
ODBC Connection
1 -
Onpremise
1 -
open source
2 -
OpenAI API
1 -
Oracle
1 -
PaPM
1 -
PaPM Dynamic Data Copy through Writer function
1 -
PaPM Remote Call
1 -
PAS-C01
1 -
Pay Component Management
1 -
PGP
1 -
Pickle
1 -
PLANNING ARCHITECTURE
1 -
Popup in Sap analytical cloud
1 -
PostgrSQL
1 -
POSTMAN
1 -
Process Automation
2 -
Product Updates
4 -
PSM
1 -
Public Cloud
1 -
Python
4 -
Qlik
1 -
Qualtrics
1 -
RAP
3 -
RAP BO
2 -
Record Deletion
1 -
Recovery
1 -
recurring payments
1 -
redeply
1 -
Release
1 -
Remote Consumption Model
1 -
Replication Flows
1 -
Research
1 -
Resilience
1 -
REST
1 -
REST API
1 -
Retagging Required
1 -
Risk
1 -
Rolling Kernel Switch
1 -
route
1 -
rules
1 -
S4 HANA
1 -
S4 HANA Cloud
1 -
S4 HANA On-Premise
1 -
S4HANA
3 -
S4HANA_OP_2023
2 -
SAC
10 -
SAC PLANNING
9 -
SAP
4 -
SAP ABAP
1 -
SAP Advanced Event Mesh
1 -
SAP AI Core
8 -
SAP AI Launchpad
8 -
SAP Analytic Cloud Compass
1 -
Sap Analytical Cloud
1 -
SAP Analytics Cloud
4 -
SAP Analytics Cloud for Consolidation
2 -
SAP Analytics Cloud Story
1 -
SAP analytics clouds
1 -
SAP BAS
1 -
SAP Basis
6 -
SAP BODS
1 -
SAP BODS certification.
1 -
SAP BTP
20 -
SAP BTP Build Work Zone
2 -
SAP BTP Cloud Foundry
5 -
SAP BTP Costing
1 -
SAP BTP CTMS
1 -
SAP BTP Innovation
1 -
SAP BTP Migration Tool
1 -
SAP BTP SDK IOS
1 -
SAP Build
11 -
SAP Build App
1 -
SAP Build apps
1 -
SAP Build CodeJam
1 -
SAP Build Process Automation
3 -
SAP Build work zone
10 -
SAP Business Objects Platform
1 -
SAP Business Technology
2 -
SAP Business Technology Platform (XP)
1 -
sap bw
1 -
SAP CAP
2 -
SAP CDC
1 -
SAP CDP
1 -
SAP CDS VIEW
1 -
SAP Certification
1 -
SAP Cloud ALM
4 -
SAP Cloud Application Programming Model
1 -
SAP Cloud Integration for Data Services
1 -
SAP cloud platform
8 -
SAP Companion
1 -
SAP CPI
3 -
SAP CPI (Cloud Platform Integration)
2 -
SAP CPI Discover tab
1 -
sap credential store
1 -
SAP Customer Data Cloud
1 -
SAP Customer Data Platform
1 -
SAP Data Intelligence
1 -
SAP Data Migration in Retail Industry
1 -
SAP Data Services
1 -
SAP DATABASE
1 -
SAP Dataspher to Non SAP BI tools
1 -
SAP Datasphere
9 -
SAP DRC
1 -
SAP EWM
1 -
SAP Fiori
2 -
SAP Fiori App Embedding
1 -
Sap Fiori Extension Project Using BAS
1 -
SAP GRC
1 -
SAP HANA
1 -
SAP HCM (Human Capital Management)
1 -
SAP HR Solutions
1 -
SAP IDM
1 -
SAP Integration Suite
9 -
SAP Integrations
4 -
SAP iRPA
2 -
SAP Learning Class
1 -
SAP Learning Hub
1 -
SAP Odata
2 -
SAP on Azure
1 -
SAP PartnerEdge
1 -
sap partners
1 -
SAP Password Reset
1 -
SAP PO Migration
1 -
SAP Prepackaged Content
1 -
SAP Process Automation
2 -
SAP Process Integration
2 -
SAP Process Orchestration
1 -
SAP S4HANA
2 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud
1 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud for Finance
1 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud private edition
1 -
SAP Sandbox
1 -
SAP STMS
1 -
SAP SuccessFactors
2 -
SAP SuccessFactors HXM Core
1 -
SAP Time
1 -
SAP TM
2 -
SAP Trading Partner Management
1 -
SAP UI5
1 -
SAP Upgrade
1 -
SAP Utilities
1 -
SAP-GUI
8 -
SAP_COM_0276
1 -
SAPBTP
1 -
SAPCPI
1 -
SAPEWM
1 -
sapmentors
1 -
saponaws
2 -
SAPS4HANA
1 -
SAPUI5
4 -
schedule
1 -
Secure Login Client Setup
8 -
security
9 -
Selenium Testing
1 -
SEN
1 -
SEN Manager
1 -
service
1 -
SET_CELL_TYPE
1 -
SET_CELL_TYPE_COLUMN
1 -
SFTP scenario
2 -
Simplex
1 -
Single Sign On
8 -
Singlesource
1 -
SKLearn
1 -
soap
1 -
Software Development
1 -
SOLMAN
1 -
solman 7.2
2 -
Solution Manager
3 -
sp_dumpdb
1 -
sp_dumptrans
1 -
SQL
1 -
sql script
1 -
SSL
8 -
SSO
8 -
Substring function
1 -
SuccessFactors
1 -
SuccessFactors Time Tracking
1 -
Sybase
1 -
system copy method
1 -
System owner
1 -
Table splitting
1 -
Tax Integration
1 -
Technical article
1 -
Technical articles
1 -
Technology Updates
1 -
Technology Updates
1 -
Technology_Updates
1 -
Threats
1 -
Time Collectors
1 -
Time Off
2 -
Tips and tricks
2 -
Tools
1 -
Trainings & Certifications
1 -
Transport in SAP BODS
1 -
Transport Management
1 -
TypeScript
2 -
unbind
1 -
Unified Customer Profile
1 -
UPB
1 -
Use of Parameters for Data Copy in PaPM
1 -
User Unlock
1 -
VA02
1 -
Validations
1 -
Vector Database
1 -
Vector Engine
1 -
Visual Studio Code
1 -
VSCode
1 -
Web SDK
1 -
work zone
1 -
workload
1 -
xsa
1 -
XSA Refresh
1
- « Previous
- Next »
- New webcast series on “SAP BTP DevOps and Observability in Action” in Technology Blogs by SAP
- Revolutionizing Business through the Power of SAP’s Artificial Intelligence Superheroes in Technology Blogs by SAP
- SAP Extensibility with SAP Build Code in Technology Blogs by SAP
- Safeguard your SAP BW conversion with SAP Enterprise Support services in Technology Blogs by SAP
- AI-Embedded Flexible Energy Grid: introduction & architecture in Technology Blogs by SAP
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 11 | |
| 10 | |
| 7 | |
| 6 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 |