
- SAP Community
- Groups
- Industry Groups
- SAP for Utilities
- Blogs
- The Why, How and What of IT-OT integration for Ene...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Strenghths and challenges of current IT landscapes
The business process integration of data among Information Technologies and Operation Technologies is an already known concept and has become a major driver of the transformation at energy distribution companies. As the example below shows, the capabilities to relate data from sensors to business applications provide incredible benefits and improvements to the existing business processes of the companies. In fact, the smart grids concept relies in the same principle as for example substation automation.
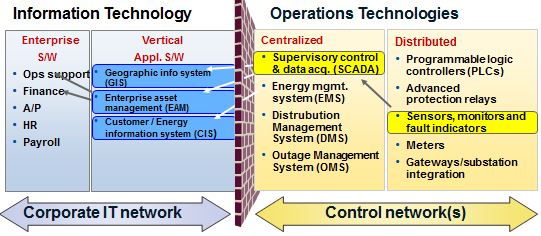
Source: Gartner
Once clarified the concept, the debate which may be the right IT strategy and its benefits. The usual approach is to define as a goal the establishment of an end to end Integrated process for the entire Asset Lifecycle, this is to cover both from Cash to Asset business scenario and the Operate and Maintain business scenario as well. With this goal many sinergies and IT – OT integration areas are identified and implemented. The main guideline and measurable framework to do it is by adopting of PAS55 (future ISO).
However, we believe there is another approach possible. IT – OT integration, and the foundational technologies which enable it, are unveiling a
new generation of systems, this si IT –OT convergence platforms which may gather data from all these systems and bring back value added information to improve their processes

As the picture copied above shows, the concept of an IT – OT convergence platform, where the SAP “Real Time Data Platform” can be accommodated does not replace any of the existing systems or functional domains but provides additional information, such as condition based maintenance or predictive maintenance
Evolution steps, the roadmap
With the decision to have an IT – OT integration platform for energy distribution companies, the scooping of it requires a clear idea on what do companies current have and what do they want to have.

As the picture above shows, the starting point is usually a very good amount of IT assets and information both from the IT area (historical data, technical datamodel) and OT (signals, time series historical data) and a very good perception on what is currently happening in the network, this is the real time information provided mainly by the process control systems and scada.
However, all this historical information and datamodels are not optimized. Just used for the real time information. We think that an IT – OT convergence platform has to enable capabilities to look into the past (retrospective analytics) as well into the future (forecasting, prediction).
One Step of the set up of ths platform are the datamoel definition and the dataquality policy. In the case of energy distributors, we think that the adoption of CIM standards (specified in the IEC 61970 for Transmission and 61968 for Distribution) , this is a semantic model that describes the components and structure of electric power system, will enable the exchange of information between applications.
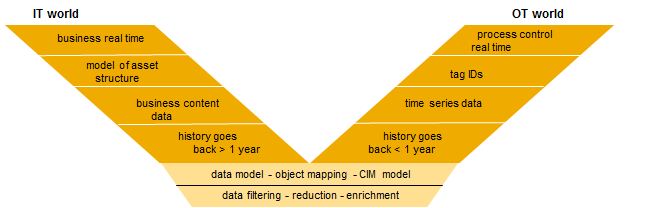
Additional Step is to Define the data services of the platform, and more precisely to set up a Data Quality Policy. Energy Distribution companies as other asset intensive industries have difficulties in managing their master data quality over the life of the asset. Organizations pursue the ability to assess, validate and continuously monitor the quality of their asset master data through the use of quality management tools, and predefined content in order to: Create or change business and validation rules, Identification of corresponding data quality issues, and ongoing analysis of historical data with continuous insight for IT systems as well as set up Pre-defined business rules to cover critical master data such as Technical equipment, Bills of Materials, Maintenance Plans, Task
Lists etc.
The result is a platform where can be performed both retrospective analytics and forecasting, this is the complete view of the asset information (360º )

