
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Technology
- Technology Blogs by SAP
- HANA Cloud Integration (HCI) - Application Edition...
Technology Blogs by SAP
Learn how to extend and personalize SAP applications. Follow the SAP technology blog for insights into SAP BTP, ABAP, SAP Analytics Cloud, SAP HANA, and more.
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
Product and Topic Expert
Options
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
07-04-2014
6:42 AM
In this blog we will look at the one of the most important aspects of any cloud based solution, Security. We will keep our focus limited to the transport layer security aspects which are relevant for using the pre-packaged content only. Security being a vast topic, we will cover in two posts. On this post we will talk about the client side security and on the next we will talk about server side security.
Client Side Security
Let’s first understand what client side security is, with a very simple example. Let’s take the example of any site which uses SSL.
Note: I am using Google Chrome bowser for this post, but the same is true for any browser.
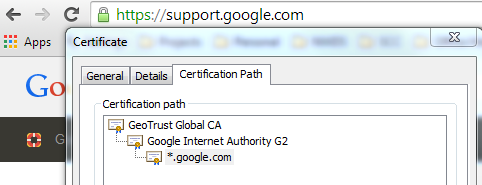
The point of interest here is the green lock icon as shown above. The lock symbol states that the site using SSL and the green color states that browser has successfully established a secure connection with the site. Here the bowser is acting as a client and the site is the server (SSL provider). Now why does the browser trust the site? This is because browser trusts the root issuer certificate for the given site.
For example for this site the own certificate is the last entry *.google.com, which is issued by Google Internet Authority G2 (Intermediate authority), which in turn is signed by GeoTrust Global CA (Root certificate). Every client maintains a list of trusted root certification authority, in case of chrome (browser) this can be seen below

So for client to continue with the SSL handshake a very basic requirement is client must trust the root CA of the server certificate otherwise the SSL handshake will terminate on the client side with an error Peer certificate rejected by chain verifier or unable to find valid certification path to requested target.
Additionally in case of certificate based mutual authentication where client authenticates itself with a certificate, client certificate should be signed a CA which is in trust list of Server (In the next blog post we will look at the server side authentication). During a client authenticated SSL handshake in the negotiation phase Server presents a list of issuer (CA) it trusts and expects client certificate must be signed by one of the issuers from the list.
HCI (Certificate Based authentication)
Now with this basic understanding let’s now shift our focus to HCI. HCI acts as a client when it is sending request to a destination system example SAP Cloud for Customer or SAP Business suite systems (CRM or ERP).
We configure if HCI would use basic authentication or certificate based authentication in the receiver channel as shown below (here below I have used IDOC receiver adapter, but it holds true for all other adapters as well). By default receiver channel use client cert authentication, but in case we want to use basic authentication we need to select the check box Connect using Basic authentication (more on this a bit latter)

Now where we store the issuer certificates for the service provider for which HCI is the client.
On Every HCI tenant we can deploy a keystore artifact and this keystore contains HCI own keypair (key + Public certificate) and the list of trusted issuers. The public certificate from this keypair is used for client authentication. There can only be one key store per tenant and the default name is system.jks

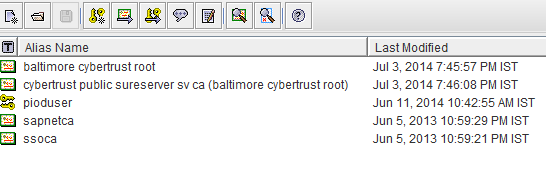
Let’s examine the content of this key store (I am using a free software Portecle, but any other tool can be used as well)

Here we can see there is one own key (alias pioduser) and few trusted issuers. We can add any number of trusted CA’s but there can be only one key per keystore. Let’s assume HCI is consuming a C4C service at endpoint https://vf4-cust234.dev.sapbydesign.com/sap/bc/srt/scs/sap/materialreplicationinitiatedby
With the key store as shown above if we try to send a message to this endpoint using HCI then we will get the following error: "unable to find valid certification path to requested target"

This is expected as HCI does not trust the issuer CA for the above service.

