
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Enterprise Resource Planning
- ERP Blogs by Members
- How to set the optimal number of sessions for MRP ...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
One of the features within SAP’s MRP functionality is the ability to assign processing across multiple servers or sessions to improve the runtime performance of the planning run. This feature is called parallel processing and is accessed through configuration using OMIQ to define parallel processing in MRP.
To figure out how to determine the optimal number of sessions for parallel processing, we need to understand how this works. When using parallel processing, it will execute in terms of packages that use the low level code. This low level code is a component of the bill of material structure which we can use as a guideline for this. A bill of material is broken down by low level codes for each of the BOM levels. Determine what the deepest bill of material is and use this as your baseline number for low level codes. If the deepest bill of material is 3 levels deep, then you have low level codes 000 (end item), 001,
002 for your BOM levels. Thus your baseline number should be 3.

Since reorder point materials are not planned by requirements, these types of materials will be assigned a low level code 999 by the MRP program. That adds one more to your number for sessions. Now we have the 3 BOM levels and 1 reorder point level equals a total of 4 sessions. In example below, I have configured 4 sessions for parallel processing.

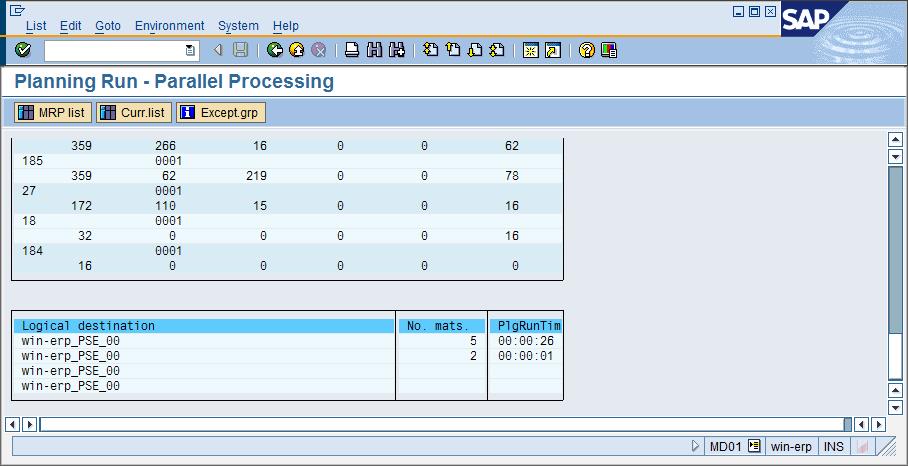
Each low level code is a work package that once completed; the next package will begin processing. Therefore if you have multiple sessions configured, then multiple work packages will be distributed over this number with a fixed number of materials assigned by the MRP program. When you set your MRP planning variant or run directly using MD01, you have an indicator that you may now set for parallel processing. This indicator will set the planning run to check the configuration setting for how many sessions to create. In my example, it was set to 4.

After the MRP run, you can then see where the low level codes are identified for the materials and at the end of the statistics shows how many material planned for each session. This method provides you a quick and easy way to determine the appropriate configuration level for using MRP Parallel processing.

