
- SAP Community
- Groups
- Industry Groups
- SAP for Automotive
- Blogs
- Data Archival in IS-Auto
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
INTRODUCTION
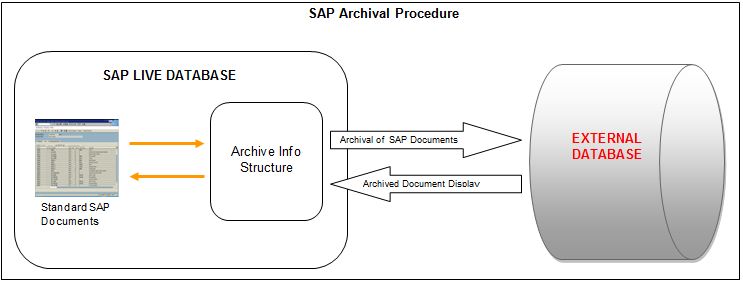
When enterprises use ERP for their business transactions, they generate a lot of data on their daily transactions. Over the years, this data is stored in the ERP servers and slowly cause deterioration of system performance. SAP, for its customers offers standard data archival solution. Using this, one can move the data from SAP server to an alternate location (separate server) which can be accessed on need basis.
In this document, the archival process has been explained at high level for automotive solution from SAP (IS Auto)
PREPARATIONS FOR DATA ARCHIVAL
Archival of data from the servers require a detailed planning, careful analysis and meticulous execution. Thorough testing of the archival process in test systems and establishing the approach to archive the data in production environment is the key to successful project. Following sections list out the general preparations that are required for an archival project.
Identification of data for archival
Following are different topics to be considered as part of data identification process.
1. Scope of data to be archived
Identifying the data to be archived is an important aspect in the archival process. The scope definition can either stem from the business decision (To reduce the database size) or from an organization policy (E.g. All data older than 5 years should be archived). Accordingly cut-off is decided.
There can be three different types of data in any business database. These are:
- Master data
- Transaction data
- System Admin data
Following are the list of archival objects which are bracketed into 3 different types of data:
Transactional Data | System Admin. Data | Master Data | |||
Arch. Object | Description | Arch. Object | Description | Arch. Object | Description |
VEHICLE | Vehicle | BC_DBLOGS | DB Tab Logs | MC_S600 | Evaluation Structure (S600) |
FI_DOCUMNT | FI Documents | IDOC | Idocs | MM_SPSTOCK | Batches and Special Stock |
MM_EKKO | Purchasing documents | BC_SBAL | Application Logs | MC_S033 | Evaluation Structure (S033) |
SD_VBAK | Sales documents | CATPROARCH | CATT-Log/Procedure | CA_BUPA | Business Partners |
MM_MATBEL | Material documents | FI_ACCRECV | Customer Master | ||
MM_REBEL | MM Invoice documents | MM_MATNR | Material Master | ||
RV_LIKP | Delivery documents | MM_HDEL | Material Valuation: History | ||
SD_VBRK | Billing documents | MC_S034 | Evaluation Structure (S034) | ||
MC_S035 | Evaluation Structure (S035) | ||||
MC_S012 | Evaluation Structure (S012) | ||||
MC_S014 | Evaluation Structure (S014) | ||||
FI_ACCPAYB | Vendor Master | ||||
MM_EINA | Purchasing Info records | ||||
Among these, master data consumes only a minute amount of space in data base. Following diagram pictorially represents the database usage of different types of data:

There can be different types of data and accordingly the filter criteria should be applied:
- All tables (Standard or Custom) whose size > ‘X’ megabyte (MB) should be considered for archiving
- All vehicle records older than ‘Y’ years should be considered for archiving
- All non – SAP documents (Such as PDF) older than ‘Y’ years OR pertaining vehicles selected in step 2 should be considered for archiving.
2. Residence and Retention Period
Residence Time is the minimum length of time that data must spend in the database before it is archived.
Retention Period is the entire duration of time before the data is completely deleted. This is based on the organization’s policy.
While archiving the data, organizations need to decide on residence time and retention period.

3. Exclusion rule sets
It is possible that certain information however old they are, very important for the organizations and these shouldn’t be archived. While archiving, it is important to identify such data sets and formulate certain rules in order to exclude such data from archiving. Certain custom programming will be necessary in order to frame the rule sets in ABAP/3.
4. Strategy for non-standard SAP data
Non – standard SAP constitutes bulk of data in VMS archival process. These can be classified into two categories.
- PDF Documents: Normally organizations will have PDF documents for customer relevant documents such as customer order, customer offer, Sales Invoice documents and Credit or Debit notes. Such documents can be archived and stored separately and can be accessed separately (Independent of vehicle data). Therefore, archival strategy has to be adopted for this type of data.
- Custom Tables: Non-standard SAP tables are another source of huge data. These tables also need to be considered along with standard SAP tables. A list of custom tables used in SAP environment needs to be prepared. From this list, all tables above the pre-decided cut off size need to be considered for archival.
5. Creation of DART Files
DAta Retention Tool (DART) is a functionality provided by SAP to meet the requirements by tax authorities. This tool extracts company code and period dependent data from database and corresponding master data and prepares file formats in ASCII. These files can be read using certain external tools.
Hence if there are requirements from tax authorities or local laws require such documents to be created, it is required as part of project to create DART files.
6. Identification of server to store the archived data
Normally archived data is stored in a separate server which can be accessed with certain restricted user permissions. Organization need to identify the retention period for the data after which this data can be discarded. Since it is expensive to manage the data in house, normally certain service providers (e.g. SAPERION) offer the service for a certain fee. Based on the organization’s data retention and audit policies, agreement can be made with the service providers in order to retain the data.
7. Security of the Data
Once the data has been stored in an external database, there could be certain occasions where users need to access the data. It has to be ensured to restrict the data access only to the information requested. In multi-country/market environment, access to the data from one market should be restricted to the users of another market.
8. Rule sets to access the archived data
Once the data has been archived and stored (either internally or externally) policy has to be formulated in order to access these stored data. Also the way in which data is accessed differs from the normal way of displaying the data in the system. Short training can be organized along with service provider who is providing the data storage facility.
Even though data is available for display, service providers grant limited access and multiple access comes with a price. It is advisable to access these data only for legal and auditing purposes.
9. Identification sequence of archival
It is not possible to archive the objects/documents if there are certain dependent object/ document present in the system. As a first step, all the dependent objects need to be archived and then the remaining objects can be archived. Following figure shows how the sequence can be organized for VMS archival procedure. PDF content can be archived separately before the archival of SAP documents begin.

