
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Technology
- Technology Blogs by Members
- Whitepaper - Governance Over Material Master Data ...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Applies to
SAP Master Data Governance, as of SAP ERP 6.0 Enhancement Package 5. For more information, visit the Master Data Management homepage.
Summary
The main purpose of this article is to show how to maintain a simple scenario of Master Data Governance for material master data in Production MDR. A basic step by step guide to create,change,activate and de-activate material in master data governance over the Production and Pre-Production stages using transaction codes MM02, MM03 and MM06.
Author: Nithesh Kona
Company: Mahindra Satyam
Created on: 5 June 2013
Author Biography
Nithesh Kona has been associated with Mahindra Satyam and has been a part of SAP Data Management Services Team for the client Nestle.
He is skilled in SAP ABAP, SAP SRM, SAP CRM Technical, SAP MDM/MDG, Java. He completed his Bachelor’s degree in Computer Science engineering.
Presently in Mahindra Satyam ( Bangalore area, India) working for Client Nestle Food , water and health care on module SAP MDM ( Master Data Management) on sub module SAP MDG ( Master Data Governance ) and doing as a Senior Functional Consultant and working on the master data management as per the requests coming from the client market in Global locations and the requirements will be done in Production and Pre-production.

Table of Contents
1. Business Scenario
2. Prerequisites
3.Maintenance of Material Master Data Incidents
3.1 Material related Incidents
3.1.1 What is a Material.
3.1.2 Types of Materials.
3.1.3 Material Life Cycle.
3.1.4 IMSP & Shared Materials.
3.1.5 GTIN / EAN ( European Article Number)
3.2 Activating Material Manually and/or Setting Area of Interest.
3.2.1 Setting Area Of Interest for a Material
3.3 Deactivating a Material.
3.3.1 De-activating a Material
3.3.2 Flagging a material for deletion
3.4 Reactivating a Material.
3.4.1 Performing the checks
3.4.2 Reactivating a Material
3.5 IMSP Dual Maintenance.
3.5.1 Creating Material Manually.
3.5.2 Changing IMSP materials manually.
3.6 EAN Harmonization.
3.6.1 EAN Inconsistency
3.6.2 Executing EAN CONSISTENCY Transaction
3.7 Updating Materials with Status Z6.
3.8 Updating MLEA table.
4. Working with Master Data Governance for Vendors and Customers.
5. Related Content
6. Copyright
1. Business Scenario
Proper maintenance of Master Data is a big challenge in present business environments. Customers are facing challenges where there is no governing body to manage master data. No clearly defined roles and responsibilities for creating and approving master data. No transparency and visibility on who has done what. Lot of manual work where the request and reasons for new or changed master data had to be communicated by phone or email to master data specialists. Follow up processing by certain specialist have to be manually triggered. The whole process is time consuming. Need for single source of truth and data quality is the top priority. Data has to be replicated to SAP and Non-SAP systems.
SAP Master Data Governance (MDG) which delivers out of the box governance is the solution to the above challenges. SAP MDG is a domain specific, embedded MDM solution for SAP Business Suite to ensure data quality and regulatory compliance. Currently MDG is offered for material, supplier, financial and customer master data. This article gives you a detailed view of MDG for Supplier configuration and working.
2. Prerequisites
- You are working on ECC 6.0 EHP 5 or higher.
- You have installed the software component SAP Business Suite Foundation (SAP_BS_FND 702).
- You have activated the following business functions
* Master Data Governance, Generic Functions (MDG_FOUNDATION)
* Master Data Governance for Material (ERP) (MDG_ERP_MATERIAL)
- You are assigned to the following roles
o SAP_BC_TREX_ADMIN
o SAP_QAP_ESH or SAP_ESH_LOCAL_ADMIN if it is not available.
o SAP_MDGS
- Webdynpro services are activated
- Technical configuration of Embedded search is done with TREX version 7.10.40.00 or higher.
- Workflow material related incidents are procured.
3. Maintenance of Material Master Data Incidents
3.1 Material related Incidents
3.1.1 What is a Material.
A Material is defined as being made up of Substance and Packaging. When there is change in either one of the two parts that requires separate logistical control, a new Material is created.

3.1.2 Types of Materials:
Raw Materials or Ingredients (identified as ROH from the German 'roh' meaning raw) are components of semi-finished or finished goods
Semi-Finished Goods (HALB) are components of a finished product that you can either purchase or produce. You can combine semi-finished products to create a finished product
Packaging Materials (ZPCK) are components of finished products. For example, boxes, cartons, labels, shrink-wrap and adhesives
Rework (ZRWK) is planned or unplanned semi-finished Materials. You can use rework Materials in finished products. 'Chocolate tablets-plain' is an example of a rework Material
Finished Goods (identified as FERT from the German 'fertig' or finished) are products that are ready for retail. Complete list of all material types maintained at different levels:
MDR ( Master Data Repository) Materials: FERT, HALB, ROH, ZPCK, ZGNV, ZSIM, DIEN, VERP, ZTAS, ZGNS (10)
SDR (Supplementary Data Repository) Materials: ZRWK, UNBW, ERSA, NLAG, INTR, ZTRN, ZTRV (7)
Local Materials: PROD (SOS), WETT (COM), ZQST (COM), ZQVM (SOS), IBAU (SOS) (5)
Local Materials refer to those materials that are created in the local SAP R/3 systems in SOS (Supply/Operation system), COM (commercial system) or FI (Finance system) boxes.
3.1.3 Material Life Cycle:
Material Life Cycle is a process starting with the identification of a new Material and following it through the whole business process until it is no longer required. The Material Life Cycle is an E2E (End to End) process, which tracks a Material from the identification of a requirement for a new Material to its archiving. It only covers supply chain materials like ROH, ZPCK, FERT and HALB.
- A Material is created and activated in the MDR level as soon as it is identified by the resuestor.
- A material would be reactivated in the system at MDR level if it is required for Production or Procurement or Sales in any one of the plants or Purchase Organization or Sales Organization.
- When a material is no longer been used by a specific plant it is deactivated for that plant at SDR level.
- When a material is no longer been used by any of the plants, it is archived in the system and then it is flagged for deletion at both MDR & SDR levels.
- When materials are shared across the plant markets within the Organization, IMSP/Shared flag is set for the material.
Follow fields are used to track their flow through the lifecycle.
- Cross Plant Status
- Plant Specific Status
- Distribution Specific Status
The Material Life Cycle process may involve:
- Creating a new Material
- Extending an existing Material for new markets
- Changing an existing Material on MDR level