- SAP Managed Tags:
- SAP ERP,
- MAN Production Planning (PP)
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
"mm02"
1 -
A_PurchaseOrderItem additional fields
1 -
ABAP
1 -
ABAP Extensibility
1 -
ACCOSTRATE
1 -
ACDOCP
1 -
Adding your country in SPRO - Project Administration
1 -
Advance Return Management
1 -
AI and RPA in SAP Upgrades
1 -
Approval Workflows
1 -
ARM
1 -
ASN
1 -
Asset Management
1 -
Associations in CDS Views
1 -
auditlog
1 -
Authorization
1 -
Availability date
1 -
Azure Center for SAP Solutions
1 -
AzureSentinel
2 -
Bank
1 -
BAPI_SALESORDER_CREATEFROMDAT2
1 -
BRF+
1 -
BRFPLUS
1 -
Bundled Cloud Services
1 -
business participation
1 -
Business Processes
1 -
CAPM
1 -
Carbon
1 -
Cental Finance
1 -
CFIN
1 -
CFIN Document Splitting
1 -
Cloud ALM
1 -
Cloud Integration
1 -
condition contract management
1 -
Connection - The default connection string cannot be used.
1 -
Custom Table Creation
1 -
Customer Screen in Production Order
1 -
Data Quality Management
1 -
Date required
1 -
Decisions
1 -
desafios4hana
1 -
Developing with SAP Integration Suite
1 -
Direct Outbound Delivery
1 -
DMOVE2S4
1 -
EAM
1 -
EDI
2 -
EDI 850
1 -
EDI 856
1 -
edocument
1 -
EHS Product Structure
1 -
Emergency Access Management
1 -
Energy
1 -
EPC
1 -
Financial Operations
1 -
Find
1 -
FINSSKF
1 -
Fiori
1 -
Flexible Workflow
1 -
Gas
1 -
Gen AI enabled SAP Upgrades
1 -
General
1 -
generate_xlsx_file
1 -
Getting Started
1 -
HomogeneousDMO
1 -
IDOC
2 -
Integration
1 -
Learning Content
2 -
LogicApps
2 -
low touchproject
1 -
Maintenance
1 -
management
1 -
Material creation
1 -
Material Management
1 -
MD04
1 -
MD61
1 -
methodology
1 -
Microsoft
2 -
MicrosoftSentinel
2 -
Migration
1 -
MRP
1 -
MS Teams
2 -
MT940
1 -
Newcomer
1 -
Notifications
1 -
Oil
1 -
open connectors
1 -
Order Change Log
1 -
ORDERS
2 -
OSS Note 390635
1 -
outbound delivery
1 -
outsourcing
1 -
PCE
1 -
Permit to Work
1 -
PIR Consumption Mode
1 -
PIR's
1 -
PIRs
1 -
PIRs Consumption
1 -
PIRs Reduction
1 -
Plan Independent Requirement
1 -
Premium Plus
1 -
pricing
1 -
Primavera P6
1 -
Process Excellence
1 -
Process Management
1 -
Process Order Change Log
1 -
Process purchase requisitions
1 -
Product Information
1 -
Production Order Change Log
1 -
Purchase requisition
1 -
Purchasing Lead Time
1 -
Redwood for SAP Job execution Setup
1 -
RISE with SAP
1 -
RisewithSAP
1 -
Rizing
1 -
S4 Cost Center Planning
1 -
S4 HANA
1 -
S4HANA
3 -
Sales and Distribution
1 -
Sales Commission
1 -
sales order
1 -
SAP
2 -
SAP Best Practices
1 -
SAP Build
1 -
SAP Build apps
1 -
SAP Cloud ALM
1 -
SAP Data Quality Management
1 -
SAP Maintenance resource scheduling
2 -
SAP Note 390635
1 -
SAP S4HANA
2 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud private edition
1 -
SAP Upgrade Automation
1 -
SAP WCM
1 -
SAP Work Clearance Management
1 -
Schedule Agreement
1 -
SDM
1 -
security
2 -
Settlement Management
1 -
soar
2 -
SSIS
1 -
SU01
1 -
SUM2.0SP17
1 -
SUMDMO
1 -
Teams
2 -
User Administration
1 -
User Participation
1 -
Utilities
1 -
va01
1 -
vendor
1 -
vl01n
1 -
vl02n
1 -
WCM
1 -
X12 850
1 -
xlsx_file_abap
1 -
YTD|MTD|QTD in CDs views using Date Function
1
- « Previous
- Next »
- Advance Return Management complete configuration(SAP ARM) in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by Members
- Purchase Ordre Accrual in S/4HANA - Part 1 in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by Members
- Purchase Requisition doesn't create in MDBT but create in MD02 in Enterprise Resource Planning Q&A
- Q&A collection for program BUPTDTRANSMIT in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
- New Installation of SAP S/4HANA 2023 FPS1 – Part 4 – Rapid Activation for Fiori in Enterprise Resource Planning Blogs by SAP
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 1 | |
| 1 |