10. Planning for Volume Testing
Success of archival project relies on the effective implementation and realization. In order to have defect free application, it is essential to have thorough testing of customizations and changes. It is also recommended to have volume testing since it gives better picture of the system behavior and estimate of the total time required for the archival process.
ARCHIVAL PROCEDURE
1. Standard customizations
In standard customization, user needs to set up the system in order to archive the standard SAP objects such as billing document, sales document etc. System is customized to select the files for archiving based on pre-determined conditions.
In VMS, users can select vehicles based on following different criteria:
- Specific primary status of the vehicle
- Specific secondary status of the vehicle
- Specific action on the vehicle
- Residence period
Following figure shows the duration between vehicle creation till the end of residence period.

Below is the screenshot of the standard SAP transaction (OBR8) where the residence period in days can be customized.
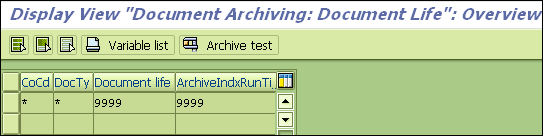
2. Data Backup
Similar to all critical projects where database back up is taken before the Go-Live of new software, it is essential to take the back up of complete data before the data archival is started. This helps if data restore is required in case of inadvertent deletion of data (that was not supposed deleted/archived) or some issues during archival which may corrupt the data.
Hence this step needs to be considered during the project planning so that, this step is considered as mandatory step before archival step.
3. Archival
Archive Development Kit or ADK is a technical framework provided by SAP for the secure archival process. This framework provides a cluster of tools for enabling the complete archival procedure. ADK provides the interfaces, function modules, example programs and documentation that one needs to develop own archiving programs. Through ADK, SAP ensures that data archiving is independent of hardware and release changes.
ADK includes:
- Archive Administration (SARA) functions
- Pre processing
- Write
- Delete
- Post processing
- Read
- Index
- Storage System
- Management
- Database Tables
- Info System
- Statistics
- An API to develop customer-specific archiving programs
- Archiving-specific function modules
- Automatic Job scheduling
- File management using SAP Content Management Infrastructure
- Connection to the storage system
- Compression during archiving
- Possibility of archiving while the system is running
- Network graphic for showing object dependencies
- Access to individual data objects in the archive
- Sample programs and documentation
Once the customizations related to archival is completed, archival process can be initiated. Archival process is managed through a tool SARA. Following functions are possible using this tool:
- Archiving Customizing
- Overview of the archiving jobs
- Assigning tables to archiving objects (DB15)
- Data archiving statistics
- Archive Information System
If there are custom tables in VMS system, then based on the size of these tables also need to be considered for archival. While customizing, these tables also need to be considered.
4. Reconciliation
After archival procedure is completed, reconciliation of the data before archival and after archival is advisable. (i.e., sum of errors during archival process and data archived = original data set) It will help to identify if any data was missed in the archival or error has occurred in the process. If some issues have occurred during the archival procedure, this can help to identify, fix it and minimize the impact.
OVERSIGHT OF THE PROCEDURE AND DOCUMENTATION
During data archiving, it is important to consider the legal and other compliance aspects.
1. Legal Compliance
While archiving the data from the business database, it is important to consult the legal and auditing team. All local laws pertaining to retaining of documents need to be complied with. All the information related to archiving process need to be documented and preserved.
It is advisable to involve an auditing team in the project and take signoff from them. This also ensures the transparency and helps to analyse the issues that may come up at later point in time.
2. Documentation
From the project management and auditing point of view, it is important to keep the documentation of each and every project milestone such as requirement gathering, solution design etc. in the archival project. Necessary approvals (sign off) have to be obtained from all the concerned stake holders. This process has to be established early in the project life cycle so as to ensure the compliance from all the team members.
CHANGE REQUEST HANDLING
After the execution of initial archival process, there could be requirements for further improvements and changes to the archival programs and processes. These changes should be handled very diligently and carefully. This is because archival process involves the live database. Any issues arising because of changes to the archiving program can cause problems to live database. Following points need to be considered while changes to archiving programs are taken up:
- All the concerned stake holders should be consulted about the changes
- Thorough regression testing should be taken up in order to rule out any issues due to the changes taken up
PROJECT RISKS
Since the operational data is taken out of the database, it is necessary to tread caution. Following are the possible risks during the project execution which needs to be taken care of.
- Project execution delays
- Wrong data being archived
- Inefficient co-ordination between stake holders
- Legal complications
- SAP Managed Tags:
- Automotive
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.