
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Technology
- Technology Blogs by Members
- The Infrastructure/Architecture that supports SAP ...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
This document is something, that's not more on the technical side of sap BW, but it talks about the essential infrastructure and the architecture that’s required to setup a complex SAP BW system. The architecture for a business warehouse or application is driven by a business. There is a lot of thought process involved in making the business decisions on what software/hardware to be installed to support any application or a business warehouse.
The following infrastructure entities need to be identified before the actual installation of SAP BW Product.
- Operating System (Servers)
- Storage
- Database
The above 3 are the major entities, but there are other different components, that we need to identify like…
Middleware - ODBC, OLE, OLE DB, DCE, ORBs, and JDBC.
Data base connectivity - ODBC, JDBC, OLE DB, and others.
Data management - ANSI SQL and FTP.
Network access - DCE, DNS, and LDAP.
For now, we will focus on the 3 major entities (server, storage, and database) which majorly contribute to the business warehouse Infrastructure framework or architecture.
What is a Server ??
Server provides an environment where applications can run, no matter what the applications are or what they do, It is dedicated to the efficient execution of procedures (programs, routines, scripts) for supporting the construction of applications. A Server is like PC, with the components processor, RAM, hard disk etc. Depending on the complexity of the architecture or business need, We can either have the Storage, Database and SAP BW on a single server, but this is not supported in a real scenario. In any ideal scenario, there will be a dedicated server’s like, application server for hosting the SAP BW, Database server for database and storage server for Storage.
Based on some of the following criteria's a server is determined.
- Reliability and Scalability
- Performance, Security, Transaction supports.
- Flexibility
The popular Servers that are currently available in market are Aix, Unix, Solaris, Linux, Zos, Windows etc.
What is a Storage ???
As the Business Warehouse data increases, the server farm continues to grow until it reaches a capacity whereby it is no longer feasible to store data in each server's local hard disk. The more efficient method is to set up a SAN (Storage Area Network) and relocate all data into it.
SAN is basically a collection of storage disks which run on its own network to ensure super fast transmission speeds. To ensure fast response times when sending and receiving data, the SAN runs on its own set of protocols and is connected via fiber channels for maximum bandwidth.
Since the SAN (Storage Area Network) is one giant storage box comprising many pieces of hard disks, it requires its own management system to handle its operations. No one server controls the SAN as its disks are allocated to all servers. Via a central console, the SAN administrator switches from disk to disk as though moving around all servers' storage disk.
Based on the some of the following criteria a Storage device is determined.
- Data capacity, Reliability and Scalability
- Archiving
- Performance/Speed
- OS compatibility
- Cost
The popular storage System Vendors are EMC, NetApp, IBM, Hitachi and HP etc..
What is a Database ???
Database is an application that manages data and allows fast storage and retrieval of data. There are different types of databases like Network, hierachical, relational etc. The most popular and efficient is Relational Database Management System.
Based on the following criteria a Database is determined.
- Data Capacity
- performance, scalability, high availability
d Security.
- Flexibility
- Cost
- Disaster recover/ backup and restore stratergies.
The popular Databases Vendors are Oracle , DB2, SQL Server.
All the 3 entities Servers, Storage ,Database are chosen based on their cost,compatibility,security, scalability,performance,parallelism , with each other in terms of how the work requests flow from one server to the other.
The following are some of the combinations chosen by most of the vendors/customers to establish a efficient infrastructure running.
- Sunsolaris, EMC2-storage, Oracle , SAP BW
- ZOS(z-series),IBM-storage,DB2 ZOS,SAP BW
- Aix, IBM-Storage,Db2 LUW, SAP BW
- Windows, EMC/NetApp,, sql server, SAP BW.
Please note, from a business perspective or licensing perspective this combination may change accordingly, for example a small business warehouse with 1 terabyte can go with the combination of (Windows, netapps, sql server, SAP BW.).
A banking sector or a large retail business warehouse with 100's of terabyte can go with the combination of (ZOS,IBM,DB2 ZOS,SAP BW)..
Let's consider a business warehouse, where we want to develop a Business Warehouse architecture for the following business scenario:
Nightly updates - batch runs.
Worldwide availability - parallel or distributed servers.
