
- SAP Community
- Groups
- Interest Groups
- Application Development
- Blog Posts
- General properties of ABAP Classes / Interfaces
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Technically speaking, an ABAP class consists of several parts. In order to figure them out, I just create a simple class with the following source code:
CLASS zcl_abap_class DEFINITION
PUBLIC FINAL CREATE PUBLIC .
PUBLIC SECTION.
DATA public_attribure TYPE i .
TYPES:BEGIN OF ty_global,
name TYPE string,
score TYPE i,
END OF ty_global.
METHODS public .
protected section.
data PROTECTED_ATTRIBUTE type I .
methods PROTECTED .
PRIVATE SECTION.
DATA private_attribute TYPE i .
METHODS private .
ENDCLASS.
CLASS ZCL_ABAP_CLASS IMPLEMENTATION.
METHOD private.
ENDMETHOD.
method PROTECTED.
endmethod.
METHOD public.
ENDMETHOD.
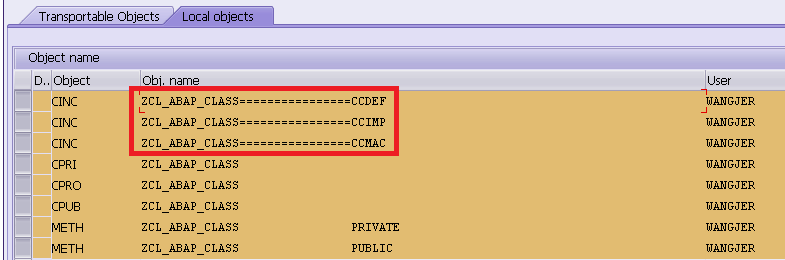
ENDCLASS.I have also generated a local test class for it via SE80. After activation, look into corresponding entry in TRDIR.

The object name under column NAME could be opened via SE38. Take CCAU for example:

So CCAU contains the source code of local test class implementation:
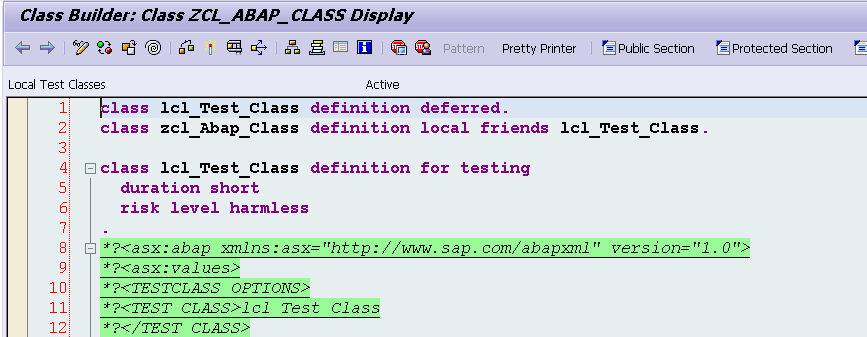
Here below is the list of each part and its meaning:
| Part Name | Part meaning |
|---|---|
| CCAU | contains the source code of local test class implementation |
| CCDEF | Class-Relevant Local Definitions, contains the definitions of local classes inside the public class |
| CCIMP | It contains the implementation for those local classes which definitions are stored in the Definitions-Include |
| CCMAC | contains the macros of the public class |
| CI | source code of private section |
| CO | source code of protected section |
| CU | source code of public section |
| CP | open it in SE38, it will automatically navigate to class builder |
| CT | open it in SE38, it will automatically navigate to class builder |
| CMXXX | source code of each method |
The constant of part name is defined in type group SEOP:

If you need to get the part name of a given class via ABAP code, you can use utility class CL_OO_CLASSNAME_SERVICE. There are corresponding getter method for each kind of part defined.
For example, if you need to get the part name of all methods of class CL_CRM_BOL_CORE, just set breakpoint in method CL_OO_CLASSNAME_SERVICE =>GET_ALL_METHOD_INCLUDES, and open the class CL_CRM_BOL_CORE in SE24, and click "Source Code-Based" button:

Here you can find the name class part for each method are populated with one incremental step in hexadecimal.
- SAP Managed Tags:
- ABAP Development,
- ABAP Testing and Analysis
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
A Dynamic Memory Allocation Tool
1 -
ABAP
8 -
abap cds
1 -
ABAP CDS Views
14 -
ABAP class
1 -
ABAP Cloud
1 -
ABAP Development
4 -
ABAP in Eclipse
1 -
ABAP Keyword Documentation
2 -
ABAP OOABAP
2 -
ABAP Programming
1 -
abap technical
1 -
ABAP test cockpit
7 -
ABAP test cokpit
1 -
ADT
1 -
Advanced Event Mesh
1 -
AEM
1 -
AI
1 -
API and Integration
1 -
APIs
8 -
APIs ABAP
1 -
App Dev and Integration
1 -
Application Development
2 -
application job
1 -
archivelinks
1 -
Automation
4 -
BTP
1 -
CAP
1 -
CAPM
1 -
Career Development
3 -
CL_GUI_FRONTEND_SERVICES
1 -
CL_SALV_TABLE
1 -
Cloud Extensibility
8 -
Cloud Native
7 -
Cloud Platform Integration
1 -
CloudEvents
2 -
CMIS
1 -
Connection
1 -
container
1 -
Debugging
2 -
Developer extensibility
1 -
Developing at Scale
4 -
DMS
1 -
dynamic logpoints
1 -
Eclipse ADT ABAP Development Tools
1 -
EDA
1 -
Event Mesh
1 -
Expert
1 -
Field Symbols in ABAP
1 -
Fiori
1 -
Fiori App Extension
1 -
Forms & Templates
1 -
IBM watsonx
1 -
Integration & Connectivity
10 -
JavaScripts used by Adobe Forms
1 -
joule
1 -
NodeJS
1 -
ODATA
3 -
OOABAP
3 -
Outbound queue
1 -
Product Updates
1 -
Programming Models
13 -
RFC
1 -
RFFOEDI1
1 -
SAP BAS
1 -
SAP BTP
1 -
SAP Build
1 -
SAP Build apps
1 -
SAP Build CodeJam
1 -
SAP CodeTalk
1 -
SAP Odata
1 -
SAP UI5
1 -
SAP UI5 Custom Library
1 -
SAPEnhancements
1 -
SapMachine
1 -
security
3 -
text editor
1 -
Tools
16 -
User Experience
5
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 6 | |
| 5 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 1 | |
| 1 | |
| 1 |