
- SAP Community
- Products and Technology
- Additional Blogs by SAP
- About Complaint Processing with SAP CRM
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
About Complaint Processing with SAP CRM
What are Complaints?
A complaint is an expression of dissatisfaction that a customer makes with regards to a service or product.
Once the complaint is tracked, an investigation starts and finally the process ends with a decision on whether the complaint is valid. If yes, there are several ways to trigger follow up processes with the goal to find a resolution to the issue raised in the complaint.
This blog will answer the following questions...
- What the process of complaints in SAP CRM is?
- Typical cases of Complaints.
- How many information will be included in Complaint document in SAP CRM?
- What kinds of process can be triggered by complain in both SAP CRM & ERP.
- How important Complaints analysis is.
Complaint Management belongs to the SAP CRM service scenario and like all other service processes, Complaint Management has final goal to provide a excellent service, to satisfy your customer and thus to have loyal customers that continues the business relationship.
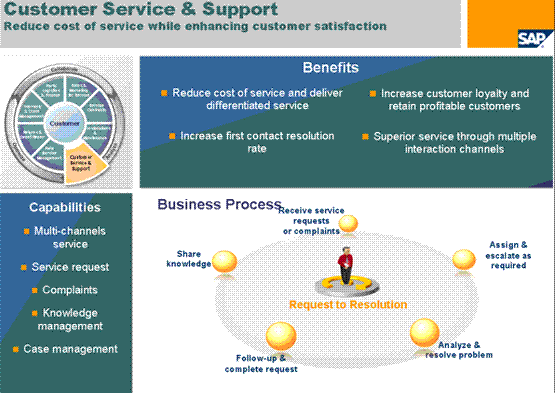
SAP CRM gives you an end to end complaint management as part of the Customer Service and Support scenario. In a nutshell the complaint provides
- Possibility to enter all relevant information about the complaint, like partners, descriptive texts, dates, the product or service to complain about.
- For reporting purpose it is very important to document the complaint reasons; therefore a configurable categorization structure is offered.
- In addition the complaints process flow can be supported with help actions that can be executed manually or automatically
- Last not least the complaint offers several follow-up processes which can be related to monetary transactions or logistics transactions, like e.g. a delivery processing, accounting bookings, quality management, etc
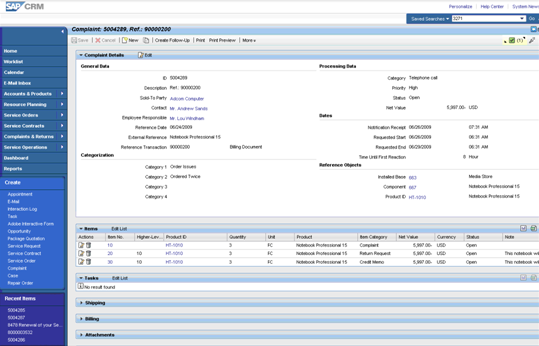
The following screenshot will show you how the complaint document in SAP CRM is:
Typical Complaint reasons:
Let's to do further research on Complaints through business scenario, on why complaints typically are created...
A complaint very often is related to a process that happened before. Thus in complaints processing, you can create complaints with or without reference to a preceding transaction in both SAP ERP and CRM like sales transaction (sales order, billing document) or a service process (service order).You can specify the reason for complain by using categorization in the header screen:
Case 1: Quality related
A customer makes a complaint because he is not satisfied with product or service from you, and he wants something e.g. repair, replacement, returning and refundment, price compensate or other options, depends on how angry he is or your contract. For repair or a replacement, you only need to fix (on site repair or in-house repair, only in-house repair needs return) or change to his new. If he wants returning and refundment, or price compensate, a credit memo will be triggered.
Case 2: Price related
A Customer ordered a product and notice later on that the product is being offered at a lower price within the context of a trade promotion. This complaint triggers you to create a credit memo for the original amount and a debit memo based on the product price that is valid during the trade promotion.
Case 3: Quantity related
After Customer received the ordered products, they find out the quantity is not correct, the customer complain to you about the quantity, you will check order for your customer, once you confirm the gap, the complaint from your customer becomes effective, thus you will create a Complaints document in system.
Example of a Complaint process:
Your customer (Jane) calls your service represent (Tom) complaints about the washing machine which is bought yesterday. After analysis by checking system, Tom confirms that they sent the machine with wrong color and they have no stock for the color that Jane wants in this week. So Tom creates a Complaint in SAP CRM with a return request and a credit memo. Then, Jane returns this machine and gets full refund. Two days later, Jane gets a call from your service analysis team, to confirm Jane's satisfaction.
You will see the process and document flow about this example in the following picture:

Formalize the follow-up process of a complaint: What are typical follow-up processes that a complaint can trigger:

From the complaint, you can:
- Generate a (sub-) items of type credit memo request
- Generate a (sub-) items of type debit memo request items
- Generate a (sub-) items of type return request item
- Create a quality notification in ERP
- Create a CRM document e.g. of type task.
Sub-items can be created by actions triggered either manually or by the system, based on predefined planning and start conditions.
Complaints analysis:
Back to the scenario, the result of each Complaint depends on how happy your customer is, so you will find how important the analysis is. You can use this business process to analyze key figures that provide information about the quality of your services and your product related (for vender triggered returns) and enables you to draw conclusions about the level of customer satisfaction. While you can use the process customer satisfaction and loyalty analysis to measure customer satisfaction on an abstract level, Service Quality Analysis enables you to identify the possible causes of dissatisfaction with the quality of individual service products, whether this be problems related to your internal processes, such as long processing times, or the quality of the service performed by the service representative.
- Mass processing direct activation steps in Technology Q&A
- Feature Request: Allow Process Intelligence Consumers to save personal filters in Technology Q&A
- Table DDNTF is not active in the dictionary error during DMO in Technology Q&A
- SAP Build Process Automation Pre-built content for Finance Use cases in Technology Blogs by SAP
- Start page of SAP Signavio Process Insights, discovery edition, the 4 pillars and documentation in Technology Blogs by SAP