Customer-level analysis - [large] server size.
New data sources - flexible tools with support for meta data.
Reliability - job control features.
We divide the Entire Business Warehouse Architecture into Data Architecture, Infrastructure Architecture and Technical Architecture.
Data Architecture - This is completely driven by business processes. A entity relationship/data model /dimension model is established, for example in a manufacturing environment the data model might include orders, shipping, and billing.
Technical Architecture - This can also be part of a data architecture, focus on the interfaces, Security, how to handle the data from different sources, gives a picture on some of the below entities.
Middleware - ODBC, OLE, OLE DB, DCE, ORBs, and JDBC.
Data base connectivity - ODBC, JDBC, OLE DB, and others.
Infrastructure Architecture - Defines the flow diagram/structure for all the entities that support the business warehouse.
- i.e., Application Server, Database Server and Storage Server, Below is a sample Architecture.
As this is an overview, I will not go further into detail of the Architecture design, below is one of the logical and functional architecture designed for a typical business warehouse.
Logical Architecture :
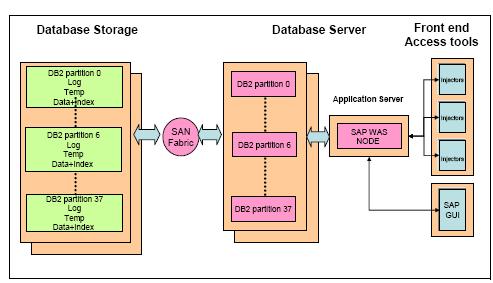
Functional Architecture

- SAP Managed Tags:
- BW (SAP Business Warehouse)
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
-
"automatische backups"
1 -
"regelmäßige sicherung"
1 -
"TypeScript" "Development" "FeedBack"
1 -
505 Technology Updates 53
1 -
ABAP
18 -
ABAP API
1 -
ABAP CDS Views
4 -
ABAP CDS Views - BW Extraction
1 -
ABAP CDS Views - CDC (Change Data Capture)
1 -
ABAP class
2 -
ABAP Cloud
3 -
ABAP DDIC CDS view
1 -
ABAP Development
5 -
ABAP in Eclipse
3 -
ABAP Platform Trial
1 -
ABAP Programming
2 -
abap technical
1 -
abapGit
1 -
absl
2 -
access data from SAP Datasphere directly from Snowflake
1 -
Access data from SAP datasphere to Qliksense
1 -
Accrual
1 -
action
1 -
adapter modules
1 -
Addon
1 -
Adobe Document Services
1 -
ADS
1 -
ADS Config
1 -
ADS with ABAP
1 -
ADS with Java
1 -
ADT
2 -
Advance Shipping and Receiving
1 -
Advanced Event Mesh
3 -
Advanced formula
1 -
AEM
1 -
AI
8 -
AI Launchpad
1 -
AI Projects
1 -
AIML
10 -
Alert in Sap analytical cloud
1 -
Amazon S3
1 -
Analytic Models
1 -
Analytical Dataset
1 -
Analytical Model
1 -
Analytics
1 -
Analyze Workload Data
1 -
annotations
1 -
API
1 -
API and Integration
4 -
API Call
2 -
API security
1 -
Application Architecture
1 -
Application Development
5 -
Application Development for SAP HANA Cloud
3 -
Applications and Business Processes (AP)
1 -
Artificial Intelligence
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
5 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) 1 Business Trends 363 Business Trends 8 Digital Transformation with Cloud ERP (DT) 1 Event Information 462 Event Information 15 Expert Insights 114 Expert Insights 76 Life at SAP 418 Life at SAP 1 Product Updates 4