The stages in Material Life Cycle Process are defined in the system as Material Statuses, I.e.,
Z1 | Under Development |
Z2 | Pre-go decision |
Z3 | Active |
Z4 | Under Discontinuation |
Z5 | Discontinued |
Z6 | To be Archived |
- All six statuses shown above are used by the Plant Specific status in SDR level so the status of a Material in each Plant/Market might be different.
- However, the Cross Plant status, controlled at MDR level, only uses the status Z2, Z3, Z5 and Z6.
- As per the latest MDR and SDR release, Z4 status is allowed in MDR.
3.1.4 IMSP & Shared Materials
- Intra Market Supply Products (IMSP) are those materials which are bought and sold among different Affiliates in addition being sold to Third party. Only FERT and HALB fall under this category.
- Only producing Market can create these Materials but any receiving Market can raise a request to change them.
- The term Shared Materials applies to ROH and ZPCK Materials. These Materials are created in MDR and shared by several Markets. They are not sold and purchased among various Affiliates. Only the data maintained at MDR level, is shared by more than one market.
- IMSP/ Shared field in Basic data 3 is used to identify the Material. Markets using these Materials are listed in Market Usage tab in additional data.
3.1.5 GTIN / EAN
GTIN is an abbreviation for ( Global Trading Identification Number) and EAN stands for ( European Article Number) . The GTIN is used for the unique identification of trade items worldwide. A trade item is any item (product or service) upon which there is a need to retrieve pre-defined information and that may be priced or ordered or invoiced at any point in the supply chain. Each trade item, which differs from another, is allocated a unique identification number, which remains the same as long as it is being traded.
GTIN Variant is an additional identification number that differentiates items with the same GTIN. It is intended only for internal use of Nestle.
In SAP, Number Category of a European Article Number (EAN) defines how the system determines EAN.UCC numbers to be assigned internally. The Number Category also defines which check criteria an EAN of this category must satisfy.
GTIN are given by the GS1 organization to identify a material at a particular level. GTINs are specific to Each, Case and Display level. In some markets they are also assigned at pallet level.
Examples of when GTIN and GTIN Variants change:
- a) Material manufacture moves from AU (Australia) to TH (Thailand) with no changes in the product. In the below example there is no changes in the Material thus the GTIN remains the same. The Variant has changed as the place of manufacturing has been shifted and the supply chain wants to capture the change.

b) TH (Thailand) exports a material to MY (Malaysia) who changes its Case configuration from 12x85g to 24x85g. In the below example the Net weight of the product at Case level has changed which results in the GTIN change.

Note: More details of when GTINs change and when only GTIN variants change are available in a separate presentation on GTIN (attached).
3.2 Activating Material Manually and Setting Area of Interest
Live markets create materials via workflow. Materials created via workflow get automatically activated i.e. their Area of Interested (AOI) is set automatically. Most materials (over 99%) fall in this category. Non-live markets might have requirements to create some IMSP materials in SAP. This will be done by the NBS manually. For this, such markets will raise RM Tickets. They need to get the data approved by the receiving markets and attach the approved data with the Ticket. This process has been separately described under Section 5.4 (IMSP Dual Maintenance). If Area of Interest (AOI) for a material was previously not set for any reason, it would have to be done manually.
Checks:
Before activating a Material in MDR (via Transaction ZAOI1) following information must to be checked:
- Classification view has been created in MDR if x-plant status is Z3 (Also see point 10 under Section 5.4)
- Data in all MDR views is data standard compliant
- If you see an obvious error in the data, ask for clarification.
Process:
- If X-plant status is Z3 and the Classification view does not exist, then create classification view. See points 10 & 11 under Section 5.4 on how to create classification view.
- If X-Plant Status is Z2 change it to Z3 using MM02
- Set AOI by using transaction ZAOI1. This is done in two steps
- Create Area of Interest (AOI)
- Approve it
3.2.1 Setting AOI – Steps in details:
1. Log in to the right System e.g. Pre-production (C37) or Production (CA7) in MDR as the case which the request has been raised in an issue to solve or to maintain.use specific transaction codes were the job is to be done.
2. In the SAP Easy Access screen, enter the transaction code ZAOI1 ( used for setting Area of Interest in Production MDR) and press ENTER.

3. Enter values for MD Object Type ‘Material’ for Materil and MD Record Material no. ###### as per the given request.

4. Choose CREATE option to create the Area of Interest for the given object located a the menu bar of the SAP screen.
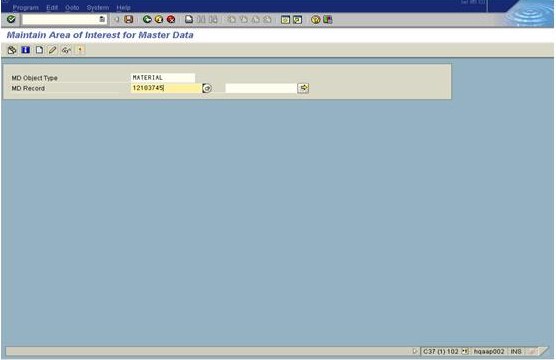
5. Enter ISO code of any country for ex: 'IN' as shown below screen or some other country as per issue and click Transfer button as seen in the SAP screen.

6. Press TRANSFER button which is located in the bottom of AOI's and carry on with the further steps.
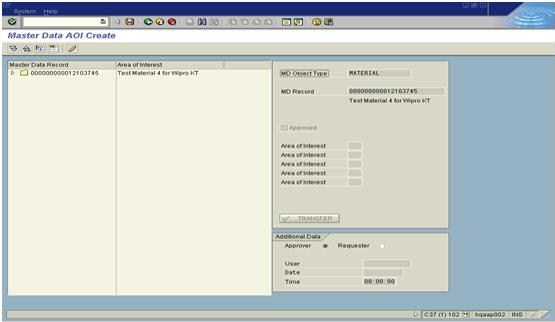
7. Click on SAVE icon at the top on menu bar. The AOI has been created. The next step is to approve it.so For doing this follow steps from 8 to 10.
8. Following screen shows that how to approve AOI for a given material. Enter the Material number and click on candle button (it is called 'Activate button').