As shown above the C4C service is signed by issuer Cybertrust Public SureServer SV CA, which is in turn signed by Baltimore CyberTrust Root. So now we need to add the Baltimore CyberTrust Root cert to the HCI key store and redeploy.
Now if we send another message to the above endpoint using HCI, it should result in a success message.

Basic Authentication
In addition to Client certificate based authentication HCI PI also support basic authentication. For basic authentication we need to simply provide the username and password in the receiver communication channel. But the way we provide it is bit different in HCI
First we need to deploy an artifact type Basic authentication

And then we need to provide it a name and provide the authentication information (credentials) for the destination system
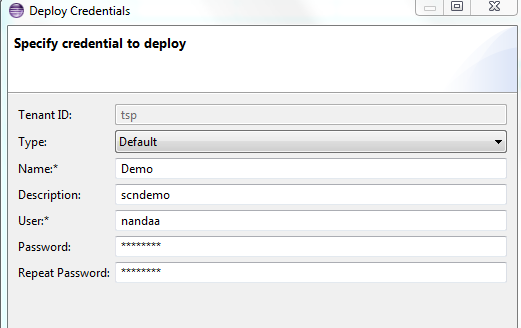
And as a last step provide this credential name in the receiver communication channel

Please keep in mind even if Basic authentication is used on receive channel still HCI needs to trust the endpoint to which it is sending the data, so the issuer CA needs to be maintained in the HCI key store.
That’s it for this post. In the next blog we will look at the Server side authentication. Watch out for this series and happy learning!!!
- SAP Managed Tags:
- Cloud Integration,
- Security
Labels:
9 Comments
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
Labels in this area
-
ABAP CDS Views - CDC (Change Data Capture)
2 -
AI
1 -
Analyze Workload Data
1 -
BTP
1 -
Business and IT Integration
2 -
Business application stu
1 -
Business Technology Platform
1 -
Business Trends
1,661 -
Business Trends
88 -
CAP
1 -
cf
1 -
Cloud Foundry
1 -
Confluent
1 -
Customer COE Basics and Fundamentals
1 -
Customer COE Latest and Greatest
3 -
Customer Data Browser app
1 -
Data Analysis Tool
1 -
data migration
1 -
data transfer
1 -
Datasphere
2 -
Event Information
1,400 -
Event Information
65 -
Expert
1 -
Expert Insights
178 -
Expert Insights
280 -
General
1 -
Google cloud
1 -
Google Next'24
1 -
Kafka
1 -
Life at SAP
784 -
Life at SAP
11 -
Migrate your Data App
1 -
MTA
1 -
Network Performance Analysis
1 -
NodeJS
1 -
PDF
1 -
POC
1 -
Product Updates
4,577 -
Product Updates
330 -
Replication Flow
1 -
RisewithSAP
1 -
SAP BTP
1 -
SAP BTP Cloud Foundry
1 -
SAP Cloud ALM
1 -
SAP Cloud Application Programming Model
1 -
SAP Datasphere
2 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud
1 -
SAP S4HANA Migration Cockpit
1 -
Technology Updates
6,886 -
Technology Updates
408 -
Workload Fluctuations
1
Related Content
- ABAP Cloud Developer Trial 2022 Available Now in Technology Blogs by SAP
- Hack2Build on Business AI – Highlighted Use Cases in Technology Blogs by SAP
- Convert multiple xml's into single Xlsx(MS Excel) using groovy script in Technology Blogs by Members
- New Machine Learning features in SAP HANA Cloud in Technology Blogs by SAP
- Unify your process and task mining insights: How SAP UEM by Knoa integrates with SAP Signavio in Technology Blogs by SAP
Top kudoed authors
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 13 | |
| 10 | |
| 10 | |
| 7 | |
| 6 | |
| 5 | |
| 5 | |
| 5 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 |