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise Oil Gas IoT Exploration Production
1 -
Artificial Intelligence (AI) blockchain Data & Analytics Intelligent Enterprise sustainability responsibility esg social compliance cybersecurity risk
1 -
AS Java
1 -
ASE
1 -
ASR
2 -
Asset Management
2 -
Associations in CDS Views
1 -
ASUG
1 -
Attachments
1 -
Authentication
1 -
Authorisations
1 -
Automating Processes
1 -
Automation
2 -
aws
2 -
Azure
2 -
Azure AI Studio
1 -
Azure API Center
1 -
Azure API Management
1 -
B2B Integration
1 -
Background job
1 -
Backorder Processing
1 -
Backpropagation
1 -
Backup
1 -
Backup and Recovery
1 -
Backup schedule
1 -
BADI_MATERIAL_CHECK error message
1 -
Bank
1 -
Bank Communication Management
1 -
BAS
1 -
basis
2 -
Basis Monitoring & Tcodes with Key notes
2 -
Batch Management
1 -
BDC
1 -
Best Practice
1 -
BI
1 -
bitcoin
1 -
Blockchain
3 -
bodl
1 -
BOP in aATP
1 -
BOP Segments
1 -
BOP Strategies
1 -
BOP Variant
1 -
BPC
1 -
BPC LIVE
1 -
BTP
15 -
BTP AI Launchpad
1 -
BTP Destination
2 -
Business AI
1 -
Business and IT Integration
1 -
Business application stu
1 -
Business Application Studio
1 -
Business Architecture
1 -
Business Communication Services
1 -
Business Continuity
2 -
Business Data Fabric
3 -
Business Fabric
1 -
Business Partner
13 -
Business Partner Master Data
11 -
Business Technology Platform
2 -
Business Trends
4 -
BW4HANA
1 -
CA
1 -
calculation view
1 -
CAP
4 -
Capgemini
1 -
CAPM
1 -
Catalyst for Efficiency: Revolutionizing SAP Integration Suite with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and
1 -
CCMS
2 -
CDQ
13 -
CDS
2 -
CDS Views
1 -
Cental Finance
1 -
Certificates
1 -
CFL
1 -
Change Management
1 -
chatbot
1 -
chatgpt
3 -
CICD
1 -
CL_SALV_TABLE
2 -
Class Runner
1 -
Classrunner
1 -
Cloud ALM Monitoring
1 -
Cloud ALM Operations
1 -
cloud connector
1 -
Cloud Extensibility
1 -
Cloud Foundry
4 -
Cloud Integration
6 -
Cloud Platform Integration
2 -
cloudalm
1 -
communication
1 -
Compensation Information Management
1 -
Compensation Management
1 -
Compliance
1 -
Compound Employee API
1 -
Configuration
1 -
Connectors
1 -
Consolidation
1 -
Consolidation Extension for SAP Analytics Cloud
3 -
Control Indicators.
1 -
Controller-Service-Repository pattern
1 -
Conversion
1 -
Corrective Maintenance
1 -
Cosine similarity
1 -
CPI
1 -
cryptocurrency
1 -
CSI
1 -
ctms
1 -
Custom chatbot
3 -
Custom Destination Service
1 -
custom fields
1 -
Custom Headers
1 -
Customer Experience
1 -
Customer Journey
1 -
Customizing
1 -
cyber security
5 -
cybersecurity
1 -
Data
1 -
Data & Analytics
1 -
Data Aging
1 -
Data Analytics
2 -
Data and Analytics (DA)
1 -
Data Archiving
1 -
Data Back-up
1 -
Data Flow
1 -
Data Governance
5 -
Data Integration
2 -
Data Quality
13 -
Data Quality Management
13 -
Data Synchronization
1 -
data transfer
1 -
Data Unleashed
1 -
Data Value
9 -
Database and Data Management
1 -
database tables
1 -
Databricks
1 -
Dataframe
1 -
Datasphere
3 -
Datasphere Delta
1 -
datenbanksicherung
1 -
dba cockpit
1 -
dbacockpit
1 -
Debugging
2 -
Defender
1 -
Delimiting Pay Components
