The United Nations Centre for Trade Facilitation is recognized as one of the four de jure international standards bodies along with ISO, IEC, and ITU. SAP actively participates in UN/CEFACT and uses its common methodology standards stack as the basis for our own methodologies for defining our core and global data types.
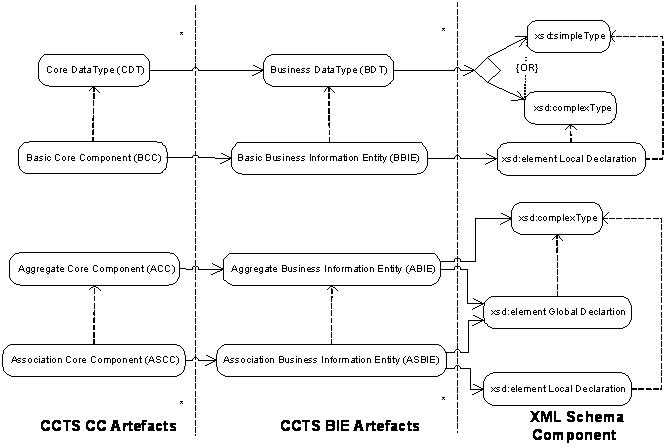
A key part of the common methodology standards stack is the XML Naming and Design Rules Technical Specification (NDR). The NDR is essentially a profile of the W3C XML Schema Definition Language. This technical specification has been developed to provide for XML standards based expressions of semantic data models representing business information exchanges. It describes and specifies the rules and guidelines UN/CEFACT will use for developing XML schema and schema documents based on Core Component Technical Specification (CCTS) conformant artefacts and information models.
 "
"
The most recent version of the NDR -UN/CEFACT XML Naming and Design Rules Version 3.0 - has recently been published by UN/CEFACT. It was developed in accordance with the UN/CEFACT Core Components Technical Specification Version 3.0 and using the UN/CEFACT Core Components Data Type Catalogue Version 3.0. It represents the work of a number of standards organizations working together to develop a single standard that can be universally adopted for schema development for information exchanges. Participants included representatives of UN/CEFACT, SWIFT, OAGi, HR-XML, AIAG, ACORD, STAR, Odette, UBL, CIDX, RAPID, AgGateway, and the US Government.
In addition to increasing the precision of the rules around generating schema, version 3.0 incorporates a new concept - one of levels of conformance for individual rules that ensure developers understand the direct impact on interoperability as a result of a rule use or non-use as defined in this table:
[R B998] | Conformance SHALL be determined through adherence to the content of the normative sections and rules. Furthermore each rule is categorized to indicate the intended audience for the rule by the following: Rule Categorization | ID | Description | 1 | Rules which must not be violated by individual organizations else conformance and interoperability is lost - such as named types. | 2 | Rules which may be modified by individual organizations while still conformant to the NDR structure - such as namespace string contents and namespace tokens. | 3 | Rules which may be modified by individual organizations while still conformant to agreed upon data models - such as the use of global or local element declarations. (Changes to the XML Schema Architecture.) | 4 | Rules that if violated lose conformance with the UN/CEFACT data/process model - such as xsd:redefine, xsd:any, and xsd:substitutionGroups. | 5 | Rules that relate to extension that are not used by UN/CEFACT and have specific restrictions on their use by other than UN/CEFACT organizations. | 6 | Rules that relate to extension that are determined by specific organizations. | 7 | Rules that can be modified while not changing instance validation capability. |
| 1 |
Over the last 3 years, SAP has had a lead role the development this new version of the specification. This new version incorporates years of lessons learned from a wide variety of implementers using earlier versions and is based on business requirements from different industries and stakeholders in both the private and public sectors.
Going forward, SAP will continue to develop its Global Data Types using the UN/CEFACT XML NDRs, and is developing a next generation data modeling, mapping, and integration tool - Warp 10 - that leverages the CCTS Common Methodology Standards Stack.