9.After Activating then should click in the Check box “Approved”.

10. So after clicking the check box to approval we should save the screen so click on "SAVE" button on the top menu bar.

The above screen shot shows that the Approval flag has been updated. Material will replicate to SDR by a batch program.
3.3 Deactivating a Material
When a material is no longer used by a plant, Then it is de-activated for that plant at SDR level i.e. plant specific status is changed to 'Z6'. If it is not required in any plant, it must be de-activated in all plants and flagged for deletion at the MDR and SDR levels. It is expected that before such a request is received, the concerned market should have changed plant-specific status for all plants to Z6 and the materials should have been flagged for deletion at the SDR levels. Below mentioned points should to be followed for deactivating a Material.
Checks:
- Request for de-activation has come from MDR Record owner.
- For IMSP/Shared materials, approval of all receiving markets is needed.
Do the checks by using the transaction MM03 (Material Display mode) in MDR.
Process:
- Add “ZZ” at the start of description including the other language descriptions in additional data
(If available) using the transaction MM02 at MDR level. If the description is 40 characters long and there is no room to add “ZZ” remove most insignificant component from the description.
- Change the value of X-plant from Z2 or Z3 (as the case may be) to Z6 using the transaction MM02 at MDR level.
- The date should be changed for every modification as current date in Transaction MM02.
- Flag the material for deletion at MDR level using the transaction MM06.
3.3.1 Deactivating a Material:
- Enter transaction code MM02 (Material changing mode) in MDR.
- Enter material number as given by the issue requestor and press ENTER.

3. Following dialog box shows the list of views.Then select as needed view to do the job as per issue and press ENTER.

4. We get a box where the organizational data is to be provided then again press ENTER.

5. Now to deactivate the Material just prefix 'ZZ' at the start of description. change the X-plant status of the Material from Z3 to Z6 as shown below, the field from Valid date to current date. Then click on additional data tab as shown below.

6. As the material is shared to different country markets.It should be deactivated in all markets. so, select the description option. Prefix ZZ at the start of other language description (if available) and save the data.

3.3.2 Flagging material for deletion
1. For flagging the Material for deletion just execute transaction code MM06.

2. Here we get and enter the material number and press ENTER

3. Then we will get a data screen there just put a Tick mark in the Material box as shown below.

4. After that just press SAVE. Then the Material has been flagged for deletion.

3.4 Reactivating a Material
There might be some situations when a material that was made inactive i.e. flagged for deletion in MDR and SDR and x-plant status changed to Z6 and description modified to have ZZ in front of it, needs to be re-activated. This could happen when this was done by mistake or there are other reasons (returns, production restarted). Whatever be the reason, it is possible to re-activate a material.
However, request for this change should come from the MDR Record Owner.
Checks:
1. Request for re-activation has come from MDR Record owner
2. Material X-plant status in MDR is Z6 and/or there is “ZZ” in description and/or it is flagged for deletion in MDR (use MM03)
Process:
1. Reverse Deletion Flag (use MM06)
2. Change X-Plant Status from Z6 to Z3 (use MM02)
3. Remove ZZ from description (use MM02)
Note: If the requester market has asked x-plant status to be re-set to Z2 (instead of Z3), then do the same.
3.4.1 Performing these checks
1. To see who the MDR Record owner is, use MM03 and look at the MDR Record Owner field in Basic Data 3 view. It should be the same as the market that has raised the Ticket. this should be one of the check to process an issue.

2. To see X-plant status, display the material via MM03 in MDR & have a look at the Basic Data 1.

3. Review x-plant status and material description in the screen after the display screen is opened..

3.4.2 Re-activating a material
1. To un-flag the Material for deletion, enter the transaction code MM06 in SAP Easy Access screen in MDR and press ENTER.
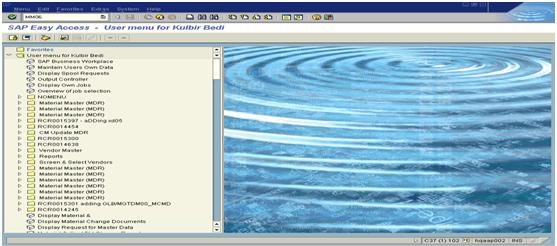
2 Then now after the T-code is opened enter the Material number and press ENTER.

3. After opening the screen just remove the tick mark from the Check box in the screen and press ENTER

4. As you put a tick then SAVE and then following screen shows a message that the given material is un-flagged from deletion.
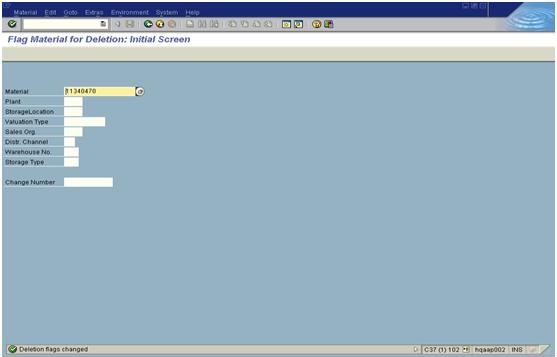
5. To change the X-plant status from Z6 to Z3 and to remove ZZ from description, go to MM02 transaction and give the Material number and press ENTER.

6.We get the following pop up window which shows the list of view as below screen. Select the respective view and press ENTER.

7. Select the Basic Data 1 and know press ENTER. System displays this screen. Press enter again.

8. Change the value of the X-plant status from Z6 to Z3 and remove ZZ from the description, mark today’s date in Valid from field. Then 'click' on additional data tab as shown below.