1 -
Delta Integrations
1 -
Destination
3 -
Destination Service
1 -
Developer extensibility
1 -
Developing with SAP Integration Suite
1 -
Devops
1 -
digital transformation
1 -
Disaster Recovery
1 -
Documentation
1 -
Dot Product
1 -
DQM
1 -
dump database
1 -
dump transaction
1 -
e-Invoice
1 -
E4H Conversion
1 -
Eclipse ADT ABAP Development Tools
2 -
edoc
1 -
edocument
1 -
ELA
1 -
Embedded Consolidation
1 -
Embedding
1 -
Embeddings
1 -
Emergency Maintenance
1 -
Employee Central
1 -
Employee Central Payroll
1 -
Employee Central Time Off
1 -
Employee Information
1 -
Employee Rehires
1 -
Enable Now
1 -
Enable now manager
1 -
endpoint
1 -
Enhancement Request
1 -
Enterprise Architecture
1 -
Enterprise Asset Management
2 -
Entra
1 -
ESLint
1 -
ETL Business Analytics with SAP Signavio
1 -
Euclidean distance
1 -
Event Dates
1 -
Event Driven Architecture
1 -
Event Mesh
2 -
Event Reason
1 -
EventBasedIntegration
1 -
EWM
1 -
EWM Outbound configuration
1 -
EWM-TM-Integration
1 -
Existing Event Changes
1 -
Expand
1 -
Expert
2 -
Expert Insights
2 -
Exploits
1 -
Fiori
16 -
Fiori App Extension
2 -
Fiori Elements
2 -
Fiori Launchpad
2 -
Fiori SAPUI5
13 -
first-guidance
1 -
Flask
2 -
FTC
1 -
Full Stack
9 -
Funds Management
1 -
gCTS
1 -
GenAI hub
1 -
General
3 -
Generative AI
1 -
Getting Started
1 -
GitHub
11 -
Google cloud
1 -
Grants Management
1 -
groovy
2 -
GTP
1 -
HANA
6 -
HANA Cloud
2 -
Hana Cloud Database Integration
2 -
HANA DB
2 -
Hana Vector Engine
1 -
HANA XS Advanced
1 -
Historical Events
1 -
home labs
1 -
HowTo
1 -
HR Data Management
1 -
html5
9 -
HTML5 Application
1 -
Identity cards validation
1 -
idm
1 -
Implementation
1 -
Improvement Maintenance
1 -
Infuse AI
1 -
input parameter
1 -
instant payments
1 -
Integration
3 -
Integration Advisor
1 -
Integration Architecture
1 -
Integration Center
1 -
Integration Suite
1 -
intelligent enterprise
1 -
Internal Table
1 -
IoT
2 -
Java
1 -
JMS Receiver channel ping issue
1 -
job
1 -
Job Information Changes
1 -
Job-Related Events
1 -
Job_Event_Information
1 -
joule
4 -
Journal Entries
1 -
Just Ask
1 -
Kafka
1 -
Kerberos for ABAP
10 -
Kerberos for JAVA
9 -
KNN
1 -
Launch Wizard
1 -
Learning Content
3 -
Life at SAP
5 -
lightning
1 -
Linear Regression SAP HANA Cloud
1 -
Live Sessions
1 -
Loading Indicator
1 -
local tax regulations
1 -
LP
1 -
Machine Learning
4 -
Marketing
1 -
Master Data
3 -
Master Data Management
15 -
Maxdb
2 -
MDG
1 -
MDGM
1 -
MDM
1 -
Message box.
1 -
Messages on RF Device
1 -
Microservices Architecture
1 -
Microsoft
1 -
Microsoft Universal Print
1 -
Middleware Solutions
1 -
Migration
5 -
ML Model Development
1 -
MLFlow
1 -
Modeling in SAP HANA Cloud
9 -
Monitoring
3 -
MPL
1 -
MTA
1 -
Multi-factor-authentication
1 -
Multi-Record Scenarios
1 -
Multilayer Perceptron
1 -
Multiple Event Triggers
1 -
Myself Transformation
1 -
Neo
1 -
Neural Networks
1 -
New Event Creation
1 -
New Feature
1 -
Newcomer
1 -
NodeJS
3 -
ODATA
2 -
OData APIs
1 -
odatav2
1 -
ODATAV4
1 -
ODBC
1 -
ODBC Connection
1 -
Onpremise
1 -