To complete the evaluation of the how is it possible it is necessary to mention HANA. The usage of an in-memory, column-oriented, relational database
management system makes it possible removing constraints for analyzing large data: make Decisions Closer to Real-time, fast and easy creation of
ad-hoc views on business, access to real time analysis, accelerate Business Performance and provide the sufficient speed of information process to reach new functional areas such as planning, forecasting, data mining, predictive analytic and simulations for structured and unstructured data
Use Cases of new generation of applications based on IT OT integration - Real Time Data Platform
A very interesting scenario has been prototyped by Dr. Ralph Kühne, from the SAP Innovation Center Potsdam. Where they built a prototype to experience how SAP HANA platform may analyze large volumes of operational data using the latest Web UI technology to visualize transformed overload situations in the context of a co-innovation project with the SAP innovation Center
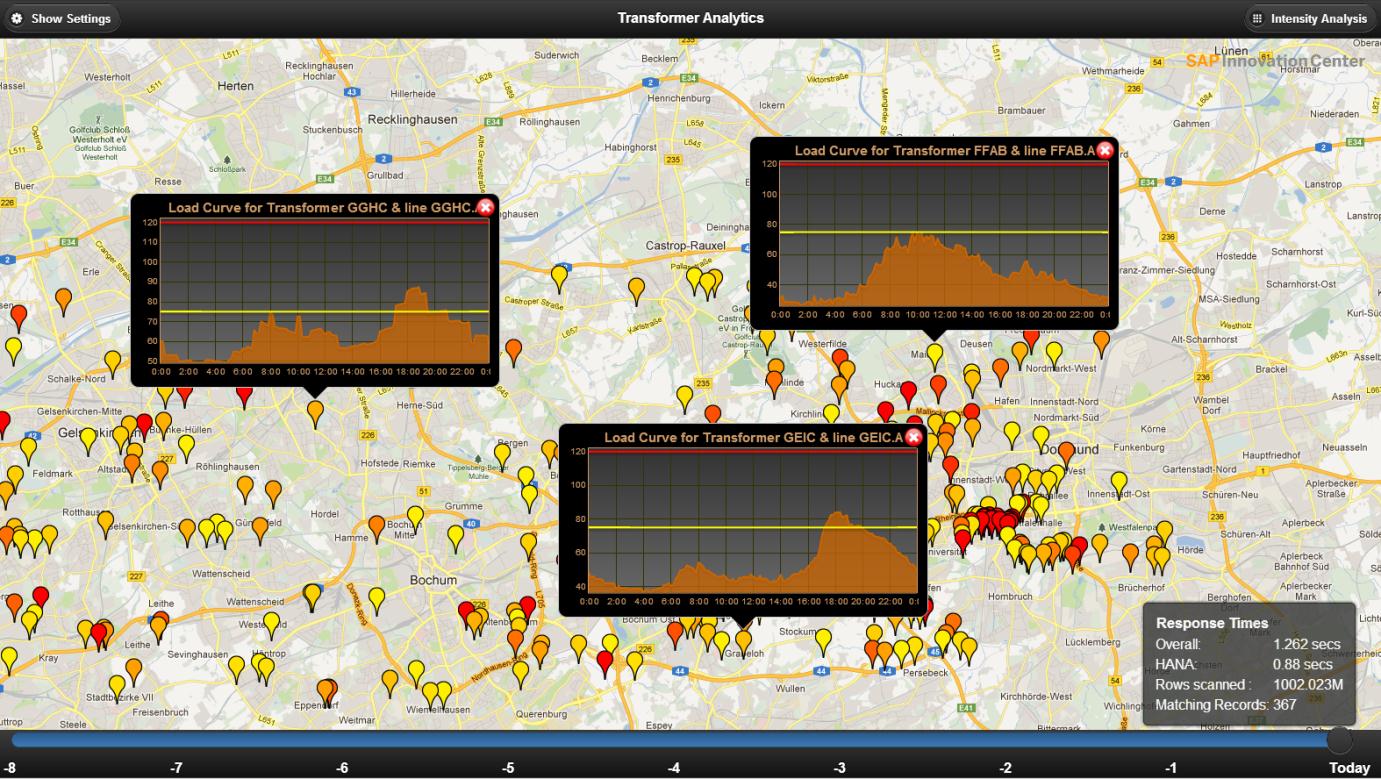
Figure: screen copy of SAP Innovation Center Potsdam's prototype for Transformer Analytics
The prototype characteristics are amazing for an implementation on SAP HANA on 16-core machine with 256 GB RAM with simple HTML5 user interface which comprises 87 weeks of load measurements for ~12,000 transformers , ~1 billion records (10 minute measurement interval), ~20 GB compressed in main memory, No materialized aggregates with incredible scenarios for : Transformer overload overview, comparison, Identifying hot spots, Examining weekly patterns and next-day forecasting, Weather correlation of loadand load peaks Investigation.
Other impressive case is Space Time Insight, which offers Asset Analytics based on Situational Intelligence and to support the day to day management of
transmission and distribution assets. With this platform, companies can have an enterprise system for identifying Alerts, asset risks, priorities to optimize
asset lifecycle decisions, and what-if scenarios.

Figure: screen copy of STI application used at Hydro One
Last, but not least, is Alert Enterprise. Goal is to provide a Unified Identity and Risk Management System to manage security information, operations and threat prevention out of the traditional silos of IT applications, physical security and Sensor (scada) data: “Silos are Costly, Inefficient: Organizations Respond to Threats in Silos - Attackers Don’t think that Way.”

Figure: screen copy of Enterprise Guardian application by Alert Enterprise
An example may be to prevent access to a critical area, like a substation, to a person with an authorized badge but outside of normal working hours without a workorder. It is not only about detection through video integration but to facilitate intelligence by providing remediation scripts for automated and\or manual response and give the security personnel the broader context of what is happing on location
Conclusion
IT – OT integration at Energy companies is about the capacity of freely manage Big Data. As technology is becoming a commodity while application esigns and content are being produced , it is feasible to think about consolidating all data in a single instance to explore and benefit of new business scenarios. Achieving a significantly high return is feasible as the large investments in smart infrastructure are already done in most cases and IT investments are very little in comparison.
- SAP Managed Tags:
- Utilities
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
customer centricity
1 -
cx
1 -
Life at SAP
2 -
Master Data
1 -
newsletter
1 -
Product Updates
2 -
Roadmap
1 -
S4 HANA
1 -
S4 HANA On-Premise
1 -
Utilities
2 -
utilities event
1