9. Select the description option and remove ZZ from the other language description (if available) due to the material is shared to different country markets. then after just SAVE the data. Reactivation of Material in done by the above method as shown on screen.
3.5 IMSP Dual Maintenance
The process of maintaining data for legacy and SAP systems by the non-live markets (Producing Market) with the approval of live markets (Receiving Market) is known as “IMSP Dual Maintenance”. To explain when we need to create such materials manually in SAP for non-live markets, let us take an example:
As of today, Nestle Israel is a non-live market. Let us say it exports a material A to Nestle Germany, which is a live market. Nestle Germany would therefore want Material A, to be created in SAP although there is no such requirement from Nestle Israel who are using a legacy system. Nestle Israel, will need to have Material A created in SAP. For this, they will populate the data in loading sheet; send it to Nestle Germany to validate it. After the validation, they will raise a Ticket to have the material created in SAP.
Checks:
1. Requesting market is a non-live market .
2. Material involved has to be an IMSP material
3. Material type is FERT or HALB.
4. Only a Producing market can raise a request for creation of Materials. (Receiving market can raise a request only for changing a Material via workflow). 5. Data has been provided in the loading sheet which has been approved by the Receiving Market.
Process:
1. Create Material using MM01. Detailed steps are provided in the below sections
Following diagram explains the flow:

Loading Sheet:
The requesting market (Israel, in our example) must send data to the receiving market (Germany in our example) in this template which is a standard loading sheet used for approvals by live markets for creation of Materials. They should then attach this with the Ticket they will later raise for the Business Solutions.
Validating Data:
Data is validated as per rules specified in the loading system and Following rule as given by the market.
3.5.1 Creating Material Manually:
1. The SAP Easy Access screen is the initial screen which is displayed as soon as you log into a SAP.
2. Execute the transaction code MM01
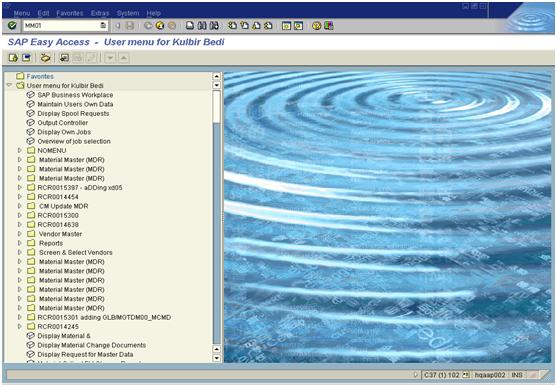
3. System displays this screen shown below
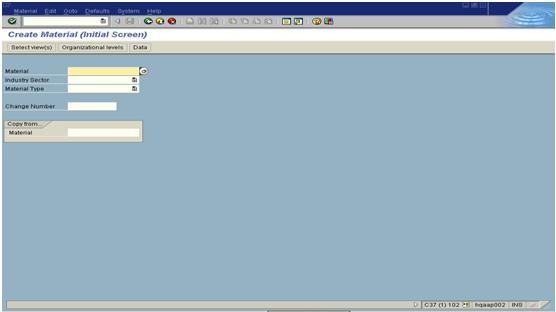
4. Enter Industry sector (Food) and Material Type given for the material which is to be created in MDR production.

5. After the ENTER key is pressed, a pop up screen as shown in picture below appears which will list all the existing views for a Material. The respective views are selected and the ENTER key is pressed to get the next screen.

6. The user is prompted to enter the plant details to enable the plant specific details is shown in picture. Press enter key

7. Picture below shows all the mandatory fields for a material. The fields which are displayed along with a tick mark are mandatory fields. These fields must be populated. The other fields will also be populated based on the available data supplied by the market.

8. Populate data from loading sheet provided by the market.

9. Once the ENTER key is pressed, the transaction will display the next view to get the data for the remaining fields. The picture below shows the view of
Basic data 2.

10. Creating Classification View: When you choose “Classification” tab, the system will display a list of class type description. The picture below shows the list of Class type description. For FERT and HALB Materials, only class 023 is used.
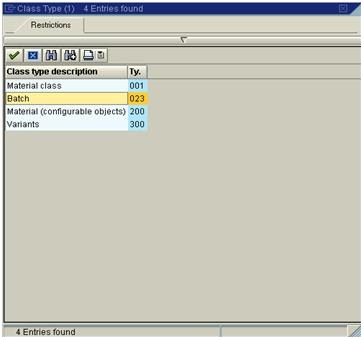
11. Picture below shows the classification view of a material. Only class 023 is needed for FERT materials. Material Group of the material must be the same as that mentioned in the class (In the below example it is F50). Populate appropriate Class from the drop-down and click on save icon or press enter key.

12. The picture below shows the Plant / Storage location data 1 view wherein the value for Storage conditions is entered and the ENTER key is pressed to go to the next view.

13. The Plant / Storage location data 2 view is shown in the picture below. We are not required to enter any data in this view. The ENTER key is pressed to go to the next view.

14. The Quality Management view is shown in the picture below. In the Quality management view put a tick in QM Proc. Active field & press ENTER.

15. As soon as the ENTER key is pressed, the system will display the Basic data 3 view which is shown in picture below. The values for BAI, PTC, MDR Record Owner are entered and the ENTER key is pressed.

16. The QM Additional data view is shown in the picture below. Allergen Data is entered here. The producing market must provide Allergen Data. For water & pet food this data is not needed. Enter data in this screen as provided by the user in loading sheet.

17. Enter Alternate units of measure & their related fields (GTINs, Variants, L, W, H) & click on save button.

Consult check list for validating these fields
18. The picture below shows the Material number which is generated for a newly created Material in the status bar.