open source
2 -
OpenAI API
1 -
Oracle
1 -
Overhead and Operational Maintenance
1 -
PaPM
1 -
PaPM Dynamic Data Copy through Writer function
1 -
PaPM Remote Call
1 -
Partner Built Foundation Model
1 -
PAS-C01
1 -
Pay Component Management
1 -
PGP
1 -
Pickle
1 -
PLANNING ARCHITECTURE
1 -
Plant Maintenance
2 -
Popup in Sap analytical cloud
1 -
PostgrSQL
1 -
POSTMAN
1 -
Practice Systems
1 -
Prettier
1 -
Proactive Maintenance
1 -
Process Automation
2 -
Product Updates
6 -
PSM
1 -
Public Cloud
1 -
Python
5 -
python library - Document information extraction service
1 -
Qlik
1 -
Qualtrics
1 -
RAP
3 -
RAP BO
2 -
React
1 -
Reactive Maintenance
2 -
Record Deletion
1 -
Recovery
1 -
recurring payments
1 -
redeply
1 -
Release
1 -
Remote Consumption Model
1 -
Replication Flows
1 -
Report Malfunction
1 -
report painter
1 -
research
1 -
Resilience
1 -
REST
1 -
REST API
1 -
Retagging Required
1 -
RFID
1 -
Risk
1 -
rolandkramer
2 -
Rolling Kernel Switch
1 -
route
1 -
rules
1 -
S4 HANA
2 -
S4 HANA Cloud
2 -
S4 HANA On-Premise
3 -
S4HANA
6 -
S4HANA Cloud
1 -
S4HANA_OP_2023
2 -
SAC
11 -
SAC PLANNING
10 -
SAP
4 -
SAP ABAP
1 -
SAP Advanced Event Mesh
2 -
SAP AI Core
10 -
SAP AI Launchpad
9 -
SAP Analytic Cloud
1 -
SAP Analytic Cloud Compass
1 -
Sap Analytical Cloud
1 -
SAP Analytics Cloud
5 -
SAP Analytics Cloud for Consolidation
3 -
SAP Analytics cloud planning
1 -
SAP Analytics Cloud Story
1 -
SAP analytics clouds
1 -
SAP API Management
1 -
SAP Application Logging Service
1 -
SAP BAS
1 -
SAP Basis
6 -
SAP BO FC migration
1 -
SAP BODS
1 -
SAP BODS certification.
1 -
SAP BODS migration
1 -
SAP BPC migration
1 -
SAP BTP
25 -
SAP BTP Build Work Zone
2 -
SAP BTP Cloud Foundry
8 -
SAP BTP Costing
1 -
SAP BTP CTMS
1 -
SAP BTP Generative AI
1 -
SAP BTP Innovation
1 -
SAP BTP Migration Tool
1 -
SAP BTP SDK IOS
1 -
SAP BTPEA
1 -
SAP Build
12 -
SAP Build App
1 -
SAP Build apps
1 -
SAP Build CodeJam
1 -
SAP Build Process Automation
3 -
SAP Build work zone
11 -
SAP Business Objects Platform
1 -
SAP Business Technology
2 -
SAP Business Technology Platform (XP)
1 -
sap bw
1 -
SAP CAP
2 -
SAP CDC
1 -
SAP CDP
1 -
SAP CDS VIEW
1 -
SAP Certification
1 -
SAP Cloud ALM
4 -
SAP Cloud Application Programming Model
1 -
SAP Cloud Integration
1 -
SAP Cloud Integration for Data Services
1 -
SAP cloud platform
9 -
SAP Companion
1 -
SAP CPI
3 -
SAP CPI (Cloud Platform Integration)
2 -
SAP CPI Discover tab
1 -
sap credential store
1 -
SAP Customer Data Cloud
1 -
SAP Customer Data Platform
1 -
SAP Data Intelligence
1 -
SAP Data Migration in Retail Industry
1 -
SAP Data Services
1 -
SAP DATABASE
1 -
SAP Dataspher to Non SAP BI tools
1 -
SAP Datasphere
9 -
SAP DRC
1 -
SAP EWM
1 -
SAP Fiori
3 -
SAP Fiori App Embedding
1 -
Sap Fiori Extension Project Using BAS
1 -
SAP GRC
1 -
SAP HANA
1 -
SAP HANA PAL
1 -
SAP HANA Vector
1 -
SAP HCM (Human Capital Management)
1 -
SAP HR Solutions
1 -
SAP IDM
1 -
SAP Integration Suite
10 -
SAP Integrations
4 -
SAP iRPA
2 -
SAP LAGGING AND SLOW
1 -
SAP Learning Class
2 -
SAP Learning Hub
1 -