3.5.2 Changing IMSP materials manually
Changes to IMSP materials are always made via workflow. But there are some situations where the changes to the IMSP Material are not possible via Workflow (i.e. Batch management flag). In this type of situation we may receive tickets from markets to do the changes manually.
Notes:
Assigning the 76 series of EAN to any Material will be done by BTC.
All the manual changes to ZSIM materials will be done by GCC_SAP P2P.
We can change Batch management flag if the market requests for it.
While making the changes manually if you come across any system warning message, consult with the initiator and proceed further as it may affect any other live material.
Checks:
1. Request should come from the MDR record owner. Otherwise approval from the owning
market should be given in the ticket.
2. Approval from the sharing market is required even if the materials are in Z5 or Z6 status.
3. We can go ahead with the changes to IMSP Material which is in Z6 status and has sharing
markets in market usage tab, but do not have any of the sharing market plants extended in
system CBX (SDR). No Approval is required.
Process:
1: Execute the transaction MM02 in MDR and do the changes as requested in the ticket and save the data
3.6 EAN Harmonization:
3.6.1 EAN Inconsistency:
If two or more materials share the same GTIN and GTIN variant, then the following fields must be identical for these materials:
- Length
- Width
- Height
- Net Weight
- Gross Weight
If these fields do not have identical values, then at the time of modification of one of the Materials involved, System will give EAN inconsistency error. You will get a similar error when you want to create a material that shares its GTIN & variant with an existing material but either their Net Wt or Length or Width or Height or Gross Weight do not match with each other.
The process of changing the dissimilar values of these fields in the Materials involved, to one set of values by using EAN harmonization template is termed as EAN harmonization process.
It is obvious that more than one materials & possibly more than one market could be involved in this. If so, we will need approval of all such markets before we change any of the above fields. For this there is a Harmonization Template used (See attached).
When a Ticket comes to the NBS for EAN Harmonization, the requesting market should attach agreed values of these fields by all concerned. If not, the Ticket should be sent back requesting for the same.
Below attached is the procedure that further explains the Harmonization process. It also contains a template that is circulated by the requesting market to owners of the other materials. All markets must agree to one set of values. The template is attached to the peregrine Ticket. The NBS will carry out harmonization as per issue requested.
3.6.2 Executing EAN CONSISTENCY Transaction:
Checks
- Has the template been provided requesting market with agreed values? If no, send the request back. If yes, execute the transaction to harmonize the data as explained below.
- Check the market usage tab if the Material given for harmonization has been shared by any market, if yes check in SDR whether the Material is extended to any market or not (only for Z3 Materials), If not extended or if the material is in Z6 status then carry on with the harmonization and close the ticket. If it is extended to any market, approval is needed from the concern market.
Changes to IMSP Material which is in Z6 status and has sharing markets in market usage tab, but all the sharing market plants extended in system CBX (SDR) are in Z6 status.
Process
The screenshots shown below depicts the difference in heights of two Materials. These two Materials have the same GTIN (9556001004659) and same GTIN Variants (05). But their heights are different. For Material 12008200 the height is 270 MM and the height of 12013209 is 215 MM.


When we try to make the two heights equal by using MM02, the system gives us the EANINCONSISTENCYCHECK error as shown below. The transaction has been changed for EAN Harmonization after the Production MDR/SDR outage which happened recently.
The new transaction is EANCONSISTENCYCHECK.

1. To harmonize the height, we run the transaction " EANCONSISTENCYCHECK "

2. We need to enter all the above parameters and along with the correct height. In this case we want the height to be changed to 215 MM so we have entered 215 in the height field.
When we execute the transaction, system automatically changes the height from 270 MM to 215 MM for Material 12008200 as shown below.

Tickets requesting EAN swap or change at any levels for the Materials have EAN Category 1A should be escalated to BTC.
3.7 Updating Materials with Status Z6
Sometimes because of EAN inconsistency problems, there might be a requirement to fix incorrect assignment of Parent Product Code or GTIN or a GTIN variant etc. Changes to materials with Z6 status are not supported by the SAP ZREQ7 request. So markets requests for these changes outside of the Workflow process i.e. via Ticket.
The brand denomination for a material can be changed even if the Material is in Z6 status.
Checks:
1. The requestor should give reason for updating of Materials with Z6 status.
Process:
Change the requested field(s) manually using MM02. You need not change x-plant status from Z6 to Z3.
Changes to IMSP Material which is in Z6 status and has sharing markets in market usage tab, but all the sharing market plants extended in system CBX (SDR) are in Z6 status.
3.8 Updating MLEA table
MLEA table is used for maintaining Material, Vendor and GTIN number is /GLB/RGTVERPOC01.
An entry in the table is required for only ROH and ZPCK.
However if the market is requesting, you can go ahead with the MLEA Table updation even for FERT material.
For updating the MLEA table the following checks to be done.
Checks:
- An entry for given material and vendor should not already exist.
- Vendor & material provided should exist in MDR.
Execution will be done via transaction /GLB/RGTPP02_EANP or SM30.
This document explains how it is done via /GLB/RGTPP02_EANP
Step 1: Enter the transaction code /GLB/RGTPP02_EANP in SAP Easy Access screen

Step 2: Enter the Material & Vendor number provided in the ticket which is to be resolved as an issue.

Step 3: If the combination of Material and Vendor exists, then the system will display the GTIN for the given combination. If the given combination doesn’t exist, then click on the pencil icon to go to change mode to feed in the Unit of Measure and GTIN. (See below screenshot)
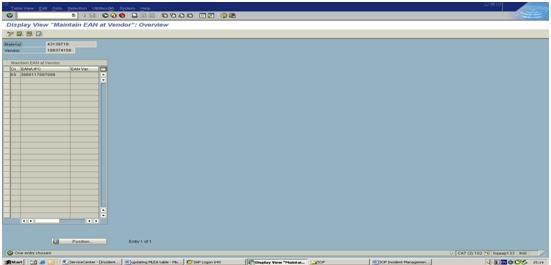
Step 4: Click on the New Entries button to get the screen fields editable to feed in the data.

Enter the Unit of Measure and GTIN / EAN / UPC and click on Save Button. (EAN Variant column has to be left blank.)

Step 5: Once the Save button is clicked, there is a message “1 IDoc created” as shown in the below screen - 'foot of the SAP screen'..