SAP Master Data
1 -
SAP Odata
3 -
SAP on Azure
2 -
SAP PAL
1 -
SAP PartnerEdge
1 -
sap partners
1 -
SAP Password Reset
1 -
SAP PO Migration
1 -
SAP Prepackaged Content
1 -
sap print
1 -
SAP Process Automation
2 -
SAP Process Integration
2 -
SAP Process Orchestration
1 -
SAP Router
1 -
SAP S4HANA
2 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud
3 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud for Finance
1 -
SAP S4HANA Cloud private edition
1 -
SAP Sandbox
1 -
SAP STMS
1 -
SAP successfactors
3 -
SAP SuccessFactors HXM Core
1 -
SAP Time
1 -
SAP TM
2 -
SAP Trading Partner Management
1 -
SAP UI5
1 -
SAP Upgrade
1 -
SAP Utilities
1 -
SAP-GUI
9 -
SAP_COM_0276
1 -
SAPBTP
1 -
SAPCPI
1 -
SAPEWM
1 -
sapfirstguidance
3 -
SAPHANAService
1 -
SAPIQ
2 -
sapmentors
1 -
saponaws
2 -
saprouter
1 -
SAPRouter installation
1 -
SAPS4HANA
1 -
SAPUI5
5 -
schedule
1 -
Script Operator
1 -
Secure Login Client Setup
9 -
security
10 -
Selenium Testing
1 -
Self Transformation
1 -
Self-Transformation
1 -
SEN
1 -
SEN Manager
1 -
Sender
1 -
service
2 -
SET_CELL_TYPE
1 -
SET_CELL_TYPE_COLUMN
1 -
SFTP scenario
2 -
Simplex
1 -
Single Sign On
9 -
Singlesource
1 -
SKLearn
1 -
Slow loading
1 -
SOAP
2 -
Software Development
1 -
SOLMAN
1 -
solman 7.2
2 -
Solution Manager
3 -
sp_dumpdb
1 -
sp_dumptrans
1 -
SQL
1 -
sql script
1 -
SSL
9 -
SSO
9 -
Story2
1 -
Substring function
1 -
SuccessFactors
1 -
SuccessFactors Platform
1 -
SuccessFactors Time Tracking
1 -
Sybase
1 -
Synthetic User Monitoring
1 -
system copy method
1 -
System owner
1 -
Table splitting
1 -
Tax Integration
1 -
Technical article
1 -
Technical articles
1 -
Technology Updates
15 -
Technology Updates
1 -
Technology_Updates
1 -
terraform
1 -
Testing
1 -
Threats
2 -
Time Collectors
1 -
Time Off
2 -
Time Sheet
1 -
Time Sheet SAP SuccessFactors Time Tracking
1 -
Tips and tricks
2 -
toggle button
1 -
Tools
1 -
Trainings & Certifications
1 -
Transformation Flow
1 -
Transport in SAP BODS
1 -
Transport Management
1 -
TypeScript
3 -
ui designer
1 -
unbind
1 -
Unified Customer Profile
1 -
UPB
1 -
Use of Parameters for Data Copy in PaPM
1 -
User Unlock
1 -
VA02
1 -
Validations
1 -
Vector Database
2 -
Vector Engine
1 -
Vectorization
1 -
Visual Studio Code
1 -
VSCode
2 -
VSCode extenions
1 -
Vulnerabilities
1 -
Web SDK
1 -
Webhook
1 -
work zone
1 -
workload
1 -
xsa
1 -
XSA Refresh
1
- « Previous
- Next »
- New Release Available: SAP Cloud Connector 2.17.0 in Technology Blogs by SAP
- Not able to locate sap:updatable or sap:creatable tags in metadata for SAP S/4HANA OData V4 APIs in Technology Q&A
- Tracking HANA Machine Learning experiments with MLflow: A technical Deep Dive in Technology Blogs by SAP
- How to Store API Tokens in SAP ABAP? in Technology Q&A
- Embedding Business Context with the SAP HANA Cloud, Vector Engine in Technology Blogs by SAP
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 50 | |
| 5 | |
| 5 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 4 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 3 | |
| 2 |