4. Working with Master Data Governance for Vendors and Customers : Whitepaper - Governance Over Vendor and Customer Master Data in Production MDR Using MDG.
5. Related Content
(for ECC 6 Ehp06) : Master Data Governance - SAP Documentation
http://help.sap.com/erp2005_ehp_05/helpdata/EN/3e/b67a9facd34cb09ce87e3bc24b4c52/content.htm
http://www.sdn.sap.com/irj/boc/master-data-governance
http://wiki.sdn.sap.com/wiki/display/SAPMDM/SAP+Master+Data+Governance
6. Copyright
© Copyright 2012 SAP AG. All rights reserved.
No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or for any purpose without the express permission of SAP AG. The information contained herein may be changed without prior notice.
Some software products marketed by SAP AG and its distributors contain proprietary software components of other software vendors.
Microsoft, Windows, Excel, Outlook, and PowerPoint are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
IBM, DB2, DB2 Universal Database, System i, System i5, System p, System p5, System x, System z, System z10, System z9, z10, z9, iSeries, pSeries, xSeries, zSeries, eServer, z/VM, z/OS, i5/OS, S/390, OS/390, OS/400, AS/400, S/390 Parallel Enterprise Server, PowerVM, Power Architecture, POWER6+, POWER6, POWER5+, POWER5, POWER, OpenPower, PowerPC, BatchPipes, BladeCenter, System Storage, GPFS, HACMP, RETAIN, DB2 Connect, RACF, Redbooks, OS/2, Parallel Sysplex, MVS/ESA, AIX, Intelligent Miner, WebSphere, Netfinity, Tivoli and Informix are trademarks or registered trademarks of IBM Corporation.
Linux is the registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the U.S. and other countries.
Adobe, the Adobe logo, Acrobat, PostScript, and Reader are either trademarks or registered trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated in the United States and/or other countries.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation.
UNIX, X/Open, OSF/1, and Motif are registered trademarks of the Open Group.
Citrix, ICA, Program Neighborhood, MetaFrame, WinFrame, VideoFrame, and MultiWin are trademarks or registered trademarks of Citrix Systems, Inc.
HTML, XML, XHTML and W3C are trademarks or registered trademarks of W3C®, World Wide Web Consortium, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Java is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation.
JavaScript is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation, used under license for technology invented and implemented by Netscape.
SAP, R/3, SAP NetWeaver, Duet, PartnerEdge, ByDesign, SAP Business ByDesign, and other SAP products and services mentioned herein as well as their respective logos are trademarks or registered trademarks of SAP AG in Germany and other countries.
Business Objects and the Business Objects logo, BusinessObjects, Crystal Reports, Crystal Decisions, Web Intelligence, Xcelsius, and other Business Objects products and services mentioned herein as well as their respective logos are trademarks or registered trademarks of Business Objects S.A. in the United States and in other countries. Business Objects is an SAP company.
All other product and service names mentioned are the trademarks of their respective companies. Data contained in this document serves informational purposes only. National product specifications may vary.
These materials are subject to change without notice. These materials are provided by SAP AG and its affiliated companies ("SAP Group") for informational purposes only, without representation or warranty of any kind, and SAP Group shall not be liable for errors or omissions with respect to the materials. The only warranties for SAP Group products and services are those that are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services, if any. Nothing here in should be construed as constituting an additional warranty.
- SAP Managed Tags:
- SAP Master Data Governance
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
"automatische backups"
1 -
"regelmäßige sicherung"
1 -
"TypeScript" "Development" "FeedBack"
1 -
505 Technology Updates 53
1 -
ABAP
14 -
ABAP API
1 -
ABAP CDS Views
2 -
ABAP CDS Views - BW Extraction
1 -
ABAP CDS Views - CDC (Change Data Capture)
1 -
ABAP class
2 -
ABAP Cloud
2 -
ABAP Development
5 -
ABAP in Eclipse
1 -
ABAP Platform Trial
1 -
ABAP Programming
2 -
abap technical
1 -
absl
1 -
access data from SAP Datasphere directly from Snowflake
1 -
Access data from SAP datasphere to Qliksense
1 -
Accrual
1 -
action
1 -
adapter modules
1 -
Addon
1 -
Adobe Document Services
1 -
ADS
1 -
ADS Config
1 -
ADS with ABAP
1 -
ADS with Java
1 -
ADT
2 -
Advance Shipping and Receiving
1 -
Advanced Event Mesh
3 -
AEM
1 -
AI
7 -
AI Launchpad
1 -
AI Projects
1 -
AIML
9 -
Alert in Sap analytical cloud
1 -
Amazon S3
1 -
Analytical Dataset
1 -
Analytical Model
1 -
Analytics
1 -
Analyze Workload Data
1 -
annotations
1 -
API
1 -
API and Integration
3 -
API Call
2 -
Application Architecture
1 -
Application Development
5 -
Application Development for SAP HANA Cloud
3 -
Applications and Business Processes (AP)
1 -
Artificial Intelligence
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
4 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) 1 Business Trends 363 Business Trends 8 Digital Transformation with Cloud ERP (DT) 1 Event Information 462 Event Information 15 Expert Insights 114 Expert Insights 76 Life at SAP 418 Life at SAP 1 Product Updates 4
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise Oil Gas IoT Exploration Production
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise sustainability responsibility esg social compliance cybersecurity risk
1 -
ASE
1 -
ASR
2 -
ASUG
1 -
Attachments
1 -
Authorisations
1 -
Automating Processes
1 -
Automation
1 -
aws
2 -
Azure
1 -
Azure AI Studio
1 -
B2B Integration
1 -
Backorder Processing
1 -
Backup
1 -
Backup and Recovery
1 -
Backup schedule
1 -
BADI_MATERIAL_CHECK error message
1 -
Bank
1 -
BAS
1 -
basis
2 -
Basis Monitoring & Tcodes with Key notes
2 -
Batch Management
1 -
BDC
1 -
Best Practice
1 -
bitcoin
1 -
Blockchain
3 -
BOP in aATP
1 -
BOP Segments
1 -
BOP Strategies
1 -
BOP Variant
1 -
BPC
1 -
BPC LIVE
1 -
BTP
11 -
BTP Destination
2 -
Business AI
1 -
Business and IT Integration
1 -
Business application stu
1 -
Business Application Studio
1 -
Business Architecture
1 -
Business Communication Services
1 -
Business Continuity
1 -
Business Data Fabric
3 -
Business Partner
12 -
Business Partner Master Data
10 -
Business Technology Platform
2 -
Business Trends
1 -
CA
1 -
calculation view
1 -
CAP
3 -
Capgemini
1 -
CAPM
1 -
Catalyst for Efficiency: Revolutionizing SAP Integration Suite with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and
1 -
CCMS
2 -
CDQ
12 -
CDS
2 -
Cental Finance
1 -
Certificates
1 -
CFL
1 -
Change Management
1 -
chatbot
1 -
chatgpt
3 -
CL_SALV_TABLE
2 -
Class Runner
1 -
Classrunner
1 -
Cloud ALM Monitoring
1 -
Cloud ALM Operations
1 -
cloud connector
1 -
Cloud Extensibility
1 -
Cloud Foundry
4 -
Cloud Integration
6 -
Cloud Platform Integration
2 -
cloudalm
1 -
communication
1 -
Compensation Information Management
1 -
Compensation Management
1 -
Compliance
1 -
Compound Employee API
1 -
Configuration
1 -
Connectors
1 -
Consolidation Extension for SAP Analytics Cloud
1 -
Controller-Service-Repository pattern
1 -
Conversion
1 -
Cosine similarity
1 -
cryptocurrency
1 -
CSI
1 -
ctms
1 -
Custom chatbot
3 -
Custom Destination Service
1 -
custom fields
1 -
Customer Experience
1 -
Customer Journey
1 -
Customizing
1 -
cyber security
2 -
Data
1 -
Data & Analytics
1 -
Data Aging
1 -
Data Analytics
2 -
Data and Analytics (DA)
1 -
Data Archiving
1 -
Data Back-up
1 -
Data Governance
5 -
Data Integration
2 -
Data Quality
12 -
Data Quality Management
12 -
Data Synchronization
1 -
data transfer
1 -
Data Unleashed
1 -
Data Value
8 -
database tables
1 -
Datasphere
2 -
datenbanksicherung
1 -
dba cockpit
1 -
dbacockpit
1 -
Debugging
2 -
Delimiting Pay Components
1 -
Delta Integrations
1 -
Destination
3 -
Destination Service
1 -
Developer extensibility
1 -
Developing with SAP Integration Suite
1 -
Devops
1 -
digital transformation
1 -
Documentation
1 -
Dot Product
1 -
DQM
1 -
dump database
1 -
dump transaction
1 -
e-Invoice
1 -
E4H Conversion
1 -
Eclipse ADT ABAP Development Tools
2 -
edoc
1 -
edocument
1 -
ELA
1 -
Embedded Consolidation
1 -
Embedding
1 -
Embeddings
1 -
Employee Central
1 -
Employee Central Payroll
1 -
Employee Central Time Off
1 -
Employee Information
1 -
Employee Rehires
1 -
Enable Now
1 -
Enable now manager
1 -
endpoint
1 -
Enhancement Request
1 -
Enterprise Architecture
1 -
ETL Business Analytics with SAP Signavio
1 -
Euclidean distance
1 -
Event Dates
1 -
Event Driven Architecture
1 -
Event Mesh
2 -
Event Reason
1 -
EventBasedIntegration
1 -
EWM
1 -
EWM Outbound configuration
1 -
EWM-TM-Integration
1 -
Existing Event Changes
1 -
Expand
1 -
Expert
2 -
Expert Insights
1 -
Fiori
14 -
Fiori Elements
2 -
Fiori SAPUI5
12 -
Flask
1 -
Full Stack
8 -
Funds Management
1 -
General
1 -
Generative AI
1 -
Getting Started
1 -
GitHub
8 -
Grants Management
1 -
groovy
1 -
GTP
1 -
HANA
5 -
HANA Cloud
2 -
Hana Cloud Database Integration
2 -
HANA DB
1 -
HANA XS Advanced
1 -
Historical Events
1 -
home labs
1 -
HowTo
1 -
HR Data Management
1 -
html5
8 -
HTML5 Application
1 -
Identity cards validation
1 -
idm
1 -
Implementation
1 -
input parameter
1 -
instant payments
1 -
Integration
3 -
Integration Advisor
1 -
Integration Architecture
1 -
Integration Center
1 -
Integration Suite
1 -
intelligent enterprise
1 -
Java
1 -
job
1 -
Job Information Changes
1 -
Job-Related Events
1 -
Job_Event_Information
1 -
joule
4 -
Journal Entries
1 -
Just Ask
1 -
Kerberos for ABAP
8 -
Kerberos for JAVA
8 -
Launch Wizard
1 -
Learning Content
2 -
Life at SAP
1 -
lightning
1 -
Linear Regression SAP HANA Cloud
1 -
local tax regulations
1 -
LP
1 -
Machine Learning
2 -
Marketing
1 -
Master Data
3 -
Master Data Management
14 -
Maxdb
2 -
MDG
1 -
MDGM
1 -
MDM
1 -
Message box.
1 -
Messages on RF Device
1 -
Microservices Architecture
1 -
Microsoft Universal Print
1 -
Middleware Solutions
1 -
Migration
5 -
ML Model Development
1 -
Modeling in SAP HANA Cloud
8 -
Monitoring
3 -
MTA
1 -
Multi-Record Scenarios
1 -
Multiple Event Triggers
1 -
Neo
1 -
New Event Creation
1 -
New Feature
1 -
Newcomer
1 -
NodeJS
2 -
ODATA
2 -
OData APIs
1 -
odatav2
1 -
ODATAV4
1 -
ODBC
1 -
ODBC Connection
1 -
Onpremise
1 -
open source
2 -
OpenAI API
1 -
Oracle
1 -
PaPM
1 -
PaPM Dynamic Data Copy through Writer function
1 -
PaPM Remote Call
1 -
PAS-C01
1 -
Pay Component Management
1 -
PGP
1 -
Pickle
1 -
PLANNING ARCHITECTURE
1 -
Popup in Sap analytical cloud
1 -
PostgrSQL
1 -
POSTMAN
1 -
Process Automation
2 -
Product Updates
4 -
PSM
1 -
Public Cloud
1 -
Python
4 -
Qlik
1 -
Qualtrics
1 -
RAP
3 -
RAP BO
2 -
Record Deletion
1 -
Recovery
1 -
recurring payments
1 -
redeply
1 -
Release
1 -
Remote Consumption Model
1 -
Replication Flows
1 -
Research
1 -
Resilience
1 -
REST
1 -
REST API
1 -
Retagging Required
1 -
Risk
1 -
Rolling Kernel Switch
1 -
route
1 -
rules
1 -
S4 HANA
1 -
S4 HANA Cloud
1 -
S4 HANA On-Premise
1 -
S4HANA
3 -
S4HANA_OP_2023
2 -
SAC
10 -
SAC PLANNING
9 -
SAP
4 -
SAP ABAP
1 -
SAP Advanced Event Mesh
1 -
SAP AI Core
8 -
SAP AI Launchpad
8 -
SAP Analytic Cloud Compass
1 -
Sap Analytical Cloud
1 -
SAP Analytics Cloud
4 -
SAP Analytics Cloud for Consolidation
2 -
SAP Analytics Cloud Story
1 -
SAP analytics clouds
1 -
SAP BAS
1 -
SAP Basis
6 -
SAP BODS
1 -
SAP BODS certification.
1 -
SAP BTP
20 -
SAP BTP Build Work Zone
2 -
SAP BTP Cloud Foundry
5 -
SAP BTP Costing
1 -
SAP BTP CTMS
1 -
SAP BTP Innovation
1 -
SAP BTP Migration Tool
1 -
SAP BTP SDK IOS
1 -
SAP Build
11 -
SAP Build App
1 -
SAP Build apps
1 -
SAP Build CodeJam
1 -
SAP Build Process Automation
3 -
SAP Build work zone
10 -
SAP Business Objects Platform
1 -
SAP Business Technology
2 -
SAP Business Technology Platform (XP)
1 -
sap bw
1 -
SAP CAP
2 -
SAP CDC
1 -
SAP CDP
1 -
SAP CDS VIEW
1 -
SAP Certification
1 -
SAP Cloud ALM
4 -
SAP Cloud Application Programming Model
1 -
SAP Cloud Integration for Data Services
1 -
SAP cloud platform
8 -
SAP Companion
1 -
SAP CPI
3 -
SAP CPI (Cloud Platform Integration)
2 -
SAP CPI Discover tab
1 -
sap credential store
1 -
SAP Customer Data Cloud
1 -
SAP Customer Data Platform
1 -
SAP Data Intelligence
1 -
SAP Data Migration in Retail Industry
1 -
SAP Data Services
1 -
SAP DATABASE
1 -
SAP Dataspher to Non SAP BI tools
1 -
SAP Datasphere
9 -
SAP DRC
1 -
SAP EWM
1 -
SAP Fiori
2 -
SAP Fiori App Embedding
1 -
Sap Fiori Extension Project Using BAS
1 -
SAP GRC
1 -
SAP HANA
1 -
SAP HCM (Human Capital Management)
1 -
SAP HR Solutions
1 -
SAP IDM
1 -
SAP Integration Suite
9 -
SAP Integrations
4 -
SAP iRPA
2 -
SAP Learning Class
1 -
SAP Learning Hub
1 -
SAP Odata
2 -
SAP on Azure
1 -
SAP PartnerEdge
1 -
sap partners
1 -
SAP Password Reset
1 -
SAP PO Migration
1 -
SAP Prepackaged Content
1 -
SAP Process Automation
2 -
SAP Process Integration
2 -
SAP Process Orchestration
1 -
SAP S4HANA
2 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud
1 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud for Finance
1 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud private edition
1 -
SAP Sandbox
1 -
SAP STMS
1 -
SAP SuccessFactors
2 -
SAP SuccessFactors HXM Core
1 -
SAP Time
1 -
SAP TM
2 -
SAP Trading Partner Management
1 -
SAP UI5
1 -
SAP Upgrade
1 -
SAP Utilities
1 -
SAP-GUI
8 -
SAP_COM_0276
1 -
SAPBTP
1 -
SAPCPI
1 -
SAPEWM
1 -
sapmentors
1 -
saponaws
2 -
SAPS4HANA
1 -
SAPUI5
4 -
schedule
1 -
Secure Login Client Setup
8 -
security
9 -
Selenium Testing
1 -
SEN
1 -
SEN Manager
1 -
service
1 -
SET_CELL_TYPE
1 -
SET_CELL_TYPE_COLUMN
1 -
SFTP scenario
2 -
Simplex
1 -
Single Sign On
8 -
Singlesource
1 -
SKLearn
1 -
soap
1 -
Software Development
1 -
SOLMAN
1 -
solman 7.2
2 -
Solution Manager
3 -
sp_dumpdb
1 -
sp_dumptrans
1 -
SQL
1 -
sql script
1 -
SSL
8 -
SSO
8 -
Substring function
1 -
SuccessFactors
1 -
SuccessFactors Time Tracking
1 -
Sybase
1 -
system copy method
1 -
System owner
1 -
Table splitting
1 -
Tax Integration
1 -
Technical article
1 -
Technical articles
1 -
Technology Updates
1 -
Technology Updates
1 -
Technology_Updates
1 -
Threats
1 -
Time Collectors
1 -
Time Off
2 -
Tips and tricks
2 -
Tools
1 -
Trainings & Certifications
1 -
Transport in SAP BODS
1 -
Transport Management
1 -
TypeScript
2 -
unbind
1 -
Unified Customer Profile
1 -
UPB
1 -
Use of Parameters for Data Copy in PaPM
1 -
User Unlock
1 -
VA02
1 -
Validations
1 -
Vector Database
1 -
Vector Engine
1 -
Visual Studio Code
1 -
VSCode
1 -
Web SDK
1 -
work zone
1 -
workload
1 -
xsa
1 -
XSA Refresh
1
- « Previous
- Next »
- Hack2Build on Business AI – Highlighted Use Cases in Technology Blogs by SAP
- SAP Datasphere - Space, Data Integration, and Data Modeling Best Practices in Technology Blogs by SAP
- SAP Build Process Automation Agent 3 Updates and Key Benefits in Technology Blogs by SAP
- MDG DQM: Troubleshooting DQM validation rules for central governance - Product Master S/4 HANA in Technology Blogs by Members
- Data Architecture with SAP – Modern Data Stack in Technology Blogs by Members
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 11 | |
| 10 | |
| 7 | |
| 6 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 |